紅黑樹及C++代碼實現(xiàn)
紅黑樹及C++代碼實現(xiàn)
紅黑樹是二叉搜索樹的一種,單次插入、刪除、查詢的時間復(fù)雜度都是\(O(log(n))\)。紅黑樹的應(yīng)用廣泛,STL的set和map、Java的TreeSet和TreeMap等都是使用紅黑樹實現(xiàn)的
哨兵節(jié)點
在紅黑樹中,所有的葉子節(jié)點、根節(jié)點的父節(jié)點都是一個名為哨兵節(jié)點的節(jié)點。哨兵節(jié)點用于處理邊界條件,可以很方便的識別樹的邊緣,用NIL來表示。哨兵節(jié)點替代的是原來空指針的作用,哨兵節(jié)點可以降低訪問空指針的風(fēng)險,同時也可以簡化代碼中的邏輯判斷
性質(zhì)
一顆紅黑樹必須滿足下面五條性質(zhì):
- 節(jié)點為紅色或黑色
- 根節(jié)點為黑色
- NIL節(jié)點為黑色
- 紅色節(jié)點的子節(jié)點為黑色
- 從根節(jié)點到NIL節(jié)點的簡單路徑上的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)量相同(又或者說從任意一個節(jié)點出發(fā)到達NIL節(jié)點的所有簡單路徑所經(jīng)過的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)量相同)
思考下面的二叉樹是否為紅黑樹
root(B)
\
N(R)
/ \
NL(B) NR(B)
乍一看好像是紅黑樹,因為根節(jié)點到NL和NR的路徑上的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)相同。但實際上這顆樹并不是紅黑樹,將NIL節(jié)點畫出來一目了然
root(B)
/ \
NIL N(R)
/ \
NL(B) NR(B)
/ \ / \
NIL NIL NIL NIL
注意到根節(jié)點到達NIL節(jié)點有5條路徑,經(jīng)過的黑色節(jié)點(NIL算作黑色節(jié)點)數(shù)量分別為2、3、3、3、3,并不是全相等的,所以這顆二叉樹不是紅黑樹
同時這也解釋了為什么要使用哨兵節(jié)點
為什么紅黑樹效率高
從紅黑樹的性質(zhì)出發(fā),在不考慮NIL節(jié)點的情況下,假設(shè)根節(jié)點到葉節(jié)點的路徑上經(jīng)過的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)為\(r\),假設(shè)樹的高度為\(h\),那么有
其實很好理解,在沒有紅色節(jié)點的情況下,路徑上至少都會有\(r\)個黑色節(jié)點。有紅色節(jié)點的情況下,路徑節(jié)點最多的情況應(yīng)該是黑紅相間
假設(shè)紅黑樹中有\(n\)個節(jié)點(不包含NIL節(jié)點)那么有
節(jié)點最少的情況下,節(jié)點應(yīng)該全為黑色,此時紅黑樹是一顆滿二叉樹(紅黑樹的性質(zhì)決定)
root(B)
/ \
N(R) S(B)
/ \ / \
NL(B) NR(B) SL(B) SR(B)
/ \ / \ / \ / \
NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL NIL
上面的紅黑樹的高度為3(不計NIL節(jié)點),其節(jié)點數(shù)為\(2^3-1\),對于全黑的紅黑樹,其節(jié)點數(shù)為\(2^r - 1\)
而在全黑的情況下,我們還可以加上一些紅色節(jié)點,也不會破壞紅黑樹的性質(zhì)5,所以有\(n \ge 2^r - 1\)
做一個變形
又因為\(r\le h \le 2r\)
所以可以得到樹高\(h\),與節(jié)點數(shù)\(n\)的關(guān)系
紅黑樹又是一顆二叉搜索樹,二叉搜索樹進行插入、刪除、查找的復(fù)雜度取決于樹的最大高度,于是我們就可以知道紅黑樹進行插入、刪除、查找的復(fù)雜度為\(O(log(n))\)
為什么使用紅黑樹而不是AVL樹
AVL樹的最大高度大約為\(\lfloor log_2(n) \rfloor + 1\),比紅黑樹少一個常數(shù),那為什么STL和Java使用紅黑樹而不使用AVL樹呢?
AVL樹的高度小于紅黑樹,這讓它在查詢操作的表現(xiàn)比紅黑樹更加優(yōu)秀,因為查詢操作并不會改變樹的結(jié)構(gòu)。但是在面對大量數(shù)據(jù)寫入和刪除的情況,AVL樹為了保持平衡性,會經(jīng)常進行旋轉(zhuǎn),以保證AVL樹的左子樹和右子樹的高度差不超過1。而紅黑樹對樹結(jié)構(gòu)的要求并不像AVL樹那么嚴格,旋轉(zhuǎn)的次數(shù)會少于AVL樹。這就導(dǎo)致紅黑樹的整體性能比AVL樹更加優(yōu)秀
旋轉(zhuǎn)
旋轉(zhuǎn)操作用于調(diào)整樹的結(jié)構(gòu),很常用
左旋
假如對P點左旋,那么將P的右節(jié)點B變?yōu)镻的父節(jié)點,將P變?yōu)槠渥蠊?jié)點A的父節(jié)點,將P的右節(jié)點B的左節(jié)點BL變?yōu)镻的右節(jié)點
P B
/ \ P點左旋 / \
A B -----> P BR
/ \ / \ / \
AL AR BL BR A BL
/ \
AL AR
右旋
與左旋完全反過來
假如對P點右旋,那么將P的左節(jié)點A變?yōu)镻的父節(jié)點,將P變?yōu)槠溆夜?jié)點B的父節(jié)點,將P的左節(jié)點A的右節(jié)點AR變?yōu)镻的左節(jié)點
P A
/ \ P點右旋 / \
A B -----> AL P
/ \ / \ / \
AL AR BL BR AR B
/ \
BL BR
插入
插入節(jié)點顏色選取
根據(jù)紅黑樹的性質(zhì),節(jié)點必須為紅色或者黑色中的一種。那么對于插入操作,插入的節(jié)點應(yīng)該是什么顏色呢?
