mybatis
<一>:創(chuàng)建核心配置文件mybatis-config.xml(官方推薦名)
如果一個(gè)屬性在不只一個(gè)地方進(jìn)行了配置,那么,MyBatis 將按照下面的順序來(lái)加載:
- 首先讀取在 properties 元素體內(nèi)指定的屬性。
- 然后根據(jù) properties 元素中的 resource 屬性讀取類路徑下屬性文件,或根據(jù) url 屬性指定的路徑讀取屬性文件,并覆蓋之前讀取過的同名屬性。
- 最后讀取作為方法參數(shù)傳遞的屬性,并覆蓋之前讀取過的同名屬性。
因此,通過方法參數(shù)傳遞的屬性具有最高優(yōu)先級(jí),resource/url 屬性中指定的配置文件次之,最低優(yōu)先級(jí)的則是 properties 元素中指定的屬性。
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?><!DOCTYPE configuratio
PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Config 3.0//EN"
"http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-config.dtd">
<!--configuration核心配置文件--><configuration>
<properties resource="db.properties"/> //外部關(guān)聯(lián)和內(nèi)部屬性同時(shí)存在時(shí),優(yōu)先外部關(guān)聯(lián) <typeAliases>
<!--<typeAlias type="com.whily.pojo.Emp" alias="Emp"/> 限定這個(gè)類的別名--> <package name="com.whily.pojo"/><!--將這個(gè)包下的類的首字母小寫作為別名--> </typeAliases> <!--default-設(shè)置默認(rèn)加載的環(huán)境 --> <environments default="development"> <environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC"/>
<!-- 配置數(shù)據(jù)源 -->
<dataSource type="POOLED">
<!-- 配置數(shù)據(jù)源的屬性 -->
<property name="driver" value="${driver}"/> <property name="url" value="${url}"/> <property name="username" value="${uid}"/> <property name="password" value="${pwd}"/> </dataSource> </environment> </environments> <!--每一個(gè)Mapper都需要在Mybatis核心配置文件中注冊(cè)--> <mappers> <mapper resource="EmpMapper.xml"/> </mappers> </configuration>
<二>:創(chuàng)建工具類
import org.apache.ibatis.io.Resources; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactory; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSessionFactoryBuilder; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.InputStream; //sqlSessionFactory--> sqlSession public class MybatisUtils { private static SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory; static { try { String resource = "mybatis-config.xml"; InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource); sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } public static SqlSession getSqlSession() { return sqlSessionFactory.openSession(); } }
<三>:創(chuàng)建實(shí)體類以及Dao接口
import org.apache.ibatis.type.Alias; @Alias(value = "Emp") //注解別名 public class Emp { private int empid; private String name; private String username; private String password; private int deptid; public Emp(int empid, String name, String username, String password, int deptid) { this.empid = empid; this.name = name; this.username = username; this.password = password; this.deptid = deptid; } public Emp() { } public int getEmpid() { return empid; } public void setEmpid(int empid) { this.empid = empid; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public String getUsername() { return username; } public void setUsername(String username) { this.username = username; } public String getPassword() { return password; } public void setPassword(String password) { this.password = password; } public int getDeptid() { return deptid; } public void setDeptid(int deptid) { this.deptid = deptid; } @Override public String toString() { return "emp{" + "empid=" + empid + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", username='" + username + '\'' + ", pwd='" + password + '\'' + ", deptid=" + deptid + '}'; } }
