SpringBoot2核心技術(shù)-核心功能 2 Web開發(fā)1
https://www.yuque.com/atguigu/springboot/vgzmgh
二 Web開發(fā)
1、SpringMVC自動(dòng)配置概覽
Spring Boot provides auto-configuration for Spring MVC that works well with most applications.(大多場(chǎng)景我們都無(wú)需自定義配置)
The auto-configuration adds the following features on top of Spring’s defaults:
● Inclusion of ContentNegotiatingViewResolver and BeanNameViewResolver beans.
○ 內(nèi)容協(xié)商視圖解析器和BeanName視圖解析器
● Support for serving static resources, including support for WebJars (covered later in this document)).
○ 靜態(tài)資源(包括webjars)
● Automatic registration of Converter, GenericConverter, and Formatter beans.
○ 自動(dòng)注冊(cè) Converter,GenericConverter,F(xiàn)ormatter
● Support for HttpMessageConverters (covered later in this document).
○ 支持 HttpMessageConverters (后來(lái)我們配合內(nèi)容協(xié)商理解原理)
● Automatic registration of MessageCodesResolver (covered later in this document).
○ 自動(dòng)注冊(cè) MessageCodesResolver (國(guó)際化用)
● Static index.html support.
○ 靜態(tài)index.html 頁(yè)支持
● Custom Favicon support (covered later in this document).
○ 自定義 Favicon
● Automatic use of a ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer bean (covered later in this document).
○ 自動(dòng)使用 ConfigurableWebBindingInitializer ,(DataBinder負(fù)責(zé)將請(qǐng)求數(shù)據(jù)綁定到JavaBean上)
If you want to keep those Spring Boot MVC customizations and make more MVC customizations
(interceptors, formatters, view controllers, and other features), you can add your own @Configuration class
of type WebMvcConfigurer but without @EnableWebMvc.
不用@EnableWebMvc注解。使用 @Configuration + WebMvcConfigurer 自定義規(guī)則
If you want to provide custom instances of RequestMappingHandlerMapping,
RequestMappingHandlerAdapter, or ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver, and still keep the Spring
Boot MVC customizations, you can declare a bean of type WebMvcRegistrations and use it to provide
