【RAY TRACING THE REST OF YOUR LIFE 超詳解】 光線追蹤 3-4 基于重要性采樣的材質初探
Preface
我們今天來把第三本書從開局到現在講的一大堆理論運用到我們的框架中,那么今天我們首先將原始的材質改為基于重要性采樣原理的材質
這一篇是代碼工程中進行MC理論應用的初步嘗試篇
Ready
我們需要這幾個重要的文件,我擔心大家手上的文件可能不太對,所以再貼一下

/// rectangle.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1 // [brief ] the rectangle-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing the next week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { //the statement of xy_rect class class xy_rect : public intersect { public: xy_rect() { } /* @brief: the rectangle in the x-y plane @param: the boundary of x axis the boundary of y axis the value of z axis the material of rectangle */ xy_rect(rtvar x1, rtvar x2, rtvar y1, rtvar y2, rtvar z0, material* mat); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; private: material * _materialp; rtvar _x1, _x2; rtvar _y1, _y2; rtvar _other; }; //the statement of xz_rect class class xz_rect : public intersect { public: xz_rect() { } /* @brief: the rectangle in the x-z plane @param: the boundary of x axis the boundary of z axis the value of y axis the material of rectangle */ xz_rect(rtvar x1, rtvar x2, rtvar z1, rtvar z2, rtvar y0, material* mat); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; private: material * _materialp; rtvar _x1, _x2; rtvar _z1, _z2; rtvar _other; }; //the statement of yz_rect class class yz_rect : public intersect { public: yz_rect() { } /* @brief: the rectangle in the y-z plane @param: the boundary of y axis the boundary of z axis the value of x axis the material of rectangle */ yz_rect(rtvar y1, rtvar y2, rtvar z1, rtvar z2, rtvar x0, material* mat); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; private: material * _materialp; rtvar _z1, _z2; rtvar _y1, _y2; rtvar _other; }; // the implementation of xy_rect class inline xy_rect::xy_rect(rtvar x1, rtvar x2, rtvar y1, rtvar y2, rtvar z0, material* mat) :_x1(x1) , _x2(x2) , _y1(y1) , _y2(y2) , _other(z0) , _materialp(mat) { } bool xy_rect::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const { rtvar t = (_other - sight.origin().z()) / sight.direction().z(); if (t < t_min || t > t_max)return false; rtvar x = sight.origin().x() + t*sight.direction().x(); rtvar y = sight.origin().y() + t*sight.direction().y(); if (x < _x1 || x > _x2 || y < _y1 || y > _y2) return false; info._u = (x - _x1) / (_x2 - _x1); info._v = (y - _y1) / (_y2 - _y1); info._t = t; info._materialp = _materialp; info._p = sight.go(t); info._n = rtvec(0, 0, 1); return true; } aabb xy_rect::getbox()const { return aabb(rtvec(_x1, _y1, _other - 0.0001), rtvec(_x2, _y2, _other + 0.0001)); } // the implementation of xz_rect class inline xz_rect::xz_rect(rtvar x1, rtvar x2, rtvar z1, rtvar z2, rtvar y0, material* mat) :_x1(x1) , _x2(x2) , _z1(z1) , _z2(z2) , _other(y0) , _materialp(mat) { } bool xz_rect::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const { rtvar t = (_other - sight.origin().y()) / sight.direction().y(); if (t < t_min || t > t_max)return false; rtvar x = sight.origin().x() + t*sight.direction().x(); rtvar z = sight.origin().z() + t*sight.direction().z(); if (x < _x1 || x > _x2 || z < _z1 || z > _z2) return false; info._u = (x - _x1) / (_x2 - _x1); info._v = (z - _z1) / (_z2 - _z1); info._t = t; info._materialp = _materialp; info._p = sight.go(t); info._n = rtvec(0, 1, 0); return true; } aabb xz_rect::getbox()const { return aabb(rtvec(_x1, _other - 0.0001, _z1), rtvec(_x2, _other + 0.0001, _z2)); } // the implementation of yz_rect class inline yz_rect::yz_rect(rtvar y1, rtvar y2, rtvar z1, rtvar z2, rtvar x0, material* mat) :_y1(y1) , _y2(y2) , _z1(z1) , _z2(z2) , _other(x0) , _materialp(mat) { } bool yz_rect::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const { rtvar t = (_other - sight.origin().x()) / sight.direction().x(); if (t < t_min || t > t_max)return false; rtvar y = sight.origin().y() + t*sight.direction().y(); rtvar z = sight.origin().z() + t*sight.direction().z(); if (y < _y1 || y > _y2 || z < _z1 || z > _z2) return false; info._u = (y - _y1) / (_y2 - _y1); info._v = (z - _z1) / (_z2 - _z1); info._t = t; info._materialp = _materialp; info._p = sight.go(t); info._n = rtvec(1, 0, 0); return true; } aabb yz_rect::getbox()const { return aabb(rtvec(_other - 0.0001, _y1, _z1), rtvec(_other + 0.0001, _y2, _z2)); } }// rt namespace