如果插入節(jié)點為黑色,那么我們將節(jié)點插入以后,紅黑樹的性質(zhì)5一定會被打破,有一條路徑上的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)會增加1,好像并不好調(diào)整,如果要調(diào)整,我們就需要將路徑上的一個節(jié)點變?yōu)榧t色,以保證性質(zhì)5成立,但是一個節(jié)點變?yōu)榧t色又可能會打破性質(zhì)4
如果插入節(jié)點為紅色,那么我們將節(jié)點插入以后,紅黑樹的性質(zhì)5不會被打破,但性質(zhì)4卻也有可能會被打破
而在后面可以知道,連續(xù)兩個紅色節(jié)點是可以調(diào)整的
插入紅色節(jié)點可以省去變紅的操作,更加方便。因此選擇紅色作為插入節(jié)點的顏色
Case 1:樹為空
直接插入節(jié)點,并將節(jié)點的顏色變?yōu)楹谏?/p>
Case 2:父節(jié)點為黑色節(jié)點
直接插入,不需要額外操作
Case 3:父節(jié)點為紅色節(jié)點
-
叔叔節(jié)點為紅色節(jié)點
將父節(jié)點以及叔叔節(jié)點變?yōu)楹谏瑢⒆嫦裙?jié)點變?yōu)榧t色。但是調(diào)整后祖先節(jié)點的父節(jié)點可能為紅色,違反了性質(zhì)4,因此我們需要遞歸的去調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點,直到?jīng)]有沖突出現(xiàn)
G(B) G(R) / \ / \ P(R) U(R) -----> P(B) U(B) / / N(R) N(R) -
叔叔節(jié)點為黑色,且插入節(jié)點與父節(jié)點同為左節(jié)點或右節(jié)點
這種情況可以直接調(diào)整,將祖先節(jié)點G旋轉(zhuǎn),方向與父節(jié)點P方向相反,旋轉(zhuǎn)后將父節(jié)點變成黑色,祖先節(jié)點變?yōu)榧t色
G(B) P(B) / \ G左旋 / \ U(B) P(R) -----> G(R) N(R) \ / N(R) U(B) -
叔叔節(jié)點為黑色,且插入節(jié)點與父節(jié)點方向相反
這種情況可以轉(zhuǎn)換為上面一種情況,從而直接進行調(diào)整。先將父節(jié)點P旋轉(zhuǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)方向與插入節(jié)點的方向相反,旋轉(zhuǎn)后即可按照上面一種情況調(diào)整
G(B) G(B) N(B) / \ P右旋 / \ G左旋 / \ U(B) P(R) -----> U(B) N(R) -----> G(R) P(R) / \ N(R) P(R)
刪除
雙黑節(jié)點
在進行刪除操作之前,有必要先了解一下雙黑節(jié)點是什么
在紅黑樹中,雙黑節(jié)點(Double Black Node) 是一個邏輯標(biāo)記,用于表示在刪除操作后某個位置需要“補足”一個額外的黑色節(jié)點,以維護紅黑樹的黑高一致性(所有路徑的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)量相同)。它本身不是一種真實的顏色,而是修復(fù)紅黑樹性質(zhì)時的一種臨時狀態(tài)。
從上面的解釋中可以知道,如果某節(jié)點被打上雙黑節(jié)點標(biāo)記,就意味著這個節(jié)點會額外算作一個黑色節(jié)點,以保證紅黑樹的性質(zhì)。但一個節(jié)點不能扮演兩個角色,我們需要通過旋轉(zhuǎn)、變色等操作將雙黑節(jié)點標(biāo)記消除(注意雙黑節(jié)點是一個邏輯標(biāo)記),消除后整棵樹仍然是紅黑樹。
在刪除操作時,如果出現(xiàn)了雙黑節(jié)點,不會立即調(diào)整樹的結(jié)構(gòu),而是在之后的刪除調(diào)整操作進行統(tǒng)一的操作
近侄節(jié)點與遠侄節(jié)點
-
近侄節(jié)點:兄弟節(jié)點靠近刪除節(jié)點的子節(jié)點
-
遠侄節(jié)點:兄弟節(jié)點遠離刪除節(jié)點的子節(jié)點
P
/ \
N S
/ \
SL SR
現(xiàn)在有上面一棵樹,對于節(jié)點N來說,S為N的兄弟節(jié)點,SL則為N的近侄節(jié)點,SR則為N的遠侄節(jié)點
Case 1:刪除節(jié)點為樹中唯一節(jié)點
若刪除節(jié)點為樹中的唯一節(jié)點,直接刪除即可
Case 2:刪除節(jié)點沒有非NIL的子節(jié)點
-
刪除節(jié)點為紅色節(jié)點
如果刪除的節(jié)點為紅色,直接刪除即可,刪除后的樹依舊是一顆紅黑樹,滿足紅黑樹的五條性質(zhì)
P(?) P(?) / \ 刪除后 / \ N(R) S(?) ------> NIL S(?) / \ / \ / \ NIL NIL SL(?) SR(?) SL(?) SR(?) -
刪除的節(jié)點為黑色節(jié)點
P(?) / \ N(B) S(?) / \ / \ NIL NIL SL(?) SR(?)我們首先刪除需要刪除的節(jié)點N,補上一個NIL節(jié)點,所補的NIL節(jié)點會被打上雙黑節(jié)點標(biāo)記,我們用C來表示這個NIL節(jié)點
如果C節(jié)點只算做一個黑色節(jié)點,那么肯定是不滿足性質(zhì)5的,但是如果C節(jié)點算作兩個黑色節(jié)點,那么就滿足性質(zhì)5了。在后面的刪除調(diào)整操作我們考慮如何將雙黑節(jié)點標(biāo)記去除掉
P(?) P(?) / \ / \ N(B) S(?) ------> C(DB) S(?) / \ / \ / \ NIL NIL SL(?) SR(?) SL(?) SR(?)
Case 3:刪除節(jié)點有且僅有一個非NIL的子節(jié)點
這種情況下刪除節(jié)點只能是黑色,并且刪除節(jié)點的非NIL子節(jié)點只能是紅色
-
如果刪除節(jié)點是紅色,那么刪除節(jié)點的非NIL子節(jié)點一定為黑色,只有這樣才能滿足性質(zhì)4。但是注意,從刪除節(jié)點出發(fā),如果直接走NIL子節(jié)點方向,那么路徑上經(jīng)過的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)為1,但走非NIL子節(jié)點方向,路徑上經(jīng)過的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)是大于1的,至少有非NIL子節(jié)點和非NIL子節(jié)點下面的NIL子節(jié)點兩個黑色節(jié)點,因此該情況不滿足紅黑樹的性質(zhì)。
N(R) / \ NIL NR(B) / \ NIL NIL -
如果刪除節(jié)點是黑色,刪除節(jié)點的非NIL節(jié)點也為黑色,如同第一種情況,從刪除節(jié)點出發(fā),走NIL節(jié)點方向,路徑上經(jīng)過2個黑色節(jié)點,而走非NIL節(jié)點方向,路徑上至少經(jīng)過3個黑色節(jié)點,因此該情況也不滿足紅黑樹的性質(zhì)
N(B) / \ NIL NR(B) / \ NIL NIL
因此刪除節(jié)點只能是黑色,刪除節(jié)點的非NIL子節(jié)點只能是紅色
對于這種情況,可以直接調(diào)整。刪除節(jié)點,用非NIL子節(jié)點代替該節(jié)點,并將節(jié)點顏色變成黑色
P(?) P(?)
/ /
N(B) NR(B)
/ \ / \
NIL NR(R) -----> NIL NIL
/ \
NIL NIL
Case 4:刪除節(jié)點有兩個非NIL的子節(jié)點
這種情況我們需要找到刪除節(jié)點的后繼節(jié)點,即右子樹中最小的節(jié)點,然后交換兩個節(jié)點,顏色不交換,然后繼續(xù)刪除需要刪除的節(jié)點
此時會發(fā)現(xiàn),刪除的情況變成了Case 2或者Case 3
這是因為二叉搜索樹的后繼節(jié)點沒有左節(jié)點,因此后繼節(jié)點最多只有一個非NIL節(jié)點
刪除調(diào)整
刪除調(diào)整操作的目的是為了去除在刪除過程中出現(xiàn)的雙黑節(jié)點標(biāo)記,下面會分成幾種情況進行討論
Case 1: 兄弟節(jié)點為黑色且兄弟節(jié)點的兩個子節(jié)點為黑色
-
如果父節(jié)點為紅色
只需要將兄弟節(jié)點S變成紅色,父節(jié)點P變成黑色就可以直接去掉雙黑節(jié)點
P(R) P(B) / \ / \ C(DB) S(B) -----> C(B) S(R) / \ / \ SL(B) SR(B) SL(B) SR(B)調(diào)整前后,根節(jié)點經(jīng)過P點到達NIL節(jié)點的所有簡單路徑經(jīng)過的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)量是相同的
-
如果父節(jié)點為黑色
還是先將兄弟節(jié)點S變成紅色
但是注意這里并不能像上面那樣,直接將S變成紅色然后去掉雙黑節(jié)點就完了,雖然調(diào)整后在這顆子樹上滿足了性質(zhì)5,但是在整棵樹上,經(jīng)過P節(jié)點的路徑的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)會減少一個,與其他路徑的黑色節(jié)點數(shù)量不同,不滿足性質(zhì)5
因此我們需要為父節(jié)點打上雙黑節(jié)點標(biāo)記,如果P節(jié)點算作兩個黑色節(jié)點,那么就滿足性質(zhì)5了,然后繼續(xù)調(diào)整父節(jié)點P,直到?jīng)]有雙黑節(jié)點出現(xiàn)
P(B) P(DB) / \ / \ C(DB) S(B) -----> C(B) S(R) / \ / \ SL(B) SR(B) SL(B) SR(B)
Case 2:兄弟節(jié)點為黑色并且遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
這種情況可以直接進行調(diào)整
這里以刪除節(jié)點為父節(jié)點的左節(jié)點為例,將父節(jié)點P進行旋轉(zhuǎn)(刪除節(jié)點在哪邊就往哪邊旋轉(zhuǎn)),將兄弟節(jié)點S的顏色變?yōu)楦腹?jié)點P的顏色,父節(jié)點P和遠侄節(jié)點SR的顏色變?yōu)楹谏サ綦p黑標(biāo)記
P(?) S(?)
