實(shí)驗(yàn)二
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)1
代碼:
T.h:
#pragma once
#include <string>
class T {
public:
T(int x = 0, int y = 0);
T(const T& t);
T(T&& t);
~T();
void adjust(int ratio);
void display() const;
private:
int m1, m2;
public:
static int get_cnt();
public:
static const std::string doc;
static const int max_cnt;
private:
static int cnt;
friend void func();
};
void func();
T.cpp:
#include "T.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
const std::string T::doc{ "a simple class sample" };
const int T::max_cnt = 999;
int T::cnt = 0;
int T::get_cnt() {
return cnt;
}
T::T(int x, int y) : m1{ x }, m2{ y } {
++cnt;
std::cout << "T constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(const T& t) : m1{ t.m1 }, m2{ t.m2 } {
++cnt;
std::cout << "T copy constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(T&& t) : m1{ t.m1 }, m2{ t.m2 } {
++cnt;
std::cout << "T move constructor called.\n";
}
T::~T() {
--cnt;
std::cout << "T destructor called.\n";
}
void T::adjust(int ratio) {
m1 *= ratio;
m2 *= ratio;
}
void T::display() const {
std::cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")";
}
void func() {
T t5(42);
t5.m2 = 2049;
std::cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); std::cout << '\n';
std::cout << "test: T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << std::endl;
}
task1.cpp:
#include "T.h"
#include <iostream>
void test_T();
int main() {
std::cout << "test Class T: \n";
test_T();
std::cout << "\ntest friend func: \n";
func();
}
void test_T() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl;
cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl;
cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl;
T t1;
cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl;
T t2(3, 4);
cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl;
T t3(t2);
t3.adjust(2);
cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl;
T t4(std::move(t2));
cout << "t4 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl;
cout << "test: T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl;
}
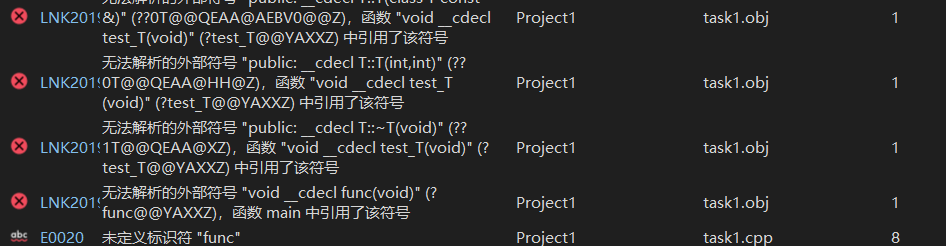
運(yùn)行測試截圖:
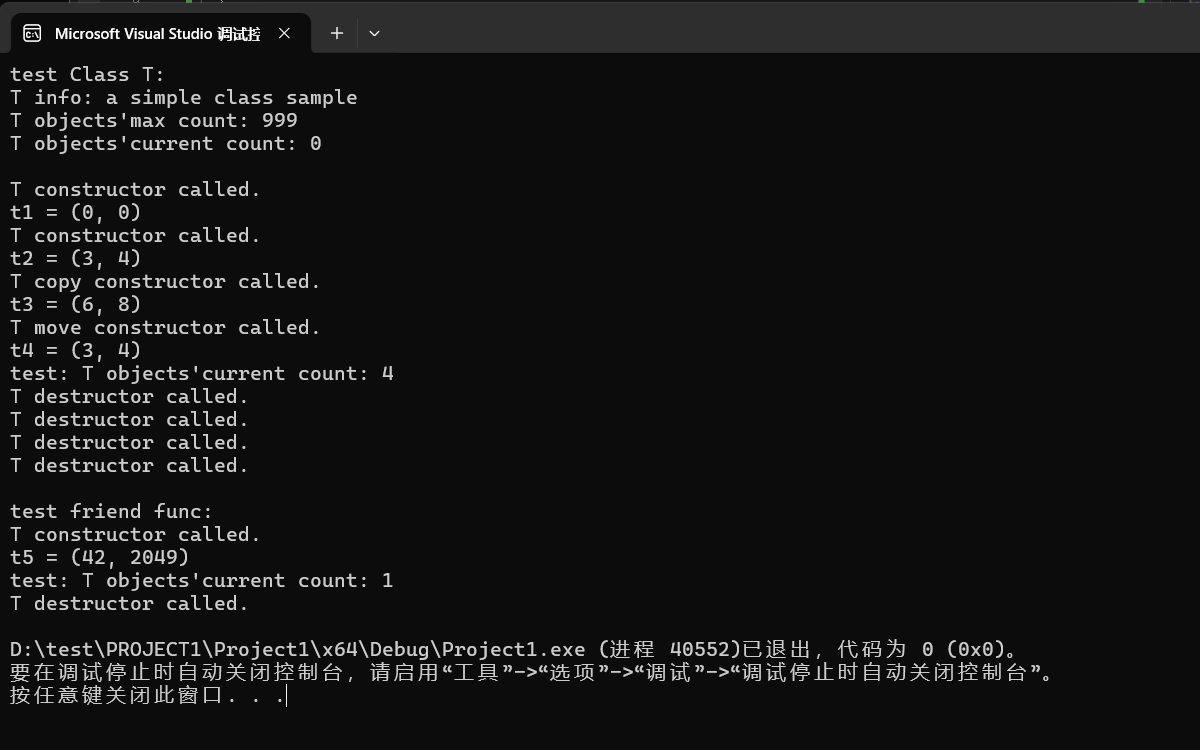
回答問題:
問題1:不能
友元函數(shù)如果要被調(diào)用在類外要有聲明和定義,由于在調(diào)用時找不到func函數(shù)的相關(guān)聲明和定義,程序報(bào)錯。
問題2:
普通構(gòu)造函數(shù):用于創(chuàng)建T類對象并傳參,將x,y取默認(rèn)值0;當(dāng)使用T類定義一個對象且不是通過復(fù)制或移動已有對象
來創(chuàng)建時調(diào)用。
復(fù)制構(gòu)造函數(shù):用一個已存在的T類對象來創(chuàng)建一個新的T類對象,新對象會復(fù)制原來對象的成員變量值;
當(dāng)用一個已有的T類對象去初始化另一個新的T類對象時調(diào)用。
移動構(gòu)造函數(shù):將一個臨時的T類對象的資源移動到新創(chuàng)建的對象中;當(dāng)用右值來初始化一個新的T類對象時使用。
析構(gòu)函數(shù):在T類對象生命周期結(jié)束時,執(zhí)行清理工作;當(dāng)T類對象生命周期結(jié)束時調(diào)用。
問題3:可以成功編譯
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)2
代碼
Complex.h:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
class Complex {
private:
double real;
double imag;
public:
static std::string doc;
Complex(double a = 0, double b = 0);
Complex(const Complex &other);
~Complex();
double get_real() const;
double get_imag() const;
Complex add(Complex& c);
friend void output(Complex &c);
friend double abs(Complex &c) ;
friend Complex add(Complex &a,Complex &b);
friend bool is_equal(Complex& a, Complex& b) ;
friend bool is_not_equal(Complex& a, Complex& b);
};
Complex.cpp:
#include"Complex.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
std::string Complex::doc = "a simplified complex class";
Complex::Complex(double a, double b) :real(a), imag(b) {};
Complex::Complex(const Complex &other) {
real = other.real;
imag = other.imag;
};
Complex::~Complex() {};
double Complex::get_real() const{
