WebGL-工作原理
此文上接WebGL 基礎(chǔ)概念。 在繼續(xù)學(xué)習(xí)之前,我們需要探討一下WebGL在GPU上究竟做了什么。 WebGL在GPU上的工作基本上分為兩部分,第一部分是將頂點(diǎn)(或數(shù)據(jù)流)轉(zhuǎn)換到裁剪空間坐標(biāo), 第二部分是基于第一部分的結(jié)果繪制像素點(diǎn)。
當(dāng)你調(diào)用:
var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES; var offset = 0; var count = 9; gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count);
這里的9表示“處理9個頂點(diǎn)”,所以將會有9個頂點(diǎn)被轉(zhuǎn)換。
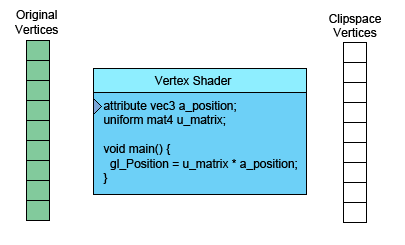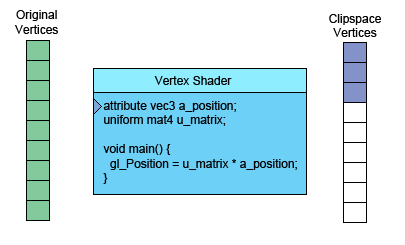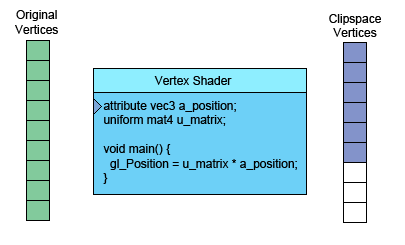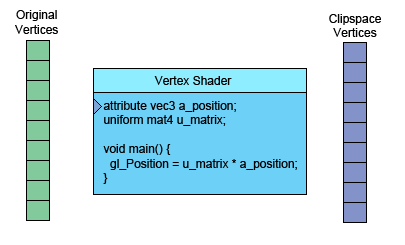
左側(cè)是你提供的數(shù)據(jù)。頂點(diǎn)著色器(Vertex Shader)是你寫進(jìn)GLSL 中的一個方法,每個頂點(diǎn)調(diào)用一次,在這個方法中做一些數(shù)學(xué)運(yùn)算后設(shè)置了一個特殊的gl_Position變量, 這個變量就是該頂點(diǎn)轉(zhuǎn)換到裁剪空間中的坐標(biāo)值,GPU接收該值并將其保存起來。
假設(shè)你正在畫三角形,頂點(diǎn)著色器每完成三次頂點(diǎn)處理,WebGL就會用這三個頂點(diǎn)畫一個三角形。 它計算出這三個頂點(diǎn)對應(yīng)的像素后,就會光柵化這個三角形,“光柵化”其實(shí)就是“用像素畫出來” 的花哨叫法。對于每一個像素,它會調(diào)用你的片斷著色器詢問你使用什么顏色。 你通過給片斷著色器的一個特殊變量gl_FragColor設(shè)置一個顏色值,實(shí)現(xiàn)自定義像素顏色。
使用它們可以做出非常有趣的東西,但如你所見,到目前為止的例子中, 處理每個像素時片斷著色器可用信息很少,幸運(yùn)的是我們可以給它傳遞更多信息。 想要從頂點(diǎn)著色器傳值到片斷著色器,我們可以定義“可變量(varyings)”。
一個簡單的例子,將頂點(diǎn)著色器計算出的裁剪空間坐標(biāo)從頂點(diǎn)著色器傳遞到片斷著色器。
我們來畫一個簡單的三角形,從之前的例子繼續(xù),讓我們把矩形改成三角形。
// 定義一個三角形填充到緩沖里 function setGeometry(gl) { gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array([ 0, -100, 150, 125, -175, 100]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); }
我們只需要畫三個頂點(diǎn):
// 繪制場景 function drawScene() { ... // 繪制幾何體 var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES; var offset = 0; var count = 3; gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count); }
然后在我們的頂點(diǎn)著色器中定義一個varying(可變量)用來給片斷著色器傳值。
varying vec4 v_color; ... void main() { // 將位置和矩陣相乘 gl_Position = vec4((u_matrix * vec3(a_position, 1)).xy, 0, 1); // 從裁減空間轉(zhuǎn)換到顏色空間 // 裁減空間范圍 -1.0 到 +1.0 // 顏色空間范圍 0.0 到 1.0 v_color = gl_Position * 0.5 + 0.5; }
在片斷著色器中定義同名varying變量:
precision mediump float; varying vec4 v_color; void main() { gl_FragColor = v_color; }
WebGL會將同名的可變量從頂點(diǎn)著色器輸入到片斷著色器中。
運(yùn)行下面的代碼:
"use strict"; function main() { // Get A WebGL context /** @type {HTMLCanvasElement} */ var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas"); var gl = canvas.getContext("webgl"); if (!gl) { return; } // setup GLSL program var program = webglUtils.createProgramFromScripts(gl, ["2d-vertex-shader", "2d-fragment-shader"]); // look up where the vertex data needs to go. var positionAttributeLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_position"); // lookup uniforms var matrixLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_matrix"); // Create a buffer. var positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer(); gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer); // Set Geometry. setGeometry(gl); var translation = [200, 150]; var angleInRadians = 0; var scale = [1, 1]; drawScene(); // Setup a ui. webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#x", {value: translation[0], slide: updatePosition(0), max: gl.canvas.width }); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#y", {value: translation[1], slide: updatePosition(1), max: gl.canvas.height}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#angle", {slide: updateAngle, max: 360}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleX", {value: scale[0], slide: updateScale(0), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleY", {value: scale[1], slide: updateScale(1), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2}); function updatePosition(index) { return function(event, ui) { translation[index] = ui.value; drawScene(); } } function updateAngle(event, ui) { var angleInDegrees = 360 - ui.value; angleInRadians = angleInDegrees * Math.PI / 180; drawScene(); } function updateScale(index) { return function(event, ui) { scale[index] = ui.value; drawScene(); } } // Draw the scene. function drawScene() { webglUtils.resizeCanvasToDisplaySize(gl.canvas); // Tell WebGL how to convert from clip space to pixels gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height); // Clear the canvas. gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // Tell it to use our program (pair of shaders) gl.useProgram(program); // Turn on the attribute gl.enableVertexAttribArray(positionAttributeLocation); // Bind the position buffer. gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer); // Tell the attribute how to get data out of positionBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER) var size = 2; // 2 components per iteration var type = gl.FLOAT; // the data is 32bit floats var normalize = false; // don't normalize the data var stride = 0; // 0 = move forward size * sizeof(type) each iteration to get the next position var offset = 0; // start at the beginning of the buffer gl.vertexAttribPointer( positionAttributeLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset) // Compute the matrix var matrix = m3.projection(gl.canvas.clientWidth, gl.canvas.clientHeight); matrix = m3.translate(matrix, translation[0], translation[1]); matrix = m3.rotate(matrix, angleInRadians); matrix = m3.scale(matrix, scale[0], scale[1]); // Set the matrix. gl.uniformMatrix3fv(matrixLocation, false, matrix); // Draw the geometry. var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES; var offset = 0; var count = 3; gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count); } } // Fill the buffer with the values that define a triangle. // Note, will put the values in whatever buffer is currently // bound to the ARRAY_BUFFER bind point function setGeometry(gl) { gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array([ 0, -100, 150, 125, -175, 100]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); } main();
當(dāng)你移動,縮放,旋轉(zhuǎn)三角形時,發(fā)現(xiàn)顏色隨位置變化,不跟著三角形移動。
回想一下,我們只計算了三個頂點(diǎn),調(diào)用了三次頂點(diǎn)著色器,所以也只計算出了三個顏色值, 但是我們的三角形卻有很多顏色,這就是稱之為可變量的varying的原因啦!
