Java數據轉換及屬性獲取
一、數據轉換
(1)數據轉換工具類
/** * 數據轉換工具類 * @author songwp */ public class DataUtils{ /** * 定義分割常量 * #用于list中每個元素間的分割 * |用于map中每一個kv對間的分割 * =用于map中key與value間的分割 */ private static final String SEP1 = ","; private static final String SEP2 = "|"; private static final String SEP3 = "="; private static final String SEP4 = ";"; /** * List轉換String * * @param list 需要轉換的List * @return String 轉換后的字符串 */ public static String ListToString(List<?> list) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); if (list != null && list.size() > 0) { for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) { if (list.get(i) == null || list.get(i) == "") { continue; } // 如果值是list類型則調用自己 if (list.get(i) instanceof List) { sb.append(ListToString((List<?>) list.get(i))); sb.append(SEP1); } else if (list.get(i) instanceof Map) { sb.append(MapToString((Map<?, ?>) list.get(i))); sb.append(SEP1); } else { sb.append(list.get(i)); sb.append(SEP1); } } } return sb.toString(); } /** * Map轉換String * * @param map 需要轉換的Map * @return String 轉換后的字符串 */ public static String MapToString(Map<?, ?> map) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); // 遍歷map for (Object obj : map.keySet()) { if (obj == null) { continue; } Object key = obj; Object value = map.get(key); if (value instanceof List<?>) { sb.append(key.toString() + SEP1 + ListToString((List<?>) value)); sb.append(SEP2); } else if (value instanceof Map<?, ?>) { sb.append(key.toString() + SEP1 + MapToString((Map<?, ?>) value)); sb.append(SEP2); } else { if (value == null) { sb.append(key.toString() + SEP3 + "0"); sb.append(SEP2); } else { sb.append(key.toString() + SEP3 + value.toString()); sb.append(SEP2); } } } return sb.toString(); } /** * String轉換Map * * @param mapText 需要轉換的字符串 * @return Map<?,?> */ public static Map<String, Object> StringToMap(String mapText) { if (mapText == null || mapText.equals("")) { return null; } mapText = mapText.substring(1); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); String[] text = mapText.split("\\" + SEP2); // 轉換為數組 for (String str : text) { String[] keyText = str.split(SEP3); // 轉換key與value的數組 if (keyText.length < 1) { continue; } String key = keyText[0]; // key String value = keyText[1]; // value if (value.charAt(0) == 'M') { Map<?, ?> map1 = StringToMap(value); map.put(key, map1); } else if (value.charAt(0) == 'L') { List<?> list = StringToList(value); map.put(key, list); } else { map.put(key, value); } } return map; } /** * String轉換List * * @param listText 需要轉換的文本 * @return List<?> */ public static List<Object> StringToList(String listText) { if (listText == null || listText.equals("")) { return null; } listText = listText.substring(0); List<Object> list = new ArrayList<Object>(); String[] text = listText.split("\\" + SEP1); String listStr = ""; boolean flag = false; for (String str : text) { if (!str.equals("")) { if (str.charAt(0) == 'M') { Map<?, ?> map = StringToMap(str); list.add(map); } else if (str.charAt(0) == 'L' || flag) { flag = true; listStr += str + SEP1; } else { list.add(str); } } if (str.equals("")) { flag = false; List<?