模型上下文協議MCP
MCP(Model Context Protocol) Anthropic推出的一種開放協議,旨在統一LLM應用于外部數據源之間的通訊協議使之無縫集成,MCP提供了標準化協議使得LLM與所需要的上下文無縫銜接。使用MCP可以插件式為LLM的集成各種外部數據源。
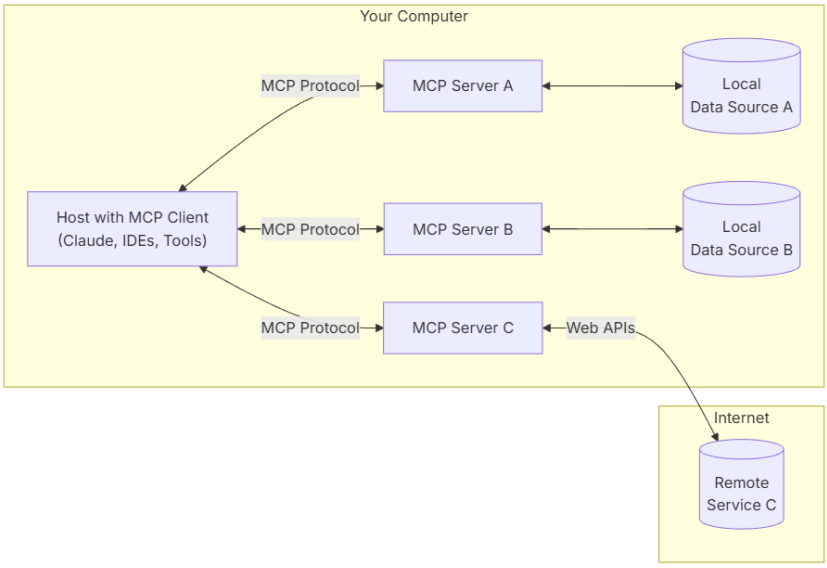
MCP概念
上圖為MCP官方所描述的MCP架構圖,MCP Hosts本身也是一個MCP Client,MCP Server端與各種類型外部數據源集成,一個Server可對應一個或多個外部數據源,數據源可以說本地數據或是網絡數據。Client與Server建立一對一的連接,其通過MCP協議與Server端進行通訊獲取Server所提供的各類數據。
host:一個包含MCP Client的應用,可以是Web、App、或其他類型的程序等。
MCP Client:使用MCP協議與Server建立一對一連接。
MCP Server:連接內部、外部、網絡資源,使用MCP協議對外提供服務。
Local:內部資源
Remote:外部/網絡資源
MCP Server
根據MCP協議定義,Server可以提供三種類型的標準能力,Resources、Tools、Prompts,每個Server可同時提供者三種類型能力或其中一種。
Resources:資源,類似于文件數據讀取,可以是文件資源或是API響應返回的內容。
Tools:工具,第三方服務、功能函數,通過此可控制LLM可調用哪些函數。
Prompts:提示詞,為用戶預先定義好的完成特定任務的模板。
通訊機制
MCP定義了Client與Server進行通訊的協議與消息格式,其支持兩種類型通訊機制:標準輸入輸出通訊、基于SSE的HTTP通訊,分別對應著本地與遠程通訊。Client與Server間使用JSON-RPC 2.0格式進行消息傳輸。
本地通訊:使用了stdio傳輸數據,具體流程Client啟動Server程序作為子進程,其消息通訊是通過stdin/stdout進行的,消息格式為JSON-RPC 2.0。
遠程通訊:Client與Server可以部署在任何地方,Client使用SSE與Server進行通訊,消息的格式為JSON-RPC 2.0,Server定義了/see與/messages接口用于推送與接收數據。
MCP定義了三類消息類型:Requests、Results、Errors、Notifications。
代碼示例
按照MCP協議的定義其是客戶端-服務端模型,客戶端請求使用服務端提供的工具、資源、提示詞。這里會先編寫Server端Demo然后再編寫Client端,使用Client調用Server端。
Server
在下面Server Demo中定義了Tool、Reource、Prompt各一個。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
from codecs import encode
import logging
from typing import Any
import asyncio
import httpx
from mcp.server.models import InitializationOptions
import mcp.types as types
from mcp.server import NotificationOptions, Server
import mcp.server.stdio
from pydantic import AnyUrl
server = Server("demo")
@server.list_prompts()
async def handle_list_prompts() -> list[types.Prompt]:
"""
提示模版定義
"""
return [
types.Prompt(
name="example-prompt",
description="An example prompt template",
arguments=[
types.PromptArgument(
name="arg1",
description="Example argument",
required=True
)
]
)
]
@server.get_prompt()