<四>:創(chuàng)建sql語(yǔ)句Mapper.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?> <!DOCTYPE mapper PUBLIC "-//mybatis.org//DTD Mapper 3.0//EN" "http://mybatis.org/dtd/mybatis-3-mapper.dtd"> <!--namespace綁定一個(gè)對(duì)應(yīng)的Dao/Mapper接口--> <mapper namespace = "com.whily.dao.EmpDao"> <select id="getEmpList" resultType="Emp"> select * from employee; </select> <select id="getEmpByid" parameterType="int" resultType="Emp"> select * from employee where empid=#{id}; </select> <insert id="addEmp" parameterType="Emp" > insert into employee(empid,name,username,password,deptid)values (#{empid},#{name},#{username},#{password},#{deptid}); </insert> <update id="update" parameterType="Emp"> update employee set name=#{helloname},username=#{hellousername},password=#{hellopassword},deptid=#{hellodeptid} where empid=#{helloempid}; </update> <!--萬(wàn)能Mapper--> <delete id="delete" parameterType="map" > delete from employee where empid=#{Helloid}; </delete> <select id="getEmpLike" parameterType="map" resultType="Emp"> select * from employee where name like "%"#{value}"%"; </select> </mapper>
<五>:創(chuàng)建測(cè)試類
增刪改一定要提交事務(wù)
sqlSession.commit();
sqlSession.close();
package com.whily.dao; import com.whily.pojo.Emp; import com.whily.utils.MybatisUtils; import org.apache.ibatis.session.SqlSession; import org.junit.Test; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map; public class EmpDaoTest { @Test public void test() { //獲取SqlSession對(duì)象 SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); //執(zhí)行SQL //方式一:getMapper EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class); List<Emp> empList = mapper.getEmpList(); for (Emp emp : empList) { System.out.println(emp); } System.out.println("******************"); //方式二: List<Emp> emps = sqlSession.selectList("com.whily.dao.EmpDao.getEmpList"); for (Emp emp : emps) { System.out.println(emp); } sqlSession.close(); } @Test public void getEmpByid() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class); Emp emp = mapper.getEmpByid(196); System.out.println(emp); sqlSession.close(); } @Test public void addEmp() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class); int emps = mapper.addEmp(new Emp(500, "qqq", "hahaha", "1111", 5)); if (emps > 0) { System.out.println("成功"); } sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); } @Test public void update() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("helloname", "qqq"); map.put("hellousername", "qqq"); map.put("hellopassword", "www"); map.put("hellodeptid", 1); map.put("helloempid", 196); int emp = mapper.update(map); if (emp > 0) { System.out.println("成功"); } sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); } @Test public void delete() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("Helloid", 500); EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class); mapper.delete(map); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); } @Test public void getEmpLike() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class); List<Emp> emps = mapper.getEmpLike("%qq%"); for (Emp emp : emps) { System.out.println(emp); } sqlSession.close(); } }
六、生命周期
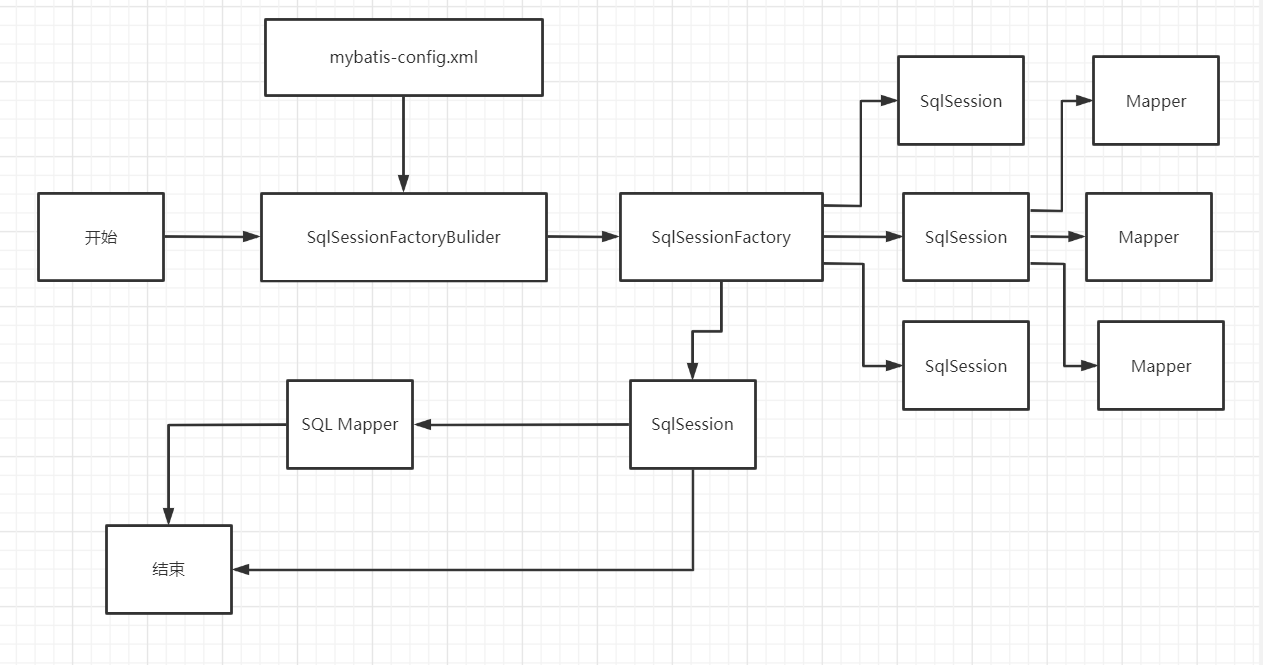
每一個(gè)Mapper都是一個(gè)業(yè)務(wù)
生命周期和作用域是至關(guān)重要的,因?yàn)殄e(cuò)誤的使用會(huì)導(dǎo)致非常嚴(yán)重的并發(fā)問題。
SqlSessionFactoryBulider:
- 一旦創(chuàng)建了SqlSessionFactoryBulider,就不需要他了
- 局部變量
SqlSessionFactory:
- 說白了可以想象為數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)連接池;
- SqlSessionFactory一旦被創(chuàng)建就應(yīng)該在應(yīng)用的運(yùn)行期間一直存在,沒有任何理由放棄或重新創(chuàng)建
- 因此SqlSessionFactory的最簡(jiǎn)作用域是應(yīng)用作用域;
- 最簡(jiǎn)單的就是單例模式或者靜態(tài)單例模式。
SqlSession:
- 連接到連接池的一個(gè)請(qǐng)求
- SqlSession的實(shí)例不是線程安全的,因此不是共享的,所以他的作用域是請(qǐng)求或方法作用域
- 用完之后要趕緊關(guān)閉,否則資源被占用!
