享元模式(Flyweight)
1.1.1 摘要
今天是國慶節,祝大家國慶節快樂身體健康,在我們面向對象設計過程中,我們常常會面臨著對象實例過多的問題,如果對象實例過多這將是我們系統性能提高的一個瓶頸。假設我們要設計一個星空場景,現在我們需要實例星星對象,我們可以實例每一顆星星,但隨著我們實例星星對象增多整個場景就越來越慢了,如果你實例了1000+顆星星要你去維護,這可是一個吃力不討好的工作。我們必須找到一個合適的方法解決以上問題,這就是今天要介紹的享元模式(Flyweight)。
1.1.2 正文
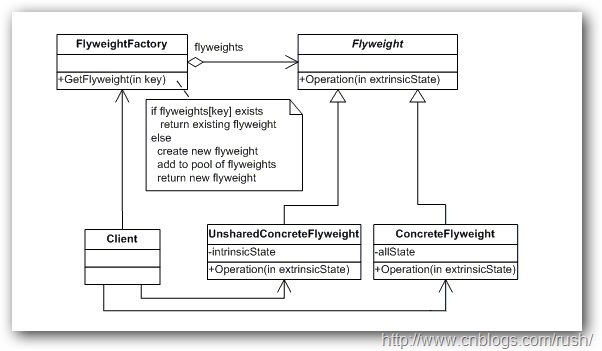
圖1享元模式(Flyweight)結構圖
享元模式(Flyweight):運用共享的技術有效地支持大量細粒度的對象。
抽象享元角色(Flyweight):此角色是所有的具體享元類的超類,為這些類規定出需要實現的公共接口或抽象類。那些需要外部狀態(External State)的操作可以通過方法的參數傳入。抽象享元的接口使得享元變得可能,但是并不強制子類實行共享,因此并非所有的享元對象都是可以共享的。
具體享元(ConcreteFlyweight)角色:實現抽象享元角色所規定的接口。如果有內部狀態的話,必須負責為內部狀態提供存儲空間。享元對象的內部狀態必須與對象所處的周圍環境無關,從而使得享元對象可以在系統內共享。有時候具體享元角色又叫做單純具體享元角色,因為復合享元角色是由單純具體享元角色通過復合而成的。
復合享元(UnsharableFlyweight)角色:復合享元角色所代表的對象是不可以共享的,但是一個復合享元對象可以分解成為多個本身是單純享元對象的組合。復合享元角色又稱做不可共享的享元對象。這個角色一般很少使用。
享元工廠(FlyweightFactoiy)角色:本角色負責創建和管理享元角色。本角色必須保證享元對象可以被系統適當地共享。當一個客戶端對象請求一個享元對象的時候,享元工廠角色需要檢查系統中是否已經有一個符合要求的享元對象,如果已經有了,享元工廠角色就應當提供這個已有的享元對象;如果系統中沒有一個適當的享元對象的話,享元工廠角色就應當創建一個新的合適的享元對象。
客戶端(Client)角色:本角色還需要自行存儲所有享元對象的外部狀態。
內部狀態與外部狀態:在享元對象內部并且不會隨著環境改變而改變的共享部分,可以稱之為享元對象的內部狀態,反之隨著環境改變而改變的,不可共享的狀態稱之為外部狀態。
現在讓我們通過一個面向對象的文本編輯器設計來說明享元模式的應用。假設我們要設計一個文本編輯器,而且它必須創建字符對象來表示文檔中的每個字符,現在讓我們考慮字符對象保持什么信息呢?如:字體、字體大小和位置等等信息。
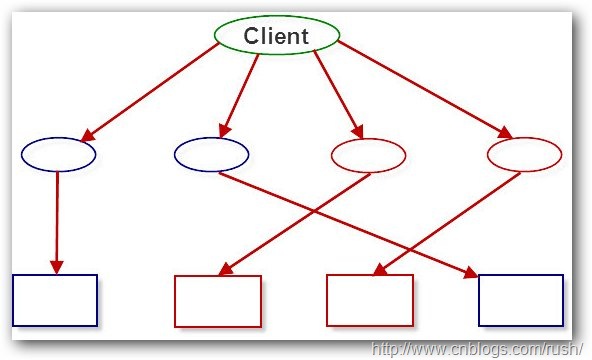
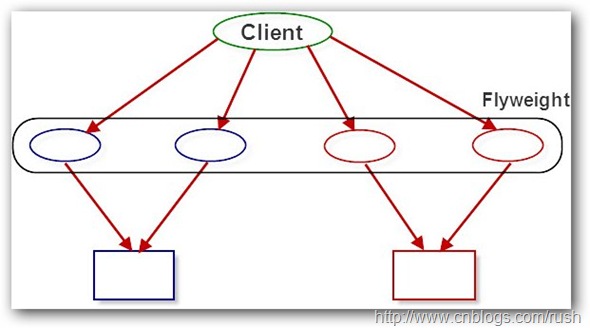
一個文檔通常包含許多字符對象,它們需要大容量的內存。值得我們注意的是一般字符都是由數字、字母和其他字符組成的(它們是固定的,可知的),這些字符對象可以共享字體和字體大小等信息,現在它們專有屬性只剩下位置了,每個字符對象只需保持它們在文檔中的位置就OK了,通過分析我們已經降低了編輯器的內存需求。
圖2享元模式(Flyweight)共享對象
/// <summary> /// The 'Flyweight' class. /// </summary> public class Character { // intrinsic state protected char _symbol; protected int _size; protected string _font; // extrinsic state protected Position _position; public void Display(Position position) { Console.WriteLine( String.Format("Symbol: {0} Size: {1} Font: {2} Position: {3} {4}", _symbol, _size, _font, position._x, position._y)); } }
現在我們定義了一個字符享元類,其中符合、字體和字體大小都是內部狀態,而位置則是外部狀態。