/ \ / \
C(DB) S(B) 左旋 P(B) SR(B)
/ \ -----> / \
SL(?) SR(R) C(B) SL(?)
可以看到調(diào)整后無論是在局部,還是在整體都是滿足紅黑樹的性質(zhì)的
Case 3:兄弟節(jié)點為黑色并且近侄節(jié)點為紅色,遠侄點為黑色
這種情況需要轉(zhuǎn)換為 Case 2 狀態(tài),進而進行調(diào)整
這里以刪除節(jié)點為父節(jié)點的左節(jié)點為例,將兄弟節(jié)點S進行旋轉(zhuǎn)(刪除節(jié)點在哪邊,往反方向旋轉(zhuǎn)),將S的顏色變?yōu)榧t色,將SL的顏色變?yōu)楹谏{(diào)整后按照 Case 2 繼續(xù)調(diào)整
P(?) P(?)
/ \ / \
C(DB) S(B) 右旋 C(DB) SL(B)
/ \ -----> \
SL(R) SR(B) S(R)
\
SR(B)
Case 4:兄弟節(jié)點為紅色
根據(jù)性質(zhì)4,父節(jié)點一定為黑色,兄弟節(jié)點的兩個子節(jié)點一定是黑色
策略是將兄弟節(jié)點變成黑色,然后繼續(xù)調(diào)整。
將父節(jié)點P進行旋轉(zhuǎn)(刪除節(jié)點在哪邊就往哪邊旋轉(zhuǎn)),將兄弟節(jié)點S變成黑色,將父節(jié)點P變?yōu)榧t色。之后就可以按照前面的情況進行處理了
P(B) S(B)
/ \ / \
C(DB) S(R) -----> P(R) SR(B)
/ \ / \
SL(B) SR(B) C(DB) SL(B)
此時SL作為新的兄弟節(jié)點,繼續(xù)調(diào)整C(DB)節(jié)點
測試
正確性測試
-
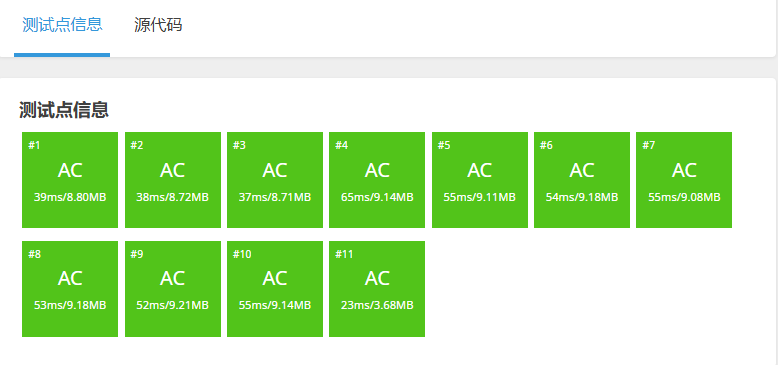
插入
我們使用洛谷P3879來驗證我們的插入是否有問題。經(jīng)過測試可以AC這道題,通過代碼放在最后面(有點長)
![]()
-
刪除
刪除沒有找到什么簡單的題目,于是就造了一個簡單的數(shù)據(jù),數(shù)據(jù)規(guī)模為\(10^7\)
下面為生成數(shù)據(jù)的python代碼
import random in_path = "./data.in" out_path = "./data.out" # 數(shù)據(jù)大小 N = int(1e7) # 數(shù)據(jù)范圍 minNum = 0 # 最大范圍我們?nèi)」?jié)點數(shù)的十倍 maxNum = int(N * 10) # 刪除節(jié)點為一般節(jié)點 erase_num = N // 2 if __name__ == '__main__': # 生成N個區(qū)間內(nèi)不重復(fù)的隨機數(shù) x = random.sample(range(minNum, maxNum), N) # 獲取刪除的下標(biāo) idxs = random.sample(range(0, len(x)), erase_num) # 獲取到需要刪除的數(shù) y = [x[idx] for idx in idxs] # 我們要算出哪些還存在,需要進行集合運算 set_y = set(y) set_x = set(x) # 計算出最終的答案 set_y = list(set_x - set_y) # 輸入 with open(in_path, mode='w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write(f"{N}\n") for each in x: f.write(f"{each}\n") f.write(f"{erase_num}\n") for each in y: f.write(f"{each}\n") # 輸出 with open(out_path, mode='w', encoding='utf-8') as f: f.write(f"{len(set_y)}\n") for each in set_y: f.write(f"{each}\n")下面為驗證的python代碼
import subprocess import time from subprocess import * cpp_path = "./RBTree.cpp" exe_path = "./RBTree.exe" test_cpp_path = "./test.cpp" test_exe_path = "./test.exe" out_path = "./out.out" data_path = "./data.out" in_path = "./data.in" with open(in_path,"r",encoding="utf-8") as f : stdin = f.read() compile_res = subprocess.run(["g++",cpp_path,"-o",exe_path],capture_output=True,text=True,timeout=5) # 編譯成功 if compile_res.returncode == 0: st = time.time() run_res = subprocess.run([exe_path],input=stdin,capture_output=True,text=True,timeout=100) ed = time.time() print(f"running time: {(ed - st) * 1000.0}ms") out = run_res.stdout with open(out_path, "w", encoding="utf-8") as f: f.write(out) with open(data_path,"r",encoding="utf-8") as f1,open(out_path,"r",encoding="utf-8") as f2: N1 = int(f1.readline().strip()) N2 = int(f2.readline().strip()) if(N1 != N2) : print("Wrong Answer!") else: # 由于數(shù)據(jù)是不重復(fù)的且輸出順序并不固定,直接用集合判斷 data1 = set([int(x.strip()) for x in f1.readlines()]) data2 = set([int(x.strip()) for x in f2.readlines()]) if data1 == data2: print("Accept!") else : print("Wrong Answer!")下面為測試結(jié)果,沒問題
![]()
-
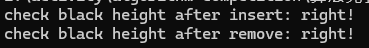
黑高檢驗
我們還是來檢測一下整顆紅黑樹的黑高是否正確,檢測代碼如下
void checkBlackHeight() { bool flag = true; checkBlackHeightHelp(root, flag); if (flag) cout << "right!" << endl; else cout << "error!" << endl; } int checkBlackHeightHelp(Node *N, bool &flag) { // NIL節(jié)點為黑色 if (N == NIL) return 1; int left = checkBlackHeightHelp(N->left, flag); int right = checkBlackHeightHelp(N->right, flag); if (left != right) flag = false; return left + (N->color == Color::BLACK ? 1 : 0); }我們在插入和刪除后分別進行一次黑高檢驗,沒有問題
![]()
-
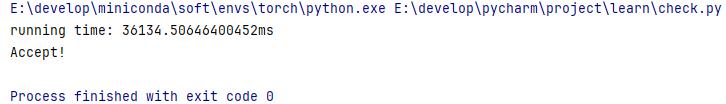
性能測試
我們使用STL的set進行對比,數(shù)據(jù)還是上面刪除檢驗的數(shù)據(jù)。但首先我們先對程序優(yōu)化一下,主要是優(yōu)化輸入和輸出,數(shù)據(jù)量大了cin和cout的速度很慢,關(guān)閉流同步速度會快很多
在主函數(shù)中加入下面的代碼即可
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
set測試代碼如下
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <set>
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
set<int> s;
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
s.insert(x);
}
int m;
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
s.erase(x);
}
cout << s.size() << endl;
for (auto x : s)
cout << x << endl;
}
-
RBTree測試結(jié)果
![]()
-
set測試結(jié)果
![]()
我們實現(xiàn)的紅黑樹快了將近10秒,還不錯
代碼實現(xiàn)
顏色表示
這里用枚舉類型表示紅色和黑色
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
紅黑樹節(jié)點表示
使用結(jié)構(gòu)體來表示紅黑樹的節(jié)點
template <typename Key, typename Value>
struct RBTreeNode
{
// 按照key值進行插入刪除等操作
Key key;
// value為存儲的數(shù)據(jù)
Value value;
// 左節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *left;
// 右節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *right;
// 父節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *parent;
// 節(jié)點顏色
Color color;
RBTreeNode(Color c, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *l = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *r = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *p = nullptr)
{
color = c, left = l, right = r, parent = p;
}
RBTreeNode(Key k, Value v, Color c, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *l = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *r = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *p = nullptr)
{
key = k, value = v, color = c, left = l, right = r, parent = p;
}
};
創(chuàng)建節(jié)點
為了避免直接New內(nèi)存(因為不好看),寫四個輔助函數(shù)用于創(chuàng)建紅黑樹的節(jié)點
但首先我們先給節(jié)點類型取個別名,原來節(jié)點類型太長了
typedef RBTreeNode<Key, Value> Node;
-
創(chuàng)建紅色空節(jié)點
// 創(chuàng)建一個空的紅色節(jié)點 Node *createEmptyRedNode(Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr) { return new Node(Color::RED, l, r, p); } -
創(chuàng)建紅色非空節(jié)點
// 創(chuàng)建一個非空紅色節(jié)點 Node *createRedNode(Key key, Value value, Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr) { return new Node(key, value, Color::RED, l, r, p); } -
創(chuàng)建黑色空節(jié)點
// 創(chuàng)建一個空的黑色節(jié)點 Node *createEmptyBlackNode(Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr) { return new Node(Color::BLACK, l, r, p); } -
創(chuàng)建黑色非空節(jié)點
// 創(chuàng)建一個非空黑色節(jié)點 Node *createBlackNode(Key key, Value value, Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr) { return new Node(key, value, Color::BLACK, l, r, p); }
也為了避免直接用delete釋放內(nèi)存,同樣寫一個輔助函數(shù)來刪除節(jié)點
// 銷毀節(jié)點