字段和屬性名不一致
- 起別名
7、ResultMap映射:結(jié)果集映射
<resultMap id="EmpMap" type="Emp"> <!--column數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)的字段 property實(shí)體類的屬性--> <result column="empid" property="empid"/> <result column="username" property="username"/> <result column="deptid" property="deptid"/> <result column="name" property="name"/> <result column="password" property="pwd"/> // </resultMap> <select id="getEmpList" resultMap="EmpMap" //對(duì)應(yīng)ResultMap的id值> select * from employee; </select>
- resultMap元素是MyBatis中最重要最強(qiáng)大的元素
- ResultMap的設(shè)計(jì)思想是,對(duì)于簡(jiǎn)單的語(yǔ)句根本不需要配置顯示的結(jié)果映射,而對(duì)于復(fù)雜一點(diǎn)的語(yǔ)句只需要描述他們的關(guān)系就行
- ResultMap最優(yōu)秀的地方在于,雖然你已經(jīng)對(duì)他相當(dāng)了解了,但根本就不需要顯示地用到他們
設(shè)置
<settings>
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadingEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="multipleResultSetsEnabled" value="true"/>
<setting name="useColumnLabel" value="true"/>
<setting name="useGeneratedKeys" value="false"/>
<setting name="autoMappingBehavior" value="PARTIAL"/>
<setting name="autoMappingUnknownColumnBehavior" value="WARNING"/>
<setting name="defaultExecutorType" value="SIMPLE"/>
<setting name="defaultStatementTimeout" value="25"/>
<setting name="defaultFetchSize" value="100"/>
<setting name="safeRowBoundsEnabled" value="false"/>
<setting name="mapUnderscoreToCamelCase" value="false"/>
<setting name="localCacheScope" value="SESSION"/>
<setting name="jdbcTypeForNull" value="OTHER"/>
<setting name="lazyLoadTriggerMethods" value="equals,clone,hashCode,toString"/>
</settings>
8、日志
8.1 日志工廠
如果一個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)操作出現(xiàn)了異常,我們需要拍錯(cuò)。日志就是最好的幫手
以前:sout、debug
現(xiàn)在:日志工廠! logImpl 指定Mybatis所用日志的具體表現(xiàn),未指定時(shí)將自動(dòng)查找。
- SLF4J
- LOG4J (掌握)
- LOG4J2
- JDK_LOGGING
- STDOUT_LOGGING (掌握)
- NO_LOGGING
- COMMONS_LOGGING
具體用使用哪一個(gè)日志實(shí)現(xiàn),在設(shè)置中設(shè)定!
STDOUT_LOGGING
<settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="STDOUT_LOGGING"/> //必須規(guī)范書寫,按官方書寫,不能有空格 </settings>
@Test
public void getEmpLike() {
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
List<Emp> emps = mapper.getEmpLike("%qq%");
for (Emp emp : emps) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
Opening JDBC Connection
Created connection 385337537.
Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@16f7c8c1]
==> Preparing: select * from employee where name like "%"?"%";
==> Parameters: %qq%(String)
<== Columns: empid, name, username, password, deptid
<== Row: 229, qaaqq, 1111, dsa, 2
<== Row: 231, qqaqq, dsad5, dsa, 7
<== Total: 2
emp{empid=229, name='qaaqq', username='1111', pwd='dsa', deptid=2}
emp{empid=231, name='qqaqq', username='dsad5', pwd='dsa', deptid=7}
Resetting autocommit to true on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@16f7c8c1]
Closing JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@16f7c8c1]
Returned connection 385337537 to pool.
log4j:
1、導(dǎo)入依賴:
<dependency> <groupId>log4j</groupId> <artifactId>log4j</artifactId> <version>1.2.17</version> </dependency>
2、mybatis-config.xml設(shè)置
<settings> <setting name="logImpl" value="LOG4J"/> </settings>
3、創(chuàng)建log4j.properties文件
log4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,console,file #控制臺(tái)輸出的相關(guān)設(shè)置 log4j.appender.console = org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender log4j.appender.console.Target = System.out log4j.appender.console.Threshold=DEBUG log4j.appender.console.layout = org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.console.layout.ConversionPattern=[%c]-%m%n #文件輸出的相關(guān)設(shè)置 log4j.appender.file = org.apache.log4j.RollingFileAppender log4j.appender.file.File=./log/whily.log log4j.appender.file.MaxFileSize=10mb log4j.appender.file.Threshold=DEBUG log4j.appender.file.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout log4j.appender.file.layout.ConversionPattern=[%p][%d{yy-MM-dd}][%c]%m%n #日志輸出級(jí)別 log4j.logger.org.mybatis=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.Statement=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.ResultSet=DEBUG log4j.logger.java.sql.PreparedStatement=DEBUG
