實(shí)驗(yàn)一
2-28 實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)簡(jiǎn)單的菜單程序,運(yùn)行時(shí)顯示"Menu:A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select one:"提示用戶(hù)輸入。A表示增加,D表示刪除,S表示排序,Q表示退出。出入為A,D,S時(shí)分別提示"數(shù)據(jù)已增加、刪除、排序。",輸入Q時(shí)程序結(jié)束。
(1)要求使用if…else 語(yǔ)句進(jìn)行判斷,用break,continue控制程序流程。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { char c; cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select One:"<<endl; cin>>c; while(c!='Q') { if(c=='A') { cout<<"Data has Added"<<endl; cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select One:"<<endl; } else if (c=='D') { cout<<"Data has Deleted"<<endl; cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select One:"<<endl; } else if(c=='S') { cout<<"Data has Sorted"<<endl; cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select One:"<<endl; } else { cout<<"no such choise,please select again."<<endl; cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select One:"<<endl; } cin>>c; } return 0; }
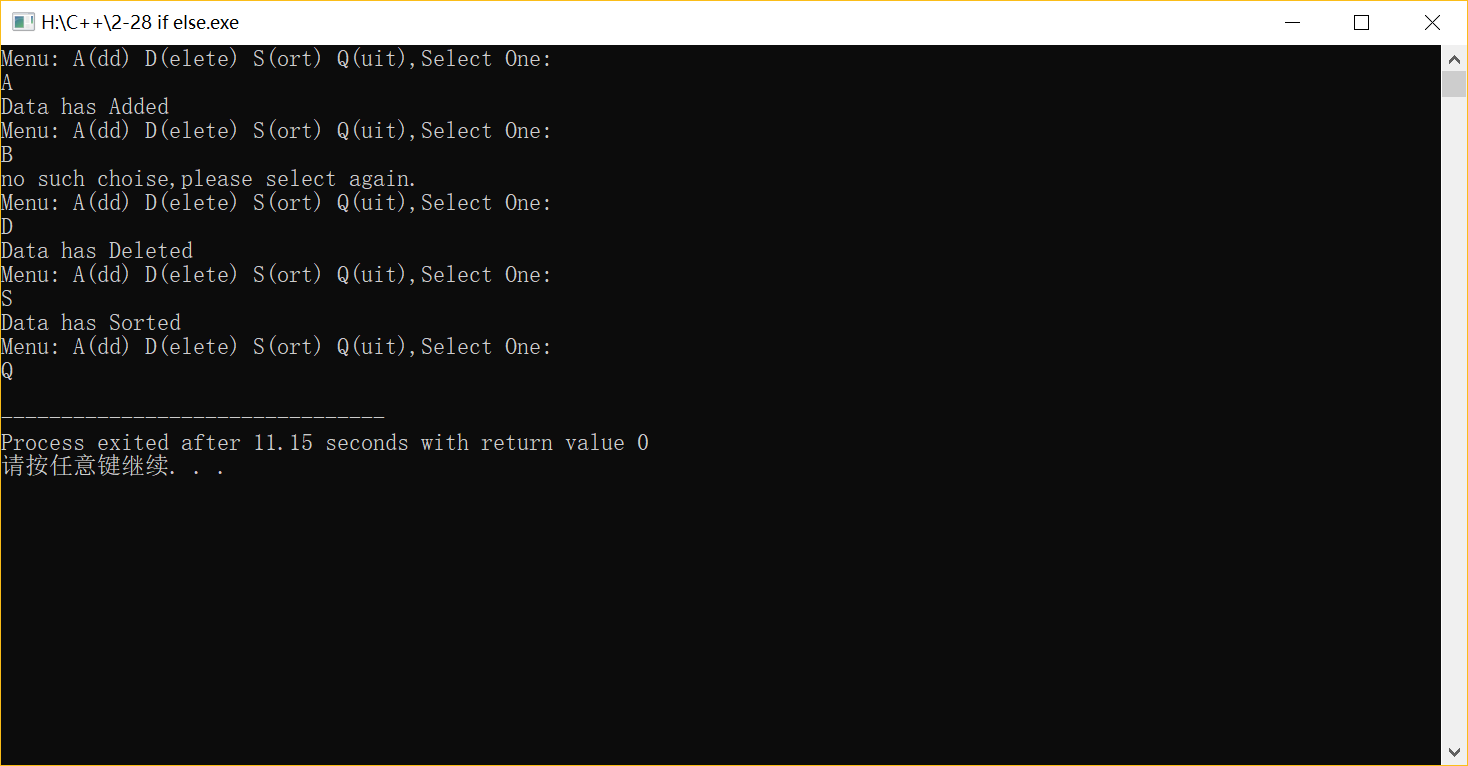