/// box.hpp // http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10307569.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1 // [brief ] the box-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing the next week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { // the statement of box class class box: public intersect { public: box() { } box(const rtvec& pointmin, const rtvec& pointmax, material * mat); virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const override; virtual aabb getbox()const override; /* public: // the normal of xy_rect, the normal's direction is + inline const rtvec& xy_n() const { return _list[0].Getnormal(); } // the normal of xy_rect, the normal's direction is - inline const rtvec& xy_nflip() const { return _list[1].Getnormal(); } inline const rtvec& xz_n() const { return _list[2].Getnormal(); } inline const rtvec& xz_nflip() const { return _list[3].Getnormal(); } inline const rtvec& yz_n() const { return _list[4].Getnormal(); } inline const rtvec& yz_nflip() const { return _list[5].Getnormal(); } inline void set_xy_material(material* m) { _list[0].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_xy_flipmaterial(material* m) { _list[1].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_xz_material(material* m) { _list[2].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_xz_flipmaterial(material* m) { _list[3].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_yz_material(material* m) { _list[4].setmaterial(m); } inline void set_yz_flipmaterial(material* m) { _list[5].setmaterial(m); } */ private: rtvec _min; rtvec _max; intersections* _list; //rectangles* _list; }; // the implementation of box class inline box::box(const rtvec& pointmin, const rtvec& pointmax, material * mat) :_min(pointmin) ,_max(pointmax) { intersect ** list = new intersect*[6]; list[0] = new xy_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.y(), _max.y(), _max.z(), mat); list[1] = new flip_normal(new xy_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), mat)); list[2] = new xz_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _max.y(), mat); list[3] = new flip_normal(new xz_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _min.y(), mat)); list[4] = new yz_rect(_min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _max.x(), mat); list[5] = new flip_normal(new yz_rect(_min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _min.x(), mat)); _list = new intersections(list, 6); /* rectangle ** list = new rectangle*[6]; list[0] = new xy_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.y(), _max.y(), _max.z(), mat); list[1] = new xy_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), mat, true); list[2] = new xz_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _max.y(), mat); list[3] = new xz_rect(_min.x(), _max.x(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _min.y(), mat, true); list[4] = new yz_rect(_min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _max.x(), mat); list[5] = new yz_rect(_min.y(), _max.y(), _min.z(), _max.z(), _min.x(), mat, true); _list = new rectangles(list, 6);*/ } bool box::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& info)const { return _list->hit(sight, t_min, t_max, info); } aabb box::getbox()const { return aabb(_min, _max); } } // rt namespace
為了統一測試效果,所以把main文件代碼也貼在下面了
#define LOWPRECISION //#define uvwtest //#define listtest //#define accumulatetest //#define attenuationtest //#define colortest #define STB_IMAGE_IMPLEMENTATION #include <fstream> #include <stb\stb_image.h> #include "include\texture\RTtexture.hpp" #include "include\material\RTmaterial.hpp" #include "include\hit\RThit.hpp" #include "camera.hpp" using namespace rt; rtvec lerp(const ray& sight, intersect* world, int depth) { hitInfo info; if (world->hit(sight, (rtvar)0.001, rtInf(), info)) { ray scattered; rtvec attenuation; rtvec light = info._materialp->emitted(info._u, info._v, info._p); if (depth < 50 && info._materialp->scatter(sight, info, attenuation, scattered)) return light + attenuation * lerp(scattered, world, depth + 1); else return light; } else return rtvec(); } void Cornell(intersections** scene, camera** cam, rtvar aspect) { intersect ** list = new intersect*[9]; size_t cnt = 0; material * red = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.65, 0.05, 0.05))); material * blue = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.05, 0.05, 0.73))); material * white = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.88, 0.88, 0.88))); material * green = new lambertian(new constant_texture(rtvec(0.12, 0.45, 0.15))); material * light = new areaLight(new constant_texture(rtvec(20, 20, 20))); list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new yz_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, green)); list[cnt++] = new yz_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 0, red); list[cnt++] = new xz_rect(200, 350, 220, 340, 550, light); list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xz_rect(200, 350, 220, 340, 550, light)); list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xz_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, white)); list[cnt++] = new xz_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 0, white); list[cnt++] = new flip_normal(new xy_rect(0, 555, 0, 555, 555, blue)); list[cnt++] = new translate(new rotate_x(new rotate_y(new box(rtvec(), rtvec(165, 165, 165), white), -45), -30), rtvec(130, 200, 65)); list[cnt++] = new translate(new rotate_z(new rotate_y(new box(rtvec(), rtvec(165, 330, 165), white), 30), 20), rtvec(265, 60, 295)); *scene = new intersections(list, cnt); rtvec lookfrom(278, 278, -800); rtvec lookat(278, 278, 0); rtvar dist_to_focus = 10.0; rtvar aperture = 0.; rtvar vfov = 40.0; *cam = new camera(lookfrom, lookat, rtvec(0, 1, 0), vfov, 1, aperture, dist_to_focus, 0., 1.); } void build_1_1() { stds ofstream file("graph-1-1.ppm"); size_t W = 200, H = 200, sample = 200; if (file.is_open()) { file << "P3\n" << W << " " << H << "\n255\n" << stds endl; intersections * world; camera * cma; Cornell(&world, &cma, (rtvar)W / H); for (int y = H - 1; y >= 0; --y) for (int x = 0; x < W; ++x) { rtvec color; for (int cnt = 0; cnt < sample; ++cnt) { lvgm::vec2<rtvar> para{ (lvgm::rand01() + x) / W, (lvgm::rand01() + y) / H }; color += lerp(cma->get_ray(para), world, 0); } color /= sample; #ifdef colortest if (color.x() < 0)stds cout << "color.x < 0 " << stds endl; if (color.y() < 0)stds cout << "color.y < 0 " << stds endl; if (color.z() < 0)stds cout << "color.z < 0 " << stds endl; #endif color = rtvec(sqrt(color.r()), sqrt(color.g()), sqrt(color.b())); //gamma 校正 int r = int(255.99 * color.r()); int g = int(255.99 * color.g()); int b = int(255.99 * color.b()); file << r << " " << g << " " << b << stds endl; } file.close(); if (world)delete world; if (cma)delete cma; stds cout << "complished" << stds endl; } else stds cerr << "open file error" << stds endl; } int main() { build_1_1(); }
Chapter4 Important Sampling Materials
我們的目標就是向光源發送額外的光線使得我們的圖片噪聲更少
讓我們假定我們發送的一束朝向光源的光線的pdf為pLight(direction)
讓我們假定一個和s有關的pdf函數,我們叫它為pSurface(direction)
我們可以把兩者進行線性組合,得到一個綜合的pdf,最簡單的形式如下
p(direction) = 0.5*pLight(direction) + 0.5*pSurface(direction)
其實,只要我們的權重是正的,并且加起來等于1,也就是我們經常提到的——pdf積分一定要能積到1,任意pdf函數組合形成的pdf只要滿足這兩點都是合理的,所以我們可以將幾個分量因素的pdf組合控制,使我們的pdf函數更加貼近真實效果。雖然我們可以使用任何的pdf,但是它一定不能改變我們收斂的答案,這是最重要的一點
因此,這就是一個關于尋找pdf的小游戲,要弄清楚如何使s(direction)*color(direction)大的pdf更大,也就是找到合適的pdf,創造更真實的顏色比例效果
對于漫反射(diffuse or Lambertian)表面,我們猜測它更偏重color(direction)因子。 對于鏡面(metal)材質表面來說,s()因子只在一個方向附近很大,所以它更重要。
事實上,大多數渲染器將鏡面設計成一種特殊情況,只是隱含地使用s / p 進行計算,所以,我們的代碼目前也是這樣。
我們今天先來測試一下漫反射表面,我們用之前的Cornell盒子做測試,為了方便,我們把相機的設置也放在里面,因為很多時候放在外面,經常換場景,無法記錄每個場景采用的合適的攝像機參數,所以就把它和場景放在一起了。
already中的main函數中有Cornell函數,這里就不貼了
我們先用之前的方法跑一個200*200的圖,sample為200,光線渲染路徑計算遞歸上限50次
可能效果不是很好,但是噪聲多一點,方便看效果
用時如圖
效果如圖
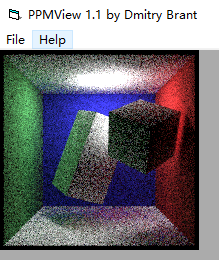
我們的目的是減少噪聲,我們將構造一個pdf,使得更多的光線反射到光源
趁著等待渲染的時間,再叨叨兩句我們的核心思想,我們的渲染路徑是這樣計算的
首先我們從eye(或者 camera)發射采樣光線,它指向投影屏幕的一個像素位置,也就是當前采樣光線正在計算的那個像素位置。
然后光線以射線的形式計算eye與投影屏幕之間所有的幾何體交點,得到與eye最近的那個,然后我們以那個交點為落腳點,作為新的eye,按照光學表面散射原理計算新的射線的方向(結合具體的材質),然后繼續測交。
如果在遞歸深度上限范圍內沒有找到光源,那么說明該像素位置不會有光傳入眼睛,也就是當前像素位置是黑色的;如果它找到光源了,也就是經過多次散射最后指向了光源,那么就說明光源發出的光線可以沿著我們的路徑逆向進入眼睛,那么我們就看到了這個像素,那么如何計算像素值呢?