4、測(cè)試類
public class EmpDaoTest { static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(EmpDaoTest.class); @Test public void getEmpLike() {
logger.info("測(cè)試:進(jìn)入getEmpLike方法成功");
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class);
List<Emp> emps = mapper.getEmpLike("%qq%");
for (Emp emp : emps) {
System.out.println(emp);
}
logger.info("info:進(jìn)入了testLog4j");
logger.error("error:進(jìn)入了testLog4j");
logger.debug("debug:進(jìn)入了testLog4j");
sqlSession.close();
}
}
簡(jiǎn)單使用:
1.在使用Log4j的類中,導(dǎo)入import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
2.日志對(duì)象,參數(shù)為當(dāng)前類的class:static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger(EmpDaoTest.class);
3.日志級(jí)別:
logger.info("info:進(jìn)入了testLog4j");
logger.debug("debug:進(jìn)入了testLog4j");
logger.error("error:進(jìn)入了testLog4j");
9、分頁(yè)
分頁(yè)可以減少數(shù)據(jù)的處理量
使用Limit分頁(yè):
語(yǔ)法:
select * from tableName limit startIndex,pageSize;
select * from employee limit 3; #[0,n]
9.1:Limit分頁(yè)
1.接口
分頁(yè) List<Emp> getEmpLimit(Map<String,Object> map);
2.Mapper.xml
<select id="getEmpLimit" parameterType="map" resultMap="EmpMap"> select * from employee limit #{i},#{n}; </select>
3.測(cè)試
@Test public void getEmpLimit() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("i", 1); map.put("n", 3); List<Emp> empLimit = mapper.getEmpLimit(map); for (Emp emp:empLimit){ System.out.println(emp); } sqlSession.close(); }
9.2:使用RowBounds(不推薦,因?yàn)樾枰褂胹electList(),官方放棄了這個(gè)方法)
1.接口 :List<Emp> getEmpRowBounds();
2.Mapper.xml
<select id="getEmpLimit" parameterType="map" resultMap="EmpMap"> select * from employee; </select>
3.測(cè)試
@Test
public void getEmpRowBounds(){
SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession();
//RowBounds實(shí)現(xiàn)
RowBounds rowBounds = new RowBounds(1,3);
List<Emp> emps = sqlSession.selectList("com.whily.dao.EmpDao.getEmpRowBounds",null,rowBounds);
for (Emp emp:emps){
System.out.println(emp);
}
sqlSession.close();
}
9.3:插件分頁(yè)
1.到依賴
<dependency> <groupId>com.github.pagehelper</groupId> <artifactId>pagehelper</artifactId> <version>5.1.2</version> </dependency>
2.導(dǎo)入插件
<plugins> <plugin interceptor="com.github.pagehelper.PageInterceptor"> <property name="helperDialect" value="mysql"/> <property name="reasonable" value="true"/> </plugin> </plugins>
3.Dao
List<Emp> listByHelper(); //條件查詢是需要傳入?yún)?shù)
4.Mapper.xml
<select id="listByHelper" resultMap="EmpMap"> select * from employee </select>
sql語(yǔ)句后面不能加“;”
5.測(cè)試
@Test public void ss() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); EmpDao mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(EmpDao.class); PageHelper.startPage(2, 2); List<Emp> emps = mapper.listByHelper(); PageInfo<Emp> info = new PageInfo<Emp>(emps); emps = info.getList(); for (Emp emp : emps) { System.out.println(emp); } }
10.注解開發(fā)
修飾在接口方法上,然后加相應(yīng)的sql語(yǔ)句 @Select @Select("select * from emp") public List<Emp> listAnn(Emp emp); @Insert @Insert("insert into emp (ename) values (#{ename})") public int saveAnn(Emp emp); @Update @Update("update emp set ename=#{ename} where empno=#{empno}") public int editAnn(Emp emp); @Delete @Delete("delete from emp where empno=#{empno}") public int deleteAnn(Emp emp); @Results @Results(value={ @Result(property = "sal", column = "salary") }) @Select("select * from emp") public List<Emp> listAnn(Emp emp);
#{}和${}:
where role_id = #{roleId};
#{}:傳來(lái)參數(shù)時(shí),sql在解析時(shí)會(huì)家伙是哪個(gè)“ ”,當(dāng)成字符串來(lái)解析,防止sql注入。
${}:傳入數(shù)據(jù)直接顯示在生成的sql中,解析式就成了role_id = roleId,運(yùn)行時(shí)會(huì)報(bào)錯(cuò)。
所以盡可能用#{},除非Mybatis排序時(shí)使用order by動(dòng)態(tài)參數(shù)時(shí)需要使用${}而不是#{}
11、 連表查詢
一:多對(duì)一映射
1、創(chuàng)建mybatis-config.xml 實(shí)體類 接口(Dao或Mapper)
2、Mapeer.xml文件:
1.方式一,不使用連接查詢,效率一般:
<resultMap id="StudentTeacher" type="stu"> <result property="stuid" column="stuid" javaType="int"/> <result property="stuName" column="stuName" javaType="string"/> <association property="teacher" column="tid" javaType="tea" select="getTeacher" //連接第二條查詢語(yǔ)句 > <id property="tchid" column="tchid" javaType="int"></id> <result property="tchName" column="tchName" javaType="string"></result> </association> </resultMap> <select id="getStudents" resultMap="StudentTeacher"> select * from student </select> <select id="getTeacher" resultType="tea" parameterType="int"> select * from teacher where tchid =#{tchid} ; </select>