Node *destroyNode(Node *node)
{
delete node;
}
左旋
// 左旋操作
void leftRotate(Node *p)
{
// 獲取旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點的右兒子
Node *rightSon = p->right;
// 獲取祖先節(jié)點
Node *grandParent = p->parent;
// 更新旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點
p->right = rightSon->left;
p->parent = rightSon;
// 更新右節(jié)點
// 如果右兒子的左節(jié)點不為NIL,則將右兒子的左節(jié)點的父節(jié)點設(shè)置為p
if (rightSon->left != NIL)
rightSon->left->parent = p;
rightSon->parent = grandParent;
rightSon->left = p;
// 更新祖先節(jié)點
// 如果p為根節(jié)點
if (grandParent == NIL)
root = rightSon;
// 如果p為左節(jié)點
else if (grandParent->left == p)
grandParent->left = rightSon;
// 如果p為右節(jié)點
else
grandParent->right = rightSon;
}
右旋
// 右旋操作
void rightRotate(Node *p)
{
// 獲取旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點的左兒子
Node *leftSon = p->left;
// 獲取祖先節(jié)點
Node *grandParent = p->parent;
// 更新旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點
p->left = leftSon->right;
p->parent = leftSon;
// 更新左節(jié)點
// 如果左兒子的右節(jié)點不為NIL,則將左兒子的右節(jié)點的父節(jié)點設(shè)置為p
if (leftSon->right != NIL)
leftSon->right->parent = p;
leftSon->parent = grandParent;
leftSon->right = p;
// 更新祖先節(jié)點
// 如果p為根節(jié)點
if (grandParent == NIL)
root = leftSon;
// 如果p為左節(jié)點
else if (grandParent->left == p)
grandParent->left = leftSon;
// 如果p為右節(jié)點
else
grandParent->right = leftSon;
}
插入調(diào)整
// 插入調(diào)整
void insertFixup(Node *N)
{
// 一直向上調(diào)整,直到父節(jié)點不是紅色,或者父節(jié)點為根節(jié)點
// 注意這里的N節(jié)點一定為紅色
while (N->parent->color == Color::RED && N->parent != root)
{
// 如果父節(jié)點為左子節(jié)點
if (N->parent == N->parent->parent->left)
{
// 獲取叔叔節(jié)點
Node *U = N->parent->parent->right;
// 如果叔叔節(jié)點的顏色也為紅色,則將父節(jié)點和叔叔節(jié)點都變?yōu)楹谏嫦裙?jié)點變?yōu)榧t色,繼續(xù)向上調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
if (U->color == Color::RED)
{
U->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 繼續(xù)調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
N = N->parent->parent;
}
else
{
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點不同向,需旋轉(zhuǎn)為同向
if (N == N->parent->right)
{
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)N的父節(jié)點
N = N->parent;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)父節(jié)點
leftRotate(N);
}
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點同向
// 注意要先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)之后會改變父子關(guān)系,到時候很混亂
// 父節(jié)點設(shè)置為黑色
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
// 祖先節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)祖先節(jié)點
rightRotate(N->parent->parent);
}
}
// 如果父節(jié)點為右子節(jié)點
else
{
// 獲取叔叔節(jié)點
Node *U = N->parent->parent->left;
// 如果叔叔節(jié)點的顏色也為紅色,則將父節(jié)點和叔叔節(jié)點都變?yōu)楹谏嫦裙?jié)點變?yōu)榧t色,繼續(xù)向上調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
if (U->color == Color::RED)
{
U->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 繼續(xù)調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
N = N->parent->parent;
}
else
{
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點不同向,需旋轉(zhuǎn)為同向
if (N == N->parent->left)
{
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)N的父節(jié)點
N = N->parent;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)父節(jié)點
rightRotate(N);
}
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點同向
// 注意要先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)之后會改變父子關(guān)系,到時候很混亂
// 父節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
// 祖先節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)祖先節(jié)點
leftRotate(N->parent->parent);
}
}
}
// 根節(jié)點可以無責(zé)任變成黑色
root->color = Color::BLACK;
}
插入節(jié)點
void insert(Key key, Value value)
{
Node *N = createRedNode(key, value, NIL, NIL, NIL);
// 查詢節(jié)點的父節(jié)點
Node *p = NIL;
// 迭代查找臨時節(jié)點
Node *temp = root;
// 樹為空,直接插入
if (root == NIL)
{
N->color = BLACK;
root = N;
size++;
return;
}
while (temp != NIL)
{
p = temp;
// 往左查找
if (N->key < temp->key)
temp = temp->left;
// 往右查找
else if (N->key > temp->key)
temp = temp->right;
// key值已經(jīng)存在,則替換數(shù)據(jù)
else
{
temp->value = value;
return;
}
}
size++;
N->parent = p;
// 如果key值比父節(jié)點小,則作為左子節(jié)點
if (N->key < p->key)
p->left = N;
// 如果key值比父節(jié)點大,則作為右子節(jié)點
else
p->right = N;
insertFixup(N);
}
節(jié)點替換
在刪除操作中,我們會經(jīng)常將一個節(jié)點替換為另外一個節(jié)點。為了方便,我們封裝一個函數(shù)用于節(jié)點替換
注意在這個替換函數(shù)中,只是更新了父節(jié)點與替換節(jié)點的關(guān)系,子節(jié)點并沒有更新
// 用v替換u
void replace(Node *u, Node *v)
{
// 如果u為root
if (u->parent == NIL)
root = v;
// u為左子節(jié)點
else if (u->parent->left == u)
u->parent->left = v;
// u為右子節(jié)點
else
u->parent->right = v;
v->parent = u->parent;
}
查詢后繼節(jié)點
在刪除操作中,有些情況需要找到刪除節(jié)點的后繼節(jié)點,為了方便,依舊是封裝一個函數(shù)來查詢后繼節(jié)點
后繼節(jié)點為右子樹中最小的一個節(jié)點
// 獲取最小節(jié)點
Node *getMinNode(Node *p)
{
while (p->left != NIL)
p = p->left;
return p;
}
刪除調(diào)整
// 刪除調(diào)整
void removeFixup(Node *C)
{
while (C != root && C->color == BLACK)
{
// 如果C為左子節(jié)點
if (C == C->parent->left)
{
// 獲取兄弟節(jié)點
Node *S = C->parent->right;
// 如果兄弟節(jié)點為紅色,我們需要通過旋轉(zhuǎn)將兄弟節(jié)點變?yōu)楹谏? if (S->color == Color::RED)
{
// 先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn)
S->color = Color::BLACK;
C->parent->color = Color::RED;
leftRotate(C->parent);
// 獲取新的兄弟節(jié)點
S = C->parent->right;
}
// 兄弟節(jié)點的左兒子和右兒子都為黑色
if (S->left->color == Color::BLACK && S->right->color == Color::BLACK)
{
// 父節(jié)點為紅色
if (C->parent->color == Color::RED)
{
C->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
S->color = Color::RED;
// 已經(jīng)調(diào)整完畢,不需要再進行調(diào)整就將C設(shè)置為根節(jié)點
C = root;
}
// 父節(jié)點為黑色
else
{
S->color = Color::RED;
// 父節(jié)點成為雙黑節(jié)點,繼續(xù)調(diào)整父節(jié)點
C = C->parent;
}
}
else
{
// 近侄節(jié)點為紅色,遠侄子節(jié)點為黑色,需要調(diào)整為遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
if (S->right->color == Color::BLACK)
{
// 先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn)
S->color = Color::RED;
S->left->color = Color::BLACK;
rightRotate(S);
// 由于旋轉(zhuǎn)改變了父子關(guān)系,所以重新獲取一下兄弟節(jié)點
S = C->parent->right;
}
// 調(diào)整后遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
S->color = C->parent->color;
C->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
S->right->color = Color::BLACK;
