【Java】- Servlet管理機制
一、什么是Servlet
簡單的說,瀏覽器發(fā)出請求到tocat服務(wù)器,服務(wù)器就會初始化一個servlet實例(servlet采取生命托管的方式實現(xiàn)單例,不存在時才會創(chuàng)建實例),servlet示例會啟動一個線程來處理該請求,并進行響應(yīng)該請求,動態(tài)生成web內(nèi)容
二、什么是Tomcat服務(wù)器
Tomcat是Apache開發(fā)的一種servlet容器,實現(xiàn)了對servlet和jsp等的支持,用來處理并響應(yīng)瀏覽器發(fā)送過來的請求,實際上Tomcat是Apache 服務(wù)器的擴展,但運行時它是獨立運行的,所以當你運行tomcat 時,它實際上作為一個與 Apache 獨立的進程單獨運行的。
三、web.xml配置文件解析
1 <servlet> 2 <!-- servlet的內(nèi)部名稱,自定義 --> 3 <servlet-name>login</servlet-name> 4 <!-- servlet的類全名:包名+類名 --> 5 <servlet-class>com.TestServlet.servlet.LoginServlet</servlet-class> 6 <!-- 當servlet對象立即加載時 url?后攜帶的重要信息, 在加載servlet類是可以直接加載進去 7 可以通過可以在init方法內(nèi)使用帶ServletConfig的參數(shù)讀取 8 String value = config.getInitParameter("key");//某一個key對應(yīng)的value 9 Enumeration en = config.getInitParameterNames();//獲取全部的key 10 String name = config.getServletName();//獲取當前Servlet類名 11 ServletContext application = config.getServletContext();//獲取全局上下文對象 12 --> 13 <init-param> 14 <param-name>name1</param-name> 15 <param-value>value1</param-value> 16 <param-name>name2</param-name> 17 <param-value>value2</param-value> 18 </init-param> 19 <!-- servlet對象創(chuàng)建優(yōu)先級 --> 20 <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> 21 </servlet> 22 <!-- servlet的映射配置 --> 23 <servlet-mapping> 24 <!-- servlet的內(nèi)部名稱,和上面的自定義servlet-name對應(yīng)的標簽名稱一致 --> 25 <servlet-name>login</servlet-name> 26 <!-- servlet的映射路徑(訪問serclet的名稱) --> 27 <url-pattern>/index</url-pattern> 28 </servlet-mapping> 29 <!-- 整體詳情解析 以 http://localhost:8080/index--> 30 <!-- 通過解析url得到 index 去標簽 servlet-mapping中的url-pattern標簽進行匹配, 31 若是匹配上,得到servlet-name標簽中的 login定位符,在通過 login 到 32 servlet標簽下的 servlet-name 進行匹配,若是匹配上獲取 servlet-class標簽的 33 類全名 com.TestServlet.servlet.LoginServlet, 在通過反射技術(shù)創(chuàng)建 LoginServlet對象實例 34 -->
四、servlet類的繼承關(guān)系
自己定義一個類來繼承HttpServlet
1 public class LoginServlet extends HttpServlet { 2 3 @Override 4 protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { 5 super.service(req, resp); 6 } 7 8 @Override 9 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { 10 super.doGet(req, resp); 11 } 12 13 @Override 14 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { 15 super.doPost(req, resp); 16 } 17 }
由上面代碼可以看到,我們重寫了三個常用的方法,但上面除了方法名不同,其他全部相同,這是為什么呢,我們帶著這個問題,來對源碼進行追根溯源
HttpServlet類繼承關(guān)系
1 // HtppServlet繼承類GenericServlet類 2 public abstract class HttpServlet extends GenericServlet {} 3 /* GenericServlet類,實現(xiàn)了三個接口,分別為 4 Servlet: servlet接口 5 ServletConfig: 封裝servlet配置信息 6 Serializable: 序列化接口,在反序列化時進行版本比對 7 */ 8 public abstract class GenericServlet implements Servlet, ServletConfig, Serializable {}