/// <summary> /// A 'ConcreteFlyweight' class /// </summary> public class CharacterA : Character { public CharacterA() { _symbol = 'A'; _size = 10; _font = "宋體"; //_position = new Position(0, 1); } }
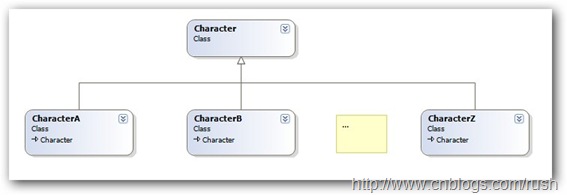
接著我們定義具體字符A的享元類,并且對內部狀態符號、字體和字體大小進行初始化,而且其他字符B到Z享元類都類似。
圖3具體享元模式(ConcreteFlyweight)設計
/// <summary> /// The 'FlyweightFactory' class /// </summary> public class CharacterFactory { // Keeps the character object by specifying key/value. private Dictionary<char, Character> _characters = new Dictionary<char, Character>(); public Character this[char key] { get { Character character = null; // Checked the character whether existed or not, // if the character existed, then directly returns, // otherwise, instantiates a character object. if (_characters.ContainsKey(key)) { character = _characters[key]; } else { string name = this.GetType().Namespace + "." + "Character" + key.ToString(); character = Activator.CreateInstance( Type.GetType(name)) as Character; _characters.Add(key, character); } return character; } } }
現在我們定義了一間字符工廠,通過一個Dictionary<Tkey, Tvalue>來保存字符對象,使用字符值來查找字符對象是否已經創建了,如果查找的字符對象已經存在,那么直接返回該對象,反之就創建字符對象實例。
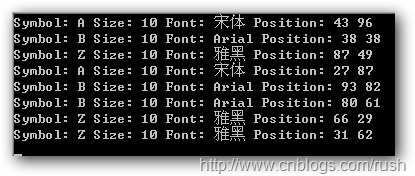
/// <summary> /// The client. /// </summary> /// <param name="args">The args.</param> [STAThread] static void Main(string[] args) { Application.EnableVisualStyles(); Application.SetCompatibleTextRenderingDefault(false); Application.Run(new FrmFlyweight()); string text = "ABZABBZZ"; char[] letters = text.ToCharArray(); var characterFactory = new CharacterFactory(); // Creates random position ranges 0 to 100. var rd = new Random(); foreach (char c in letters) { Character character = characterFactory[c]; var p = new Position(rd.Next(0, 100), rd.Next(0, 100)); character.Display(p); } Console.ReadKey(); }
圖4享元模式(ConcreteFlyweight)測試結果
接著讓我們實現一個享元模式的繪圖程序,假設我們的程序要畫各種各樣的圓,而且圓的屬性有形狀,位置和顏色,其中形狀和顏色是內部狀態,而位置是外部狀態。
設計分析:
1.提供一個抽象類Shape,讓具體的形狀如:Circle繼承于它
2.定義一個位置結構圖記錄每個圖形的位置
3.設計一間享元圖形工廠用來創建圖形對象
以上就是我們的享元模式的繪圖程序的設計,接下來讓我們實現享元模式的繪圖程序吧!