return real;
};
double Complex::get_imag () const{
return imag;
};
void output(Complex& c) {
if(c.imag>=0.0)
std::cout << c.real << "+" << c.imag << 'i';
else
std::cout << c.real<< c.imag << 'i';
};
double abs(Complex& c){
return sqrt(c.real * c.real + c.imag * c.imag);
};
Complex Complex::add(Complex &c) {
return Complex(real+ c.real,imag + c.imag);
};
Complex add(Complex& a, Complex& b) {
return Complex(a.real + b.real, a.imag + b.imag);
};
bool is_equal(Complex& a, Complex& b) {
if (a.real == b.real && a.imag == b.imag)
return true;
else
return false;
};
bool is_not_equal(Complex& a, Complex& b){
if (a.real == b.real && a.imag == b.imag)
return false;
else
return true;
};
task2.cpp:
#include"Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <iomanip>
#include <complex>
void test_Complex();
void test_std_complex();
int main() {
std::cout << "*******測試1: 自定義類Complex*******\n";
test_Complex();
std::cout << "\n*******測試2: 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫模板類complex*******\n";
test_std_complex();
}
void test_Complex() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
cout << "類成員測試: " << endl;
cout << Complex::doc << endl << endl;
cout << "Complex對象測試: " << endl;
Complex c1;
Complex c2(3, -4);
Complex c3(c2);
Complex c4 = c2;
const Complex c5(3.5);
cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl;
cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl;
cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl;
cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl;
cout << "c5.real = " << c5.get_real()
<< ", c5.imag = " << c5.get_imag() << endl << endl;
cout << "復(fù)數(shù)運(yùn)算測試: " << endl;
cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl;
c1.add(c2);
cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