servlet類源碼解析
1 public interface Servlet { 2 /** 3 * servlet聲明周期 4 * 1、init() 初始化,僅第一次servlet時執(zhí)行,同時會攜帶一個ServletConfig參數(shù) 5 * 2、service() 用戶處理請求,每次訪問servlet時都會執(zhí)行一次 6 * 3、destory() 重新配置或者重新部署項目時執(zhí)行,用于銷毀servlet對象,銷毀后的對象由gc進行回收 7 * */ 8 void init(ServletConfig var1) throws ServletException; 9 10 ServletConfig getServletConfig(); 11 12 void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException; 13 14 String getServletInfo(); 15 16 void destroy(); 17 }
ServletConfig源碼解析
1 public interface ServletConfig { 2 // 獲取當前servlet類名 3 String getServletName(); 4 // 獲取servlet全局上下文 5 ServletContext getServletContext(); 6 // 獲取web.xml文件中<init-param>標簽下某一個<param-name>標簽的值 7 String getInitParameter(String var1); 8 // 獲取web.xml文件中<init-param>標簽下所有的<param-name>標簽的值 9 Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames(); 10 }
源碼解析GenricServlet類
1 // 序列化 2 private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; 3 // ServletConfig 屬性 4 private transient ServletConfig config; 5 // 無參構(gòu)造方法 6 public GenericServlet() { 7 } 8 // 實現(xiàn)了servlet中的destroy() 方法 9 public void destroy() { 10 } 11 // 重寫了并實現(xiàn)了ServletConfig中的getInitParameter(),便于獲取web.xml配置文件中的<init-param>標簽下某一個<param-name>標簽的值 12 public String getInitParameter(String name) { 13 return this.getServletConfig().getInitParameter(name); 14 } 15 // 重寫了并實現(xiàn)了ServletConfig中的getInitParameter(),便于獲取web.xml配置文件中的<init-param>標簽下所有的<param-name>標簽的值 16 // 返回Enumeration 可以采取while循環(huán)獲取所有key值 17 // hasMoreElements 判斷是否還有key 18 // nextElement(); 獲取key值 19 public Enumeration<String> getInitParameterNames() { 20 return this.getServletConfig().getInitParameterNames(); 21 } 22 23 // 獲取當前servlet對象 24 public ServletConfig getServletConfig() { 25 return this.config; 26 } 27 28 // 獲取servlet全局上下文 29 // 30 public ServletContext getServletContext() { 31 return this.getServletConfig().getServletContext(); 32 } 33 34 public String getServletInfo() { 35 return ""; 36 } 37 38 // 實現(xiàn)了init初始化方法,將config對象賦值給自己的config屬性中,從而達到在servlet第一此加載時,就擁有config對象 39 public void init(ServletConfig config) throws ServletException { 40 this.config = config; 41 this.init(); 42 } 43 44 // 添加了一個Init無參方法,可以提供用戶進行重寫 45 public void init() throws ServletException { 46 } 47 48 // 增加了自己的log方法,控制臺打印日志 49 public void log(String msg) { 50 