custom instances of those components.
聲明 WebMvcRegistrations 改變默認(rèn)底層組件
If you want to take complete control of Spring MVC, you can add your own @Configuration annotated with
@EnableWebMvc, or alternatively add your own @Configuration-annotated
DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration as described in the Javadoc of @EnableWebMvc.
使用 @EnableWebMvc+@Configuration+DelegatingWebMvcConfiguration 全面接管SpringMVC
2、簡(jiǎn)單功能分析
new project -> Spring Initializr -> default -> com.yu->boot-05-web-01->
web -> springweb
developer tools ->
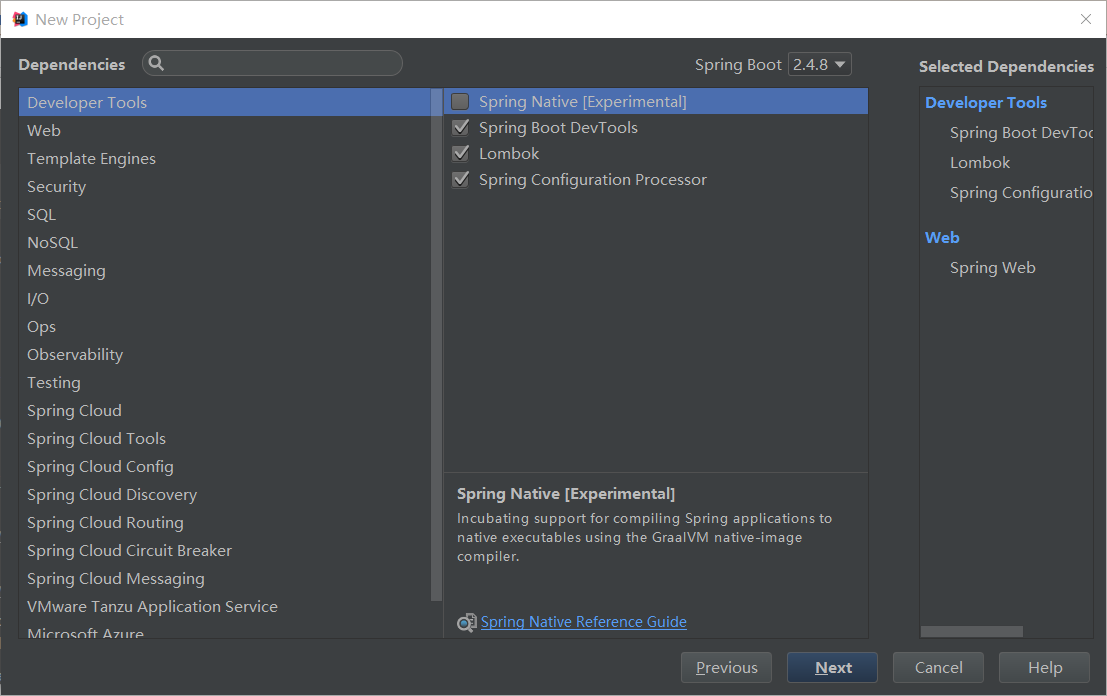
resources下新建 application.yaml
2.1、靜態(tài)資源訪問(wèn)
1、靜態(tài)資源目錄
只要靜態(tài)資源放在類路徑下: called /static (or /public or /resources or /META-INF/resources
訪問(wèn) : 當(dāng)前項(xiàng)目根路徑/ + 靜態(tài)資源名 如 localhost:8080/1.jpg
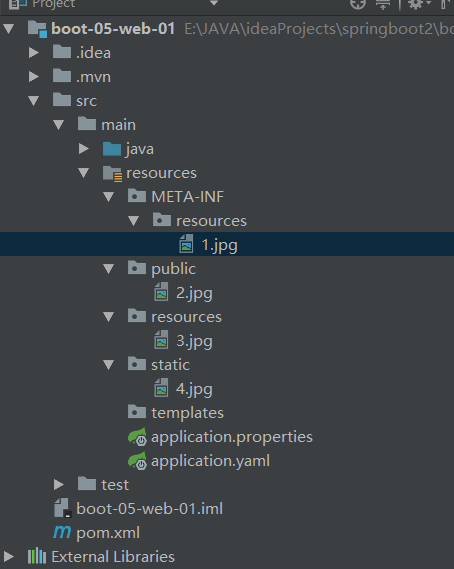
原理: 靜態(tài)映射/**。
請(qǐng)求進(jìn)來(lái),先去找Controller看能不能處理。不能處理的所有請(qǐng)求又都交給靜態(tài)資源處理器。靜態(tài)資源也找不到則響應(yīng)404頁(yè)面
添加靜態(tài)資源路徑
spring:
#改變前綴
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /res/**
#添加靜態(tài)資源路徑
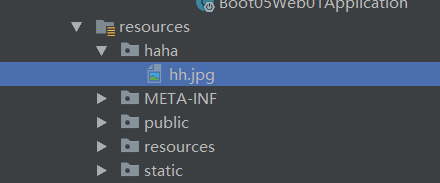
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]
2、靜態(tài)資源訪問(wèn)前綴
默認(rèn)無(wú)前綴
可以通過(guò)以下代碼改變前綴
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /res/**
當(dāng)前項(xiàng)目 + static-path-pattern + 靜態(tài)資源名 = 靜態(tài)資源文件夾下找
即 localhost:8080/res/1.jpg
3、webjar
自動(dòng)映射 /webjars/**
https://www.webjars.org/
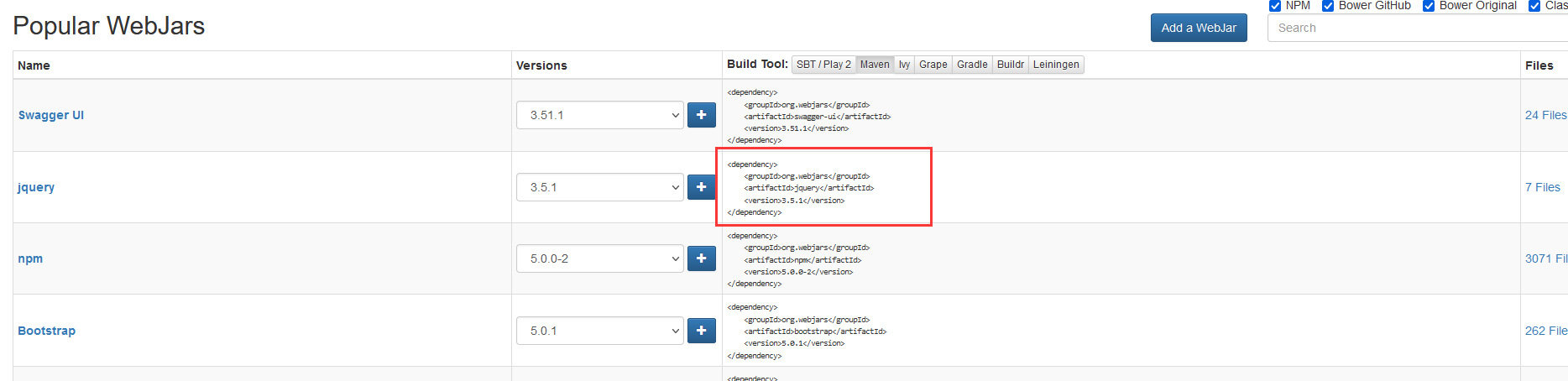
pom.xml
<dependency>
<groupId>org.webjars</groupId>
<artifactId>jquery</artifactId>
<version>3.5.1</version>
</dependency>
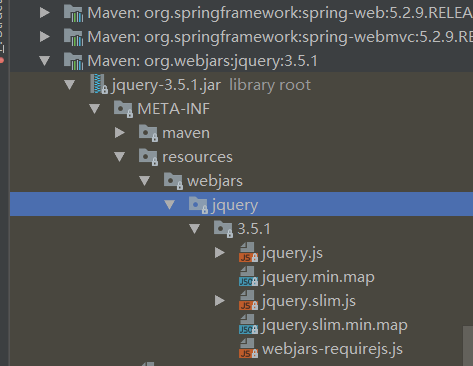
訪問(wèn)地址:http://localhost:8080/webjars/jquery/3.5.1/jquery.js 后面地址要按照依賴?yán)锩娴陌窂?/p>
2.2、歡迎頁(yè)支持
● 靜態(tài)資源路徑下 index.html
○ 可以配置靜態(tài)資源路徑
○ 但是不可以配置靜態(tài)資源的訪問(wèn)前綴。否則導(dǎo)致 index.html不能被默認(rèn)訪問(wèn)
spring:
# mvc:
# static-path-pattern: /res/** 這個(gè)會(huì)導(dǎo)致welcome page功能失效
resources:
static-locations: [classpath:/haha/]
● controller能處理/index
2.3、自定義 Favicon (訪問(wèn)標(biāo)簽小圖標(biāo))
把文件重命名為 favicon.ico 放在靜態(tài)資源目錄下即可。
spring:
# mvc:
# static-path-pattern: /res/** 這個(gè)會(huì)導(dǎo)致 Favicon 功能失效?
2.4、靜態(tài)資源配置原理(**)
● SpringBoot啟動(dòng)默認(rèn)加載 xxxAutoConfiguration 類(自動(dòng)配置類)
● SpringMVC功能的自動(dòng)配置類 WebMvcAutoConfiguration,生效
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnWebApplication(type = Type.SERVLET)
@ConditionalOnClass({ Servlet.class, DispatcherServlet.class, WebMvcConfigurer.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(WebMvcConfigurationSupport.class)
@AutoConfigureOrder(Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE + 10)
@AutoConfigureAfter({ DispatcherServletAutoConfiguration.class, TaskExecutionAutoConfiguration.class,
ValidationAutoConfiguration.class })
public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration {}
● 給容器中配了什么。
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@Import(EnableWebMvcConfiguration.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties({ WebMvcProperties.class, ResourceProperties.class })
@Order(0)
public static class WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter implements WebMvcConfigurer {}
● 配置文件的相關(guān)屬性和xxx進(jìn)行了綁定。
WebMvcProperties==spring.mvc、
ResourceProperties==spring.resources
1、配置類只有一個(gè)有參構(gòu)造器
//有參構(gòu)造器所有參數(shù)的值都會(huì)從容器中確定
//ResourceProperties resourceProperties;獲取和spring.resources綁定的所有的值的對(duì)象
//WebMvcProperties mvcProperties 獲取和spring.mvc綁定的所有的值的對(duì)象
//ListableBeanFactory beanFactory Spring的beanFactory
//HttpMessageConverters 找到所有的HttpMessageConverters
//ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer 找到 資源處理器的自定義器。=========
//DispatcherServletPath
//ServletRegistrationBean 給應(yīng)用注冊(cè)Servlet、Filter....