WebGL先獲得頂點(diǎn)著色器中計算的三個顏色值,在光柵化三角形時將會根據(jù)這三個值進(jìn)行插值。 每一個像素在調(diào)用片斷著色器時,可變量的值是與之對應(yīng)的插值。
讓我們從上例的三個頂點(diǎn)開始分析
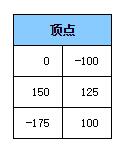
我們的給頂點(diǎn)著色器施加了一個包含平移,旋轉(zhuǎn)和縮放的的矩陣,并將結(jié)果轉(zhuǎn)換到裁剪空間。 默認(rèn)平移,旋轉(zhuǎn)和縮放值為:平移 = 200, 150,旋轉(zhuǎn) = 0,縮放 = 1,所以這里只進(jìn)行了平移。 畫布大小(背景緩沖)為 400×300,所以三個頂點(diǎn)在裁剪空間中為以下坐標(biāo)值。

同時將這些值轉(zhuǎn)換到顏色空間中賦給我們定義的可變量v_color。
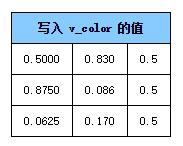
利用這三個值進(jìn)行插值后傳進(jìn)每個像素運(yùn)行的片斷著色器中。

想要給片斷著色器傳值,我們可以先把值傳遞給頂點(diǎn)著色器然后再傳給片斷著色器。 讓我們來畫一個由兩個不同顏色三角形組成的矩形。我們需要給頂點(diǎn)著色器添加一個屬性值, 把值通過屬性傳遞給它后它再直接傳遞給片斷著色器。
attribute vec2 a_position; attribute vec4 a_color; ... varying vec4 v_color; void main() { ... // 直接把屬性值中的數(shù)據(jù)賦給可變量 v_color = a_color; }
現(xiàn)在要給WebGL提供要用的顏色。
// 尋找頂點(diǎn)著色器中需要的數(shù)據(jù) var positionLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_position"); var colorLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_color"); ... // 給顏色數(shù)據(jù)創(chuàng)建一個緩沖 var colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer(); gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer); // 設(shè)置顏色 setColors(gl); ... // 給矩形的兩個三角形 // 設(shè)置顏色值并發(fā)到緩沖 function setColors(gl) { // 生成兩個隨機(jī)顏色 var r1 = Math.random(); var b1 = Math.random(); var g1 = Math.random(); var r2 = Math.random(); var b2 = Math.random(); var g2 = Math.random(); gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array( [ r1, b1, g1, 1, r1, b1, g1, 1, r1, b1, g1, 1, r2, b2, g2, 1, r2, b2, g2, 1, r2, b2, g2, 1]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); }
在渲染的時候設(shè)置顏色屬性:
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(colorLocation); // 綁定顏色緩沖 gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer); // 告訴顏色屬性怎么從 colorBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER) 中讀取顏色值 var size = 4; // 每次迭代使用4個單位的數(shù)據(jù) var type = gl.FLOAT; // 單位數(shù)據(jù)類型是32位的浮點(diǎn)型 var normalize = false; // 不需要?dú)w一化數(shù)據(jù) var stride = 0; // 0 = 移動距離 * 單位距離長度sizeof(type) // 每次迭代跳多少距離到下一個數(shù)據(jù) var offset = 0; // 從綁定緩沖的起始處開始 gl.vertexAttribPointer( colorLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset)
調(diào)整頂點(diǎn)的數(shù)量為6用來畫兩個三角形:
// 畫幾何體 var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES; var offset = 0; var count = 6; gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count);
運(yùn)行下面的代碼:
"use strict"; function main() { // Get A WebGL context /** @type {HTMLCanvasElement} */ var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas"); var gl = canvas.getContext("webgl"); if (!gl) { return; } // setup GLSL program var program = webglUtils.createProgramFromScripts(gl, ["2d-vertex-shader", "2d-fragment-shader"]); // look up where the vertex data needs to go. var positionLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_position"); var colorLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_color"); // lookup uniforms var matrixLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_matrix"); // Create a buffer for the positons. var positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer(); gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer); // Set Geometry. setGeometry(gl); // Create a buffer for the colors. var colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer(); gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer); // Set the colors. setColors(gl); var translation = [200, 150]; var angleInRadians = 0; var scale = [1, 1]; drawScene(); // Setup a ui. webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#x", {value: translation[0], slide: updatePosition(0), max: gl.canvas.width }); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#y", {value: translation[1], slide: updatePosition(1), max: gl.canvas.height}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#angle", {slide: updateAngle, max: 360}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleX", {value: scale[0], slide: updateScale(0), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleY", {value: scale[1], slide: updateScale(1), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2}); function updatePosition(index) { return function(event, ui) { translation[index] = ui.value; drawScene(); } } function updateAngle(event, ui) { var angleInDegrees = 360 - ui.value; angleInRadians = angleInDegrees * Math.PI / 180; drawScene(); } function updateScale(index) { return function(event, ui) { scale[index] = ui.value; drawScene(); } } // Draw the scene. function drawScene() { webglUtils.resizeCanvasToDisplaySize(gl.canvas); // Tell WebGL how to convert from clip space to pixels gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height); // Clear the canvas. gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // Tell it to use our program (pair of