this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + msg); 51 } 52 53 public void log(String message, Throwable t) { 54 this.getServletContext().log(this.getServletName() + ": " + message, t); 55 } 56 57 // 該類由用戶自己定以 所以沒有實現(xiàn)接口方法 58 public abstract void service(ServletRequest var1, ServletResponse var2) throws ServletException, IOException; 59 60 // 獲取serlet類對象名 61 public String getServletName() { 62 return this.config.getServletName(); 63 }
源碼解析HttpServlet類
1 // doGet方法,未進行任何處理, 2 protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { 3 String protocol = req.getProtocol(); 4 String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_get_not_supported"); 5 if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { 6 resp.sendError(405, msg); 7 } else { 8 resp.sendError(400, msg); 9 } 10 11 } 12 13 // doPost方法,未進行任何處理, 14 protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { 15 String protocol = req.getProtocol(); 16 String msg = lStrings.getString("http.method_post_not_supported"); 17 if (protocol.endsWith("1.1")) { 18 resp.sendError(405, msg); 19 } else { 20 resp.sendError(400, msg); 21 } 22 23 } 24 25 // 提供了自己的受保護的service方法,便于子類訪問,類中未進行具體操作,而是通過獲取請求類型來定位調(diào)用方法來處理 26 protected void service(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException { 27 String method = req.getMethod(); 28 long lastModified; 29 if (method.equals("GET")) { 30 lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); 31 if (lastModified == -1L) { 32 this.doGet(req, resp); 33 } else { 34 long ifModifiedSince; 35 try { 36 ifModifiedSince = req.getDateHeader("If-Modified-Since"); 37 } catch (IllegalArgumentException var9) { 38 ifModifiedSince = -1L; 39 } 40 41 if (ifModifiedSince < lastModified / 1000L * 1000L) { 42 this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); 43 this.doGet(req, resp); 44 } else { 45 resp.setStatus(304); 46 } 47 } 48 } else if (method.equals("HEAD")) { 49 lastModified = this.getLastModified(req); 50 this.maybeSetLastModified(resp, lastModified); 51 this.doHead(req, resp); 52 } else if (method.equals("POST")) { 53 this.doPost(req, resp); 54 } else if (method.equals("PUT")) { 55 this.doPut(req, resp); 56 } else if (method.equals("DELETE")) { 57 this.doDelete(req, resp); 58 } else if (method.equals("OPTIONS")) { 59 this.doOptions(req, resp); 60 } else if (method.equals("TRACE")) { 61 this.doTrace(req, resp); 62 } else { 63 String errMsg = lStrings.getString("http.method_not_implemented"); 64 Object[] errArgs = new Object[]{method}; 65 errMsg = MessageFormat.format(errMsg, errArgs); 66 resp.sendError(501, errMsg); 67 } 68 69 } 70 71 // 實現(xiàn)了接口servlet類中的service()方法,但沒有將具體處理,僅僅將ServletRequest和ServletResponse進行 72 // 此處體現(xiàn)了面向?qū)ο笏枷耄搀w現(xiàn)了適配器模式的應(yīng)用。 