async def handle_get_prompt(
name: str,
arguments: dict[str, str] | None
) -> types.GetPromptResult:
"""
提示模板處理
"""
if name != "example-prompt":
raise ValueError(f"Unknown prompt: {name}")
return types.GetPromptResult(
description="Example prompt",
messages=[
types.PromptMessage(
role="user",
content=types.TextContent(
type="text",
text="Example prompt text"
)
)
]
)
@server.list_resources()
async def list_resources() -> list[types.Resource]:
"""
資源定義
"""
test='test.txt'
return [
types.Resource(
uri=AnyUrl(f"file:///{test}.txt"),
name=test,
description=f"A sample text resource named {test}",
mimeType="text/plain",
)
# for name in SAMPLE_RESOURCES.keys()
]
@server.read_resource()
async def read_resource(uri: AnyUrl) -> str | bytes:
assert uri.path is not None
name = uri.path.replace(".txt", "").lstrip("/")
if name not in SAMPLE_RESOURCES:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown resource: {uri}")
return SAMPLE_RESOURCES[name]
@server.list_tools()
async def handle_list_tools() -> list[types.Tool]:
"""
工具定義.
每個工具都使用JSON Schema驗證指定其參數.
"""
return [
types.Tool(
name="demo-tool",
description="Get data tool for a param",
inputSchema={
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"param": {
"type": "string",
"description": "url",
},
},
"required": ["param"],
},
)
]
@server.call_tool()
async def handle_call_tool(
name: str, arguments: dict | None
) -> list[Any]:
logging.info(name)
"""
處理工具調用
"""
if not arguments:
raise ValueError("Missing arguments")
if name == "demo-tool":
param = arguments.get("param")
if not param:
raise ValueError("Missing state parameter")
param = param.upper()
return [
types.TextContent(
type="text",
text=f"text:{param}"
)
]
else:
raise ValueError(f"Unknown tool: {name}")
async def main():
from anyio.streams.text import TextStream
# Run the server using stdin/stdout streams
async with mcp.server.stdio.stdio_server() as (read_stream, write_stream):