cout << "c1 != c2 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
c4 = add(c2, c3);
cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl;
}
void test_std_complex() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
cout << "std::complex<double>對象測試: " << endl;
std::complex<double> c1;
std::complex<double> c2(3, -4);
std::complex<double> c3(c2);
std::complex<double> c4 = c2;
const std::complex<double> c5(3.5);
cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl;
cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl;
cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl;
cout << "c5.real = " << c5.real()
<< ", c5.imag = " << c5.imag() << endl << endl;
cout << "復(fù)數(shù)運(yùn)算測試: " << endl;
cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl;
c1 += c2;
cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl;
cout << "c1 != c2 : " << (c1 != c2) << endl;
c4 = c2 + c3;
cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl;
}
運(yùn)行測試截圖:
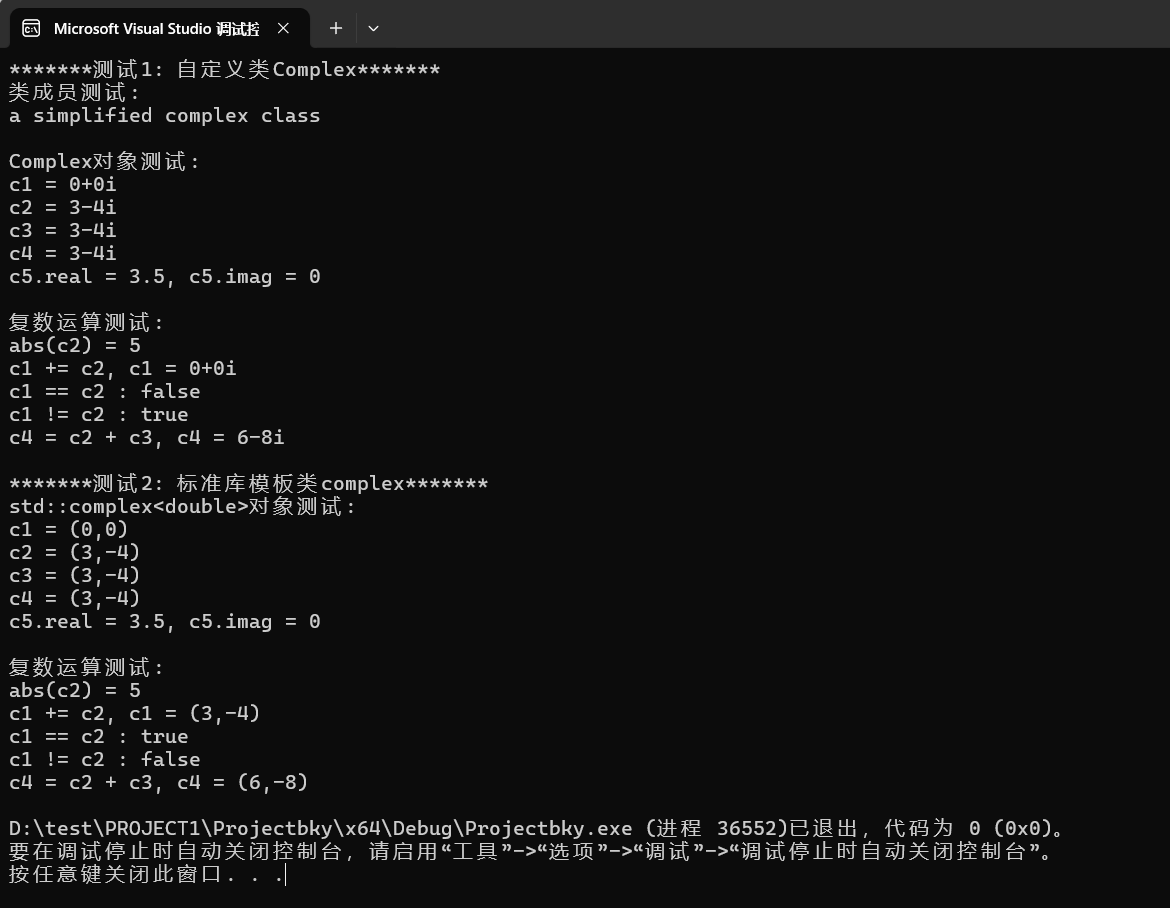
回答問題:
問題1:標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫模板類complex更簡潔,函數(shù)和運(yùn)算內(nèi)在邏輯一致。
問題2:
2.1:是,他們都通過類對象訪問私有成員real,imag,需要友元權(quán)限來訪問。
2.2:是,std::complex的實(shí)部和虛部為私有成員,abs函數(shù)計(jì)算模長需要訪問類私有成員。
2.3:當(dāng)非成員函數(shù)需要訪問類私有成員完成操作時,考慮使用friend。
問題3:使用explicit修飾拷貝構(gòu)造函數(shù)來禁止隱式轉(zhuǎn)換。
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)3
代碼:
PlayerControl.h:
#pragma once
#include <string>
enum class ControlType { Play, Pause, Next, Prev, Stop, Unknown };
class PlayerControl {
public:
PlayerControl();
ControlType parse(const std::string& control_str);
void execute(ControlType cmd) const;
static int get_cnt();
private:
static int total_cnt;
};
PlayerControl.cpp
#include "PlayerControl.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include<cctype>
