狀態(tài)管理Vuex的使用總結(jié)
1、Vuex.store 的基本使用
Vuex 是一個(gè)專為 Vue.js 應(yīng)用程序開發(fā)的狀態(tài)管理模式,它采用集中式存儲(chǔ)管理應(yīng)用的所有組件的狀態(tài),并以相應(yīng)的規(guī)則保證狀態(tài)以一種可預(yù)測(cè)的方式發(fā)生變化。
Vuex 使用單一狀態(tài)樹,即用一個(gè)對(duì)象包含全部的應(yīng)用層級(jí)狀態(tài),這也意味著,每個(gè)應(yīng)用將僅僅包含一個(gè) store 實(shí)例。Vuex是全局狀態(tài)管理倉庫,可以理解為相當(dāng)于window對(duì)象掛載了一個(gè)全局變量。
每一個(gè) Vuex 應(yīng)用的核心就是 store(倉庫)。Vuex 的狀態(tài)存儲(chǔ)是響應(yīng)式的。當(dāng) Vue 組件從 store 中讀取狀態(tài)的時(shí)候,若 store 中的狀態(tài)發(fā)生變化,那么相應(yīng)的組件也會(huì)相應(yīng)地得到高效更新。你不能直接改變 store 中的狀態(tài)。改變 store 中的狀態(tài)的唯一途徑就是顯式地提交 (commit) mutation。這樣使得我們可以方便地跟蹤每一個(gè)狀態(tài)的變化,從而讓我們更方便地使用一些工具比如 devtools 來調(diào)試我們的應(yīng)用。
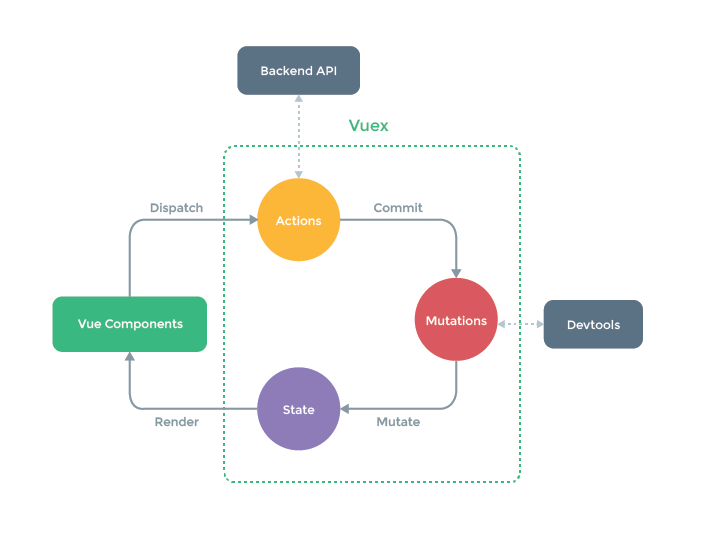
屬性:state(數(shù)據(jù)源)、actions(處理異步事件)、mutations(處理同步事件)、getters(過濾數(shù)據(jù))和modules(模塊)
1.1、創(chuàng)建 store
- 首先安裝 Vue、Vuex,在一個(gè) JS 文件中創(chuàng)建一個(gè) store
//store.js import Vue from 'vue' import Vuex from 'vuex' Vue.use(Vuex); const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, getters: { age () { return 232 } }, actions: {}, mutations: { increment(state,) { state.count++; } } }) export default store;
- 然后在 main.js 中引入 store
// main.js import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' import store from './store/store.js' Vue.config.productionTip = false new Vue({ el: '#app', router, store, components: { App }, template: '<App/>' })
通過 store 選項(xiàng)能將狀態(tài)從根組件“注入”到每一個(gè)子組件中(前面需先調(diào)用 Vue.use(Vuex))
在 main.js 文件中引入 store 后,該 store 實(shí)例會(huì)注入到根組件下的所有子組件中,其他組件就可以通過 this.$store 來訪問這個(gè) store 倉庫了。
通過 this.$store.state 來訪問數(shù)據(jù)、通過 this.$store.getters 來訪問 getters 數(shù)據(jù)、通過 this.$store.commit('') 來調(diào)用 mutations 變更狀態(tài),通過調(diào)用 this.$store.dispatch('') 來觸發(fā) actions 調(diào)用 mutations。
2、Vuex.Store 的選項(xiàng)
2.1、state 選項(xiàng)
在組件中使用 store 中的 state,我們可以直接通過 this.$store.state 來使用,也可以通過將狀態(tài)返回到組件中的計(jì)算屬性中來使用,而且每當(dāng) $store.state.count 變化的時(shí)候, 都會(huì)重新求取計(jì)算屬性。
