spring framework runtime
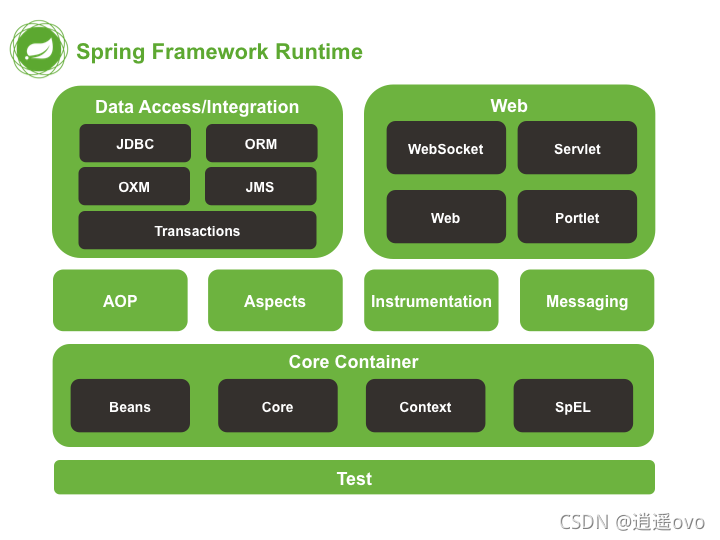
核心容器
容器:servlet 容器、集合
線程池、常量池、數據庫連接池的作用類似于容器
但是他們屬于設計模式中的享元模式,即從池子中取東西,如果取不到,再創建
spring 中的核心容器,類似于集合
作用
- 存放對象
- 取出來使用
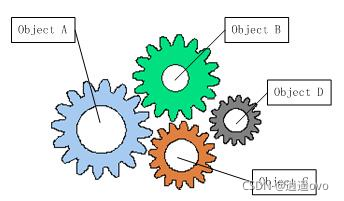
在 spring 中,有些對象是由容器來創建的,并且復制管理對象間的依賴
對于對象間的依賴:A 對象的屬性為 B 對象,A 和 B 就產生了依賴關系
IOC
概念:IOC,(Inversion of Control,控制反轉) —— 以前自己 new 對象以及組織對象間的關系,現在全部交給容器來統一管理,控制權發送了反轉,因此稱為控制反轉。
實現方式:使用 IOC 容器來實現
在 spring 在,稱為 spring bean 容器、spring 容器或 IoC 容器
DI
概念:DI, (Dependency Injection,依賴注入) —— 由 IoC 容器在運行期間,動態的將某種依賴關系注入到對象之中
注入
把 B 對象注入到 A ,稱為 A 的屬性
把 A 注入 IoC 容器中
IoC/DI 的作用
不使用:
使用:
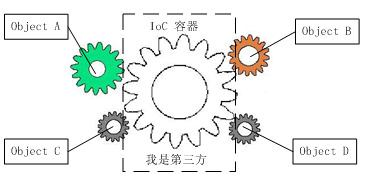
作用
解耦
spring 容器使用流程
使用流程
- 配置 pom.xml 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>spring01</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
<maven.compiler.source>${java.version}</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>${java.version}</maven.compiler.target>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring-framework.version>5.2.10.RELEASE</spring-framework.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring-framework.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<version>1.18.16</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- 明確指定一些插件的版本,以免受到 maven 版本的影響 -->
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-clean-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.8.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-install-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.5.2</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-jar-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-resources-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-site-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.3</version>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<artifactId>maven-surefire-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.22.2</version>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
點擊刷新,使得配置文件完成
- 在 resources 目錄下創建 beans.xml 文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
https://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<!-- org.example 代表掃描 org.example 包下的文件-->
<context:component-scan base-package="org.example"/>
</beans>
- 啟動 spring 容器
package org.example;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//根據Spring配置文件路徑創建容器:應用上下文對象
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
//關閉容器
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).close();
}
}
理解注入流程
- 啟動 spring 容器:new ApplicationContext 的實現類
- 注冊 / 注入對象到容器中:加載指定的配置文件,執行包掃描,指定的包,子包下,帶 spring 框架提供的四個注解,會注入到容器中
@Controller (控制器)
@Service(服務)
@Repository(存儲庫)
@Component (組件) - 裝配 / 注入依賴關系:如果注冊到容器中的對象,屬性使用一下兩個注釋
@Autowired(自動裝配)
@Resource(資源)
注入代碼講解
1.使用 Controller 注解、Bean 注解 + 方法注入
bean 注解使用在方法上,該方法所在的類也需要注解
從容器中獲取 Bean 對象的方法:
- 通過類型獲取(需要容器中只有一個對象)
- 通過名稱、id 獲取
package org.example.controller;
import org.example.model.Duck;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
