P2831 [NOIP 2016 提高組] 憤怒的小鳥 題解
傳送門
題目大意
每關給你最多18只小豬(后文皆為18只),問你最少用幾條過原點拋物線全部干掉。
注意這里 \(m\) 其實沒用,因為你要是會算最優(yōu)解了為啥還需要部分分啊?
思路
\(n\leq18\) ,不是暴搜就是狀壓。直接放棄暴搜。
狀壓dp做法:
1. 處理拋物線
首先記錄這18只小豬所有可能產(chǎn)生的拋物線,如圖所示為例1的第一組樣例:
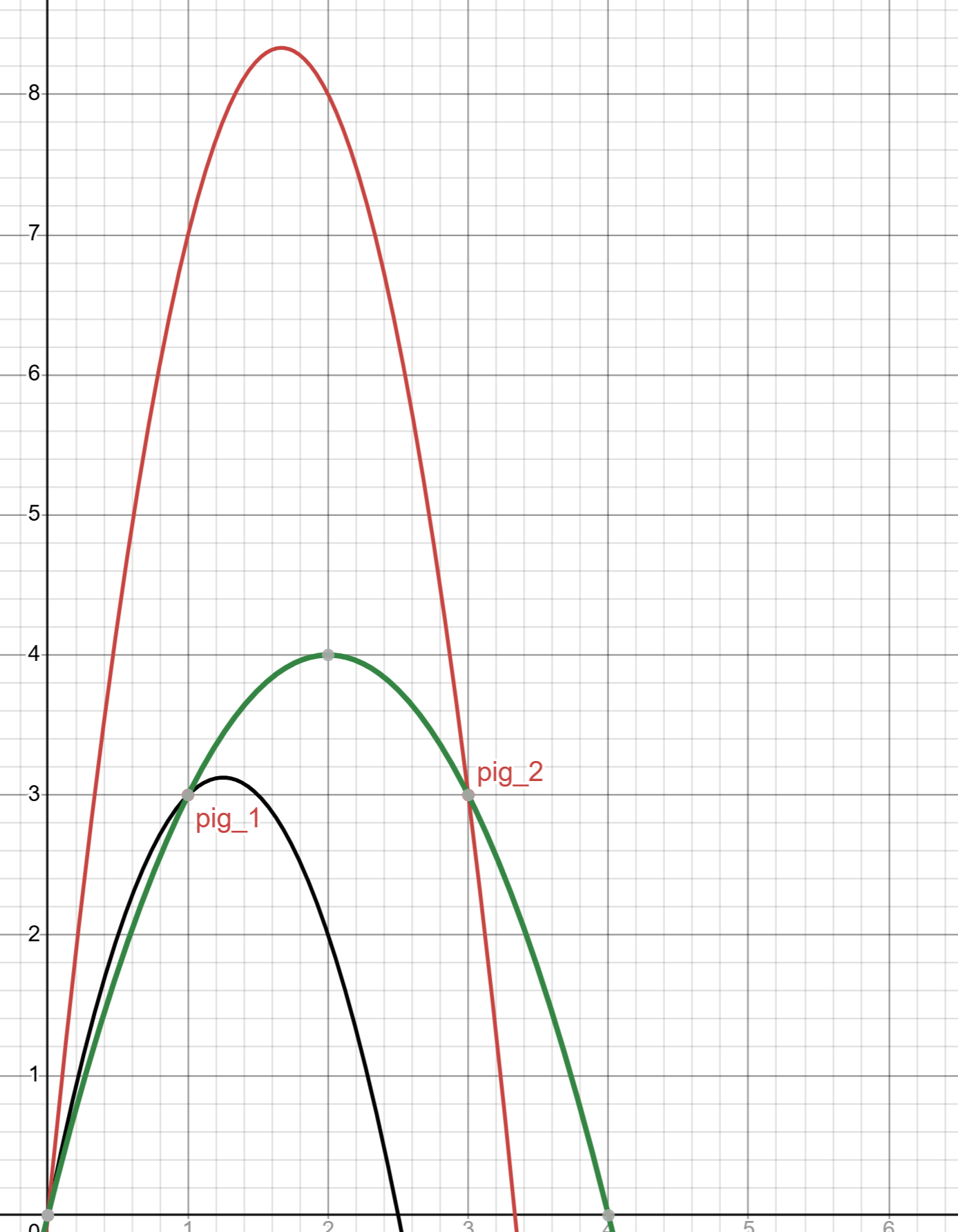
注意這里“所有”可能產(chǎn)生的拋物線,包括只經(jīng)過一只小豬(* ̄(oo) ̄) 的拋物線。
這個時候就有人會問,為了記錄拋物線,需要記錄 \(y=ax^2+bx\) 中的 \(a,b\) ,那要是記錄只經(jīng)過一只小豬的拋物線,還得考慮不經(jīng)過其他小豬,豈不是要算廢。
其實解決方法很簡單,我們對于每條拋物線不記錄兩個存在誤差的浮點 \(a,b\) 而是直接用二進制下的18位整數(shù)狀壓這條拋物線經(jīng)過的小豬,可以證明對每只小豬一定存在只過它一點的拋物線。
記錄只有一個點的拋物線很重要,我第一遍沒有搞,結(jié)果過了樣例,導致因為這個問題調(diào)了好久,有時還納悶這個dp有沒有真的考慮所有情況。
然后就是考慮過多個小豬的拋物線。先枚舉第一只小豬,然后枚舉下標在第一只小豬之后的小豬。計算出過這兩只豬的拋物線,然后看其他小豬是否在此拋物線上,記錄在對應的拋物線數(shù)組里即可。
代碼實現(xiàn):
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
const int N = 18, ZT = 1 << N;
const double eps = 1e-6; // 處理浮點數(shù)相等的精度問題, 凡差小于epsilon即算相等
int n, m;
double x[N], y[N];
int para[2000], cnt; // records parabolas
// 計算過兩點的拋物線
pdd calc(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
pdd res;
double &a = res.first, &b = res.second;
a = (x1 * y2 - x2 * y1) / (x1 * x2 * (x2 - x1));
b = (x2 * x2 * y1 - x1 * x1 * y2) / (x1 * x2 * (x2 - x1));
// printf("The parabola that goes through (%lf, %lf) and (%lf, %lf) is:\n\ty=%lfx^2+%lfx\n", x1, y1, x2, y2, a, b);
return res;
}
void solve()
{
// pre-calculate the parabolas
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
para[cnt++] = (1 << i); // 只打小豬i的拋物線
int vst = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (vst & (1 << j)) continue;
// if (x[i] == x[j]) continue; // 防止calc函數(shù)出現(xiàn)除以0,但是好像不加也沒影響照樣AC
pdd tmp = calc(x[i], y[i], x[j], y[j]);
if (tmp.first >= 0) continue; // 題面要求拋物線開口向下,這不是數(shù)學,是物理!
para[cnt] = (1 << i);
for (int k = j; k < n; ++k) { // 這里k從j開始枚舉,或者直接para[cnt]|=(1<<j),然后這里j+1開始枚舉也沒問題
// printf("trying the parabola on (%lf, %lf): ", x[k], y[k]);
double res = tmp.first * x[k] * x[k] + tmp.second * x[k];
// printf("result is %lf\n", res);
if (abs(res - y[k]) <= eps) {
// printf("Success! It IS on the parabola!\n");
vst |= (1 << k); // 防止再次枚舉到過小豬 i,j,k的拋物線
para[cnt] |= (1 << k);
}
}
++cnt;
}
}
// for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) {
// printf("parabola %d goes through these pigs: ", i);
// for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
// if (para[i] & (1 << j)) {
// printf("%d ", j);
// }
// }
// printf("\n");
// }
}
