改進版CodeTimer及XCode性能測試
在測試XCode性能的時候,發(fā)現(xiàn)每次執(zhí)行測試程序得到的執(zhí)行時間差距實在太大,于是采用了老趙的CodeTimer來計算線程時間,后來因為測試程序稍微有點復雜,在使用匿名委托時會有參數(shù)的“打包”過程,于是改進了CodeTimer,測試功能代碼通過實現(xiàn)一個繼承自CodeTimer的類來實現(xiàn),避免每次迭代時參數(shù)“打包”的過程。
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Text; using System.Runtime.InteropServices; using System.Diagnostics; using System.Threading; using NewLife.Reflection; using NewLife.Exceptions; namespace NewLife.Log { /// <summary> /// 代碼性能計時器 /// </summary> /// <remarks>參考了老趙(http://www.rzrgm.cn/jeffreyzhao/archive/2009/03/10/codetimer.html) 和eaglet(http://www.rzrgm.cn/eaglet/archive/2009/03/10/1407791.html)兩位的作品</remarks> /// <remarks>為了保證性能比較的公平性,采用了多種指標,并使用計時器重寫等手段來避免各種不必要的損耗</remarks> public class CodeTimer { #region 靜態(tài)快速計時 /// <summary> /// 計時 /// </summary> /// <param name="times"></param> /// <param name="action"></param> /// <returns></returns> public static CodeTimer Time(Int32 times, Action<Int32> action) { CodeTimer timer = new CodeTimer(); timer.Times = times; timer.Action = action; timer.TimeOne(); timer.Time(); return timer; } /// <summary> /// 計時,并用控制臺輸出行 /// </summary> /// <param name="title"></param> /// <param name="times"></param> /// <param name="action"></param> public static void TimeLine(String title, Int32 times, Action<Int32> action) { Console.Write("{0,16}:", title); CodeTimer timer = new CodeTimer(); timer.Times = times; timer.Action = action; timer.ShowProgress = true; ConsoleColor currentForeColor = Console.ForegroundColor; Console.ForegroundColor = ConsoleColor.Yellow; timer.TimeOne(); timer.Time(); Console.WriteLine(timer.ToString()); Console.ForegroundColor = currentForeColor; } #endregion #region PInvoke [DllImport("kernel32.dll")] [return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)] static extern bool QueryThreadCycleTime(IntPtr threadHandle, ref ulong cycleTime); [DllImport("kernel32.dll")] static extern IntPtr GetCurrentThread(); [DllImport("kernel32.dll", SetLastError = true)] static extern bool GetThreadTimes(IntPtr hThread, out long lpCreationTime, out long lpExitTime, out long lpKernelTime, out long lpUserTime); static Boolean supportCycle = true; private static ulong GetCycleCount() { //if (Environment.Version.Major < 6) return 0; if (!supportCycle) return 0; try { ulong cycleCount = 0; QueryThreadCycleTime(GetCurrentThread(), ref cycleCount); return cycleCount; } catch { supportCycle = false; return 0; } } private static long GetCurrentThreadTimes() { long l; long kernelTime, userTimer; GetThreadTimes(GetCurrentThread(), out l, out l, out kernelTime, out userTimer); return kernelTime + userTimer; } #endregion #region 私有字段 ulong cpuCycles = 0; long threadTime = 0; int[] gen; #endregion #region 屬性 private Int32 _Times; /// <summary>次數(shù)</summary> public Int32 Times { get { return _Times; } set { _Times = value; } } private Action<Int32> _Action; /// <summary>迭代方法,如不指定,則使用Time(int index)</summary> public Action<Int32> Action { get { return _Action; } set { _Action = value; } } private Boolean _ShowProgress; /// <summary>是否顯示控制臺進度</summary> public Boolean ShowProgress { get { return _ShowProgress; } set { _ShowProgress = value; } } private Int32 _Index; /// <summary>進度</summary> public Int32 Index { get { return _Index; } set { _Index = value; } } private ulong _CpuCycles; /// <summary>CPU周期</summary> public ulong CpuCycles { get { return _CpuCycles; } set { _CpuCycles = value; } } private long _ThreadTime; /// <summary>線程時間,單位是100ns,除以10000轉(zhuǎn)為ms</summary> public long ThreadTime { get { return _ThreadTime; } set { _ThreadTime = value; } } private Int32[] _Gen = new Int32[] { 0, 0, 0 }; /// <summary>GC代數(shù)</summary> public Int32[] Gen { get { return _Gen; } set { _Gen = value; } } private TimeSpan _Elapsed; /// <summary>執(zhí)行時間</summary> public TimeSpan Elapsed { get { return _Elapsed; } set { _Elapsed = value; } } #endregion #region 方法 /// <summary> /// 計時核心方法,處理進程和線程優(yōu)先級 /// </summary> public virtual void Time() { if (Times <= 0) throw new XException("非法迭代次數(shù)!"); // 設定進程、線程優(yōu)先級,并在完成時還原 ProcessPriorityClass pp = Process.GetCurrentProcess().PriorityClass; ThreadPriority tp = Thread.CurrentThread.Priority; try { Process.GetCurrentProcess().PriorityClass = ProcessPriorityClass.High; Thread.CurrentThread.