public WebMvcAutoConfigurationAdapter(ResourceProperties resourceProperties, WebMvcProperties mvcProperties,
ListableBeanFactory beanFactory, ObjectProvider<HttpMessageConverters> messageConvertersProvider,
ObjectProvider<ResourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer> resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider,
ObjectProvider<DispatcherServletPath> dispatcherServletPath,
ObjectProvider<ServletRegistrationBean<?>> servletRegistrations) {
this.resourceProperties = resourceProperties;
this.mvcProperties = mvcProperties;
this.beanFactory = beanFactory;
this.messageConvertersProvider = messageConvertersProvider;
this.resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizer = resourceHandlerRegistrationCustomizerProvider.getIfAvailable();
this.dispatcherServletPath = dispatcherServletPath;
this.servletRegistrations = servletRegistrations;
}
2、資源處理的默認(rèn)規(guī)則
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
return;
}
Duration cachePeriod = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getPeriod();
CacheControl cacheControl = this.resourceProperties.getCache().getCachecontrol().toHttpCacheControl();
//webjars的規(guī)則
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern("/webjars/**")) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler("/webjars/**")
.addResourceLocations("classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/")
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
//
String staticPathPattern = this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern();
if (!registry.hasMappingForPattern(staticPathPattern)) {
customizeResourceHandlerRegistration(registry.addResourceHandler(staticPathPattern)
.addResourceLocations(getResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations()))
.setCachePeriod(getSeconds(cachePeriod)).setCacheControl(cacheControl));
}
}
spring:
# mvc:
# static-path-pattern: /res/**
resources:
add-mappings: false 禁用所有靜態(tài)資源規(guī)則
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.resources", ignoreUnknownFields = false)
public class ResourceProperties {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = { "classpath:/META-INF/resources/",
"classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/" };
/**
* Locations of static resources. Defaults to classpath:[/META-INF/resources/,
* /resources/, /static/, /public/].
*/
private String[] staticLocations = CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS;
3、歡迎頁(yè)的處理規(guī)則
HandlerMapping:處理器映射。保存了每一個(gè)Handler能處理哪些請(qǐng)求。
@Bean
public WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping(ApplicationContext applicationContext,
FormattingConversionService mvcConversionService, ResourceUrlProvider mvcResourceUrlProvider) {
WelcomePageHandlerMapping welcomePageHandlerMapping = new WelcomePageHandlerMapping(
new TemplateAvailabilityProviders(applicationContext), applicationContext, getWelcomePage(),
this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern());
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setInterceptors(getInterceptors(mvcConversionService, mvcResourceUrlProvider));