#include<string>
int PlayerControl::total_cnt = 0;
PlayerControl::PlayerControl() {}
ControlType PlayerControl::parse(const std::string& control_str) {
std::string c;
for (auto i : control_str)
{
c += std::tolower(static_cast<unsigned char>(i));
}
if (c == "play")
{
total_cnt++;
return ControlType::Play;
}
if (c == "pause")
{
total_cnt++;
return ControlType::Pause;
}
if (c == "next")
{
total_cnt++;
return ControlType::Next;
}
if (c == "prev")
{
total_cnt++;
return ControlType::Prev;
}
if (c == "stop")
{
total_cnt++;
return ControlType::Stop;
}
else
{
return ControlType::Unknown;
}
};
void PlayerControl::execute(ControlType cmd) const {
switch (cmd) {
case ControlType::Play: std::cout << "[Play] Playing music...\n"; break;
case ControlType::Pause: std::cout << "[Pause] Music paused\n"; break;
case ControlType::Next: std::cout << "[Next] Skipping to next track\n"; break;
case ControlType::Prev: std::cout << "[Prev] Back to previous track\n"; break;
case ControlType::Stop: std::cout << "[Stop] Music stopped\n"; break;
default: std::cout << "[Error] unknown control\n"; break;
}
}
int PlayerControl::get_cnt() {
return total_cnt;
}
task3.cpp:
#include "PlayerControl.h"
#include <iostream>
void test() {
PlayerControl controller;
std::string control_str;
std::cout << "Enter Control: (play/pause/next/prev/stop/quit):\n";
while (std::cin >> control_str) {
if (control_str == "quit")
break;
ControlType cmd = controller.parse(control_str);
controller.execute(cmd);
std::cout << "Current Player control: " << PlayerControl::get_cnt() << "\n\n";
}
}
int main() {
test();
}
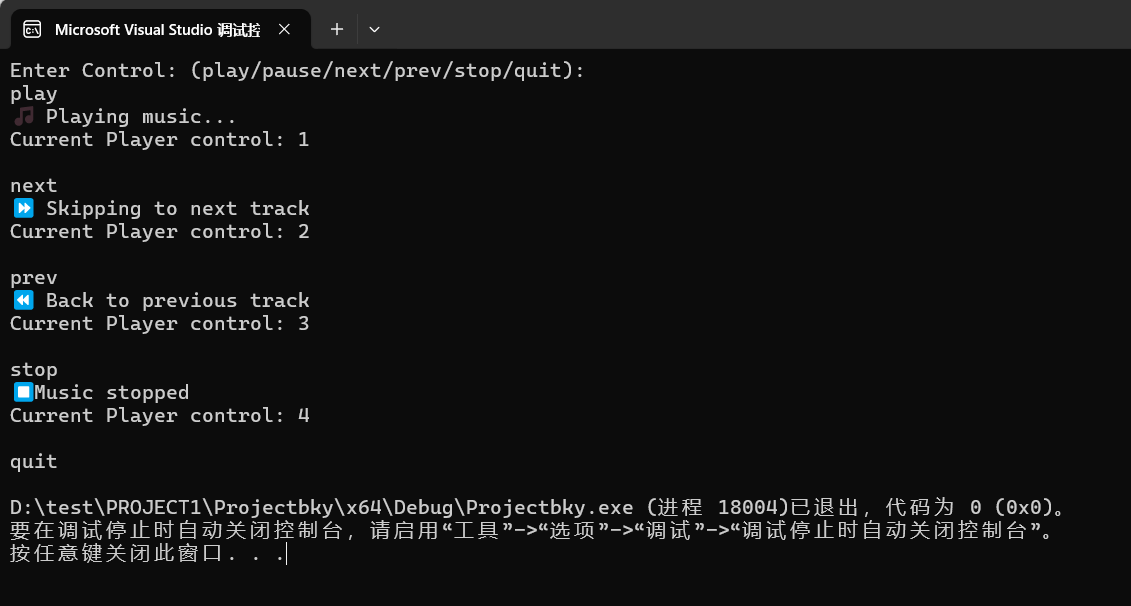
運(yùn)行測試截圖:
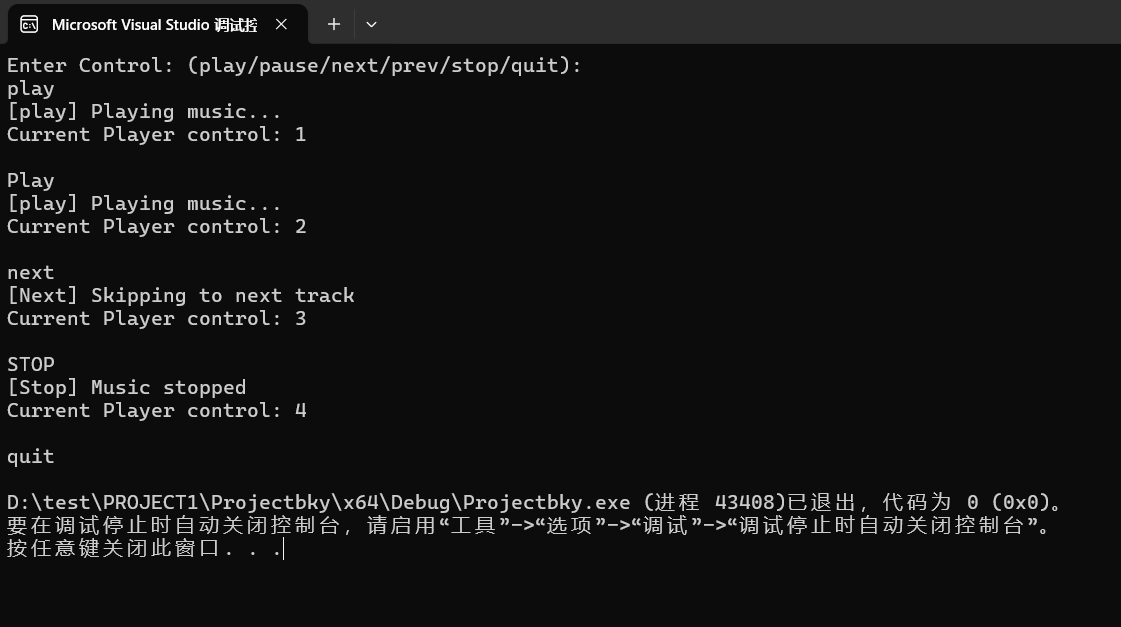
回答問題
問題:如圖:
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)4