注意拋物線數(shù)組開大點,不要以為拋物線最多只有18條,我們記錄的是每一條可能的拋物線。
2. dp
顯然對于每個狀態(tài) \(i(0\leq i\leq 2^{n+1}-1)\) ,枚舉每條拋物線 \(para_j\) 帶來的影響,有:
至此,已成藝術完結(jié)撒花。
代碼(含調(diào)試+原版注釋)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
const int N = 18, ZT = 1 << N;
const double eps = 1e-6;
int n, m;
double x[N], y[N];
int para[2000], cnt; // records parabolas
int dp[ZT];
pdd calc(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
pdd res;
double &a = res.first, &b = res.second;
a = (x1 * y2 - x2 * y1) / (x1 * x2 * (x2 - x1));
b = (x2 * x2 * y1 - x1 * x1 * y2) / (x1 * x2 * (x2 - x1));
// printf("The parabola that goes through (%lf, %lf) and (%lf, %lf) is:\n\ty=%lfx^2+%lfx\n", x1, y1, x2, y2, a, b);
return res;
}
void solve()
{
cnt = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
}
// pre-calculate the parabolas
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
para[cnt++] = (1 << i); // 只打小豬i的拋物線
int vst = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (vst & (1 << j)) continue;
// if (x[i] == x[j]) continue;
// printf("pig %d and pig %d: ", i, j);
pdd tmp = calc(x[i], y[i], x[j], y[j]);
if (tmp.first >= 0) continue;
para[cnt] = (1 << i);
for (int k = j; k < n; ++k) {
// printf("trying the parabola on (%lf, %lf): ", x[k], y[k]);
double res = tmp.first * x[k] * x[k] + tmp.second * x[k];
// printf("result is %lf\n", res);
if (abs(res - y[k]) <= eps) {
// printf("Success! It IS on the parabola!\n");
vst |= (1 << k);
para[cnt] |= (1 << k);
}
}
++cnt;
}
}
// for (int i = 0; i < cnt; ++i) {
// printf("parabola %d goes through these pigs: ", i);
// for (int j = 0; j < n; ++j) {
// if (para[i] & (1 << j)) {
// printf("%d ", j);
// }
// }
// printf("\n");
// }
const int FULL = (1 << n) - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= FULL; ++i) dp[i] = 30;
for (int i = 0; i <= FULL; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; ++j) {
dp[i | para[j]] = min(dp[i | para[j]], dp[i] + 1);
}
}
cout << dp[FULL] << '\n';
}
int main()
{
// freopen("F.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("F.out", "w", stdout);
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; ++i) {
// printf("########### TEST CASE %d ###########\n", i);
solve();
// printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
代碼(無//)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef pair<double, double> pdd;
const int N = 18, ZT = 1 << N;
const double eps = 1e-6;