welcomePageHandlerMapping.setCorsConfigurations(getCorsConfigurations());
return welcomePageHandlerMapping;
}
WelcomePageHandlerMapping(TemplateAvailabilityProviders templateAvailabilityProviders,
ApplicationContext applicationContext, Optional<Resource> welcomePage, String staticPathPattern) {
if (welcomePage.isPresent() && "/**".equals(staticPathPattern)) {
//要用歡迎頁(yè)功能,必須是/**
logger.info("Adding welcome page: " + welcomePage.get());
setRootViewName("forward:index.html");
}
else if (welcomeTemplateExists(templateAvailabilityProviders, applicationContext)) {
// 調(diào)用Controller /index
logger.info("Adding welcome page template: index");
setRootViewName("index");
}
}
4、favicon
3、請(qǐng)求參數(shù)處理
0、請(qǐng)求映射
1、rest使用與原理(**)
● @xxxMapping;
● Rest風(fēng)格支持(使用HTTP請(qǐng)求方式動(dòng)詞來(lái)表示對(duì)資源的操作)
○ 以前:/getUser 獲取用戶 /deleteUser 刪除用戶 /editUser 修改用戶 /saveUser 保存用戶
○ 現(xiàn)在: /user GET-獲取用戶 DELETE-刪除用戶 PUT-修改用戶 POST-保存用戶
○ 核心Filter;HiddenHttpMethodFilter
■ 用法: 表單method=post,隱藏域 _method=put
■ SpringBoot中手動(dòng)開啟
○ 擴(kuò)展:如何把_method 這個(gè)名字換成我們自己喜歡的。
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getUser(){
return "GET-張三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String saveUser(){
return "POST-張三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String putUser(){
return "PUT-張三";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/user",method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String deleteUser(){
return "DELETE-張三";
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(HiddenHttpMethodFilter.class)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.mvc.hiddenmethod.filter", name = "enabled", matchIfMissing = false)
public OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter() {
return new OrderedHiddenHttpMethodFilter();
}
//自定義filter
@Bean
public HiddenHttpMethodFilter hiddenHttpMethodFilter(){
HiddenHttpMethodFilter methodFilter = new HiddenHttpMethodFilter();
methodFilter.setMethodParam("_m");
return methodFilter;
}
Rest原理(表單提交要使用REST的時(shí)候)
● 表單提交會(huì)帶上_method=PUT
● 請(qǐng)求過(guò)來(lái)被HiddenHttpMethodFilter攔截
○ 請(qǐng)求是否正常,并且是POST
■ 獲取到_method的值。
■ 兼容以下請(qǐng)求;PUT.DELETE.PATCH
■ 原生request(post),包裝模式requesWrapper重寫了getMethod方法,返回的是傳入的值。
■ 過(guò)濾器鏈放行的時(shí)候用wrapper。以后的方法調(diào)用getMethod是調(diào)用requesWrapper的。
Rest使用客戶端工具,
● 如PostMan直接發(fā)送Put、delete等方式請(qǐng)求,無(wú)需Filter。
spring:
mvc:
hiddenmethod:
filter:
enabled: true #開啟頁(yè)面表單的Rest功能
2、請(qǐng)求映射原理
1、普通參數(shù)與基本注解
1.1、注解:
@PathVariable:路徑變量
@RequestHeader: 獲取請(qǐng)求頭
@ModelAttribute:
@RequestParam: 獲取請(qǐng)求參數(shù)
@MatrixVariable: 矩陣變量
@CookieValue: 獲取cookie值
@RequestBody: 獲取請(qǐng)求體【POST】
@RequestAttribute: 獲取request域?qū)傩?br>
關(guān)于矩陣變量:
/cars/{path }?xxx=xxx&aaa=ccc queryString查詢字符串可以通過(guò)@RequestParam實(shí)現(xiàn)
/cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,audi,yd ;矩陣變量
如果在頁(yè)面開發(fā)中,cookie禁用了, session里面的內(nèi)容怎么使用?
session.set(a, b )---> jsessionid ---> cookie ----〉每次發(fā)請(qǐng)求攜帶。
可以通過(guò)url重寫: /abc;jsesssionid=xxxx 把cookie的值使用矩陣變量的方式進(jìn)行傳遞.