await server.run(
read_stream,
write_stream,
InitializationOptions(
server_name="demo-server",
server_version="0.1.0",
capabilities=server.get_capabilities(
notification_options=NotificationOptions(),
experimental_capabilities={},
),
),
)
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
Client
Client的實現,主要是與需要與Server建立連接,并調用Server所提供的各類資源。需要與Server所支持的方式建立連接,如其是stdio模式就需要建立stdio模式連接否則需要建立SSE連接。
async def demo(config):
server_params = StdioServerParameters(
command=shutil.which("npx") if config['command'] == "npx" else config['command'],
args=config['args'],
env={**os.environ, **config['env']} if config.get('env') else None
)
try:
print('demo')
stdio_context = stdio_client(server_params)
read, write = await stdio_context.__aenter__()
session = ClientSession(read, write)
await session.__aenter__()
capabilities = await session.initialize()
tools_response =await session.list_tools()
resources=await session.list_resources()
tools = []
for item in tools_response:
if isinstance(item, tuple) and item[0] == 'tools':
for tool in item[1]:
tools.append(tool)
params={}
params[tools[0].inputSchema['required'][0]]='測試參數';
result =await session.call_tool(tools[0].name,params)
print(result)
await stdio_context.__aexit__(None, None, None)
except Exception as e:
print(e)
if __name__=="__main__":
asyncio.run(demo({'command':'python','args':['server_demo.py']}))
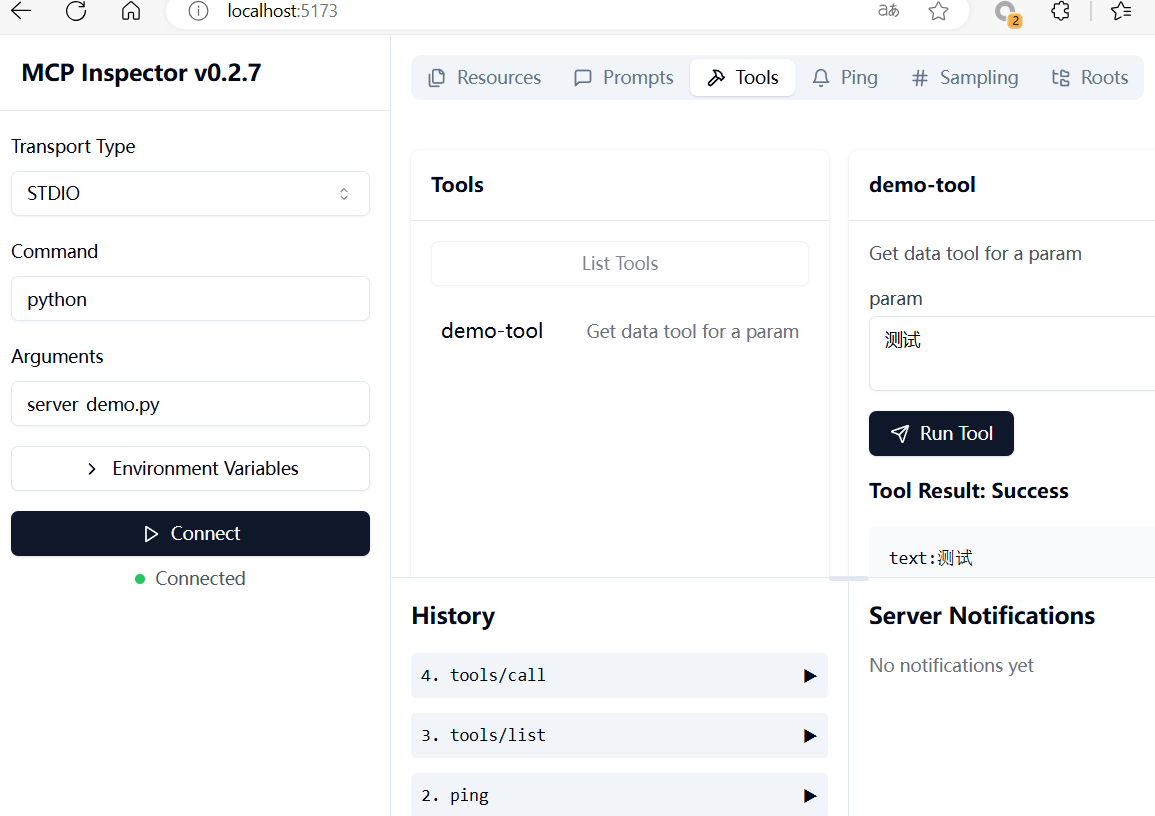
MCP Inspector
MCP提供了MCP Inspector 用于調試與測試MCP Server,使得Server開發更加方便。
使用nodejs啟動inspector程序,啟動后在瀏覽器訪問http://localhost:5173即可。可以在中查看MCP Server所提供的各種服務Tools、Resources、Prompts等,以及調用Tools服務。
npx @modelcontextprotocol/inspector
使用MCP的意義主要是統一LLM訪問外部資源的方式,可以限制LLM可使用哪些服務調用,第三方也可以定義各種類型的MCP Server提供給其他任何人使用。但Anthropic作為OpenAI的對手OpenAI跟不跟是MCP能否成為LLM上下文標準的關鍵。
參考資料:
MCP


 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號