int n, m;
double x[N], y[N];
int para[2000], cnt;
int dp[ZT];
pdd calc(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)
{
pdd res;
double &a = res.first, &b = res.second;
a = (x1 * y2 - x2 * y1) / (x1 * x2 * (x2 - x1));
b = (x2 * x2 * y1 - x1 * x1 * y2) / (x1 * x2 * (x2 - x1));
return res;
}
void solve()
{
cnt = 0;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
cin >> x[i] >> y[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
para[cnt++] = (1 << i);
int vst = 0;
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
if (vst & (1 << j)) continue;
pdd tmp = calc(x[i], y[i], x[j], y[j]);
if (tmp.first >= 0) continue;
para[cnt] = (1 << i);
for (int k = j; k < n; ++k) {
double res = tmp.first * x[k] * x[k] + tmp.second * x[k];
if (abs(res - y[k]) <= eps) {
vst |= (1 << k);
para[cnt] |= (1 << k);
}
}
++cnt;
}
}
const int FULL = (1 << n) - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= FULL; ++i) dp[i] = 30;
for (int i = 0; i <= FULL; ++i) {
for (int j = 0; j < cnt; ++j) {
dp[i | para[j]] = min(dp[i | para[j]], dp[i] + 1);
}
}
cout << dp[FULL] << '\n';
}
int main()
{
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int T;
cin >> T;
for (int i = 1; i <= T; ++i) solve();
return 0;
}
別跑,還有壓行版
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;typedef pair<double,double>pdd;const int N=18,ZT=1<<N;const double eps=1e-6;int n,m;double x[N],y[N];int para[2000],cnt;int dp[ZT];pdd calc(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){pdd res;double&a=res.first,&b=res.second;a=(x1*y2-x2*y1)/(x1*x2*(x2-x1));b=(x2*x2*y1-x1*x1*y2)/(x1*x2*(x2-x1));return res;}void solve(){cnt=0;cin>>n>>m;for(int i=0;i<n;++i){cin>>x[i]>>y[i];}for(int i=0;i<n;++i){para[cnt++]=(1<<i);int vst=0;for(int j=i+1;j<n;++j){if(vst&(1<<j))continue;pdd tmp=calc(x[i],y[i],x[j],y[j]);if(tmp.first>=0)continue;para[cnt]=(1<<i);for(int k=j;k<n;++k){double res=tmp.first*x[k]*x[k]+tmp.second*x[k];if(abs(res-y[k])<=eps){vst|=(1<<k);para[cnt]|=(1<<k);}}++cnt;}}const int FULL=(1<<n)-1;for(int i=1;i<=FULL;++i)dp[i]=30;for(int i=0;i<=FULL;++i){for(int j=0;j<cnt;++j){dp[i|para[j]]=min(dp[i|para[j]],dp[i]+1);}}cout<<dp[FULL]<<'\n';}int main(){ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(nullptr);int T;cin>>T;for(int i=1;i<=T;++i)solve();return 0;}
總結(jié)
挺容易寫的一道藍題,沒調(diào)太久。
算是自己想不出,一聽到枚舉拋物線就懂的題。


 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號