leftRotate(C->parent);
// 已經(jīng)調(diào)整完畢,不需要再進行調(diào)整就將C設(shè)置為根節(jié)點
C = root;
}
}
// 如果C為右子節(jié)點
else
{
// 獲取兄弟節(jié)點
Node *S = C->parent->left;
// 如果兄弟節(jié)點為紅色,我們需要通過旋轉(zhuǎn)將兄弟節(jié)點變?yōu)楹谏? if (S->color == Color::RED)
{
// 先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn)
S->color = Color::BLACK;
C->parent->color = Color::RED;
rightRotate(C->parent);
// 獲取新的兄弟節(jié)點
S = C->parent->left;
}
// 兄弟節(jié)點的左兒子和右兒子都為黑色
if (S->left->color == Color::BLACK && S->right->color == Color::BLACK)
{
// 父節(jié)點為紅色
if (C->parent->color == Color::RED)
{
C->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
S->color = Color::RED;
// 已經(jīng)調(diào)整完畢,不需要再進行調(diào)整就將C設(shè)置為根節(jié)點
C = root;
}
// 父節(jié)點為黑色
else
{
S->color = Color::RED;
// 父節(jié)點成為雙黑節(jié)點,繼續(xù)調(diào)整父節(jié)點
C = C->parent;
}
}
else
{
// 近侄節(jié)點為紅色,遠侄子節(jié)點為黑色,需要調(diào)整為遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
if (S->left->color == Color::BLACK)
{
// 先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn)
S->color = Color::RED;
S->right->color = Color::BLACK;
leftRotate(S);
// 由于旋轉(zhuǎn)改變了父子關(guān)系,所以重新獲取一下兄弟節(jié)點
S = C->parent->left;
}
// 調(diào)整后遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
S->color = C->parent->color;
C->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
S->left->color = Color::BLACK;
rightRotate(C->parent);
// 已經(jīng)調(diào)整完畢,不需要再進行調(diào)整就將C設(shè)置為根節(jié)點
C = root;
}
}
}
// 根節(jié)點可以無責(zé)任變成黑色
root->color = Color::BLACK;
}
刪除節(jié)點
注意在刪除節(jié)點有兩個非NIL的子節(jié)點的情況下,需要交換節(jié)點,這里為了方便是直接交換的鍵和值的,但是如果鍵和值對象比較大,那么這樣效率就很慢,最好還是通過指針交換來達到節(jié)點交換的目的
void remove(Key key)
{
Node *N = root;
while (N != NIL)
{
if (N->key == key)
break;
if (key < N->key)
N = N->left;
else
N = N->right;
}
// 樹中沒有刪除的key
if (N == NIL)
return;
// 刪除節(jié)點為樹中唯一節(jié)點
// Case 1
if (size == 1)
{
if (root != NIL)
destroyNode(root);
root = NIL;
size--;
return;
}
// Case 4
// 刪除節(jié)點有兩個非NIL的子節(jié)點
if (N->left != NIL && N->right != NIL)
{
// 獲得后繼節(jié)點
Node *minNode = getMinNode(N->right);
// 我們這里直接交換鍵值,方便,但如果鍵值都是比較大的對象就很慢了,最好還是交換指針
swap(minNode->key, N->key);
swap(minNode->value, N->value);
// 刪除節(jié)點轉(zhuǎn)換為后繼節(jié)點,轉(zhuǎn)移到case 2或 case 3
N = minNode;
}
// Case 3
if (N->left == NIL && N->right != NIL)
{
Node *rightSon = N->right;
rightSon->color = N->color;
// 用右子節(jié)點替換刪除節(jié)點
replace(N, rightSon);
// 刪除節(jié)點
destroyNode(N);
}
// Case 3
else if (N->left != NIL && N->right == NIL)
{
Node *leftSon = N->left;
leftSon->color = N->color;
// 用左子節(jié)點替換刪除節(jié)點
replace(N, leftSon);
// 刪除節(jié)點
destroyNode(N);
}
// Case 2
else
{
// 此情況為刪除節(jié)點的兩個兒子都為NIL節(jié)點
// 刪除節(jié)點為紅色,直接刪除即可
if (N->color == Color::RED)
{
Node *parent = N->parent;
if (parent->left == N)
parent->left = NIL;
else
parent->right = NIL;
destroyNode(N);
}
// 刪除節(jié)點為黑色,出現(xiàn)雙黑節(jié)點,需要向上調(diào)整
else
{
removeFixup(N);
// 調(diào)整后刪除該節(jié)點
Node *parent = N->parent;
if (parent->left == N)
parent->left = NIL;
else
parent->right = NIL;
destroyNode(N);
}
}
size--;
}
查詢
查詢操作也是很基本也很常用的操作,紅黑樹的查詢操作與其他的二叉搜索樹基本一樣:比節(jié)點小就去左子樹查,比節(jié)點大就去右子樹查,和節(jié)點一樣大說明查詢到了
pair<bool, Value> query(Key key)
{
if (root == NIL)
return {false, Value()};
Node *temp = root;
while (temp != NIL)
{
if (key < temp->key)
temp = temp->left;
else if (key > temp->key)
temp = temp->right;
else
return {true, temp->value};
}
// 最后沒有查到
return {false, Value()};
}
注意這個版本的查詢返回的value與紅黑樹中的并不是同一個,而是一個拷貝。如果想通過返回的value操作樹內(nèi)的value,可以返回引用類型
pair<bool, Value&>
遍歷數(shù)據(jù)
這里使用中序遍歷整個紅黑樹,并統(tǒng)計紅節(jié)點和黑節(jié)點個數(shù)
void print()
{
int red = 0, black = 0;
printOperation(root, red, black);
cout << "redNode num = " << red << " " << "blackNode num = " << black << endl;
}
void printOperation(Node *p, int &red, int &black)
{
if (p == NIL)
return;
printOperation(p->left, red, black);
if (p->color == Color::RED)
red++;
else
black++;
cout << "key = " << p->key << " value = " << p->value << " color = " << p->color << endl;
printOperation(p->right, red, black);
}
洛谷題目代碼
下面代碼與完整代碼不同,只是實現(xiàn)了插入和查詢操作
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template <typename Key, typename Value>
struct RBTreeNode
{
// 按照key值進行插入刪除等操作
Key key;
// value為存儲的數(shù)據(jù)
Value value;
// 左節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *left;
// 右節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *right;
// 父節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *parent;
// 節(jié)點顏色
Color color;
RBTreeNode(Color c, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *l = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *r = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *p = nullptr)
{
color = c, left = l, right = r, parent = p;
}
RBTreeNode(Key k, Value v, Color c, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *l = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *r = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *p = nullptr)
{
key = k, value = v, color = c, left = l, right = r, parent = p;
}
};
template <typename Key, typename Value>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<Key, Value> Node;
private:
// 根節(jié)點
Node *root;
// 哨兵節(jié)點
Node *NIL;
// 節(jié)點個數(shù)
int size;
// 創(chuàng)建一個空的紅色節(jié)點
Node *createEmptyRedNode(Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr)
{
return new Node(Color::RED, l, r, p);
}
// 創(chuàng)建一個非空紅色節(jié)點
Node *createRedNode(Key key, Value value, Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr)
{
return new Node(key, value, Color::RED, l, r, p);
}
// 創(chuàng)建一個空的黑色節(jié)點
Node *createEmptyBlackNode(Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr)
{
return new Node(Color::BLACK, l, r, p);
}
// 創(chuàng)建一個非空黑色節(jié)點
Node *createBlackNode(Key key, Value value, Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr)
{
return new Node(key, value, Color::BLACK, l, r, p);
}
// 銷毀節(jié)點
void destroyNode(Node *node)
{
delete node;
}
// 左旋操作
void leftRotate(Node *p)
{
// 獲取旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點的右兒子
Node *rightSon = p->right;
// 獲取祖先節(jié)點
Node *grandParent = p->parent;
// 更新旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點
p->right = rightSon->left;