// 使用 Controller 注解將該類注入到 Bean 容器中
@Controller
public class LoginController {
// 方法前使用 Bean 注解, 也能夠注入對象
@Bean
public Duck d1() {
Duck duck = new Duck();
duck.setName("唐老鴨");
return duck;
}
@Bean
public Duck d2() {
Duck duck = new Duck();
duck.setName("香酥鴨");
return duck;
}
}
- 使用 Repository 注解注入
package org.example.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
@Repository
public class LoginRepository {
}
- 創建 Bean 注入的類
package org.example.model;
import lombok.Getter;
import lombok.Setter;
import lombok.ToString;
@Getter
@Setter
@ToString
public class Duck {
private String name;
}
- 通過 Service 注解注入
package org.example.service;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
@Service
public class LoginService {
// 如果注入的對象不止一個 那么需要使用 @Qualifier 注解來確定使用的是哪個對象
@Autowired
@Qualifier("luYa")
public Duck duck;
}
- @Scope 注解每次都能創建新對象
package org.example.service;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Scope;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
// Scope 注解每次都能獲取新的 Bean 對象
@Service
@Scope("prototype")
public class LoginServicePrototype {
}
- 檢查注入結果
package org.example;
import org.example.controller.LoginController;
import org.example.dao.LoginRepository;
import org.example.model.Duck;
import org.example.service.LoginService;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
public class App {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//根據Spring配置文件路徑創建容器:應用上下文對象
// 類加載路徑下的 beans.xml 文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
// 1. 通過類型獲取
LoginRepository login1 = context.getBean(LoginRepository.class);
// 2. 通過類名獲取, 注意, 類名首字母小寫
LoginRepository login2 = (LoginRepository) context.getBean("loginRepository");
System.out.println(login1);
System.out.println(login2);
// 通過類型獲取
LoginController login3 = context.getBean(LoginController.class);
// 通過類名獲取
LoginController login4 = (LoginController) context.getBean("loginController");
System.out.println(login3);
System.out.println(login4);
LoginService login5 = context.getBean(LoginService.class);
// 通過類名獲取
LoginService login6 = (LoginService) context.getBean("loginService");
System.out.println(login5);
System.out.println(login6);
Duck d1 = (Duck) context.getBean("d1");
Duck d2 = (Duck) context.getBean("d2");
System.out.println(d1);
System.out.println(d2);
// 同一類型注冊了兩個以上對象, 不能通過類型來獲取
// Duck d3 = context.getBean(Duck.class);
// System.out.println(d3);
//關閉容器
((ClassPathXmlApplicationContext) context).close();
}
}
// 打印結果
// org.example.dao.LoginRepository@76a4d6c
// org.example.dao.LoginRepository@76a4d6c
// org.example.controller.LoginController@517cd4b
// org.example.controller.LoginController@517cd4b
// org.example.service.LoginService@6cc7b4de
// org.example.service.LoginService@6cc7b4de
// Duck(name=唐老鴨)
// Duck(name=香酥鴨)
BeanFactory 和 FactoryBean 的區別
- BeanFactory 是 Spring 的頂級接口
- FactroyBean 是工廠 Bean,本身是一個 Bean,且主要是生成 Bean 的工廠
把 getObject() 方法的返回值注冊到容器中



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號