> lists = StringToList(listStr); list.add(lists); } } return list; } public static void main(String[] args) { // 1. List轉換String List<Integer> list = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); String listToString = ListToString(list); System.out.println("List轉換String:" + listToString); Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<String, Object>(); map.put("name", "劉德華"); map.put("age", 56); map.put("address", "北京市海淀區"); // 2. Map轉換String String mapToString = MapToString(map); System.out.println("Map轉換String: " + mapToString); // 3. String轉換Map Map<String, Object> map1 = StringToMap(mapToString); System.out.println("String轉換Map: " + map1); // 4. String轉換List List<Object> list1 = StringToList(listToString); System.out.println("String轉換List: " + list1); } }
(2)控制臺輸出如下:

二、數據獲取
(1)數據獲取的具體代碼實例:
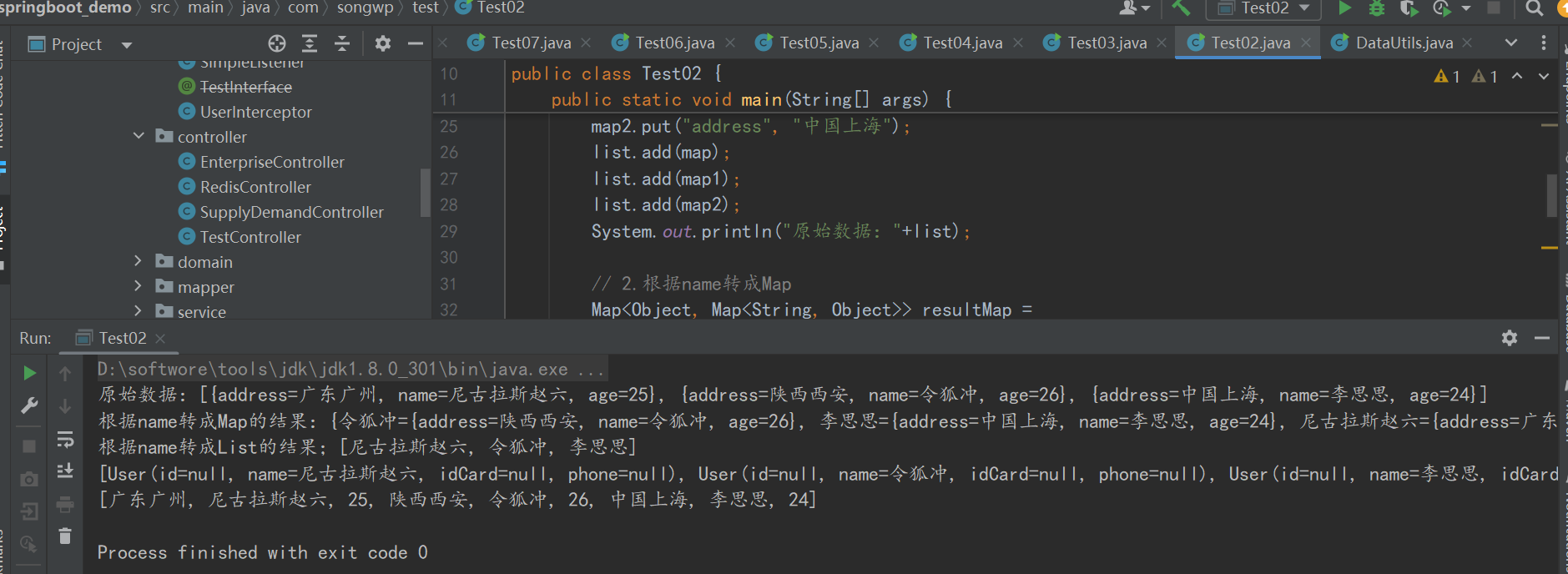
public static void main(String[] args) { // 1.數據準備 List<Map<String,Object>> list = new ArrayList<>(); Map<String,Object> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("name", "尼古拉斯趙六"); map.put("age", 25); map.put("address", "廣東廣州"); Map<String,Object> map1 = new HashMap<>(); map1.put("name", "令狐沖"); map1.put("age", 26); map1.put("address", "陜西西安"); Map<String,Object> map2 = new HashMap<>(); map2.put("name", "李思思"); map2.put("age", 24); map2.put("address", "中國上海"); list.add(map); list.add(map1); list.add(map2); System.out.println("原始數據:"+list); // 2.根據name轉成Map Map<Object, Map<String, Object>> resultMap = list.stream().collect(Collectors.toMap(m -> m.get("name"), m -> m)); System.out.println("根據name轉成Map的結果:"+resultMap); // 3.根據name轉成List List<Object> names = list.stream().map(m -> m.get("name")).collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println("根據name轉成List的結果;"+names); List<User> jsonArray = (List<User>)JSON.parseArray(JSON.toJSONString(list), User.class); System.out.println(jsonArray); // 4.將List<Map<String, Object>>轉換為List<Object> List<Object> listObject = list.stream() .flatMap(m -> m.values().stream()) .collect(Collectors.toList()); System.out.println(listObject); }
(2)控制臺輸出如下:
三、Map數據操作
Map是我們日常編程中十分常用的數據接口,的在JDK8中,Map引入了幾個新方法,可以簡化我們對Map中數據的操作。
getOrDefault
這個方法名很直觀,見名知意:嘗試獲取key對應的值,如果未獲取到,就返回默認值。
看一個使用的例子,新寫法會比老寫法更加簡潔:
private static void testGetOrDefault() { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(4); map.put("123", "123"); String key = "key"; String defaultValue = "defaultValue"; // 老寫法 String oldValue = defaultValue; if (map.containsKey(key)) { oldValue = map.get(key); } System.out.println("oldValue = " + oldValue); // 新寫法 String newValue = map.getOrDefault(key, defaultValue); System.out.println("newValue = " + newValue); }
foreach
看方法名也可以知道,這個方法是遍歷map的數據使用的。
如果沒有foreach,我們遍歷map的時候一般是使用增強for循環,有了這個方法后,可以更加方便使用entry中的key和val:
private static void testForeach() { Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(4); map.put("123", "123"); // 老寫法 for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { System.out.printf("老寫法 key = %s, value = %s%n", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue()); } // 新寫法 map.forEach((key, value) -> System.out.printf("新寫法 key = %s, value = %s%n", key, value)); }
merge
從名字可以想到,是合并entry使用的,但是具體是怎么合并呢?
