數據結構(2)
trie樹
主要作用:快速存儲、查找字符串
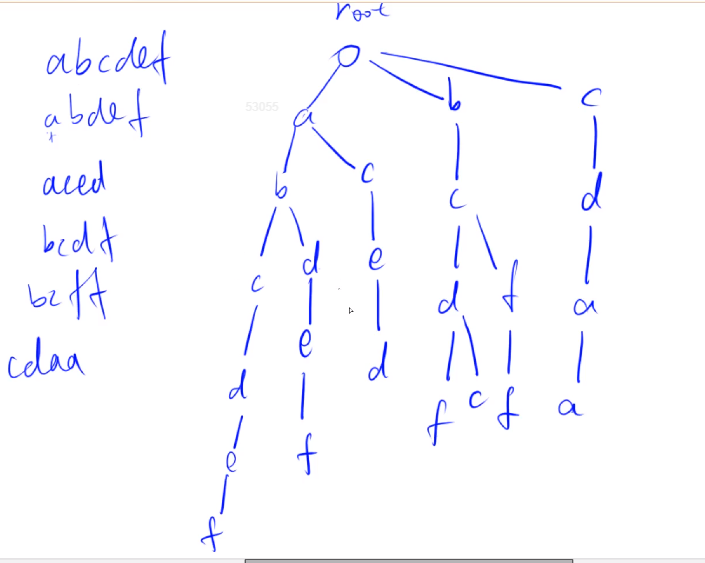
單詞的結尾要進行標記,表示“到達該節點,存在一個單詞”
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N = 1e6+10; int son[N][26] ; //字母最多26個 int cnt[N], idx ; //下標為0的點,是根節點,也是空結點 void insert(char str[ ]) { int p = 0 ; // 從根節點開始 for( int i=0; str[i] ; i++ ) { int u = str[i] -'a' ; //當前字母的結點編號 if( !son[p][u] ) son[p][u] = ++ idx ; //當前結點不存在這個字母,則創建 p = son[p][u] ; // 子節點作為新的根繼續往下查 } cnt[p] ++ ; } int query( char str[]){ int p = 0 ; for( int i=0; str[i]; i++ ) { int u = str[i]-'a'; if(!son[p][u]) return 0; //不存在這個點 p = son[p][u]; } return cnt[p]; //存在,返回這個點的出現次數 } int main(){ int m ; cin>>m ; while(m--){ char op, str[N]; cin>>op>>str ; if( op=='I') insert(str) ; else printf("%d\n", query(str)) ; }
return 0; }
題目:最大異或數
在給定的 <span id="MathJax-Span-2" class="mrow"><span id="MathJax-Span-3" class="mi">N個整數 <span id="MathJax-Span-5" class="mrow"><span id="MathJax-Span-6" class="msubsup"><span id="MathJax-Span-7" class="mi">A<span id="MathJax-Span-8" class="mn">1<span id="MathJax-Span-9" class="texatom"><span id="MathJax-Span-10" class="mrow"><span id="MathJax-Span-11" class="mo">,<span id="MathJax-Span-12" class="msubsup"><span id="MathJax-Span-13" class="mi">A<span id="MathJax-Span-14" class="mn">2<span id="MathJax-Span-15" class="mo">…<span id="MathJax-Span-16" class="mo">…<span id="MathJax-Span-17" class="msubsup"><span id="MathJax-Span-18" class="mi">A<span id="MathJax-Span-19" class="mi">N中選出兩個進行 <span id="MathJax-Span-21" class="mrow"><span id="MathJax-Span-22" class="mi">x<span id="MathJax-Span-23" class="mi">o<span id="MathJax-Span-24" class="mi">r(異或)運算,得到的結果最大是多少?