(2)要求使用switch語(yǔ)句。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main(){ char c; cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select One:"<<endl; cin>>c; while(c!='Q') { switch(c) { case 'A': {cout<<"Data has Added."<<endl;break;} case 'D': {cout<<"Data has Deleted."<<endl;break;} case 'S': {cout<<"Data has Sort."<<endl;break;} default : {cout<<"no choice, please select again."<<endl;break;} } cout<<"Menu: A(dd) D(elete) S(ort) Q(uit),Select One:"<<endl; cin>>c; } return 0; }
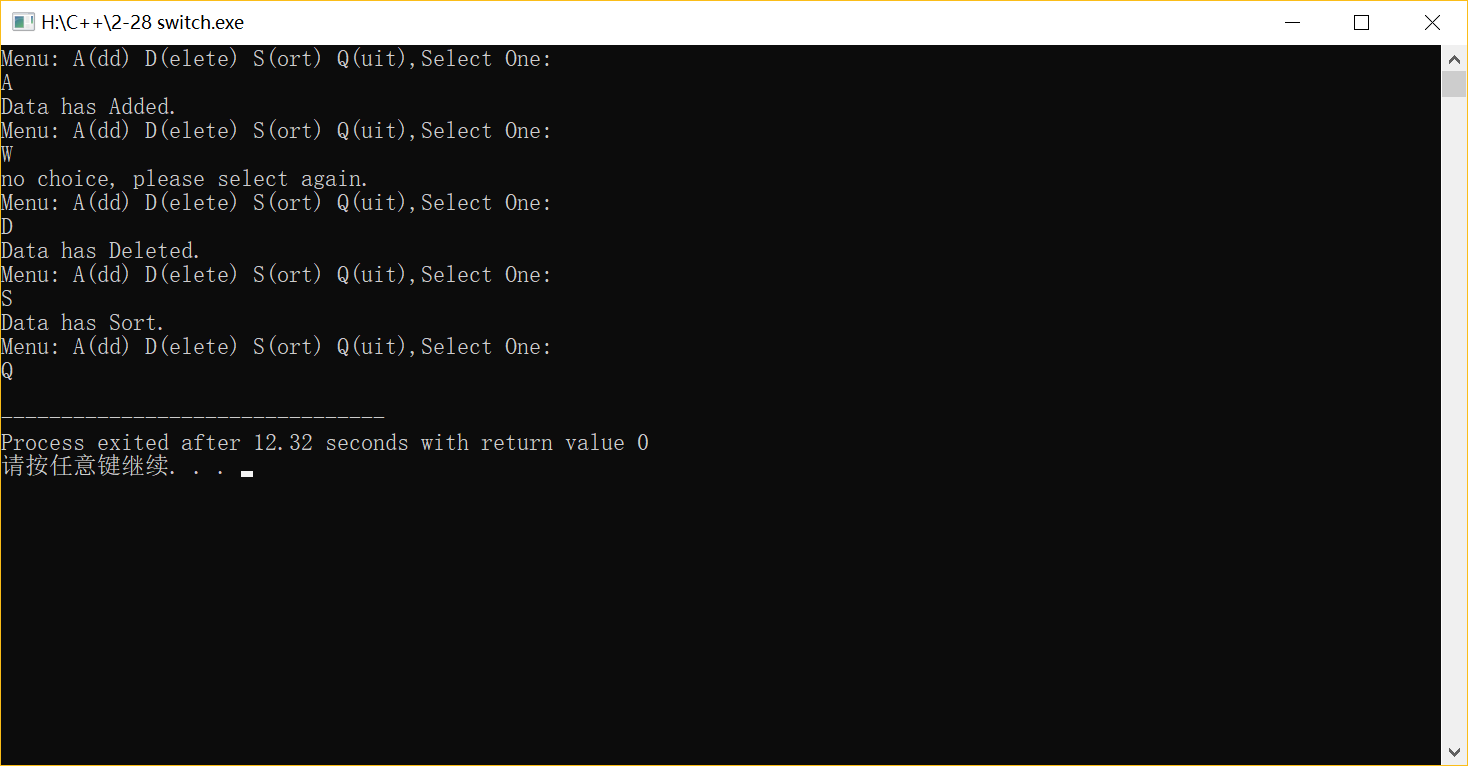
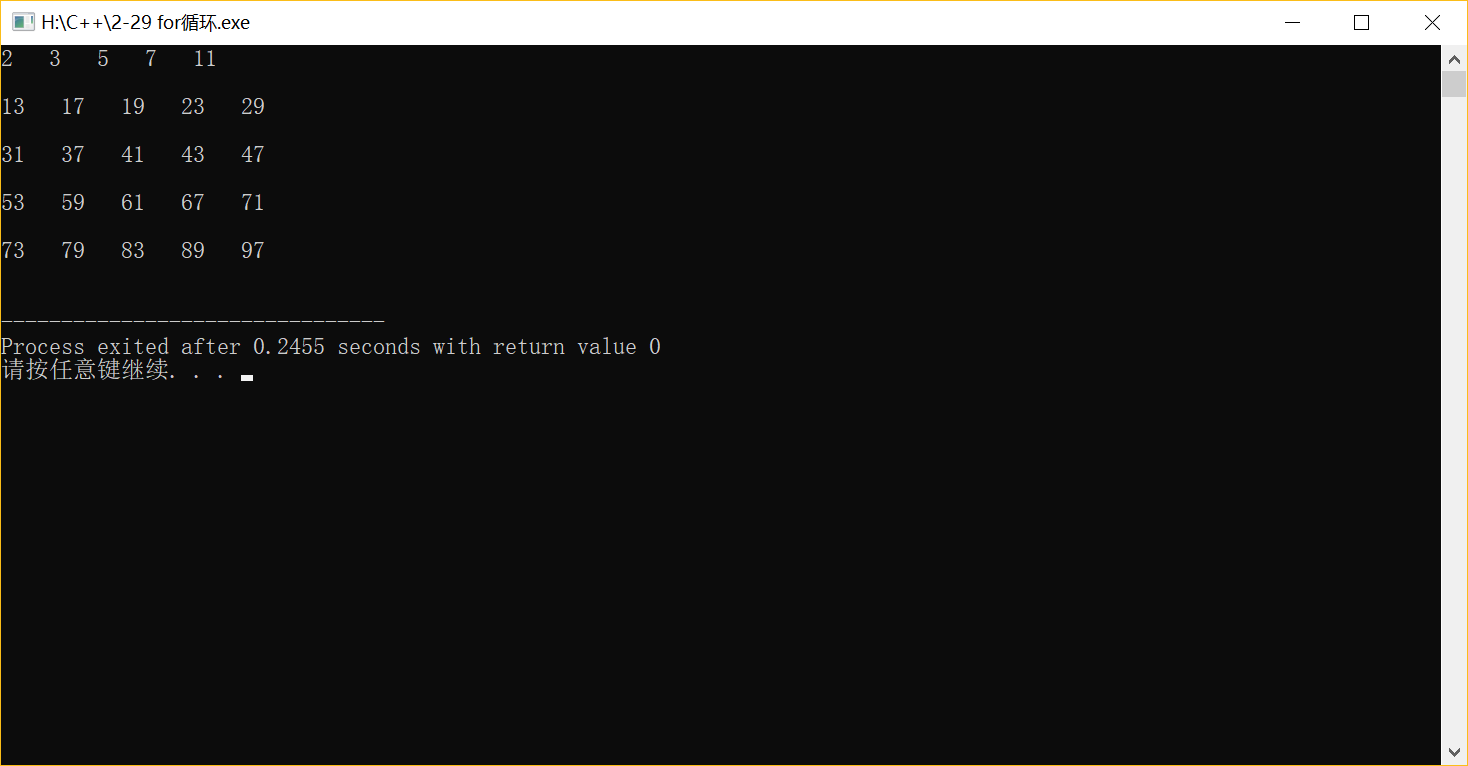