代碼:
Fraction.h:
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
class Fraction {
private:
int up;
int down;
public:
static std::string doc;
Fraction(int a, int b = 1);
Fraction(const Fraction& other) ;
~Fraction();
int get_up() const;
int get_down() const;
Fraction negative();
friend void output(const Fraction &c);
friend Fraction add(const Fraction &a, const Fraction &b);
friend Fraction sub(const Fraction &a,const Fraction &b);
friend Fraction mul(const Fraction &a,const Fraction &b);
friend Fraction div(const Fraction &a, const Fraction &b);
friend int gcd(int x, int y);
};
Fraction.cpp:
#include "Fraction.h"
#include <iostream>
#include<cmath>
std::string Fraction::doc="Fraction類 v 0.01版.\n目前僅支持分?jǐn)?shù)對象的構(gòu)造、輸出、加 / 減 / 乘 / 除運(yùn)算.";
int gcd(int x, int y) {
int a = abs(x);
int b = abs(y);
while (b != 0)
{
int temp = b;
b = a % b;
a = temp;
}
return a;
};
Fraction::Fraction(int a, int b) :up(a), down(b) {
if (b < 0)
{
up=-up;
down=-down;
}
int n = gcd(up, down);
up = up / n;
down = down / n;
};
Fraction::Fraction(const Fraction& other) {
up = other.up;
down = other.down;
};
Fraction::~Fraction() {};
int Fraction::get_up() const {
return up;
};
int Fraction::get_down() const {
return down;
};
Fraction Fraction::negative() {
int negative_up = -up;
if(negative_up<0&&down<0)
return Fraction(-negative_up,-down);
else
return Fraction(negative_up, down);
};
void output(const Fraction& c) {
int n=gcd(c.up, c.down);
if(c.up<0&&c.down<0)
std::cout << -c.up / n << "/" << -c.down / n;
if (c.down == 0)
{
std::cout << "分母不能為0";
return ;
}
if (c.up == 0)
std::cout << "0";
else
std::cout << c.up / n << "/" << c.down / n;
}
Fraction add(const Fraction &a, const Fraction &b) {
if (a.down == b.down)
return Fraction(a.up + b.up, a.down);
else
{