2.方式二,使用連接查詢:
<select id="getStudents2" resultMap="StudentTeacher2"> select s.stuid sid,s.stuName sname,t.tchid tchid,t.tchName tname from student s ,teacher t where s.tid = t.tchid </select> <resultMap id="StudentTeacher2" type="stu"> <result property="stuid" column="sid"/> <result property="stuName" column="sname"/> <association property="teacher" javaType="tea"> <id property="tchid" column="tchid"/> <result property="tchName" column="tname"/> </association> </resultMap>
二:一對(duì)多映射
1.方式一,不使用連接查詢:
<select id="getTeacher2" resultMap="TeacherStu2"> select tchid,tchName from teacher where tchid = #{tchid} </select> <resultMap id="TeacherStu2" type="tea"> <result property="tchid" column="tchid"/> <result property="tchName" column="tchName"/> <collection property="students" javaType="ArrayList" ofType="stu" column="tchid"//對(duì)應(yīng)第一條語(yǔ)句的tchid select="getStudentByID"連接第二條語(yǔ)句> <result property="stuid" column="stuid"/> <result property="stuName" column="stuName"/> <result property="tid" column="tid"/> </collection>
<select id="getStudentByID" resultType="stu">
select stuid,stuName,tid from student where tid = #{tchid}
</select>
</resultMap>
2.方式二,使用連接查詢:
<select id="getTeacher" resultType="tea" resultMap="TeacherStu"> select t.tchid ,t.tchName,s.stuid,s.stuName,s.tid from student s,teacher t where s.tid = t.tchid and tchid = #{tchid} </select> <resultMap id="TeacherStu" type="tea"> <result property="tchid" column="tchid"/> <result property="tchName" column="tchName"/> <collection property="students" ofType="stu"> <result property="stuid" column="stuid"/> <result property="stuName" column="stuName"/> <result property="tid" column="tid"/> </collection> </resultMap>
12、動(dòng)態(tài)SQL
官網(wǎng)描述:
MyBatis 的強(qiáng)大特性之一便是它的動(dòng)態(tài) SQL。如果你有使用 JDBC 或其它類似框架的經(jīng)驗(yàn),你就能體會(huì)到根據(jù)不同條件拼接 SQL 語(yǔ)句的痛苦。
例如拼接時(shí)要確保不能忘記添加必要的空格,還要注意去掉列表最后一個(gè)列名的逗號(hào)。利用動(dòng)態(tài) SQL 這一特性可以徹底擺脫這種痛苦。
雖然在以前使用動(dòng)態(tài) SQL 并非一件易事,但正是 MyBatis 提供了可以被用在任意 SQL 映射語(yǔ)句中的強(qiáng)大的動(dòng)態(tài) SQL 語(yǔ)言得以改進(jìn)這種情形。
動(dòng)態(tài) SQL 元素和 JSTL 或基于類似 XML 的文本處理器相似。在 MyBatis 之前的版本中,有很多元素需要花時(shí)間了解。MyBatis 3 大大精簡(jiǎn)了元素種類,
現(xiàn)在只需學(xué)習(xí)原來(lái)一半的元素便可。MyBatis 采用功能強(qiáng)大的基于 OGNL 的表達(dá)式來(lái)淘汰其它大部分元素。
-------------------------------
- if
- choose (when, otherwise)
- trim (where, set)
- foreach
-------------------------------
我們之前寫的 SQL 語(yǔ)句都比較簡(jiǎn)單,如果有比較復(fù)雜的業(yè)務(wù),我們需要寫復(fù)雜的 SQL 語(yǔ)句,往往需要拼接,而拼接 SQL ,稍微不注意,由于引號(hào),空格等缺失可能都會(huì)導(dǎo)致錯(cuò)誤。
那么怎么去解決這個(gè)問題呢?這就要使用 mybatis 動(dòng)態(tài)SQL,通過 if, choose, when, otherwise, trim, where, set, foreach等標(biāo)簽,可組合成非常靈活的SQL語(yǔ)句,從而在提高 SQL 語(yǔ)句的準(zhǔn)確性的同時(shí),也大大提高了開發(fā)人員的效率。
if: 接口為L(zhǎng)ist<Student> queryStuIf(Map map);
<select id="queryStuIf" parameterType="map" resultType="stu"> select * from student where <if test="stuid!=null">stuid=#{stuid}</if> <if test="stuName!=null">and stuName=#{stuName}</if> </select>
完整語(yǔ)句為select * from student where stuid = #{stuid} and stuName = #{stuName},
當(dāng)stuName為空時(shí)select * from student where stuid = #{stuid}
但當(dāng)stuid為空時(shí)語(yǔ)句就成為了select * from student where and stuName = #{stuName},sql語(yǔ)句錯(cuò)誤。
如何解決:where
WHERE:接口同上
修改以上sql語(yǔ)句:
<select id="queryStuIf" parameterType="map" resultType="stu"> select * from student where <where> <if test="stuid!=null">stuid=#{stuid}</if> <if test="stuName!=null">and stuName=#{stuName}</if> </where> </select>
public void queryOne(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<Object, Object>(); map.put("stuid",1); map.put("stuName",null); List<Student> list = mapper.queryStuIf(map); System.out.println(list); sqlSession.close(); }
這個(gè)“where” 標(biāo)簽會(huì)知道如果他包含的標(biāo)簽中有返回值的話,太插入一個(gè)‘where’。此外,如果標(biāo)簽返回的內(nèi)容是以AND
或 OR開頭的話,則會(huì)剔除掉。
SET:接口為int update(Map map);