shaders) gl.useProgram(program); // Turn on the position attribute gl.enableVertexAttribArray(positionLocation); // Bind the position buffer. gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer); // Tell the position attribute how to get data out of positionBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER) var size = 2; // 2 components per iteration var type = gl.FLOAT; // the data is 32bit floats var normalize = false; // don't normalize the data var stride = 0; // 0 = move forward size * sizeof(type) each iteration to get the next position var offset = 0; // start at the beginning of the buffer gl.vertexAttribPointer( positionLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset) // Turn on the color attribute gl.enableVertexAttribArray(colorLocation); // Bind the color buffer. gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer); // Tell the color attribute how to get data out of colorBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER) var size = 4; // 4 components per iteration var type = gl.FLOAT; // the data is 32bit floats var normalize = false; // don't normalize the data var stride = 0; // 0 = move forward size * sizeof(type) each iteration to get the next position var offset = 0; // start at the beginning of the buffer gl.vertexAttribPointer( colorLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset) // Compute the matrix var matrix = m3.projection(gl.canvas.clientWidth, gl.canvas.clientHeight); matrix = m3.translate(matrix, translation[0], translation[1]); matrix = m3.rotate(matrix, angleInRadians); matrix = m3.scale(matrix, scale[0], scale[1]); // Set the matrix. gl.uniformMatrix3fv(matrixLocation, false, matrix); // Draw the geometry. var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES; var offset = 0; var count = 6; gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count); } } // Fill the buffer with the values that define a rectangle. // Note, will put the values in whatever buffer is currently // bound to the ARRAY_BUFFER bind point function setGeometry(gl) { gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array([ -150, -100, 150, -100, -150, 100, 150, -100, -150, 100, 150, 100]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); } // Fill the buffer with colors for the 2 triangles // that make the rectangle. // Note, will put the values in whatever buffer is currently // bound to the ARRAY_BUFFER bind point function setColors(gl) { // Pick 2 random colors. var r1 = Math.random(); var b1 = Math.random(); var g1 = Math.random(); var r2 = Math.random(); var b2 = Math.random(); var g2 = Math.random(); gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array( [ r1, b1, g1, 1, r1, b1, g1, 1, r1, b1, g1, 1, r2, b2, g2, 1, r2, b2, g2, 1, r2, b2, g2, 1]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); } main();
你可能注意到這兩個三角形是純色的。我們傳遞給每個三角形的頂點(diǎn)的顏色值是相同的, 所以我們傳遞的varying會被插值成相同的顏色,如果我們傳遞不同的顏色,就會看到插值的顏色。
// 給矩形的兩個三角形 // 設(shè)置顏色值并發(fā)到緩沖 function setColors(gl) { // 給每個頂點(diǎn)定義不同的顏色 gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array( [ Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); }
運(yùn)行下面的代碼:
"use strict"; function main() { // Get A WebGL context /** @type {HTMLCanvasElement} */ var canvas = document.getElementById("canvas"); var gl = canvas.getContext("webgl"); if (!gl) { return; } // setup GLSL program var program = webglUtils.createProgramFromScripts(gl, ["2d-vertex-shader", "2d-fragment-shader"]); // look up where the vertex data needs to go. var positionLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_position"); var colorLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_color"); // lookup uniforms var matrixLocation = gl.getUniformLocation(program, "u_matrix"); // Create a buffer for the positons. var positionBuffer = gl.createBuffer(); gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer); // Set Geometry. setGeometry(gl); // Create a buffer for the colors. var colorBuffer = gl.createBuffer(); gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer); // Set the colors. setColors(gl); var translation = [200, 150]; var angleInRadians = 0; var scale = [1, 1]; drawScene(); // Setup a ui. webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#x", {value: translation[0], slide: updatePosition(0), max: gl.canvas.width }); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#y", {value: translation[1], slide: updatePosition(1), max: gl.canvas.height}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#angle", {slide: updateAngle, max: 360}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleX", {value: scale[0], slide: updateScale(0), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2}); webglLessonsUI.setupSlider("#scaleY", {value: scale[1], slide: updateScale(1), min: -5, max: 5, step: 0.01, precision: 