/boss/1/2
/boss/1;age=20/2;age=20
新建ParameterTestController
獲取params想獲取多個(gè)inters使用 @RequestParam MultiValueMap<String,String> params 即可
@RestController
public class ParameterTestController {
// localhost:8080/car/2/owner/zhangsn?age=18&inters=book&inters=lol
@GetMapping("/car/{id}/owner/{username}")
public Map<String,Object> getCar(@PathVariable("id") Integer id,
@PathVariable("username") String name,
@PathVariable Map<String,String> pv,
@RequestHeader("User-Agent") String userAgent,
@RequestHeader Map<String,String> header,
@RequestParam("age") Integer age,
@RequestParam("inters") List<String> inters,
@RequestParam Map<String,String> params,
@CookieValue("_ga") String _ga,
@CookieValue("_ga") Cookie cookie){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
// map.put("id",id);
// map.put("name",name);
// map.put("pv",pv);
// map.put("userAgent",userAgent);
// map.put("headers",header);
map.put("age",age);
map.put("inters",inters);
map.put("params",params);
map.put("_ga",_ga);
System.out.println(cookie.getName()+"===>"+cookie.getValue());
return map;
}
@PostMapping("/save")
public Map postMethod(@RequestBody String content){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("content",content);
return map;
}
//1、語(yǔ)法: 請(qǐng)求路徑:/cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,audi,yd
//2、SpringBoot默認(rèn)是禁用了矩陣變量的功能
// 手動(dòng)開啟:原理。對(duì)于路徑的處理。UrlPathHelper進(jìn)行解析。
// removeSemicolonContent(移除分號(hào)內(nèi)容)支持矩陣變量的
//3、矩陣變量必須有url路徑變量才能被解析
@GetMapping("/cars/{path}")
public Map carsSell(@MatrixVariable("low") Integer low,
@MatrixVariable("brand") List<String> brand,
@PathVariable("path") String path){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("low",low);
map.put("brand",brand);
map.put("path",path);
return map;
}
// /boss/1;age=20/2;age=10 有兩個(gè)age如何區(qū)分?
@GetMapping("/boss/{bossId}/{empId}")
public Map boss(@MatrixVariable(value = "age",pathVar = "bossId") Integer bossAge,
@MatrixVariable(value = "age",pathVar = "empId") Integer empAge){
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("bossAge",bossAge);
map.put("empAge",empAge);
return map;
}
}
手動(dòng)開啟矩陣變量的功能有兩種方式
在boot下新建config.WebConfig
方式一
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
//不移除;后面的內(nèi)容,矩陣變量功能就可以生效
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
}
方式二
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
public class WebConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer{
@Bean
public WebMvcConfigurer webMvcConfigurer(){
return new WebMvcConfigurer() {
@Override
public void configurePathMatch(PathMatchConfigurer configurer) {
UrlPathHelper urlPathHelper = new UrlPathHelper();
//不移除;后面的內(nèi)容,矩陣變量功能就可以生效
urlPathHelper.setRemoveSemicolonContent(false);
configurer.setUrlPathHelper(urlPathHelper);
}
};
}
}
測(cè)試
http://localhost:8080/car/2/owner/zhangsn?age=18&inters=book&inters=lol
http://localhost:8080/cars/sell;low=34;brand=byd,audi,yd
http://localhost:8080/boss/1;age=20/2;age=10
index.html
<form action="/save" method="post">