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest; StartProgress(); TimeTrue(); } finally { StopProgress(); Thread.CurrentThread.Priority = tp; Process.GetCurrentProcess().PriorityClass = pp; } } /// <summary> /// 真正的計時 /// </summary> protected virtual void TimeTrue() { if (Times <= 0) throw new XException("非法迭代次數(shù)!"); // 統(tǒng)計GC代數(shù) GC.Collect(GC.MaxGeneration, GCCollectionMode.Forced); gen = new Int32[GC.MaxGeneration + 1]; for (Int32 i = 0; i <= GC.MaxGeneration; i++) { gen[i] = GC.CollectionCount(i); } Stopwatch watch = new Stopwatch(); watch.Start(); cpuCycles = GetCycleCount(); threadTime = GetCurrentThreadTimes(); // 如果未指定迭代方法,則使用內(nèi)部的Time Action<Int32> action = Action; if (action == null) { action = Time; // 初始化 Init(); } for (Int32 i = 0; i < Times; i++) { Index = i; action(i); } if (Action == null) { // 結(jié)束 Finish(); } CpuCycles = GetCycleCount() - cpuCycles; ThreadTime = GetCurrentThreadTimes() - threadTime; watch.Stop(); Elapsed = watch.Elapsed; // 統(tǒng)計GC代數(shù) List<Int32> list = new List<Int32>(); for (Int32 i = 0; i <= GC.MaxGeneration; i++) { int count = GC.CollectionCount(i) - gen[i]; list.Add(count); } Gen = list.ToArray(); } /// <summary> /// 執(zhí)行一次迭代,預熱所有方法 /// </summary> public void TimeOne() { Int32 n = Times; try { Times = 1; Time(); } finally { Times = n; } } /// <summary> /// 迭代前執(zhí)行,計算時間 /// </summary> public virtual void Init() { } /// <summary> /// 每一次迭代,計算時間 /// </summary> /// <param name="index"></param> public virtual void Time(Int32 index) { } /// <summary> /// 迭代后執(zhí)行,計算時間 /// </summary> public virtual void Finish() { } #endregion #region 進度 Thread thread; void StartProgress() { if (!ShowProgress) return; // 使用低優(yōu)先級線程顯示進度 thread = new Thread(new ParameterizedThreadStart(Progress)); thread.IsBackground = true; thread.Priority = ThreadPriority.BelowNormal; thread.Start(); } void StopProgress() { if (thread != null && thread.IsAlive) { thread.Abort(); thread.Join(3000); } } void Progress(Object state) { Int32 left = Console.CursorLeft; // 設置光標不可見 Boolean cursorVisible = Console.CursorVisible; Console.CursorVisible = false; Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch(); sw.Start(); while (true) { try { Int32 i = Index; if (i >= Times) break; if (i > 0 && sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds > 10) { Double d = (Double)i / Times; Console.Write("{0,7:n0}ms {1:p}", sw.Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds, d); Console.CursorLeft = left; } } catch (ThreadAbortException) { break; } catch { break; } Thread.Sleep(500); } sw.Stop(); Console.CursorLeft = left; Console.CursorVisible = cursorVisible; } #endregion #region 重載 /// <summary> /// 已重載。輸出依次分別是:執(zhí)行時間、CPU線程時間、時鐘周期、GC代數(shù) /// </summary> /// <returns></returns> public override string ToString() { return String.Format("{0,7:n0}ms {1,7:n0}ms {2,15:n0} {3}/{4}/{5}", Elapsed.TotalMilliseconds, ThreadTime / 10000, CpuCycles, Gen[0], Gen[1], Gen[2]); } #endregion } }
對于控制臺測試項目,另外起了一個線程負責輸出進度,不知道這樣對測試會有多大影響。
XCode性能測試
XCode每次升級都會進行性能測試,不過那是為了檢查升級是否造成了性能瓶頸,實際上性能測試就是作為XCode升級的最后一道工作。
上一次與ADO.Net進行性能對比測試時XCode的版本是v3.5,XCode各種操作的耗時大概是ADO.Net的1.2倍,vs統(tǒng)計代碼只有2000行。
目前XCode最新版本是v7.3,vs統(tǒng)計代碼有5100行,并且引用一個4100行的核心庫,一些常用的擴展功能形成4800行的通用實體類庫。
由此可見,現(xiàn)在的XCode至少在代碼上是v3.5的7倍。(當然,這個代碼量是遠不如NH的,記得它有好些文件超過了1000行代碼)
廢話少說,下面開始測試!