同理:上面的對(duì)于查詢SQL語(yǔ)句包含where關(guān)鍵字,如果在進(jìn)行更新操作時(shí),含有set關(guān)鍵詞,我們?cè)趺刺幚?/p>
<update id="update" parameterType="map" > update student <set> <if test="hobby!=null">hobby=#{hobby},</if> //注意set與set之間需要加逗號(hào)隔開 <if test="stuName">stuName=#{stuName}</if> </set> where stuid = #{stuid} </update>
public void update(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); HashMap<String,Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("stuName","熊大"); map.put("hobby","dance"); map.put("stuid",1); mapper.update(map); sqlSession.commit(); sqlSession.close(); }
CHOOSE語(yǔ)句:List<Student> queryChoose(Map map);
有時(shí)候我們不想用到所有的查詢條件,只想選擇其中一個(gè),查詢條件只有一個(gè)滿足即可,
使用choose標(biāo)簽可以解決此類問題,類似于java的switch語(yǔ)句
<select id="queryChoose" parameterType="map" resultType="stu"> select * from student <where> <choose> <when test="stuid">stuid=#{stuid}</when> <when test="stuName">stuName=#{stuName}</when> <when test="hobby">hobby#{hobby}</when> <otherwise>and view = #{view}</otherwise> </choose> </where> </select>
public void queryChoose() { SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("stuName", "張三"); //map.put("stuid",1); // map.put("hobby","lol"); // map.put("view",1); List<Student> list = mapper.queryChoose(map); System.out.println(list); sqlSession.close();
SQL片段:接口List<Student> queryFra(Map map);
有時(shí)候可能某個(gè)sql語(yǔ)句用的特別多,為了增加代碼的重用性,簡(jiǎn)化代碼,我們需要將這些代碼抽取出來(lái),然后使用時(shí)直接調(diào)用。
<!--提取片段--> <sql id="if-stuid-stuName"> <if test="stuid!=null">stuid=#{stuid}</if> <if test="stuName!=null">stuName=#{stuName}</if> </sql> <!--使用片段--> <select id="queryFra" parameterType="map" resultType="stu"> select * from student <where> <include refid="if-stuid-stuName"></include> </where> </select>
public void queryFra(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); //map.put("stuName", "張三"); map.put("stuid",1); List<Student> list=mapper.queryFra(map); System.out.println(list); sqlSession.close(); }
注意:提取片段時(shí),最好基于單表來(lái)定義sql片段,提高片段的可重用性;
在sql片段中不要包括where
FOREACH:接口List<Student> queryForeach(Map map);
collection:指定輸入對(duì)象中的集合屬性 item:每次遍歷生成的對(duì)象 open:開始遍歷時(shí)的拼接字符串 close:結(jié)束時(shí)拼接的字符串 separator:遍歷對(duì)象之間需要拼接的字符串 select * from blog where 1=1 and (id=1 or id=2 or id=3) --> <select id="queryForeach" parameterType="map" resultType="stu"> select * from student <where> <foreach collection="stuids" item="stuid" open="and (" close=")" separator=" or ">stuid=#{stuid}</foreach>//注意空格 </where> </select>
public void queryForeach(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); HashMap map = new HashMap(); List<Integer> ids = new ArrayList<Integer>(); ids.add(1); ids.add(2); ids.add(3); map.put("stuids",ids); List<Student> students = mapper.queryForeach(map); System.out.println(students); sqlSession.close(); }
13、緩存
1.什么是緩存:- 存在內(nèi)存中的臨時(shí)數(shù)據(jù)。
- 將用戶經(jīng)常查詢的數(shù)據(jù)放在緩存(內(nèi)存)中,用戶去查詢數(shù)據(jù)就不用從磁盤上(關(guān)系型數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)數(shù)據(jù)文件)查詢,從緩存中查詢,從而提高查詢效率,解決了高并發(fā)系統(tǒng)的性能問題。
- 減少和數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)的交互次數(shù),減少系統(tǒng)開銷,提高系統(tǒng)效率。
- 經(jīng)常查詢并且不經(jīng)常改變的數(shù)據(jù)。
13.1、Mybatis緩存
- MyBatis包含一個(gè)非常強(qiáng)大的查詢緩存特性,它可以非常方便地定制和配置緩存。緩存可以極大的提升查詢效率。
- MyBatis系統(tǒng)中默認(rèn)定義了兩級(jí)緩存:一級(jí)緩存和二級(jí)緩存
- 默認(rèn)情況下,只有一級(jí)緩存開啟。(SqlSession級(jí)別的緩存,也稱為本地緩存)
- 二級(jí)緩存需要手動(dòng)開啟和配置,他是基于namespace級(jí)別的緩存。
- 為了提高擴(kuò)展性,MyBatis定義了緩存接口Cache。我們可以通過實(shí)現(xiàn)Cache接口來(lái)自定義二級(jí)緩存
13.1、一級(jí)緩存
一級(jí)緩存也叫本地緩存:
-
與數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)同一次會(huì)話期間查詢到的數(shù)據(jù)會(huì)放在本地緩存中。
-
以后如果需要獲取相同的數(shù)據(jù),直接從緩存中拿,沒必須再去查詢數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù);
@org.junit.Test public void queryOne(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); Student i = mapper.queryOne(1); System.out.println(i); Student j = mapper.queryOne(1); System.out.println(j); System.out.println(i==j); sqlSession.close(); }
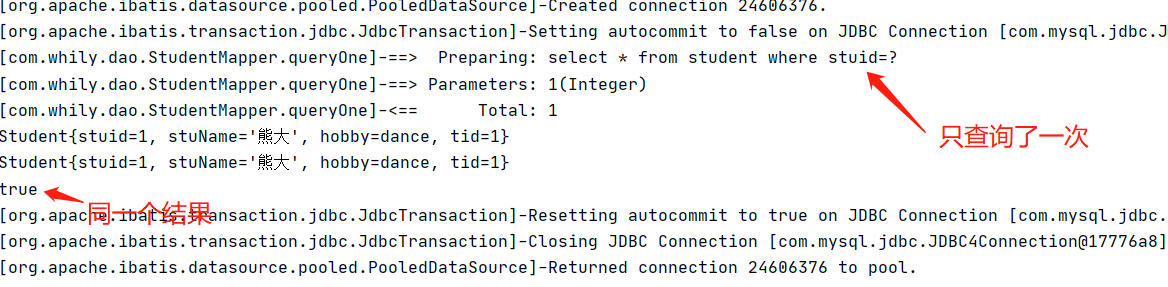
一級(jí)緩存失效的四種情況:
一級(jí)緩存是SqlSession級(jí)別的緩存,是一直開啟的,我們關(guān)閉不了它;
一級(jí)緩存失效情況:沒有使用到當(dāng)前的一級(jí)緩存,效果就是,還需要再向數(shù)據(jù)庫(kù)中發(fā)起一次查詢請(qǐng)求!
