Elasticsearch學習筆記(十一)Mapping原理
一、Mapping的功能作用
Mapping是定義如何存儲和索引一個document及其所包含字段的過程。
Mapping是index和type的元數據,每個type都有自己的一個mapping,決定了字段的數據類型和建立倒排索引的行為以及搜索的行為。mapping設置字段的數據類型的時候也設置了該字段是否為exact value還是full text
Elasticsearch將值分為exact value和full text。
exact value: ,在建立倒排索引的時候,分詞的時候,是將整個值一起作為一個關鍵詞建立到倒排索引中的。當針對exact value的字段進行搜索的時候用bool布爾值進行判斷
full text:會經歷各種各樣的處理,分詞,normaliztion(時態轉換,同義詞轉換,大小寫轉換),才會建立到倒排索引中,當針對full value的字段進行搜索的時候,需要計算相關度評分
exact value和full text類型的field就決定了,在一個搜索過來的時候,對exact value field或者是full text field進行搜索的行為也是不一樣的,會跟建立倒排索引的行為保持一致;比如說exact value搜索的時候,就是直接按照整個值進行匹配,full text query string,也會進行分詞和normalization再去倒排索引中去搜索
1、Mapping Type(ES 7.0將移除)
每個索引都有一個mapping類型以決定document如何被索引,也就是定義了一個document的索引規則
一個mapping type包括:
(1)Meta-fields:
Meta-fields被用于自定義如何處理關聯的document元數據。
例如:meta-fields包括document的_index,_type,_id,_source等字段
(2) Fields/Properties:
mapping type包括與document相關的字段或屬性列表
每個document都有一個_type元字段包含了type的名稱。_type字段聯合document的_id字段生成_uid字段。所以帶有相同_id但是type不同的document可以存在同一個索引內。
ES7.0移除mapping type的原因:
(1)index類比為數據庫中一個庫,type類比為數據庫中的一個表。但是數據庫中兩個不同的表中,相同名稱的字段是沒有關系。但是,在Elasticsearch的索引中不同的mapping type的同一個相同名稱的字段都是由同一個Lucense字段提供支持。也就說,兩個不同mapping type的相同名稱的字段都保存在同一個Lucence字段中,而且這兩個字段必須是同一個類型的數據(比如通知為date類型的數據)
(2)同一個索引中存儲少量字段和沒有字段的不同的實體存儲會導致稀疏數據,從而干擾Lucence有效壓縮document的能力
一種可選的操作是一個index下只有一個type。
2、字段數據類型(Field datatypes)
(1)每個字段都有自己的數據類型,可以是:
1)一個簡單的類型,就像text,keyword,data,long,double,boolean或者ip
2)一種支持JSON的層次結構特性的類型(就像對象或嵌套)
3)或者有專門用途的類型像geo_point,geo_shape海闊卓completion
一個string字段可以被索引成全文搜索的text字段并作為排序或者聚合的keyword字段,這么做的目的是多字段。大部分數據類型通過fields參數都可以支持多字段。
3、設置防止mapping激增
索引中定義太多的字段可能會導致mapping的激增,從而引起內存的錯誤和難以恢復的情況。這個問題可能比預期的更新普遍。例如:如果如果每個新的document被插入同時引入新的字段,這個在動態mapping里面十分普遍。每當document里面包含新的字段,這些將結束于索引的映射.如果數據量很少的話,這些都不用擔心,但是這個會成為一個mapping增長的問題。通過相關設置可以限制mapping手動或者動態創建的字段數量,以防止mapping的激增。
index.mapping.total_fields.limit :一個索引包含字段的最大數量,默認為1000
index.mapping.depth.limit: 設置一個字段的最大深度,表示字段可以包含的內部對象的數量,默認為20
index.mapping.nested_fields.limit:設置一個索引嵌套字段的最大數量,默認我50 。索引一個包含100個嵌套字段的文檔實際上索引了101個文檔,因為每個嵌套的文檔被索引為一個單獨的隱藏文檔。
4、動態映射(Dynamic mapping)
字段和mapping類型在索引使用之前不需要事先定義。由于動態mapping,新增字段名稱可以被自動添加,僅僅通過索引一個document。新字段可以被添加到頂級的mapping type中和內部的對象和嵌套的字段當中.