本地環(huán)境:win7+MSSQL2007
說明:
1,以下截圖,黃色數(shù)字分別代表執(zhí)行時間、線程時間、CPU周期、GC,白色數(shù)字表示與第一個測試項相比較的比列,兩個白色分別表示執(zhí)行時間比例和線程時間比例
2,ADO.SQL表示用sql方式執(zhí)行,ADO.Param表示用參數(shù)化執(zhí)行
3,DAL表示用XCode的數(shù)據(jù)訪問層執(zhí)行SQL,DALIdentity表示插入后查詢自增,如果開啟一級緩存,這兩項會有影響
4,Entity是普通實體類操作,WeakEntity表示弱類型操作實體,DynEntity表示動態(tài)創(chuàng)建實體類(CodeDom)執(zhí)行操作
5,所有比例的計算以ADO.SQL為基準,因為XCode也是采用這種方式
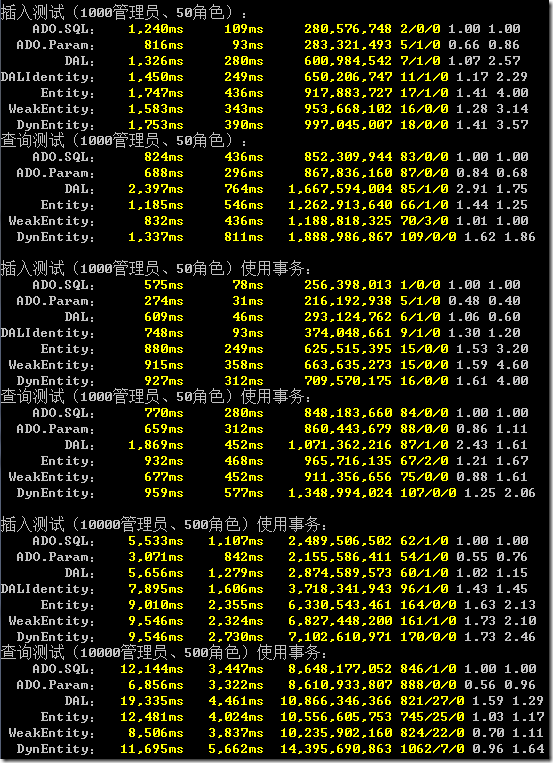
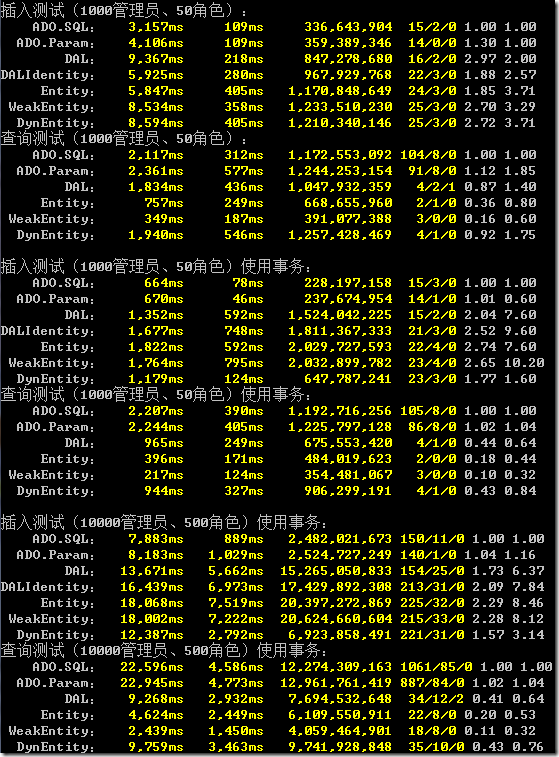
本地普通測試:
總體來看,XCode的性能大概是ADO的1.5倍。
后面的查詢中,WeakEntity和DynEntity的比例小于1,Entity也很小,主要是因為XCode的二級緩存(實體緩存)。每一次查詢測試,實際上包含了查一個管理員和一個角色,而角色表數(shù)據(jù)較少,XCode使用了實體緩存,所以XCode對角色的查詢幾乎接近于0。XCode的實體緩存能夠保證數(shù)據(jù)數(shù)據(jù)的新鮮性,這里不能說不公平。
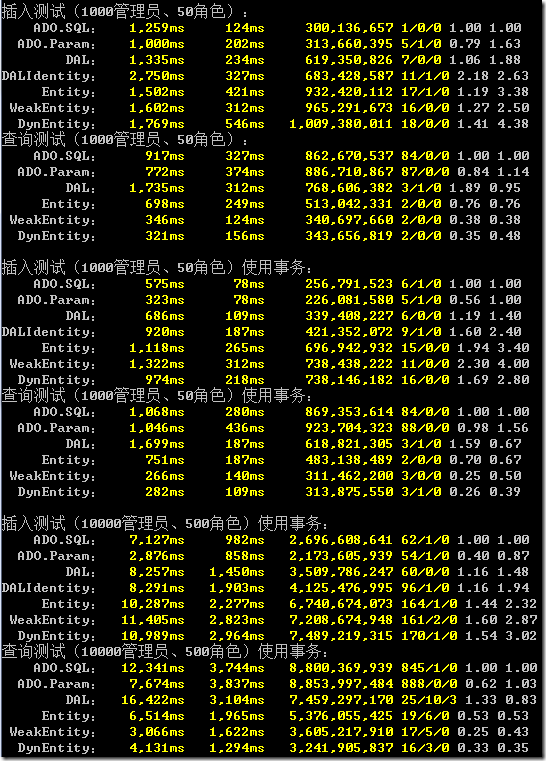
開啟一級緩存