1.sqlSession不同:
@org.junit.Test public void queryOne(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
SqlSession sqlSession1=MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper1 = sqlSession1.getMapper(StudentMapper.class);
Student i = mapper.queryOne(1); System.out.println(i);
Student j = mapper1.queryOne(1); System.out.println(j); System.out.println(i==j); sqlSession.close(); sqlSession1.close(); }

觀察結(jié)果:發(fā)現(xiàn)發(fā)送了兩條SQL語(yǔ)句!
結(jié)論:每個(gè)sqlSession中的緩存相互獨(dú)立
2.sqlSession相同,查詢條件不同
3.sqlSession相同,兩次查詢之間執(zhí)行了增刪改操作!無(wú)論改的是哪個(gè)對(duì)象,增刪改會(huì)刷新緩存
4.sqlSession相同,手動(dòng)清除一級(jí)緩存
@org.junit.Test public void queryOne(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); Student i = mapper.queryOne(1); System.out.println(i); sqlSession.clearCache();//手動(dòng)清除緩存 Student j = mapper.queryOne(1); System.out.println(j); System.out.println(i==j); sqlSession.close(); }
一級(jí)緩存就是一個(gè)map
13.2 、二級(jí)緩存
-
二級(jí)緩存也叫全局緩存,一級(jí)緩存作用域太低了,所以誕生了二級(jí)緩存
-
基于namespace級(jí)別的緩存,一個(gè)名稱空間,對(duì)應(yīng)一個(gè)二級(jí)緩存;
-
工作機(jī)制
-
一個(gè)會(huì)話查詢一條數(shù)據(jù),這個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)就會(huì)被放在當(dāng)前會(huì)話的一級(jí)緩存中;
-
如果當(dāng)前會(huì)話關(guān)閉了,這個(gè)會(huì)話對(duì)應(yīng)的一級(jí)緩存就沒了;但是我們想要的是,會(huì)話關(guān)閉了,一級(jí)緩存中的數(shù)據(jù)被保存到二級(jí)緩存中;
-
新的會(huì)話查詢信息,就可以從二級(jí)緩存中獲取內(nèi)容;
-
不同的mapper查出的數(shù)據(jù)會(huì)放在自己對(duì)應(yīng)的緩存(map)中;
使用步驟:
1、開啟全局緩存【mybatis-config.xml】
<setting name="cacheEnabled" value="true"/>
2、去每個(gè)mapper.xml中配置使用二級(jí)緩存,這個(gè)配置非常簡(jiǎn)單;【xxxMapper.xml】
<mapper namespace="com.whily.dao.StudentMapper">
// 在當(dāng)前Mapper.xml中使用二級(jí)緩存 <cache/> //開啟二級(jí)緩存 <select id="queryOne" resultType="stu"> select * from student where stuid=#{stuid} </select> </mapper>
<cache/> 官方示例=====>查看官方文檔 <cache eviction="FIFO" flushInterval="60000" size="512" readOnly="true"/>
這個(gè)更高級(jí)的配置創(chuàng)建了一個(gè) FIFO 緩存,每隔 60 秒刷新,最多可以存儲(chǔ)結(jié)果對(duì)象或列表的 512 個(gè)引用,
而且返回的對(duì)象被認(rèn)為是只讀的,因此對(duì)它們進(jìn)行修改可能會(huì)在不同線程中的調(diào)用者產(chǎn)生沖突
3.測(cè)試
@org.junit.Test public void queryOne(){ SqlSession sqlSession = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); SqlSession sqlSession1 = MybatisUtils.getSqlSession(); StudentMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); StudentMapper mapper1 = sqlSession.getMapper(StudentMapper.class); Student i = mapper.queryOne(1); System.out.println(i); Student j = mapper1.queryOne(1); System.out.println(j); System.out.println(i==j); sqlSession.close(); sqlSession1.close(); }
org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource]-PooledDataSource forcefully closed/removed all connections. [com.whily.dao.StudentMapper]-Cache Hit Ratio [com.whily.dao.StudentMapper]: 0.0 [org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction]-Opening JDBC Connection [org.apache.ibatis.datasource.pooled.PooledDataSource]-Created connection 11902257. [org.apache.ibatis.transaction.jdbc.JdbcTransaction]-Setting autocommit to false on JDBC Connection [com.mysql.jdbc.JDBC4Connection@b59d31] [com.whily.dao.StudentMapper.queryOne]-==> Preparing: select * from student where stuid=? [com.whily.dao.StudentMapper.queryOne]-==> Parameters: 1(Integer) [com.whily.dao.StudentMapper.queryOne]-<== Total: 1 Student{stuid=1, stuName='熊大', hobby=dance, tid=1} [com.whily.dao.StudentMapper]-Cache Hit Ratio [com.whily.dao.StudentMapper]: 0.0 Student{stuid=1, stuName='熊大', hobby=dance, tid=1} true