看一下日常最常用的Map實現類HashMap對merge方法的實現
@Override public V merge(K key, V value, BiFunction<? super V, ? super V, ? extends V> remappingFunction) { if (value == null || remappingFunction == null) throw new NullPointerException(); int hash = hash(key); Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> first; int n, i; int binCount = 0; TreeNode<K,V> t = null; Node<K,V> old = null; if (size > threshold || (tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0) n = (tab = resize()).length; if ((first = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) != null) { if (first instanceof TreeNode) old = (t = (TreeNode<K,V>)first).getTreeNode(hash, key); else { Node<K,V> e = first; K k; do { if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k)))) { old = e; break; } ++binCount; } while ((e = e.next) != null); } } if (old != null) { V v; if (old.value != null) { int mc = modCount; v = remappingFunction.apply(old.value, value); if (mc != modCount) { throw new ConcurrentModificationException(); } } else { v = value; } if (v != null) { old.value = v; afterNodeAccess(old); } else removeNode(hash, key, null, false, true); return v; } else { if (t != null) t.putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value); else { tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, first); if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) treeifyBin(tab, hash); } ++modCount; ++size; afterNodeInsertion(true); return value; } }
代碼比較長,但是實現的效果比較容易描述:這個方法接收3個參數:key、value、function。
- 如果key存在,將value按照function做1次計算后,更新到Map中
- 如果key不存在,將key-value放入Map中
這個方法在某些場景中挺好用的,代碼簡潔易懂,例如:我們有1個List,要統計List中每個元素出現的次數。我們要實現的邏輯是,遍歷List中的每個元素,如果這個元素在Map中存在,Map中的值+1;如果不存在,則放入Map中,次數(值)為1。
private static void testMerge() { Map<String, Integer> cntMap = new HashMap<>(8); List<String> list = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana", "orange"); // 老寫法 for (String item : list) { if (cntMap.containsKey(item)) { cntMap.put(item, cntMap.get(item) + 1); } else { cntMap.put(item, 1); } } // 新寫法 for (String item : list) { cntMap.merge(item, 1, Integer::sum); } }
可以看到我們使用merge方法的話,只用1行就簡潔實現了這個邏輯。
putIfAbsent
也是一個見名知意的方法:不存在key或者值為null時,才將鍵值對放入Map。跟put方法相比,這個方法不會直接覆蓋已有的值,在不允許覆蓋舊值的場景使用起來會比較簡潔。
private static void testPutIfAbsent() { Map<String, Integer> scoreMap = new HashMap<>(4); scoreMap.put("Jim", 88); scoreMap.put("Lily", 90); // 老寫法 if (!scoreMap.containsKey("Lily")) { scoreMap.put("Lily", 98); } // 新寫法 scoreMap.putIfAbsent("Lily", 98); }
computer
computer方法需要傳入2個參數:key、function。主要有3步操作
- 獲取到key對應的oldValue,可能為null
- 經過function計算獲取newValue
- put(key, newValue)
還是以剛剛統計單次次數需求為例,看一下computer的寫法:
private static void testComputer() { Map<String, Integer> cntMap = new HashMap<>(8); List<String> list = Arrays.asList("apple", "orange", "banana", "orange"); // 老寫法 for (String item : list) { if (cntMap.containsKey(item)) { cntMap.put(item, cntMap.get(item) + 1); } else { cntMap.put(item, 1); } } // 新寫法 for (String item : list) { cntMap.compute(item, (k, v) -> { if (v == null) { v = 1; } else { v += 1; } return v; }); } }
computeIfAbsent
看名字就知道是compute方法衍生出來的方法,這個方法只在key不存在的時候,執行computer計算,如果說key對應的value存在,就直接返回這個value。
例如,我們需要計算斐波那鍥數列的時候,可以使用這個方法來簡化代碼:
private static void testComputerIfAbsent() { Map<Integer, Integer> fabMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16); fabMap.put(0, 1); fabMap.put(1, 1); System.out.println(fab(5, fabMap)); } private static Integer fab(Integer index, Map<Integer, Integer> fabMap) { return fabMap.computeIfAbsent(index, i -> fab(i - 2, fabMap) + fab(i - 1, fabMap)); }
computeIfPresent
這個是computeIfAbsent的姊妹方法,區別在于,這個方法是只有key存在的時候,才去執行computer計算和值的更新。
replace
這個方法的效果是:
- 如果key存在,則更新值
- 如果key不存在,什么也不做


 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號