用戶名:<input name="userName"/> <br>
郵箱:<input name="email">
<input type="submit" value="提交"/>
</form>
@RequestAttribute: 獲取request域?qū)傩?br> 新建 RequestController
package com.yu.boot.controller;
@Controller
public class RequestController {
@GetMapping("/goto")
public String gotoPage(HttpServletRequest request){
request.setAttribute("msg","成功了 ~");
request.setAttribute("code",299);
return "forward:/success";//轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)到 /success請(qǐng)求
}
@ResponseBody
@GetMapping("/success")
public Map success(@RequestAttribute("msg") String msg,
@RequestAttribute("code") Integer code,
HttpServletRequest request){
Object msg1 =request.getAttribute("msg");
Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("reqMethod_msg",msg1);
map.put("code",code);
map.put("annotation_msg",msg);
return map;
}
}
測(cè)試
http://localhost:8080/goto
1.2、Servlet API:
WebRequest、ServletRequest、MultipartRequest、 HttpSession、javax.servlet.http.PushBuilder、Principal、InputStream、Reader、HttpMethod、Locale、TimeZone、ZoneId
ServletRequestMethodArgumentResolver 以上的部分參數(shù)
@Override
public boolean supportsParameter(MethodParameter parameter) {
Class<?> paramType = parameter.getParameterType();
return (WebRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
ServletRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
MultipartRequest.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
HttpSession.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
(pushBuilder != null && pushBuilder.isAssignableFrom(paramType)) ||
Principal.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
InputStream.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
Reader.class.isAssignableFrom(paramType) ||
HttpMethod.class == paramType ||
Locale.class == paramType ||
TimeZone.class == paramType ||
ZoneId.class == paramType);
}
1.3、復(fù)雜參數(shù):
Map、Model(map、model里面的數(shù)據(jù)會(huì)被放在request的請(qǐng)求域 request.setAttribute)、Errors/BindingResult、RedirectAttributes( 重定向攜帶數(shù)據(jù))、ServletResponse(response)、SessionStatus、UriComponentsBuilder、ServletUriComponentsBuilder
Map<String,Object> map, Model model, HttpServletRequest request 都是可以給request域中放數(shù)據(jù),
request.getAttribute();
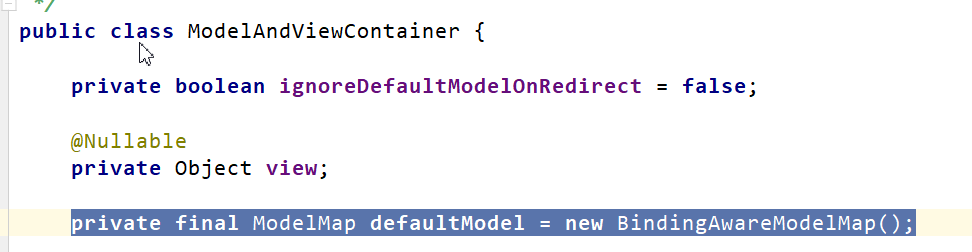
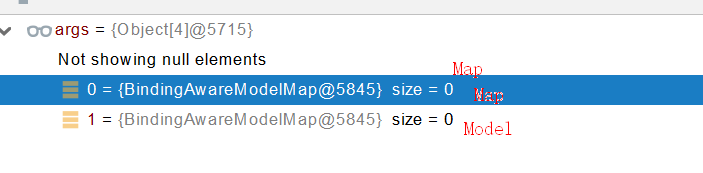
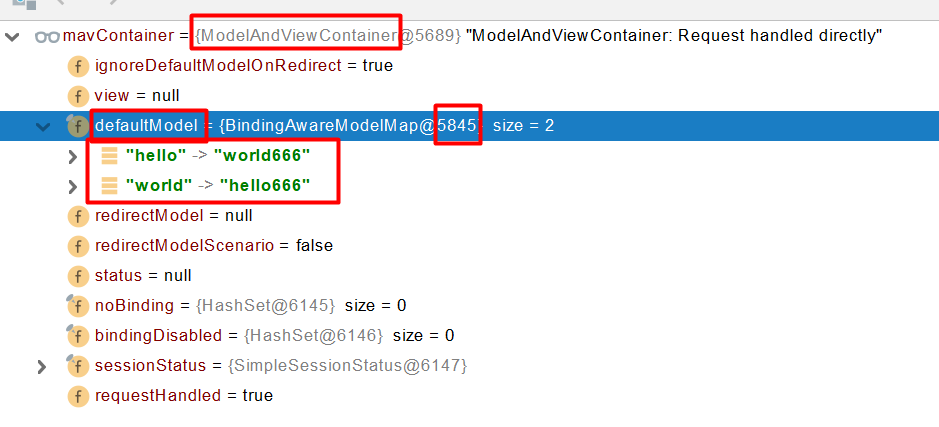
Map、Model類型的參數(shù),會(huì)返回 mavContainer.getModel();---> BindingAwareModelMap 是Model 也是Map
mavContainer.getModel(); 獲取到值的
1.4、自定義對(duì)象參數(shù):
可以自動(dòng)類型轉(zhuǎn)換與格式化,可以級(jí)聯(lián)封裝。
/**
* 姓名: <input name="userName"/> <br/>
* 年齡: <input name="age"/> <br/>
* 生日: <input name="birth"/> <br/>
* 寵物姓名:<input name="pet.name"/><br/>
* 寵物年齡:<input name="pet.age"/>
*/
@Data
public class Person {
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private Date birth;
private Pet pet;
}
@Data
public class Pet {
private String name;
private String age;
}
result
2、POJO封裝過(guò)程
● ServletModelAttributeMethodProcessor



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)