73 public void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throws ServletException, IOException { 74 HttpServletRequest request; 75 HttpServletResponse response; 76 try { 77 request = (HttpServletRequest)req; 78 response = (HttpServletResponse)res; 79 } catch (ClassCastException var6) { 80 throw new ServletException("non-HTTP request or response"); 81 } 82 83 // 調(diào)用該類的受保護類 84 this.service(request, response); 85 }
servlet生命周期
servlet對象是單實例管理,底層采用生命周期托管方式實現(xiàn)
Servlet對象是延遲加載的機制,在第一次訪問時創(chuàng)建對象,且只加載一次
Servlet對象的創(chuàng)建 使用 銷毀的三個方法分別是:
init() 第一次訪問servlet時執(zhí)行
service() 每一次訪問servlet都會調(diào)用一次
destroy() 重新配置或者部署項目時,調(diào)用該方法進行銷毀servlet對象,銷毀的對象由GC垃圾回收機制進行回收
Servlet管理機制總結(jié)
1、我們自己的類繼承了HttpServlet
2、HttpServlet繼承了GenericServlet
3、GenericServlet實現(xiàn)了三個接口
Servlet接口 ServletConfig接口 Serializable接口
ServletConfig接口擁有四個方法,但都是抽象方法
String = getInitParamName(String v) // 初始化servlet類
Enumeration<String> = getInitParamNames() // 獲取所有key
String = getServetName // 獲取類對象名稱
ServletContext = getServletContext() // 獲取類對象上下文
Servlet接口提供了五個方法,全部都是抽象
void init(ServletConfig sc); // 初始化servlet類
void service(ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res) throw ServletException, IOException
void destroy() //servlet對象銷毀方法
ServletConfig getServletConfig() // 獲取servlet類對象
String getServletInfo() // 獲取servlet類信息 若版本,作者,版權(quán)等
Serializable接口 沒有提供任何方法
4、GenericServlet類
將9個抽象方法實現(xiàn)了8個,還有一個service()沒有實現(xiàn),此處體現(xiàn)了缺省適配器模式
自己添加了 init() 無參數(shù)方法 和 log() 方法
5、HttpServlet 類,體現(xiàn)了面向?qū)ο蟮乃枷耄鶫TTP有關(guān)
該類中實現(xiàn)了service(),但僅對方法中的形參ServletRequset和ServletResponse進行了強制轉(zhuǎn)換成HttpServletRequset和HttpServletResponse
同時添加了一個protect修飾的service方法,即最終方法,但是該方法即通過 request.getMethod()來獲取請求類型,并進行方法調(diào)用
添加一些屬于自己的且和請求方式對應(yīng)的具體方法,如
doGet(HttpServletRequset req, HttpServletResponse res) throw ServletException, IOException
doGet(HttpServletRequset req, HttpServletResponse res) throw ServletException, IOException
添加了一些屬于自己的屬性
get post put等
6、 我們自己的servlet類繼承HttpServlet,重寫service方法,或者doGet/doPost等方法
若是我們自己類沒有重寫service方法,那么會從父類GenericServlet中的service去查找doGet/doPost等方法,拋出405
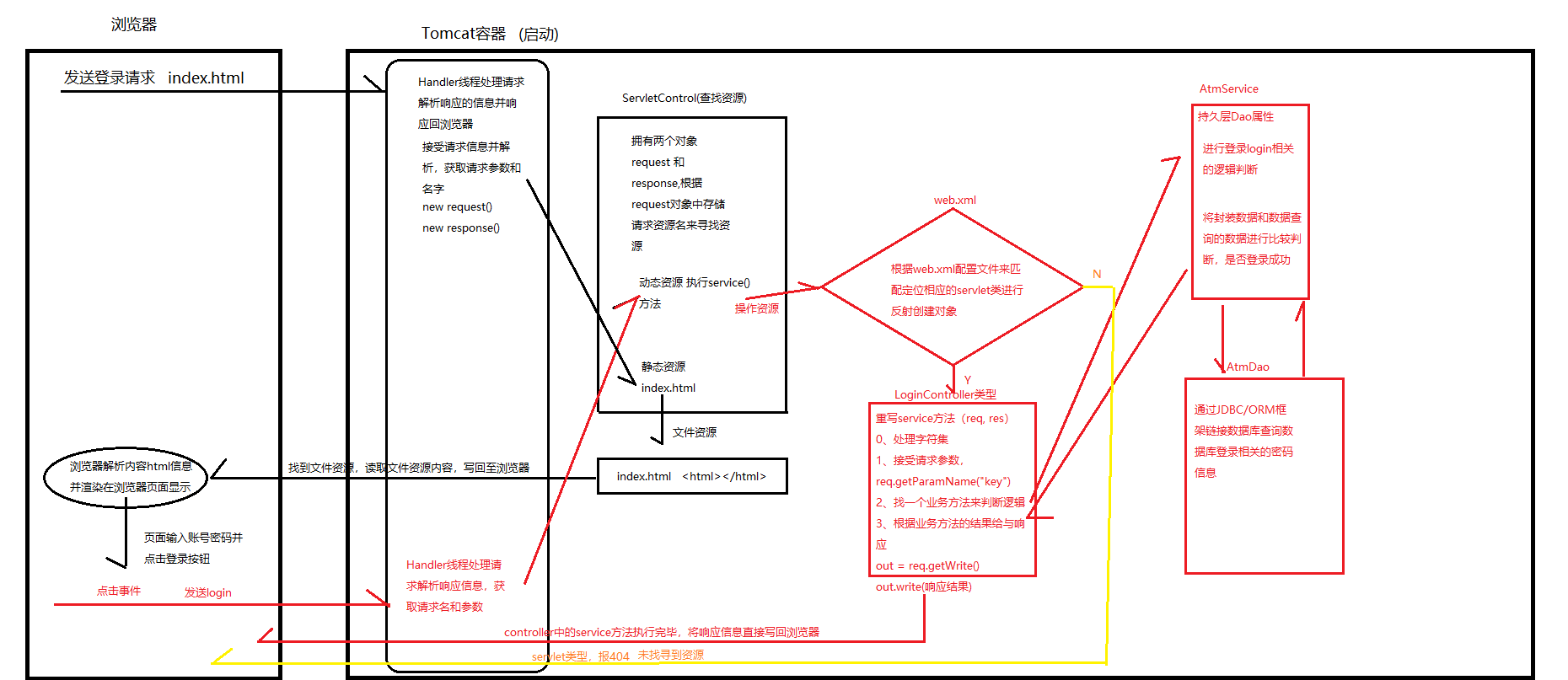
五、Tomcat請求響應(yīng)流程圖


 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號