可以注意到,開啟一級緩存后,XCode的表現(xiàn)非常出色,并且越是后面的測試項越出色。因為,后面三項都必須通過DAL來執(zhí)行,而一級緩存正是位于DAL中。所以XCode的第一個測試項DAL會比較慢,因為它的緩存命中率太低了,并且還要負責緩存數(shù)據(jù)等操作。查詢哪個管理員是隨機的,越是到了后面,隨著緩存命中率的提高,速度就越快。
XCode的一級緩存也是能保證實時更新的,也許這個測試作為與ADO的標準測試比較好。
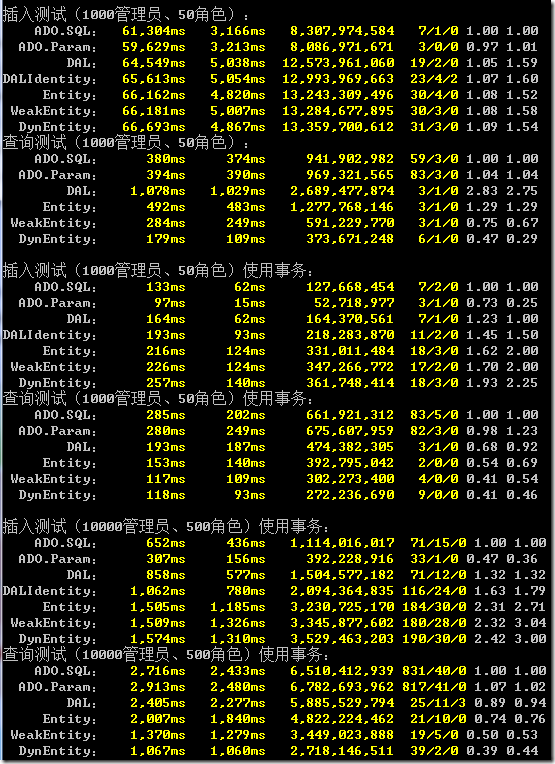
下面我們試試別的數(shù)據(jù)庫,SQLite吧,開啟一級緩存。SQLite插入后獲取自增的方法跟MSSQL不一樣,為了讓測試代碼簡單,我們放過它,允許ADO的兩個測試項不插入角色。而XCode是能夠很好支持各種數(shù)據(jù)庫獲取自增的
首先看到的是,沒有開啟事務的SQLite,實在是太不給力了,執(zhí)行時間很長,但是線程時間很短。這個測試告訴我們,用SQLite要盡可能的開事務。
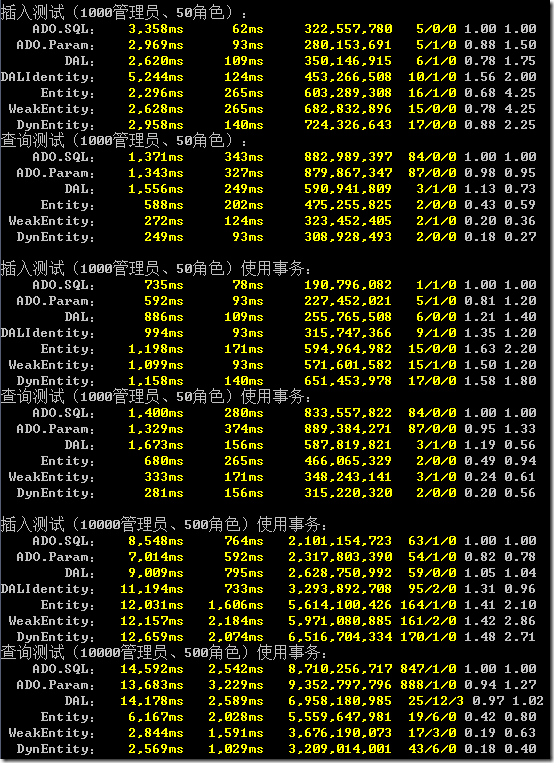
為了更切近生產(chǎn)環(huán)境,下面我們試試遠程的MSSQL,位于局域網(wǎng)內(nèi)的window 2008 r2上的MSSQL2008
可以看到,越是切近生產(chǎn)環(huán)境,數(shù)據(jù)量越大,XCode表現(xiàn)越是出色!
把MySql也拉出來溜溜
該MySql部署在一個XP虛擬機上(512M內(nèi)存安裝了MySql、Oracle、Firebird、PostgreSQL),并且各種配置都是開發(fā)用配置,測試數(shù)據(jù)不是很穩(wěn)定。