return Fraction(a.up * b.down + b.up * a.down, b.down * a.down );
}
};
Fraction sub(const Fraction &a,const Fraction &b) {
if (a.down == b.down)
return Fraction(a.up -b.up, a.down);
else
{
return Fraction(a.up * b.down -b.up * a.down, b.down * a.down );
}
};
Fraction mul(const Fraction& a,const Fraction& b) {
return Fraction(a.up * b.up , a.down * b.down );
};
Fraction div(const Fraction& a,const Fraction& b) {
return Fraction(a.up * b.down , a.down * b.up );
};
task4.cpp:
#include "Fraction.h"
#include <iostream>
void test1();
void test2();
int main() {
std::cout << "測試1: Fraction類基礎(chǔ)功能測試\n";
test1();
std::cout << "\n測試2: 分母為0測試: \n";
test2();
}
void test1() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
cout << "Fraction類測試: " << endl;
cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl;
Fraction f1(5);
Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12);
Fraction f4(f3);
cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl;
cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl;
cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl;
cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl;
const Fraction f5(f4.negative());
cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl;
cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up()
<< ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl;
cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl;
}
void test2() {
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3);
cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl;
cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl;
cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl;
}
運(yùn)行測試截圖:
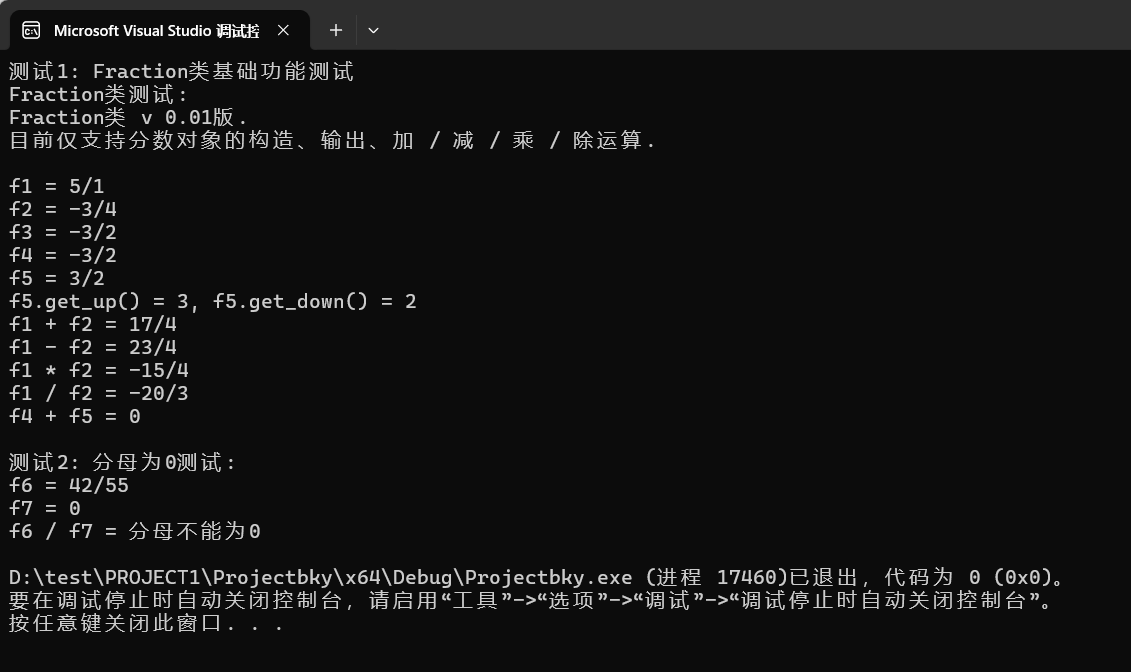
回答問題
問題:使用了友元函數(shù),邏輯簡單,效率高。




 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號