2.1.1、mapState() 函數(shù)
我們可以使用 mapState 輔助函數(shù)來幫助我們將 state 返回到組件的計(jì)算屬性中,減少我們的代碼量。
mapState(nameSpace, Array | Object),mapState 輔助函數(shù)的第一個(gè)參數(shù)可選,表示的是一個(gè)命名空間字符串(跟模塊化有關(guān)),第二個(gè)參數(shù)可以是數(shù)組或者對(duì)象。函數(shù)最終返回一個(gè)對(duì)象,我們可以使用對(duì)象展開運(yùn)算符將此對(duì)象插入到計(jì)算屬性中。
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
<script>
export default {
data () {
return {}
},
computed: {
name () { return 'wen' },
...mapState([
'count' // 組件中的 this.count 則是 this.$store.state.count
])
}
}
</script>
// 或者使用對(duì)象作為參數(shù)
computed: {
...mapState({
count: state => state.count,
// 傳字符串參數(shù) 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count`
countAlias: 'count',
// 為了能夠使用 `this` 獲取局部狀態(tài),必須使用常規(guī)函數(shù)
countPlusLocalState (state) {
return state.count + this.localCount
}
})
}
2.2、getters 選項(xiàng)
store 中的 getters 就像計(jì)算屬性一樣,getters 的返回值會(huì)根據(jù)它的依賴被緩存起來,且只有當(dāng)它的依賴值發(fā)生了改變才會(huì)被重新計(jì)算。
Getter 接受 state 作為其第一個(gè)參數(shù),Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作為第二個(gè)參數(shù)。
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { age: 23 }, getters: { //接收一個(gè)參數(shù) myAge: state => { return state.age + 2 }, //接收兩個(gè)參數(shù) myAge2: (state, getters) => { return getters.myAge + 2; } } })
在組件中可以通過 this.$store.getters 來訪問 getters 中的數(shù)據(jù)。
你也可以通過讓 getter 返回一個(gè)函數(shù),來實(shí)現(xiàn)給 getter 傳參。注意,getter 在通過方法訪問時(shí),每次都會(huì)去進(jìn)行調(diào)用,而不會(huì)緩存結(jié)果
getters: { // 返回一個(gè)函數(shù) getTodoById: (state) => (id) => { return state.todos.find(todo => todo.id === id) } } //組件中訪問時(shí)通過函數(shù)的形式訪問,傳入?yún)?shù) this.$store.getters.getTodoById(2)
2.2.1、mapGetters() 函數(shù)
類似于 mapState 輔助函數(shù)一樣,可以通過 mapGetters 輔助函數(shù)將 store 中的 getter 映射到局部計(jì)算屬性
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
export default {
computed: {
// 數(shù)組作為參數(shù)
...mapGetters([
'doneTodosCount',
'anotherGetter',
// ...