動態映射規則可以被配置以自定義用于新字段的映射過程
例如:
true or false --> boolean
123 --> long
123.45 --> double
2017-01-01 --> date
"hello world" --> string/text
5、精確映射(Explicit mapping)
我們對自己的數據要比Elasticsearch猜測更清楚多,及時剛開始的時候動態映射可以被充分使用,當時在某些時候我們想要指定我們自己的精確映射。
當創建一個索引的時候,可以創建字段映射,并且通過PUT mapping API可以給已經存在的索引添加新的字段。
6、更新存在的字段映射(field mappings)
除了文檔記錄之外,已經存在的字段映射field mappings不能夠被修改。如果改變這些mapping就意味著已經被索引的document將失效。相反,可以創建正確的mapping的索引并且重新索引數據到當前的新索引。
只能創建index時手動建立mapping,或者新增field mapping,但是不能update field mapping
例如:
curl -XPUT 'localhost:9200/my_index?pretty' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
//添加一個索引:my_index
{
"mappings": {
"doc": { //添加一個mapping type:doc
"properties": {
"title": { //指定字段或屬性
"type": "text" // 指定每個字段的數據類型和mapping
},
"name": { "type": "text" },
"age": { "type": "integer" },
"created": {
"type": "date",
"format": "strict_date_optional_time||epoch_millis"
}
}
}
}
}
PUT /website/_mapping/article
{
"properties" : {
"new_field" : {
"type" : "string",
"index": "not_analyzed"
}
}
}
7、查看mapping
GET /index/_mapping/type
測試mapping
GET /website/_analyze
{
"field": "content",
"text": "my-dogs"
}
二、Mapping的工作機制
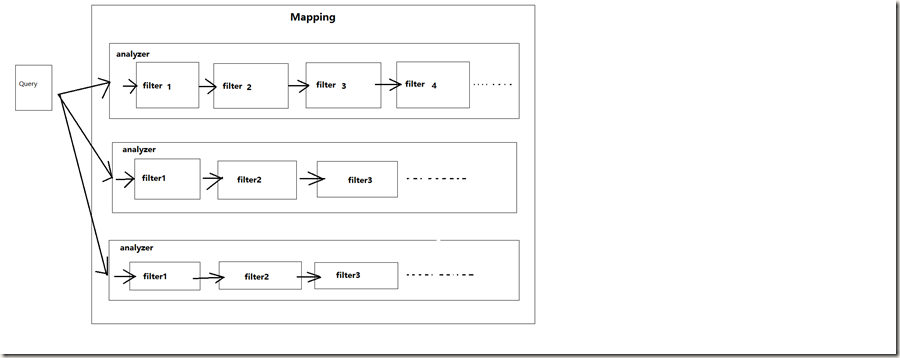
每個mapping有一至多個analyzer構成,每個analyzer由一至多個順序排列的filter組成。在進行搜索文檔的時候,將字段內存傳給相應的analyzer處理。analyzer內部根據filter順序依次進行處理
三、自定義Dynamic mapping
1、定制dynamic策略
true:遇到陌生字段,就進行dynamic mapping
false:遇到陌生字段,就忽略
strict:遇到陌生字段,就報錯
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"title": {
"type": "text"
},
"address": {
"type": "object",
"dynamic": "true"
}
}
}
}
}
測試1:
PUT /my_index/my_type/1
{ // dynamic:strict
"title": "my article",
"content": "this is my article", //新增字段
"address": { // dynamic:true
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
}
}
{
"error": {
"root_cause": [
{
"type": "strict_dynamic_mapping_exception",
"reason": "mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [content] within [my_type] is not allowed"
}
],
"type": "strict_dynamic_mapping_exception",
"reason": "mapping set to strict, dynamic introduction of [content] within [my_type] is not allowed"
},
"status": 400
}
測試2:
PUT /my_index/my_type/1
{
"title": "my article",
"address": {
"province": "guangdong",
"city": "guangzhou"
}
}
GET /my_index/_mapping/my_type
{
"my_index": {
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic": "strict",
"properties": {
"address": {
"dynamic": "true",
"properties": {
"city": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
},
"province": {
"type": "text",
"fields": {
"keyword": {
"type": "keyword",
"ignore_above": 256
}
}
}
}
},
"title": {
"type": "text"
}
}
}
}
}
}
2、定制dynamic mapping策略
(1)date_detection
默認會按照一定格式識別date,比如yyyy-MM-dd。但是如果某個field先過來一個2017-01-01的值,就會被自動dynamic mapping成date,后面如果再來一個"hello world"之類的值,就會報錯。可以手動關閉某個type的date_detection,如果有需要,自己手動指定某個field為date類型。
PUT /my_index/_mapping/my_type
{
"date_detection": false
}
(2)定制自己的dynamic mapping template(type level)
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"my_type": {
"dynamic_templates": [
{ "en": {
"match": "*_en",
"match_mapping_type": "string",
"mapping": {
"type": "string",
"analyzer": "english"
}
}}
]
}}}
1)測試1:
PUT /my_index/my_type/1
{
"title": "this is my first article"
}
title沒有匹配到任何的dynamic模板,默認就是standard分詞器,不會過濾停用詞,is會進入倒排索引,用is來搜索是可以搜索到的
2)測試2:
PUT /my_index/my_type/2
{
"title_en": "this is my first article"
}
title_en匹配到了dynamic模板,就是english分詞器,會過濾停用詞,is這種停用詞就會被過濾掉,用is來搜索就搜索不到了
(3)定制自己的default mapping template(index level)
PUT /my_index
{
"mappings": {
"_default_": {
"_all": { "enabled": false }
},
"blog": {
"_all": { "enabled": true }
}
}
}



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號