2-29 用窮舉法找出1~100間的質(zhì)數(shù)并顯示出來(lái)。分別使用 while,do-while,for循環(huán)語(yǔ)句實(shí)現(xiàn)。
(1)while
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std; int main( ) { int j,i=2,flag,t=0; while(i<=100) {flag=1;j=2; while(j<=sqrt(i)) { if(i%j==0) {flag=0; break; } j++; } if (flag==1) {t++; cout<<i<<" "; if(t%5==0) cout<<"\n"<<endl; } i++; } return 0; }
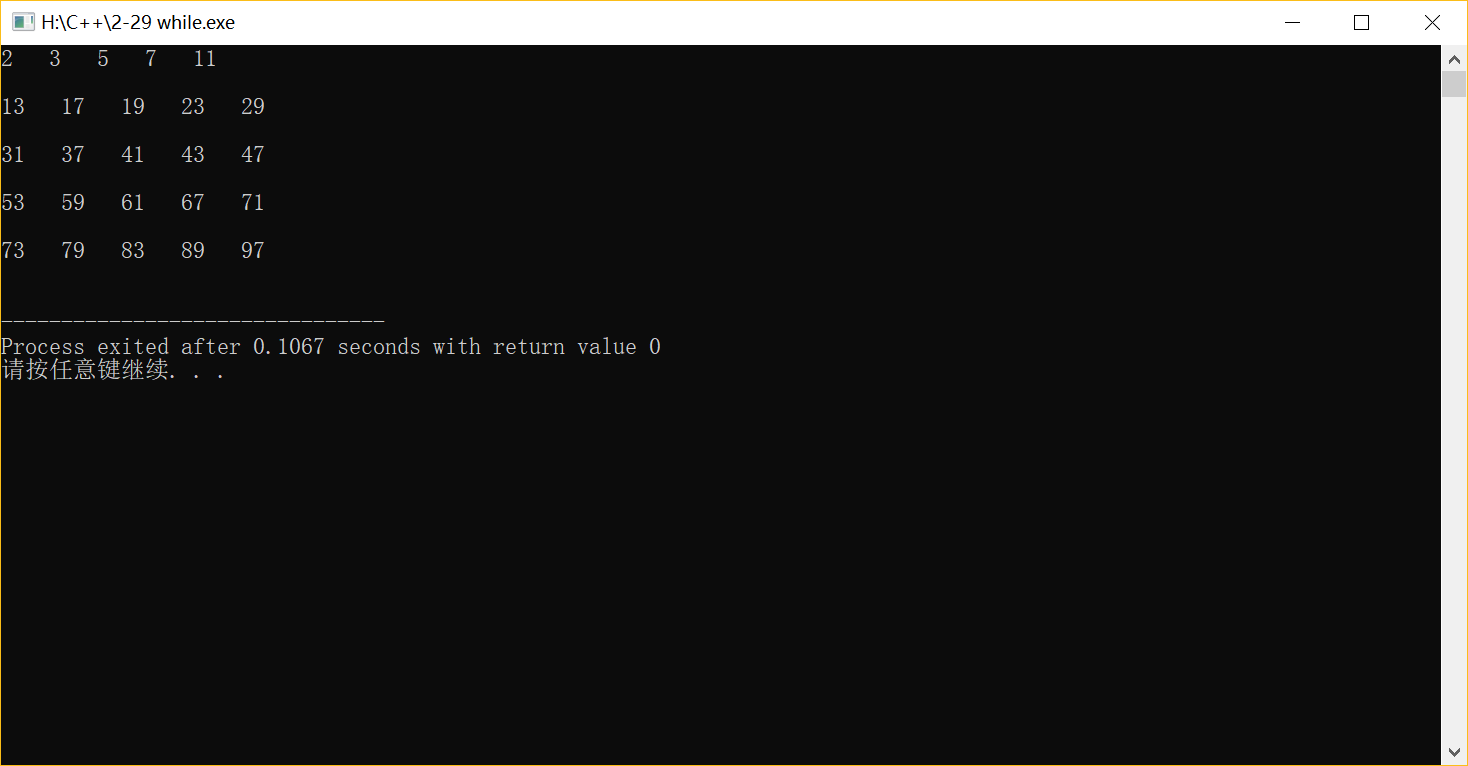
(2)do-while
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std; int main( ) { int j,i=2,flag,t=0; do {flag=1;j=2; while(j<=sqrt(i)) { if(i%j==0) {flag=0; break; } j++; } if (flag==1) {t++; cout<<i<<" "; if(t%5==0) cout<<"\n"<<endl; } i++; } while(i<100); return 0; }
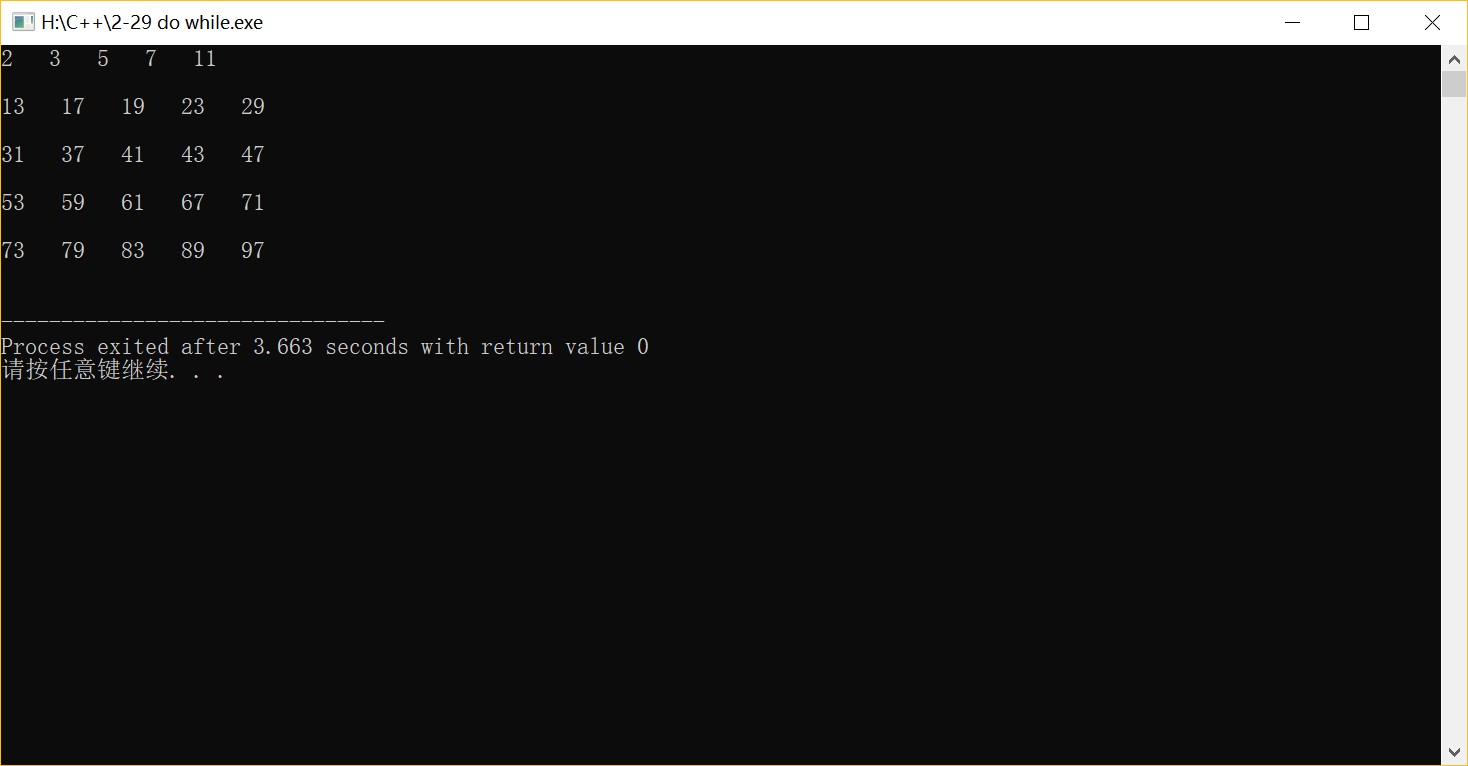
(3)for循環(huán)
#include <iostream> #include <cmath> using namespace std; int main( ) { int j,i=2,flag,t=0; while(i<=100) {flag=1; for(j=2;j<=sqrt(i);j++) { if(i%j==0) {flag=0; break; } } if (flag==1) {t++; cout<<i<<" "; if(t%5==0) cout<<"\n"<<endl; } i++; } return 0; }
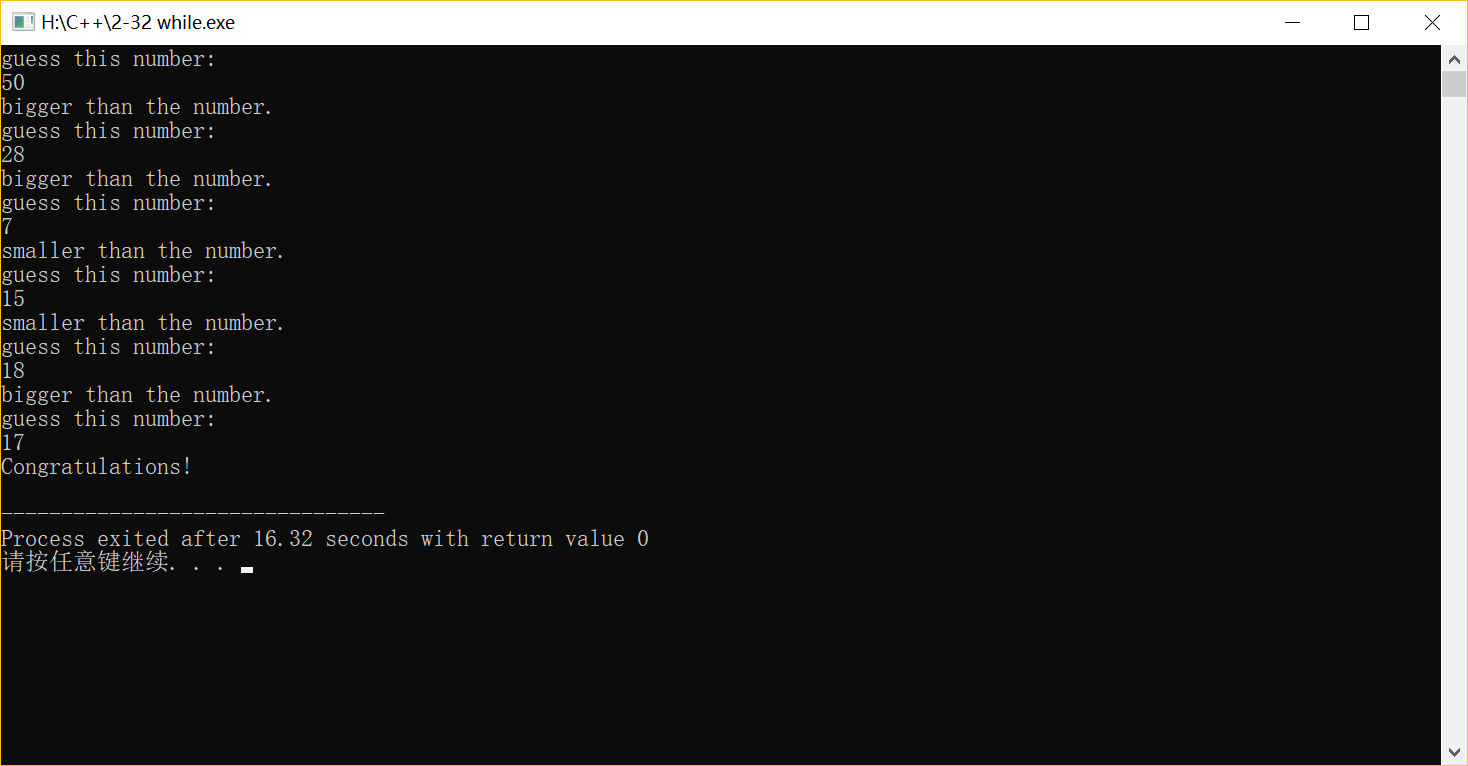
2-32 在程序中定義一個(gè)整形變量,賦予1~100的值。要求用戶(hù)猜這個(gè)數(shù),比較兩個(gè)數(shù)的大小,把結(jié)果顯示給用戶(hù),直到猜對(duì)為止。分別使用while,do-while語(yǔ)句實(shí)現(xiàn)循環(huán)。