/// <summary> /// Shape can be inherited by Circle, Retangle or triangle and so forth. /// Includes a color property and Draw methods. /// </summary> public abstract class Shape { public Color Color { get; set; } public abstract void Draw(Graphics graphics, Position position); }
上述示意代碼定義了一個抽象類Shape,我們的具體圖形都必須繼承于該類。
/// <summary> /// Circle implements Shape. /// </summary> public class Circle : Shape { public Circle(Color color) { Color = color; } /// <summary> /// Draws circle with the specified graphics and position. /// </summary> /// <param name="graphics">The graphics.</param> /// <param name="position">The position of circle.</param> public override void Draw(Graphics graphics, Position position) { var pen = new Pen(Color); graphics.DrawEllipse(pen, position.X - position.R, position.Y - position.R, position.R, position.R); } }
接著我們定義具體圖形類Circle,它實現Draw()方法通過Graphics調用DrawEllipse()方法來實現畫圓。
/// <summary> /// Generate the position of concrete shape. /// </summary> public struct Position { private int _x; private int _y; private int _r; public Position GetPosition(Form form) { var rd = new Random(); _x = rd.Next(0, form.Width); _y = rd.Next(0, form.Height); float r = _x < _y ? _x : _y; _r = rd.Next(0, (int)r); return this; } public Position(Graphics graphics, int x, int y, int r) { if (x > graphics.DpiX) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("x"); if (y > graphics.DpiY) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("y"); if (r > graphics.DpiY && r > graphics.DpiX) throw new ArgumentOutOfRangeException("r"); _x = x; _y = y; _r = r; } public int X { get { return _x; } } public int Y { get { return _y; } } public int R { get { return _r; } } }
接著我們定義享元工廠負責創建圖形對象,如果圖形對象不存在就創建該對象,反正直接返回該圖形對象。
/// <summary> /// The flyweight factory /// Generates the instance of shape if object not exists, /// otherwish returns the object directly. /// </summary> public class ShapeFactory { // Saves the shape object in Dictionary<Color, Shape> private static readonly Dictionary<Color, Shape> Shapes = new Dictionary<Color, Shape>(); // Gets the object in Dictionray. public Shape this[Color key] { get { Shape shape = null; // if the object exists return directly. // otherwish generates anew one. if (Shapes.ContainsKey(key)) { shape = Shapes[key]; } else { shape = new Circle(key); Shapes.Add(key, shape); } return shape; } } }
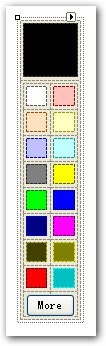
現在我們已經完成了享元圖形類,由于圖形的外部狀態包括位置和顏色,前面我們通過隨機函數生成隨機位置,我們要設計一個拾色板來提供用戶選擇自定義顏色。
由于時間的關系我們已經把拾色板的界面設置,接下來讓我們實現拾色板的具體功能。
首先我們新建一個用戶自定義控件命名為ColorPanel,接著我們要處理用戶點擊選擇顏色的事件
// Sets the default color. private Color _color = Color.Black; public delegate void ColorChangedHandler(object sender, ColorChangedEventArgs e); public event ColorChangedHandler ColorChanged; /// <summary> /// Raises the <see cref="E:ColorChanged"/> event. /// </summary> /// <param name="e">The color changed event arguments.</param> protected virtual void OnColorChanged(ColorChangedEventArgs e) { if (null != ColorChanged) ColorChanged(this, e); }