1->001 1 xor 2 = 011 1 xor 3 = 010
2->010
3->011
利用trie樹,邊插入邊查找,每個二進制數查找它對應的異或最大數只需要盡力去走插入這個數相反的路
#include <iostream> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 1e6+10; int son[N*31][2] ; //防止超出范圍 int a[N], idx ; void insert(int x) { int p = 0 ; // 從根節點開始 for( int i=30; i>=0; i-- ) { int u = x >> i & 1 ; //看個位是什么 if( !son[p][u] ) son[p][u] = ++idx; p = son[p][u]; } } int query(int x){ int p = 0, res = 0 ; for(int i=30; i>=0; i--) { int u = x >> i & 1; if( son[p][!u] ){ p = son[p][u] ; //找得到相反路就走 res = res*2 + !u ; } else{ p = son[p][u]; res = res*2 + u ; } } return res ; } void query(){ } int main(){ int m ; cin>>m ; for(int i=0; i<m; i++ ) scanf("%d", &a[i]) ; int res = 0 ; for(int i=0; i<m; i++) { insert(a[i]) ; int t = query(a[i]) ; res = max(res, a[i]^t) ; // ^ 表示異或 } printf("%d\n", res) ; return 0; }
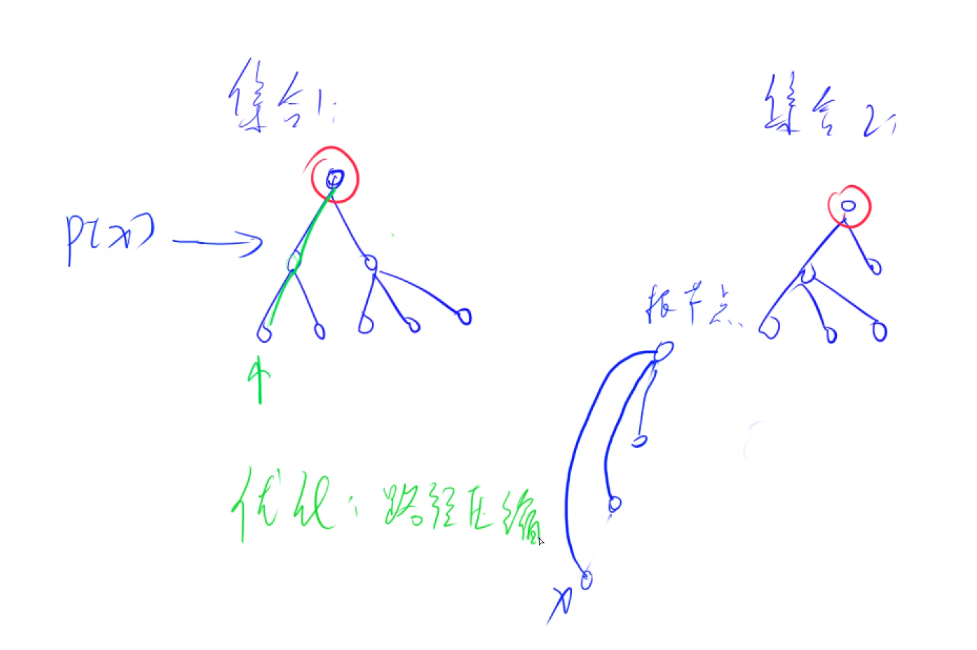
并查集(接近O(1))
查詢過一遍后,將葉子節點上直接指向根結點(路徑壓縮)

#include <iostream> using namespace std ; const int N = 1e6 ; int p[N] ; //父節點 int n,m ; int find(int x){ //返回x的祖宗結點,路徑壓縮 if( p[x] != x ) p[x] = find(p[x]) ; return p[x] ; } int main(){ cin>>n>>m ; for(int i=1 ; i<=n ; i++ ) p[i] = i ; while(m--) { char op ; int a,b ; cin>>op>>a>>b ; if( op == 'M' ) p[find(a)] = find(b) ; //合并,把b的祖宗結點變成a的祖宗的父節點 else{ if( find(a) == find(b) ) cout<<"Yes\n"; //祖宗相同,同一個集合 else cout<<"No"<<endl; } } return 0; }
PS: 本文來自博客園,作者:尊滴菜,轉載請注明原文鏈接:http://www.rzrgm.cn/zundicai/p/17257573.html




 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號