p->parent = rightSon;
// 更新右節(jié)點
// 如果右兒子的左節(jié)點不為NIL,則將右兒子的左節(jié)點的父節(jié)點設(shè)置為p
if (rightSon->left != NIL)
rightSon->left->parent = p;
rightSon->parent = grandParent;
rightSon->left = p;
// 更新祖先節(jié)點
// 如果p為根節(jié)點
if (grandParent == NIL)
root = rightSon;
// 如果p為左節(jié)點
else if (grandParent->left == p)
grandParent->left = rightSon;
// 如果p為右節(jié)點
else
grandParent->right = rightSon;
}
// 右旋操作
void rightRotate(Node *p)
{
// 獲取旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點的左兒子
Node *leftSon = p->left;
// 獲取祖先節(jié)點
Node *grandParent = p->parent;
// 更新旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點
p->left = leftSon->right;
p->parent = leftSon;
// 更新左節(jié)點
// 如果左兒子的右節(jié)點不為NIL,則將左兒子的右節(jié)點的父節(jié)點設(shè)置為p
if (leftSon->right != NIL)
leftSon->right->parent = p;
leftSon->parent = grandParent;
leftSon->right = p;
// 更新祖先節(jié)點
// 如果p為根節(jié)點
if (grandParent == NIL)
root = leftSon;
// 如果p為左節(jié)點
else if (grandParent->left == p)
grandParent->left = leftSon;
// 如果p為右節(jié)點
else
grandParent->right = leftSon;
}
// 插入調(diào)整
void insertFixup(Node *N)
{
// 一直向上調(diào)整,直到父節(jié)點不是紅色,或者父節(jié)點為根節(jié)點
// 注意這里的N節(jié)點一定為紅色
while (N->parent->color == Color::RED && N->parent != root)
{
// 如果父節(jié)點為左子節(jié)點
if (N->parent == N->parent->parent->left)
{
// 獲取叔叔節(jié)點
Node *U = N->parent->parent->right;
// 如果叔叔節(jié)點的顏色也為紅色,則將父節(jié)點和叔叔節(jié)點都變?yōu)楹谏嫦裙?jié)點變?yōu)榧t色,繼續(xù)向上調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
if (U->color == Color::RED)
{
U->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 繼續(xù)調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
N = N->parent->parent;
}
else
{
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點不同向,需旋轉(zhuǎn)為同向
if (N == N->parent->right)
{
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)N的父節(jié)點
N = N->parent;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)父節(jié)點
leftRotate(N);
}
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點同向
// 注意要先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)之后會改變父子關(guān)系,到時候很混亂
// 父節(jié)點設(shè)置為黑色
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
// 祖先節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)祖先節(jié)點
rightRotate(N->parent->parent);
}
}
// 如果父節(jié)點為右子節(jié)點
else
{
// 獲取叔叔節(jié)點
Node *U = N->parent->parent->left;
// 如果叔叔節(jié)點的顏色也為紅色,則將父節(jié)點和叔叔節(jié)點都變?yōu)楹谏嫦裙?jié)點變?yōu)榧t色,繼續(xù)向上調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
if (U->color == Color::RED)
{
U->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 繼續(xù)調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
N = N->parent->parent;
}
else
{
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點不同向,需旋轉(zhuǎn)為同向
if (N == N->parent->left)
{
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)N的父節(jié)點
N = N->parent;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)父節(jié)點
rightRotate(N);
}
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點同向
// 注意要先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)之后會改變父子關(guān)系,到時候很混亂
// 父節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
// 祖先節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)祖先節(jié)點
leftRotate(N->parent->parent);
}
}
}
// 根節(jié)點可以無責(zé)任變成黑色
root->color = Color::BLACK;
}
// 用v替換u,只更換父節(jié)點關(guān)系
void replace(Node *u, Node *v)
{
// 如果u為root
if (u->parent == NIL)
root = v;
// u為左子節(jié)點
else if (u->parent->left == u)
u->parent->left = v;
// u為右子節(jié)點
else
u->parent->right = v;
v->parent = u->parent;
}
// 獲取最小節(jié)點
Node *getMinNode(Node *p)
{
while (p->left != NIL)
p = p->left;
return p;
}
// 查詢?nèi)吭剌o助函數(shù)
void queryAllHelp(Node *N, vector<Value> &v)
{
if (N == NIL)
return;
queryAllHelp(N->left, v);
v.push_back(N->value);
queryAllHelp(N->right, v);
}
public:
RBTree(/* args */)
{
NIL = createEmptyBlackNode();
NIL->left = NIL, NIL->right = NIL, NIL->parent = NIL;
root = NIL;
size = 0;
}
pair<bool, Value &> query(Key key)
{
Value v;
if (root == NIL)
return {false, v};
Node *temp = root;
while (temp != NIL)
{
if (key < temp->key)
temp = temp->left;
else if (key > temp->key)
temp = temp->right;
else
return {true, temp->value};
}
return {false, v};
}
void insert(Key key, Value value)
{
Node *N = createRedNode(key, value, NIL, NIL, NIL);
// 查詢節(jié)點的父節(jié)點
Node *p = NIL;
// 迭代查找臨時節(jié)點
Node *temp = root;
// 樹為空,直接插入
if (root == NIL)
{
N->color = BLACK;
root = N;
size++;
return;
}
while (temp != NIL)
{
p = temp;
// 往左查找
if (N->key < temp->key)
temp = temp->left;
// 往右查找
else if (N->key > temp->key)
temp = temp->right;
// key值已經(jīng)存在,則替換數(shù)據(jù)
else
{
temp->value = value;
return;
}
}
size++;
N->parent = p;
// 如果key值比父節(jié)點小,則作為左子節(jié)點
if (N->key < p->key)
p->left = N;
// 如果key值比父節(jié)點大,則作為右子節(jié)點
else
p->right = N;
insertFixup(N);
}
int getSize()
{
return size;
}
vector<Value> queryAll()
{
vector<Value> temp;
queryAllHelp(root, temp);
return temp;
}
~RBTree()
{
}
};
int main()
{
RBTree<string, RBTree<int, int>> tr;
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int l;
cin >> l;
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++)
{
string s;
cin >> s;
pair<bool, RBTree<int, int> &> q = tr.query(s);
if (q.first == false)
{
RBTree<int, int> temp;
temp.insert(i, i);
tr.insert(s, temp);
}
else
q.second.insert(i, i);
}
}
int m;
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++)
{
string s;
cin >> s;
pair<bool, RBTree<int, int> &> q = tr.query(s);
if (q.first == false)
cout << endl;
else
{
vector<int> ans = q.second.queryAll();
for (auto x : ans)
cout << x << " ";
cout << endl;
}
}
}
完整代碼
測試情形:第一行給定一個正整數(shù)n,隨后輸入n個數(shù)存儲在紅黑樹,然后輸入一個正整數(shù)m,隨后輸入m個數(shù)表示刪除某個數(shù)。最后輸出樹中還存在多少數(shù),并按照從小到大進行輸出
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#include <ctime>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <vector>
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template <typename Key, typename Value>
struct RBTreeNode
{
// 按照key值進行插入刪除等操作
Key key;
// value為存儲的數(shù)據(jù)
Value value;
// 左節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *left;
// 右節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *right;
// 父節(jié)點指針
RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *parent;
// 節(jié)點顏色
Color color;
RBTreeNode(Color c, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *l = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *r = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *p = nullptr)
{
color = c, left = l, right = r, parent = p;
}
RBTreeNode(Key k, Value v, Color c, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *l = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *r = nullptr, RBTreeNode<Key, Value> *p = nullptr)
{
key = k, value = v, color = c, left = l, right = r, parent = p;
}
};
template <typename Key, typename Value>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<Key, Value> Node;
private:
// 根節(jié)點
Node *root;
// 哨兵節(jié)點
Node *NIL;
// 節(jié)點個數(shù)
int size;
// 創(chuàng)建一個空的紅色節(jié)點
Node *createEmptyRedNode(Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr)
{
return new Node(Color::RED, l, r, p);
}
// 創(chuàng)建一個非空紅色節(jié)點
Node *createRedNode(Key key, Value value, Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr)
{
return new Node(key, value, Color::RED, l, r, p);
}
// 創(chuàng)建一個空的黑色節(jié)點
Node *createEmptyBlackNode(Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr)
{
return new Node(Color::BLACK, l, r, p);
}
// 創(chuàng)建一個非空黑色節(jié)點
Node *createBlackNode(Key key, Value value, Node *l = nullptr, Node *r = nullptr, Node *p = nullptr)
{
return new Node(key, value, Color::BLACK, l, r, p);
}
// 銷毀節(jié)點
void destroyNode(Node *node)
{
delete node;
}
// 左旋操作
void leftRotate(Node *p)
{
// 獲取旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點的右兒子
Node *rightSon = p->right;
// 獲取祖先節(jié)點
Node *grandParent = p->parent;
// 更新旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點
p->right = rightSon->left;
p->parent = rightSon;
// 更新右節(jié)點
// 如果右兒子的左節(jié)點不為NIL,則將右兒子的左節(jié)點的父節(jié)點設(shè)置為p
if (rightSon->left != NIL)
rightSon->left->parent = p;
rightSon->parent = grandParent;
rightSon->left = p;
// 更新祖先節(jié)點
// 如果p為根節(jié)點
if (grandParent == NIL)
root = rightSon;
// 如果p為左節(jié)點
else if (grandParent->left == p)
grandParent->left = rightSon;
// 如果p為右節(jié)點
else
grandParent->right = rightSon;
}
// 右旋操作
void rightRotate(Node *p)
{
// 獲取旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點的左兒子
Node *leftSon = p->left;
// 獲取祖先節(jié)點
Node *grandParent = p->parent;
// 更新旋轉(zhuǎn)節(jié)點
p->left = leftSon->right;
p->parent = leftSon;
// 更新左節(jié)點
// 如果左兒子的右節(jié)點不為NIL,則將左兒子的右節(jié)點的父節(jié)點設(shè)置為p
if (leftSon->right != NIL)
leftSon->right->parent = p;
leftSon->parent = grandParent;
leftSon->right = p;
// 更新祖先節(jié)點
// 如果p為根節(jié)點
if (grandParent == NIL)
root = leftSon;
// 如果p為左節(jié)點
else if (grandParent->left == p)
grandParent->left = leftSon;
// 如果p為右節(jié)點
else
grandParent->right = leftSon;
}
// 插入調(diào)整
void insertFixup(Node *N)
{
// 一直向上調(diào)整,直到父節(jié)點不是紅色,或者父節(jié)點為根節(jié)點
// 注意這里的N節(jié)點一定為紅色
while (N->parent->color == Color::RED && N->parent != root)
{
// 如果父節(jié)點為左子節(jié)點
if (N->parent == N->parent->parent->left)
{
// 獲取叔叔節(jié)點
Node *U = N->parent->parent->right;
// 如果叔叔節(jié)點的顏色也為紅色,則將父節(jié)點和叔叔節(jié)點都變?yōu)楹谏嫦裙?jié)點變?yōu)榧t色,繼續(xù)向上調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
if (U->color == Color::RED)
{
U->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 繼續(xù)調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
N = N->parent->parent;
}
else
{
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點不同向,需旋轉(zhuǎn)為同向
if (N == N->parent->right)
{
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)N的父節(jié)點
N = N->parent;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)父節(jié)點
leftRotate(N);
}
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點同向
// 注意要先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)之后會改變父子關(guān)系,到時候很混亂
// 父節(jié)點設(shè)置為黑色
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
// 祖先節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)祖先節(jié)點
rightRotate(N->parent->parent);
}
}
// 如果父節(jié)點為右子節(jié)點
else
{
// 獲取叔叔節(jié)點
Node *U = N->parent->parent->left;
// 如果叔叔節(jié)點的顏色也為紅色,則將父節(jié)點和叔叔節(jié)點都變?yōu)楹谏嫦裙?jié)點變?yōu)榧t色,繼續(xù)向上調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
if (U->color == Color::RED)
{
U->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 繼續(xù)調(diào)整祖先節(jié)點
N = N->parent->parent;
}
else
{
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點不同向,需旋轉(zhuǎn)為同向
if (N == N->parent->left)
{
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)N的父節(jié)點
N = N->parent;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)父節(jié)點
rightRotate(N);
}
// 調(diào)整節(jié)點與父節(jié)點同向
// 注意要先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn),旋轉(zhuǎn)之后會改變父子關(guān)系,到時候很混亂
// 父節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
// 祖先節(jié)點設(shè)置為紅色
N->parent->parent->color = Color::RED;
// 旋轉(zhuǎn)祖先節(jié)點
leftRotate(N->parent->parent);
}
}
}
// 根節(jié)點可以無責(zé)任變成黑色
root->color = Color::BLACK;
}
// 刪除調(diào)整
void removeFixup(Node *C)
{
while (C != root && C->color == BLACK)
{
// 如果C為左子節(jié)點
if (C == C->parent->left)
{
// 獲取兄弟節(jié)點
Node *S = C->parent->right;
// 如果兄弟節(jié)點為紅色,我們需要通過旋轉(zhuǎn)將兄弟節(jié)點變?yōu)楹谏? if (S->color == Color::RED)
{
// 先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn)
S->color = Color::BLACK;
C->parent->color = Color::RED;
leftRotate(C->parent);
// 獲取新的兄弟節(jié)點
S = C->parent->right;
}
// 兄弟節(jié)點的左兒子和右兒子都為黑色
if (S->left->color == Color::BLACK && S->right->color == Color::BLACK)
{
// 父節(jié)點為紅色
if (C->parent->color == Color::RED)
{
C->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
S->color = Color::RED;
// 已經(jīng)調(diào)整完畢,不需要再進行調(diào)整就將C設(shè)置為根節(jié)點
C = root;
}
// 父節(jié)點為黑色
else
{
S->color = Color::RED;
// 父節(jié)點成為雙黑節(jié)點,繼續(xù)調(diào)整父節(jié)點
C = C->parent;
}
}
else
{
// 近侄節(jié)點為紅色,遠侄子節(jié)點為黑色,需要調(diào)整為遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
if (S->right->color == Color::BLACK)
{
// 先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn)
S->color = Color::RED;
S->left->color = Color::BLACK;
rightRotate(S);
// 由于旋轉(zhuǎn)改變了父子關(guān)系,所以重新獲取一下兄弟節(jié)點
S = C->parent->right;
}