2}); function updatePosition(index) { return function(event, ui) { translation[index] = ui.value; drawScene(); } } function updateAngle(event, ui) { var angleInDegrees = 360 - ui.value; angleInRadians = angleInDegrees * Math.PI / 180; drawScene(); } function updateScale(index) { return function(event, ui) { scale[index] = ui.value; drawScene(); } } // Draw the scene. function drawScene() { webglUtils.resizeCanvasToDisplaySize(gl.canvas); // Tell WebGL how to convert from clip space to pixels gl.viewport(0, 0, gl.canvas.width, gl.canvas.height); // Clear the canvas. gl.clear(gl.COLOR_BUFFER_BIT); // Tell it to use our program (pair of shaders) gl.useProgram(program); // Turn on the position attribute gl.enableVertexAttribArray(positionLocation); // Bind the position buffer. gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, positionBuffer); // Tell the position attribute how to get data out of positionBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER) var size = 2; // 2 components per iteration var type = gl.FLOAT; // the data is 32bit floats var normalize = false; // don't normalize the data var stride = 0; // 0 = move forward size * sizeof(type) each iteration to get the next position var offset = 0; // start at the beginning of the buffer gl.vertexAttribPointer( positionLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset) // Turn on the color attribute gl.enableVertexAttribArray(colorLocation); // Bind the color buffer. gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, colorBuffer); // Tell the color attribute how to get data out of colorBuffer (ARRAY_BUFFER) var size = 4; // 4 components per iteration var type = gl.FLOAT; // the data is 32bit floats var normalize = false; // don't normalize the data var stride = 0; // 0 = move forward size * sizeof(type) each iteration to get the next position var offset = 0; // start at the beginning of the buffer gl.vertexAttribPointer( colorLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset) // Compute the matrix var matrix = m3.projection(gl.canvas.clientWidth, gl.canvas.clientHeight); matrix = m3.translate(matrix, translation[0], translation[1]); matrix = m3.rotate(matrix, angleInRadians); matrix = m3.scale(matrix, scale[0], scale[1]); // Set the matrix. gl.uniformMatrix3fv(matrixLocation, false, matrix); // Draw the geometry. var primitiveType = gl.TRIANGLES; var offset = 0; var count = 6; gl.drawArrays(primitiveType, offset, count); } } // Fill the buffer with the values that define a rectangle. // Note, will put the values in whatever buffer is currently // bound to the ARRAY_BUFFER bind point function setGeometry(gl) { gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array([ -150, -100, 150, -100, -150, 100, 150, -100, -150, 100, 150, 100]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); } // Fill the buffer with colors for the 2 triangles // that make the rectangle. // Note, will put the values in whatever buffer is currently // bound to the ARRAY_BUFFER bind point function setColors(gl) { // Make every vertex a different color. gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Float32Array( [ Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1, Math.random(), Math.random(), Math.random(), 1]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); } main();
可能不值一提的是上例還演示了使用多個屬性并且通過頂點(diǎn)著色器向片斷著色器傳值。 如果你看了處理圖片的例子, 那里面還用了另外一個屬性傳遞紋理坐標(biāo)。
關(guān)于buffer和attribute的代碼
緩沖操作是在GPU上獲取頂點(diǎn)和其他頂點(diǎn)數(shù)據(jù)的一種方式。 gl.createBuffer創(chuàng)建一個緩沖;gl.bindBuffer是設(shè)置緩沖為當(dāng)前使用緩沖; gl.bufferData將數(shù)據(jù)拷貝到緩沖,這個操作一般在初始化完成。
一旦數(shù)據(jù)存到緩沖中,還需要告訴WebGL怎么從緩沖中提取數(shù)據(jù)傳給頂點(diǎn)著色器的屬性。
要做這些,首先需要獲取WebGL給屬性分配的地址,如下方代碼所示:
// 詢問頂點(diǎn)數(shù)據(jù)應(yīng)該放在哪里 var positionLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_position"); var colorLocation = gl.getAttribLocation(program, "a_color");
這一步一般也是在初始化部分完成。
一旦知道了屬性的地址,在繪制前還需要發(fā)出三個命令。
gl.enableVertexAttribArray(location);
這個命令是告訴WebGL我們想從緩沖中提供數(shù)據(jù)。
gl.bindBuffer(gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, someBuffer);
這個命令是將緩沖綁定到 ARRAY_BUFFER 綁定點(diǎn),它是WebGL內(nèi)部的一個全局變量。
gl.vertexAttribPointer(
location,
numComponents,
typeOfData,
normalizeFlag,
strideToNextPieceOfData,
offsetIntoBuffer);
這個命令告訴WebGL從 ARRAY_BUFFER 綁定點(diǎn)當(dāng)前綁定的緩沖獲取數(shù)據(jù)。 每個頂點(diǎn)有幾個單位的數(shù)據(jù)(1 – 4),單位數(shù)據(jù)類型是什么(BYTE, FLOAT, INT, UNSIGNED_SHORT, 等等…), stride 是從一個數(shù)據(jù)到下一個數(shù)據(jù)要跳過多少位,最后是數(shù)據(jù)在緩沖的什么位置。
單位個數(shù)永遠(yuǎn)是 1 到 4 之間。
如果每個類型的數(shù)據(jù)都用一個緩沖存儲,stride 和 offset 都是 0 。 對 stride 來說 0 表示 “用符合單位類型和單位個數(shù)的大小”。 對 offset 來說 0 表示從緩沖起始位置開始讀取。 它們使用 0 以外的值時會復(fù)雜得多,雖然這樣會取得一些性能能上的優(yōu)勢, 但是一般情況下并不值得,除非你想充分壓榨WebGL的性能。
希望這些關(guān)于緩沖和屬性的內(nèi)容對你來說講的足夠清楚。
vertexAttribPointer 中的 normalizeFlag 參數(shù)是什么意思?