(1)while
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main( ) { int a=17; int n; while(1) {cout<<"guess this number:"<<endl; cin>>n; if(a==n) {cout<<"Congratulations!"<<endl; break; } else if(a<n) {cout<<"bigger than the number."<<endl;} else if(a>n) {cout<<"smaller than the number."<<endl;} } return 0; }
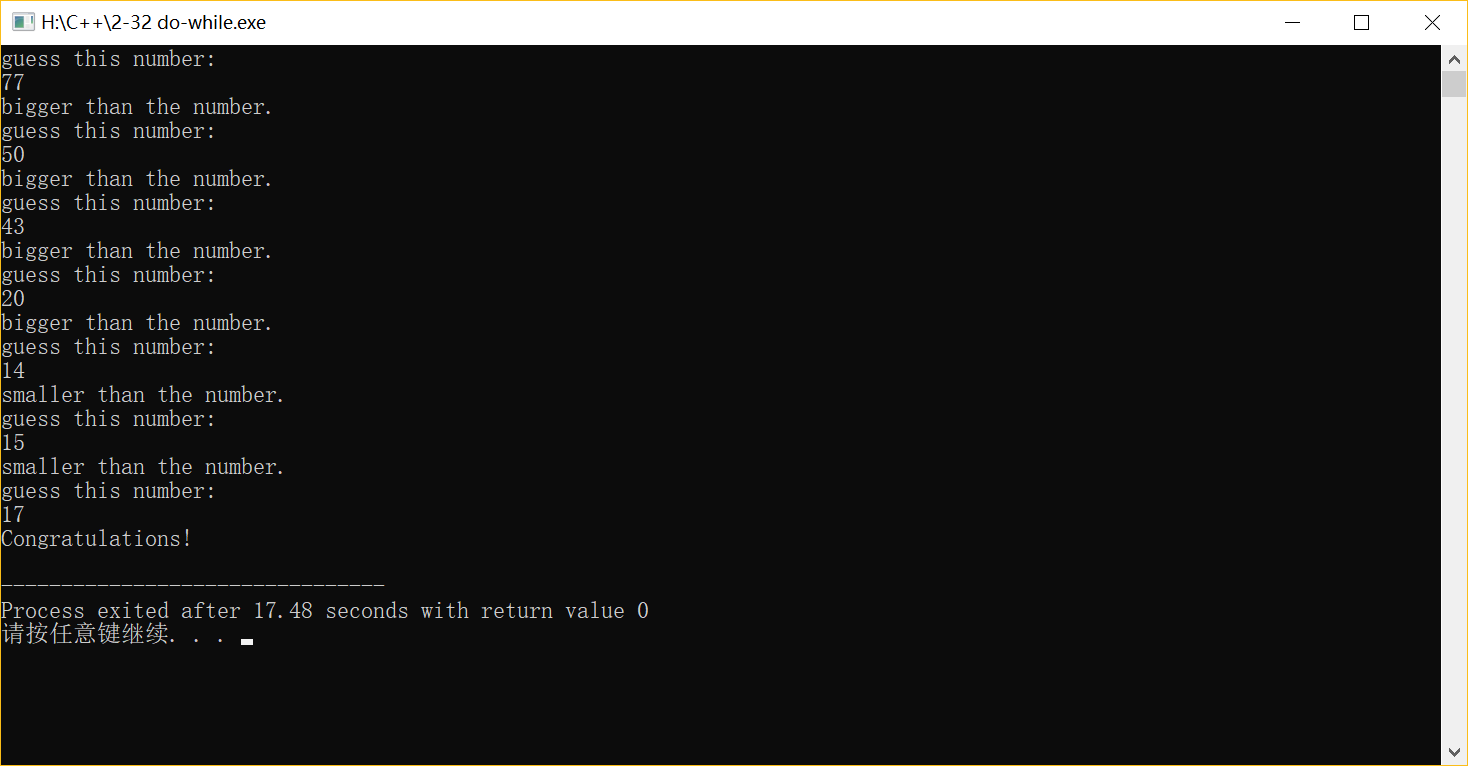
(2)do-while
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main( ) { int a=17; int n; do {cout<<"guess this number:"<<endl; cin>>n; if(a==n) {cout<<"Congratulations!"