// 調(diào)整后遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
S->color = C->parent->color;
C->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
S->right->color = Color::BLACK;
leftRotate(C->parent);
// 已經(jīng)調(diào)整完畢,不需要再進行調(diào)整就將C設(shè)置為根節(jié)點
C = root;
}
}
// 如果C為右子節(jié)點
else
{
// 獲取兄弟節(jié)點
Node *S = C->parent->left;
// 如果兄弟節(jié)點為紅色,我們需要通過旋轉(zhuǎn)將兄弟節(jié)點變?yōu)楹谏? if (S->color == Color::RED)
{
// 先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn)
S->color = Color::BLACK;
C->parent->color = Color::RED;
rightRotate(C->parent);
// 獲取新的兄弟節(jié)點
S = C->parent->left;
}
// 兄弟節(jié)點的左兒子和右兒子都為黑色
if (S->left->color == Color::BLACK && S->right->color == Color::BLACK)
{
// 父節(jié)點為紅色
if (C->parent->color == Color::RED)
{
C->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
S->color = Color::RED;
// 已經(jīng)調(diào)整完畢,不需要再進行調(diào)整就將C設(shè)置為根節(jié)點
C = root;
}
// 父節(jié)點為黑色
else
{
S->color = Color::RED;
// 父節(jié)點成為雙黑節(jié)點,繼續(xù)調(diào)整父節(jié)點
C = C->parent;
}
}
else
{
// 近侄節(jié)點為紅色,遠侄子節(jié)點為黑色,需要調(diào)整為遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
if (S->left->color == Color::BLACK)
{
// 先變色再旋轉(zhuǎn)
S->color = Color::RED;
S->right->color = Color::BLACK;
leftRotate(S);
// 由于旋轉(zhuǎn)改變了父子關(guān)系,所以重新獲取一下兄弟節(jié)點
S = C->parent->left;
}
// 調(diào)整后遠侄節(jié)點為紅色
S->color = C->parent->color;
C->parent->color = Color::BLACK;
S->left->color = Color::BLACK;
rightRotate(C->parent);
// 已經(jīng)調(diào)整完畢,不需要再進行調(diào)整就將C設(shè)置為根節(jié)點
C = root;
}
}
}
// 根節(jié)點可以無責(zé)任變成黑色
root->color = Color::BLACK;
}
// 用v替換u,只更換父節(jié)點關(guān)系
void replace(Node *u, Node *v)
{
// 如果u為root
if (u->parent == NIL)
root = v;
// u為左子節(jié)點
else if (u->parent->left == u)
u->parent->left = v;
// u為右子節(jié)點
else
u->parent->right = v;
v->parent = u->parent;
}
// 獲取最小節(jié)點
Node *getMinNode(Node *p)
{
while (p->left != NIL)
p = p->left;
return p;
}
// 打印輔助函數(shù)
void printHelp(Node *p, int &red, int &black)
{
if (p == NIL)
return;
cout << "key = " << p->key << " value = " << p->value << " color = " << p->color << endl;
printHelp(p->left, red, black);
if (p->color == Color::RED)
red++;
else
black++;
printHelp(p->right, red, black);
}
// 查詢?nèi)吭剌o助函數(shù)
void queryAllHelp(Node *N, vector<Value> &v)
{
if (N == NIL)
return;
queryAllHelp(N->left, v);
v.push_back(N->value);
queryAllHelp(N->right, v);
}
int checkBlackHeightHelp(Node *N, bool &flag)
{
if (N == NIL)
return 1;
int left = checkBlackHeightHelp(N->left, flag);
int right = checkBlackHeightHelp(N->right, flag);
if (left != right)
flag = false;
return left + (N->color == Color::BLACK ? 1 : 0);
}
public:
RBTree(/* args */)
{
NIL = createEmptyBlackNode();
NIL->left = NIL, NIL->right = NIL, NIL->parent = NIL;
root = NIL;
size = 0;
}
pair<bool, Value> query(Key key)
{
if (root == NIL)
return {false, Value()};
Node *temp = root;
while (temp != NIL)
{
if (key < temp->key)
temp = temp->left;
else if (key > temp->key)
temp = temp->right;
else
return {true, temp->value};
}
return {false, Value()};
}
void insert(Key key, Value value)
{
Node *N = createRedNode(key, value, NIL, NIL, NIL);
// 查詢節(jié)點的父節(jié)點
Node *p = NIL;
// 迭代查找臨時節(jié)點
Node *temp = root;
// 樹為空,直接插入
if (root == NIL)
{
N->color = BLACK;
root = N;
size++;
return;
}
while (temp != NIL)
{
p = temp;
// 往左查找
if (N->key < temp->key)
temp = temp->left;
// 往右查找
else if (N->key > temp->key)
temp = temp->right;
// key值已經(jīng)存在,則替換數(shù)據(jù)
else
{
temp->value = value;
return;
}
}
size++;
N->parent = p;
// 如果key值比父節(jié)點小,則作為左子節(jié)點
if (N->key < p->key)
p->left = N;
// 如果key值比父節(jié)點大,則作為右子節(jié)點
else
p->right = N;
insertFixup(N);
}
void remove(Key key)
{
Node *N = root;
while (N != NIL)
{
if (N->key == key)
break;
if (key < N->key)
N = N->left;
else
N = N->right;
}
// 樹中沒有刪除的key
if (N == NIL)
return;
// 刪除節(jié)點為樹中唯一節(jié)點
// Case 1
if (size == 1)
{
if (root != NIL)
destroyNode(root);
root = NIL;
size--;
return;
}
// Case 4
// 刪除節(jié)點有兩個非NIL的子節(jié)點
if (N->left != NIL && N->right != NIL)
{
// 獲得后繼節(jié)點
Node *minNode = getMinNode(N->right);
// 我們這里直接交換鍵值,方便,但如果鍵值都是比較大的對象就很慢了,最好還是交換指針
swap(minNode->key, N->key);
swap(minNode->value, N->value);
// 刪除節(jié)點轉(zhuǎn)換為后繼節(jié)點,轉(zhuǎn)移到case 2或 case 3
N = minNode;
}
// Case 3
if (N->left == NIL && N->right != NIL)
{
Node *rightSon = N->right;
rightSon->color = N->color;
// 用右子節(jié)點替換刪除節(jié)點
replace(N, rightSon);
// 刪除節(jié)點
destroyNode(N);
}
// Case 3
else if (N->left != NIL && N->right == NIL)
{
Node *leftSon = N->left;
leftSon->color = N->color;
// 用左子節(jié)點替換刪除節(jié)點
replace(N, leftSon);
// 刪除節(jié)點
destroyNode(N);
}
// Case 2
else
{
// 此情況為刪除節(jié)點的兩個兒子都為NIL節(jié)點
// 刪除節(jié)點為紅色,直接刪除即可
if (N->color == Color::RED)
{
Node *parent = N->parent;
if (parent->left == N)
parent->left = NIL;
else
parent->right = NIL;
destroyNode(N);
}
// 刪除節(jié)點為黑色,出現(xiàn)雙黑節(jié)點,需要向上調(diào)整
else
{
removeFixup(N);
// 調(diào)整后刪除該節(jié)點
Node *parent = N->parent;
if (parent->left == N)
parent->left = NIL;
else
parent->right = NIL;
destroyNode(N);
}
}
size--;
}
int getSize()
{
return size;
}
void print()
{
int red = 0, black = 0;
printHelp(root, red, black);
cout << "redNode num = " << red << " " << "blackNode num = " << black << endl;
}
vector<Value> queryAll()
{
vector<Value> temp;
queryAllHelp(root, temp);
return temp;
}
void checkBlackHeight()
{
bool flag = true;
checkBlackHeightHelp(root, flag);
if (flag)
cout << "right!" << endl;
else
cout << "error!" << endl;
}
~RBTree()
{
}
};
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cout.tie(0);
RBTree<int, int> tr;
int n, m, x;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
cin >> x;
tr.insert(x, x);
}
// cout << "check black height after insert: ";
// tr.checkBlackHeight();
cin >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
cin >> x;
tr.remove(x);
}
// cout << "check black height after remove: ";
// tr.checkBlackHeight();
vector<int> ans = tr.queryAll();
cout << ans.size() << endl;
for (auto x : ans)
cout << x << endl;
}
感想
紅黑樹很復(fù)雜,特別是刪除操作,要考慮很多情況,這篇文章也寫了有幾天,在網(wǎng)上也找了很多資料,終歸是搞出來了,也是見識到了紅黑樹的”厲害“
水平有限,測試的情況比較少,代碼不保證完全正確,如果有問題歡迎指正





 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號