])
}
}
//對(duì)象作為參數(shù)
...mapGetters({
// 把 `this.doneCount` 映射為`this.$store.getters.doneTodosCount`
doneCount: 'doneTodosCount'
})
2.3、mutations 選項(xiàng)
更改 Vuex 的 store 中的狀態(tài)的唯一方法是提交 mutation。mutation 必須是同步函數(shù),即里面不能有異步的操作。要想異步操作,可以使用 actions。
mutation 接受 state 作為第一個(gè)參數(shù)。
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 1 }, mutations: { increment (state) { // 變更狀態(tài) state.count++ } } })
在組件中通過 this.$store.commit('increment') 的形式來調(diào)用 mutation
mutation 可以接收其他數(shù)據(jù)作為其他參數(shù),即載荷(payload)。一般來說,其他的參數(shù)可以作為對(duì)象傳過去,這樣更加簡(jiǎn)潔一點(diǎn)。
mutations: { increment (state, n) { state.count += n } } //調(diào)用時(shí) this.$store.commit('increment', 10) // payload 是對(duì)象 mutations: { increment (state, payload) { state.count += payload.amount } } //調(diào)用時(shí) store.commit('increment', { amount: 10 }) //或者此時(shí)可以使用對(duì)象風(fēng)格進(jìn)行提交 store.commit({ type: 'increment', amount: 10 })
2.3.1、mutation 往 state 的某個(gè)對(duì)象中添加屬性
當(dāng) mutation 需要在 state 中的某個(gè)對(duì)象添加新屬性時(shí),不能直接添加,應(yīng)該使用 Vue.set 方法,比如 Vue.set(obj, 'newProp', 123) 。或者是新生成一個(gè)對(duì)象,用新對(duì)象替換舊對(duì)象:state.obj = { ...state.obj, newProp: 123 }
state: { man: { name: 'wen' } }, mutations: { //添加屬性 addProp (state) { Vue.set(state.man, 'age', 22) // 或者:state.man = Object.assgin({}, state.man, {age: 22}) } }
2.3.2、mapMutations() 函數(shù)
mapMutations() 輔助函數(shù)將 store 中的 mutations 映射到局部方法中。
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 將 `this.increment()` 映射為 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持載荷:
'incrementBy' // 將 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射為 `this.$store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 將 `this.add()` 映射為 `this.$store.commit('increment')`
})
}
}
2.4、actions 選項(xiàng)
Action 用來提交 mutation,由 mutation 來變更狀態(tài),Action 可以包含任意異步操作。
Action 函數(shù)接受一個(gè)與 store 實(shí)例具有相同方法和屬性的 context 對(duì)象,可以調(diào)用 context.commit 提交一個(gè) mutation,或者通過 context.state 和 context.getters 來獲取 state 和 getters。
const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { count: 0 }, mutations: { increment (state) { state.count++ } }, actions: { increment (context) { context.commit('increment') } // 下面的寫法更加簡(jiǎn)潔 increment ({ commit }) { commit('increment') } } })
在組件內(nèi)可以通過 this.$store.dispatch('') 來觸發(fā) action。
actions 可以接收額外的參數(shù),額外的參數(shù)寫成一個(gè)對(duì)象更加簡(jiǎn)潔。
//接收額外的參數(shù) actions: { increment ({ commit }, n) { if(n >= 0){ commit('increment') } } } //用對(duì)象作為額外的參數(shù) actions: { increment ({ commit }, payload) { if(payload.n >= 0){ commit('increment') } } } //此時(shí)的調(diào)用方式 this.$store.dispatch('increment', { amount: 10 }) // 以對(duì)象形式分發(fā) store.dispatch({ type: 'incrementAsync', amount: 10 })
2.4.1、mapActions() 函數(shù)
可以使用 mapActions 輔助函數(shù)將 actions 映射到組件的 methods 中。
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
methods: {
...mapActions([
'increment', // 將 `this.increment()` 映射為 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
// `mapActions` 也支持載荷:
'incrementBy' // 將 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射為 `this.$store.dispatch('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
...mapActions({
add: 'increment' // 將 `this.add()` 映射為 `this.$store.dispatch('increment')`
})
}
}
2.4.2、組合使用多個(gè) action
我們可以組合多個(gè) action以處理比較復(fù)雜的異步流程。
如果 action 中有異步操作,我們可以使用 promise或者 async/await 函數(shù)來更改狀態(tài)。
也可以通過返回一個(gè) promise來組合使用action,store.dispatch 可以處理 action 處理函數(shù)返回的 Promise,并且 store.dispatch 仍舊返回 Promise,由此我們可以在 store.dispatch() 后面接著寫我們需要的操作。
actions: { actionA ({ commit }) { return new Promise((resolve, reject) => { setTimeout(() => { commit('someMutation') resolve() }, 1000) }) } //在另一個(gè) action 中可以操作前面的 action 函數(shù) resolve 出的數(shù)據(jù) actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) { return dispatch('actionA').then(() => { commit('someOtherMutation') }) } } //在組件中 store.dispatch('actionA').then(() => { })
在 action 中使用 async/await
// 下面假設(shè) getData() 和 getOtherData() 返回的是 Promise actions: { async actionA ({ commit }) { commit('gotData', await getData()) }, async actionB ({ dispatch, commit }) { await dispatch('actionA') // 等待 actionA 完成 commit('gotOtherData', await getOtherData()) } }


 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)