4.結(jié)論
-
只要開啟了二級(jí)緩存,我們?cè)谕粋€(gè)Mapper中的查詢,可以在二級(jí)緩存中拿到數(shù)據(jù)
-
查出的數(shù)據(jù)都會(huì)被默認(rèn)先放在一級(jí)緩存中
-
只有會(huì)話提交或者關(guān)閉以后,一級(jí)緩存中的數(shù)據(jù)才會(huì)轉(zhuǎn)到二級(jí)緩存中
5.緩存原理圖

13.3、第三方緩存【EHCache】
第三方緩存實(shí)現(xiàn)--EhCache: 查看百度百科 Ehcache是一種廣泛使用的java分布式緩存,用于通用緩存; 要在應(yīng)用程序中使用Ehcache,需要引入依賴的jar包 <!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.mybatis.caches/mybatis-ehcache --> <dependency> <groupId>org.mybatis.caches</groupId> <artifactId>mybatis-ehcache</artifactId> <version>1.1.0</version> </dependency> 在mapper.xml中使用對(duì)應(yīng)的緩存即可 <mapper namespace = “org.acme.FooMapper” > <cache type = “org.mybatis.caches.ehcache.EhcacheCache” /> </mapper> 編寫ehcache.xml文件,如果在加載時(shí)未找到/ehcache.xml資源或出現(xiàn)問題,則將使用默認(rèn)配置。 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <ehcache xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:noNamespaceSchemaLocation="http://ehcache.org/ehcache.xsd" updateCheck="false"> <!-- diskStore:為緩存路徑,ehcache分為內(nèi)存和磁盤兩級(jí),此屬性定義磁盤的緩存位置。參數(shù)解釋如下: user.home – 用戶主目錄 user.dir – 用戶當(dāng)前工作目錄 java.io.tmpdir – 默認(rèn)臨時(shí)文件路徑 --> <diskStore path="./tmpdir/Tmp_EhCache"/> <defaultCache eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="10000" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="1800" timeToLiveSeconds="259200" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/> <cache name="cloud_user" eternal="false" maxElementsInMemory="5000" overflowToDisk="false" diskPersistent="false" timeToIdleSeconds="1800" timeToLiveSeconds="1800" memoryStoreEvictionPolicy="LRU"/> <!-- defaultCache:默認(rèn)緩存策略,當(dāng)ehcache找不到定義的緩存時(shí),則使用這個(gè)緩存策略。只能定義一個(gè)。 --> <!-- name:緩存名稱。 maxElementsInMemory:緩存最大數(shù)目 maxElementsOnDisk:硬盤最大緩存?zhèn)€數(shù)。 eternal:對(duì)象是否永久有效,一但設(shè)置了,timeout將不起作用。 overflowToDisk:是否保存到磁盤,當(dāng)系統(tǒng)當(dāng)機(jī)時(shí) timeToIdleSeconds:設(shè)置對(duì)象在失效前的允許閑置時(shí)間(單位:秒)。僅當(dāng)eternal=false對(duì)象不是永久有效時(shí)使用,可選屬性,默認(rèn)值是0,也就是可閑置時(shí)間無(wú)窮大。 timeToLiveSeconds:設(shè)置對(duì)象在失效前允許存活時(shí)間(單位:秒)。最大時(shí)間介于創(chuàng)建時(shí)間和失效時(shí)間之間。僅當(dāng)eternal=false對(duì)象不是永久有效時(shí)使用,默認(rèn)是0.,也就是對(duì)象存活時(shí)間無(wú)窮大。 diskPersistent:是否緩存虛擬機(jī)重啟期數(shù)據(jù) Whether the disk store persists between restarts of the Virtual Machine. The default value is false. diskSpoolBufferSizeMB:這個(gè)參數(shù)設(shè)置DiskStore(磁盤緩存)的緩存區(qū)大小。默認(rèn)是30MB。每個(gè)Cache都應(yīng)該有自己的一個(gè)緩沖區(qū)。 diskExpiryThreadIntervalSeconds:磁盤失效線程運(yùn)行時(shí)間間隔,默認(rèn)是120秒。 memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:當(dāng)達(dá)到maxElementsInMemory限制時(shí),Ehcache將會(huì)根據(jù)指定的策略去清理內(nèi)存。默認(rèn)策略是LRU(最近最少使用)。你可以設(shè)置為FIFO(先進(jìn)先出)或是LFU(較少使用)。 clearOnFlush:內(nèi)存數(shù)量最大時(shí)是否清除。 memoryStoreEvictionPolicy:可選策略有:LRU(最近最少使用,默認(rèn)策略)、FIFO(先進(jìn)先出)、LFU(最少訪問次數(shù))。 FIFO,first in first out,這個(gè)是大家最熟的,先進(jìn)先出。 LFU, Less Frequently Used,就是上面例子中使用的策略,直白一點(diǎn)就是講一直以來(lái)最少被使用的。如上面所講,緩存的元素有一個(gè)hit屬性,hit值最小的將會(huì)被清出緩存。 LRU,Least Recently Used,最近最少使用的,緩存的元素有一個(gè)時(shí)間戳,當(dāng)緩存容量滿了,而又需要騰出地方來(lái)緩存新的元素的時(shí)候,那么現(xiàn)有緩存元素中時(shí)間戳離當(dāng)前時(shí)間最遠(yuǎn)的元素將被清出緩存。 --> </ehcache>



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)