標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化標(biāo)記(normalizeFlag)適用于所有非浮點(diǎn)型數(shù)據(jù)。如果傳遞false就解讀原數(shù)據(jù)類型。 BYTE 類型的范圍是從 -128 到 127,UNSIGNED_BYTE 類型的范圍是從 0 到 255, SHORT 類型的范圍是從 -32768 到 32767,等等…
如果標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化標(biāo)記設(shè)為true,BYTE 數(shù)據(jù)的值(-128 to 127)將會轉(zhuǎn)換到 -1.0 到 +1.0 之間, UNSIGNED_BYTE (0 to 255) 變?yōu)?0.0 到 +1.0 之間,SHORT 也是轉(zhuǎn)換到 -1.0 到 +1.0 之間, 但比 BYTE 精確度高。
最常用的是標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化顏色數(shù)據(jù)。大多數(shù)情況顏色值范圍為 0.0 到 +1.0。 使用4個浮點(diǎn)型數(shù)據(jù)存儲紅,綠,藍(lán)和阿爾法通道數(shù)據(jù)時,每個頂點(diǎn)的顏色將會占用16字節(jié)空間, 如果你有復(fù)雜的幾何體將會占用很多內(nèi)存。代替的做法是將顏色數(shù)據(jù)轉(zhuǎn)換為四個 UNSIGNED_BYTE , 其中 0 表示 0.0,255 表示 1.0。現(xiàn)在每個頂點(diǎn)只需要四個字節(jié)存儲顏色值,省了 75% 空間。
我們來修改之前代碼實(shí)現(xiàn)。當(dāng)我們告訴WebGL如何獲取顏色數(shù)據(jù)時將這樣
// 告訴顏色屬性如何從colorBuffer中提取數(shù)據(jù) (ARRAY_BUFFER) var size = 4; // 每次迭代使用四個單位數(shù)據(jù) var type = gl.UNSIGNED_BYTE; // 數(shù)據(jù)類型是8位的 UNSIGNED_BYTE 類型。 var normalize = true; // 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化數(shù)據(jù) var stride = 0; // 0 = 移動距離 * 單位距離長度sizeof(type) // 每次迭代跳多少距離到下一個數(shù)據(jù) var offset = 0; // 從緩沖的起始處開始 gl.vertexAttribPointer( colorLocation, size, type, normalize, stride, offset)
如下向緩沖添加數(shù)據(jù):
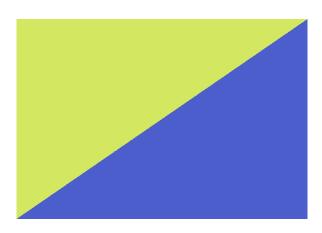
// 給矩形的兩個三角形 // 設(shè)置顏色值并發(fā)到緩沖 function setColors(gl) { // 設(shè)置兩個隨機(jī)顏色 var r1 = Math.random() * 256; // 0 到 255.99999 之間 var b1 = Math.random() * 256; // 這些數(shù)據(jù) var g1 = Math.random() * 256; // 在存入緩沖時 var r2 = Math.random() * 256; // 將被截取成 var b2 = Math.random() * 256; // Uint8Array 類型 var g2 = Math.random() * 256; gl.bufferData( gl.ARRAY_BUFFER, new Uint8Array( // Uint8Array [ r1, b1, g1, 255, r1, b1, g1, 255, r1, b1, g1, 255, r2, b2, g2, 255, r2, b2, g2, 255, r2, b2, g2, 255]), gl.STATIC_DRAW); }
運(yùn)行結(jié)果:
posted on 2020-08-01 16:59 www.blender-3d.cn 閱讀(589) 評論(0) 收藏 舉報



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號