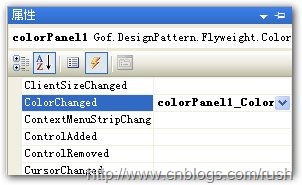
上述示意代碼定義了一個委托ColorChangedHandler,當顏色值發現改變時相應具體處理方法和一個事件ColorChangedHandler,其實事件是對委托的封裝,猶如字段和屬性的關系,具體委托和事件的介紹請參看這里和這里。
圖6自定義事件
我們先介紹一下EventArgs這個的類型。其實這個類并沒有太多的功能,它主要是作為一個基類讓其他類去實現具體的功能和定義,當我們自定義事件參數時都必須繼承于該類。
現在回到我們自定義事件參數ColorChangedEventArgs,其中包含初始化顏色值的方法和獲取顏色值的屬性。
/// <summary> /// The color changed event arguments. /// </summary> public class ColorChangedEventArgs : EventArgs { private readonly Color _color; /// <summary> /// Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ColorChangedEventArgs"/> class. /// </summary> /// <param name="color">The color.</param> public ColorChangedEventArgs(Color color) { _color = color; } /// <summary> /// Gets the color. /// </summary> public Color Color { get { return _color; } } }
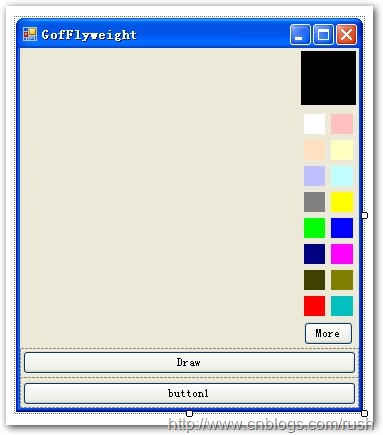
現在我們終于完成了拾色板的基本功能了,接著只需把拾色板控件添加到我們的應用程序中就OK了。
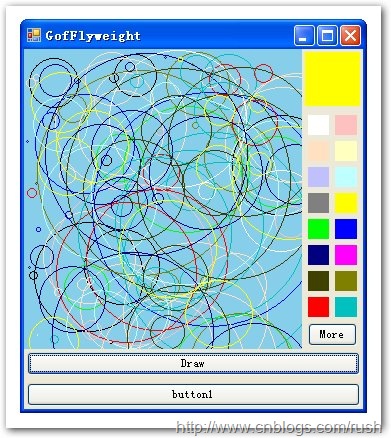
圖6享元模式繪圖程序界面
由于時間的關系我們已經把程序的界面設計好了,接下來讓我們實現一系列的事件處理方法。
/// <summary> /// Handles the Click event of the btnDrawCircle control. /// </summary> /// <param name="sender">The source of the event.</param> /// <param name="e">The <see cref="System.EventArgs"/> /// instance containing the event data.</param> private void btnDrawCircle_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Graphics graphics = Graphics.FromImage(_drawArea); // Gets shape object with specified color in flyweight object. Shape shape = _factory[colorPanel1.Color]; shape.Draw(graphics, _position.GetPosition(this)); this.Invalidate(); } /// <summary> /// Handles the Click event of the btnClear control. /// </summary> /// <param name="sender">The source of the event.</param> /// <param name="e">The <see cref="System.EventArgs"/> /// instance containing the event data.</param> private void btnClear_Click(object sender, EventArgs e) { Graphics graphics = Graphics.FromImage(_drawArea); graphics.Clear(Color.SkyBlue); graphics.Dispose(); this.Invalidate(); }
上面我們定義了處理繪圖點擊方法和清除圖形的方法,當用戶選擇顏色值時,我們的程序到享元工廠中獲取該對象實例,這個對象可能是新建的,也可能是已經存在的。
圖7繪圖程序效果
1.1.3 總結
本文通過給出享元模式的典型應用例子,來介紹了享元模式的具體應用,但享元模式在一般的開發中并不常用,而是常常應用于系統底層的開發,以便解決系統的性能問題。
適用性
Flyweight模式的有效性很大程度上取決于如何使用它以及在何處使用它。當以下情況都成立時使用Flyweight模式。
1) 一個應用程序使用了大量的對象。
2) 完全由于使用大量的對象,造成很大的存儲開銷。
3) 對象的大多數狀態都可變為外部狀態。
4) 如果刪除對象的外部狀態,那么可以用相對較少的共享對象取代很多組對象。
5) 應用程序不依賴對象標識。
優缺點
1)享元模式使得系統更加復雜。為了使對象可以共享,需要將一些狀態外部化,這使得程序的邏輯復雜化。
2)享元模式將享元對象的狀態外部化,而讀取外部狀態使得運行時間稍微變長。
|
|
關于作者:[作者]:
JK_Rush從事.NET開發和熱衷于開源高性能系統設計,通過博文交流和分享經驗,歡迎轉載,請保留原文地址,謝謝。 |

 1.1.1 摘要 在我們面向對象設計過程中,我們常常會面臨著對象實例過多的問題,如果對象實例過多這將是我們系統性能提高的一個瓶頸。假設我們要設計一個星空場景,現在我們需要實例星星對象,...
1.1.1 摘要 在我們面向對象設計過程中,我們常常會面臨著對象實例過多的問題,如果對象實例過多這將是我們系統性能提高的一個瓶頸。假設我們要設計一個星空場景,現在我們需要實例星星對象,...

 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號