后面會附上測試程序,以及測試程序的源代碼,感興趣的同學可以在自己機器上執(zhí)行測試程序看看結(jié)果如何。
建議對XCode感興趣的同學都看看Performance.cs源碼,每一個測試項,同時也展示著如何使用XCode,如何支持多數(shù)據(jù)庫,如何做到更好的性能!
BTW:
這段時間一直在準備一篇文章《XCode這樣處理無限增長的海量數(shù)據(jù)》,靈感源自于一位使用XCode做項目的同學,他用了三百多張相同結(jié)構(gòu)的表,并且表的數(shù)量可能會無限增多,每張表有數(shù)百萬的數(shù)據(jù)。沒錯,這是一個數(shù)據(jù)采集系統(tǒng),包括采集、分析整理、查詢展現(xiàn)三大塊。
他使用了XCode十八般武藝中的動態(tài)修改表,實現(xiàn)一個實體類控制幾百張表的需求,當然,也包括自動創(chuàng)建表。盡管這項功能位列于十八般武藝當中,與三級緩存并重,但實際上項目使用得不多,風險還是挺大的。至少,到現(xiàn)在為止,沒有發(fā)現(xiàn)太大的問題。
我想以他的這個項目為例子,詳細的講解一下XCode的各個緩存,以及如何去處理海量數(shù)據(jù)。當然,還要包括最新版本的分布式,是的,下一版本的XCode直接支持異構(gòu)數(shù)據(jù)庫的分布式,提高性能,或者實現(xiàn)數(shù)據(jù)的熱備,業(yè)務層不需要做任何修改。
測試代碼請看http://xcode.codeplex.com
歡迎一起討論:QQ群10193406


 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號