<<endl; break; } else if(a<n) {cout<<"bigger than the number."<<endl;} else if(a>n) {cout<<"smaller than the number."<<endl;} } while(1); return 0; }
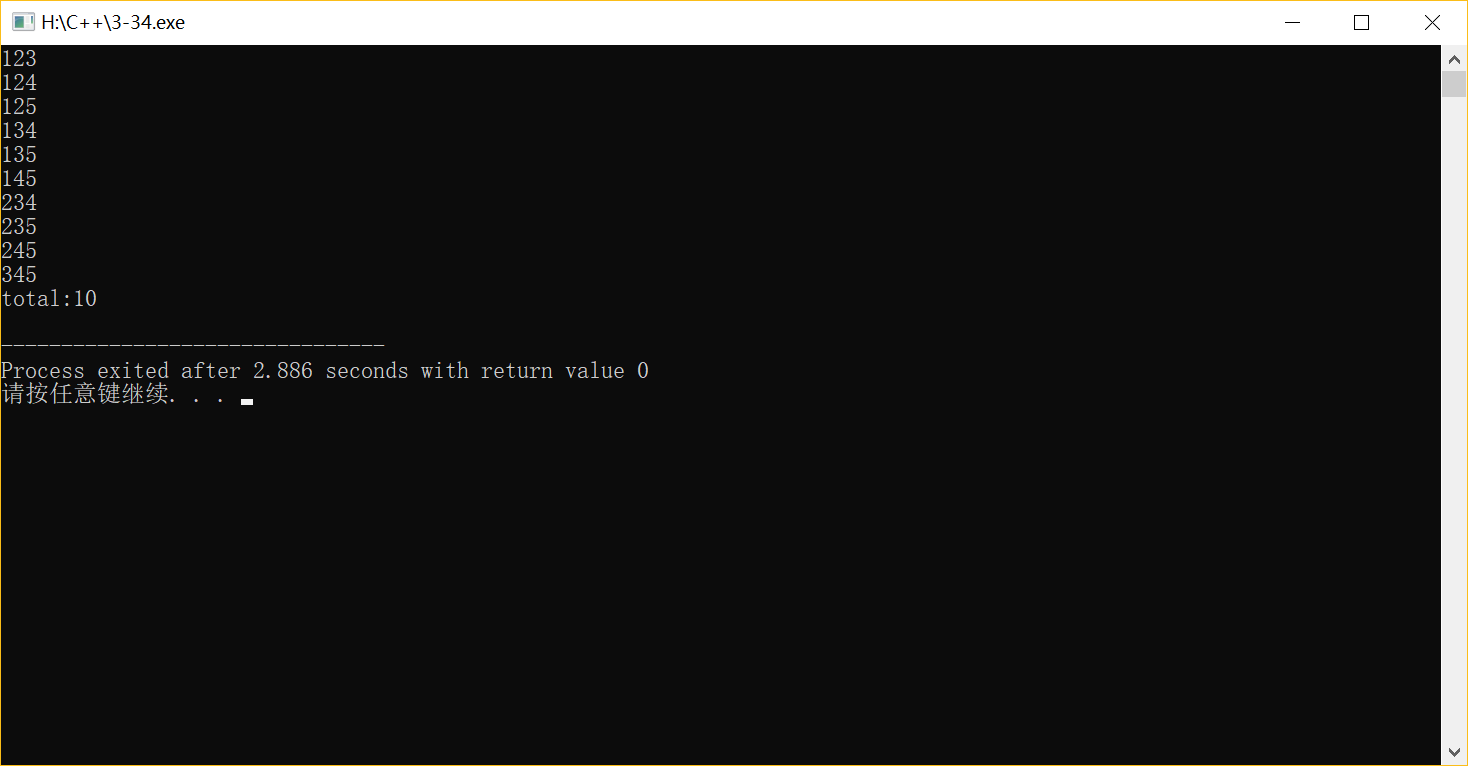
2-34 口袋中有紅、黃、藍(lán)、白、黑種顏色的球若干個(gè)。每次從口袋中取出3個(gè)不同顏色的球,請(qǐng)問(wèn)有多少種取法?
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() {int i,j,k,a=0;//1:紅,2:黃,3:藍(lán),4:白,5:黑 for(i=1;i<=5;i++) {for(j=i+1;j<=5;j++) {for(k=j+1;k<=5;k++) {cout<<i<<j<<k<<endl; a++; } } } cout<<"total:"<<a<<endl; return 0; }
實(shí)驗(yàn)總結(jié)與體會(huì):
2-28 第一個(gè)程序我用的很傻,大多都是復(fù)制粘貼,我嘗試改了之后,發(fā)現(xiàn)運(yùn)行有問(wèn)題,最后放棄了。
2-29 質(zhì)數(shù)一開(kāi)始用的j<=i-1;后來(lái)發(fā)現(xiàn)有重復(fù),所以加了個(gè)頭文件從#include <cmath> 用sqrt函數(shù)做。
3-32 中的while(1)進(jìn)入死循環(huán)我一開(kāi)始沒(méi)想到,然后參考了一下百度,通過(guò) if 函數(shù)退出死循環(huán)。
3-34 這題的枚舉法是真的不會(huì),然后我去問(wèn)了學(xué)長(zhǎng),還是沒(méi)弄明白,我就用了最簡(jiǎn)單的數(shù)字代表球的顏色,列出取法。
我覺(jué)得我需要花更多的時(shí)間去學(xué)習(xí)C++,有一些細(xì)節(jié)需要去鉆研。
posted on 2019-03-17 16:22 棲枝Fairy 閱讀(224) 評(píng)論(2) 收藏 舉報(bào)



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)