Python對(duì)excel表格的操作.
參考博客:
https://blog.csdn.net/lmj19851117/article/details/78814721
####一、excel的讀取操作xlrd####
import xlrd ##################一、excel的讀取操作xlrd###################### data =xlrd.open_workbook(r"F:\myexcel.xls") #0.打開excel操作 table = data.sheets()[0] #通過索引順序獲取 table = data.sheet_by_index(0) #通過索引順序獲取 table = data.sheet_by_name(u'Sheet1')#通過名稱獲取 #1. 獲取excel sheet對(duì)象 table1 =data.sheets()[0] table2=data.sheet_by_index(0) table3=data.sheet_by_name(U"Sheet1") print(table1) print(table2) print(table3)
輸出結(jié)果:
<xlrd.sheet.Sheet object at 0x00000131D1B1BCF8>
<xlrd.sheet.Sheet object at 0x00000131D1B1BCF8>
<xlrd.sheet.Sheet object at 0x00000131D1B1BCF8>
#2. 獲取sheet的行與列數(shù)量.
rows=table1.nrows
col =table1.ncols
print("行數(shù)為%s \n列數(shù)為%s"%(rows,col))
輸出結(jié)果:
行數(shù)為14
列數(shù)為9
#3. 獲取整行和整列的數(shù)據(jù). row =table1.row_values(0) col =table1.col_values(2) print(row) print(col)
輸出結(jié)果
['A', 'sheet', 'sheet', 'sheet', 'sheet', 'sheet', 'sheet', 'sheet', 'sheet']
['sheet', 1.0, 3.0, 3.0, 4.0, 5.0, 6.0, 7.0, 8.0, 9.0, 10.0, 11.0, 12.0, 13.0]
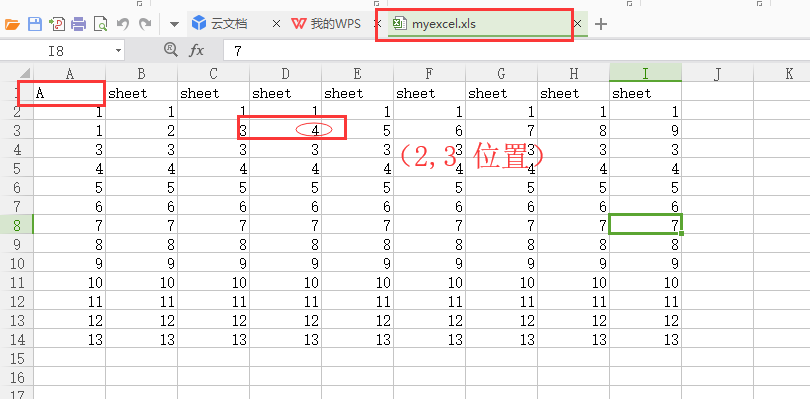
#4.獲取單元格數(shù)據(jù) cell_a1 =table1.cell_value(0,0) cell_x =table1.cell_value(2,3) #(第三行,第四列數(shù)據(jù)) print(cell_a1) print(cell_x)
輸出結(jié)果:
A
4.0
####二、excel的寫操作xlwt#####
#0.導(dǎo)入xlwt
import xlwt
#1.創(chuàng)建workbook對(duì)象
workbook =xlwt.Workbook(encoding ="utf-8",style_compression=0)
#2.創(chuàng)建一個(gè)sheet對(duì)象,一個(gè)sheet對(duì)象對(duì)應(yīng)excel文件中一張表格.
sheet =workbook.add_sheet("2",cell_overwrite_ok=True) #Cell_overwirte_ok 是能夠覆蓋單元表格的意思。
print(sheet)
<xlwt.Worksheet.Worksheet object at 0x00000131D1C3E710>
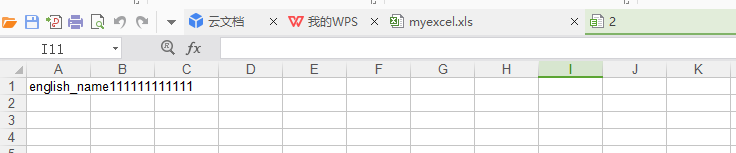
#3.向表中添加數(shù)據(jù). # sheet.write(0,0,"english_name111111111111") # sheet.write(1,0,"helloworld") # # #4.保存. workbook.save(r"2")
總結(jié): python 操作excel
import xlrd ##################一、excel的讀取操作xlrd###################### data =xlrd.open_workbook(r"F:\myexcel.xls") #0.打開excel操作 table = data.sheets()[0] #通過索引順序獲取 table = data.sheet_by_index(0) #通過索引順序獲取 table = data.sheet_by_name(u'Sheet1')#通過名稱獲取 #1. 獲取excel sheet對(duì)象 table1 =data.sheets()[0] table2=data.sheet_by_index(0) table3=data.sheet_by_name(U"Sheet1") print(table1) print(table2) print(table3) #2. 獲取sheet的行與列數(shù)量. rows=table1.nrows col =table1.ncols print("行數(shù)為%s \n列數(shù)為%s"%(rows,col)) #3. 獲取整行和整列的數(shù)據(jù). row =table1.row_values(0) col =table1.col_values(2) print(row) print(col) #4.獲取單元格數(shù)據(jù) cell_a1 =table1.cell_value(0,0) cell_x =table1.cell_value(2,3) #(第三行,第四列數(shù)據(jù)) print(cell_a1) print(cell_x) ##################二、excel的寫操作xlwt###################### #0.導(dǎo)入xlwt import xlwt #1.創(chuàng)建workbook對(duì)象 workbook =xlwt.Workbook(encoding ="utf-8",style_compression=0) #2.創(chuàng)建一個(gè)sheet對(duì)象,一個(gè)sheet對(duì)象對(duì)應(yīng)excel文件中一張表格. sheet =workbook.add_sheet("2",cell_overwrite_ok=True) #Cell_overwirte_ok 是能夠覆蓋單元表格的意思。 print(sheet) #3.向表中添加數(shù)據(jù). # sheet.write(0,0,"english_name111111111111") # sheet.write(1,0,"helloworld") # # #4.保存. workbook.save(r"2")


 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)