這就涉及到了路徑渲染方程,里面有一個rgb分量衰減比例控制參數,它依據材質和紋理計算得出,這是之前的,我們現在要加上pdf函數,幫助我們更逼真地計算像素值
好了,嘮完了,上圖片

貌似沒區別,但是我們下面還會繼續優化
剛剛那個圖跑了53min,接下來你就會知道為什么時間還多了
我們要把重要性采樣嵌入進去,首先MC模擬f(x)的積分形式為
f(r)/p(r)
對于Lambertian材質,我們用上一篇的pdf函數:
p(direction) = cosθ/π
所以我們修改material基類如下:
/// material.hpp // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] the material-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { // the statement of material class class material { public: /* @brief: produce a scattered ray @param: InRay -> Incident light info -> the information of intersect-point(hit-point) attenuation -> when scattered, how much the ray should be attenuated by tis reflectance R scattered -> as we talk, it is a new sight; or it is the scattered ray with the intersect-point pdf -> the Important Sample's pdf function @retur: the function calculate a scattered ray or not */ virtual bool scatter(const ray& InRay, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered, rtvar& pdf)const { return false; } /* @brief: produce a scattered ray @param: InRay -> Incident light info -> the information of intersect-point(hit-point) scattered -> as we talk, it is a new sight; or it is the scattered ray with the intersect-point @retur: the function calculate a scattered ray or not */ virtual rtvar scatter_pdf(const ray& InRay, const hitInfo& info, const ray& scattered)const { return false; } virtual bool scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered)const { return false; } /* @brief: 自發光 @param: 紋理所需信息 @retur: 紋理像素值 */ virtual rtvec emitted(rtvar u, rtvar v, const rtvec& p)const { return rtvec(); } }; }
/// diffuse.hpp // http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10198423.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] one of the materials // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class texture; // the statement of lambertian class class lambertian : public material { public: lambertian(texture* _tex); rtvar scatter_pdf(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, const ray& scattered)const; bool scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered, rtvar& pdf)const; public: const texture* get_texture()const { return _albedo; } void set_texture(texture* tex) { _albedo = tex; } protected: texture* _albedo; }; // the implementation of lambertian class inline lambertian::lambertian(texture* _tex) :_albedo(_tex) { } rtvar lambertian::scatter_pdf(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, const ray& scattered)const { rtvar cosine = dot(info._n, scattered.direction().ret_unitization()); if (cosine < 0)cosine = 0; return cosine / π; } bool lambertian::scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered, rtvar& pdf)const { rtvec target = info._p + info._n + lvgm::random_unit_sphere(); scattered = ray{ info._p, (target - info._p).ret_unitization(), rIn.time() }; attenuation = _albedo->value(info._u, info._v, info._p); pdf = dot(info._n, scattered.direction()) / π; return true; } } // rt namespace
以及主函數中的lerp函數
rtvec lerp(const ray& sight, intersect* world, int depth) { hitInfo info; if (world->hit(sight, (rtvar)0.001, rtInf(), info)) { ray scattered; rtvec emitted = info._materialp->emitted(info._u, info._v, info._p); rtvar pdf; rtvec albedo; if (depth < 50 && info._materialp->scatter(sight, info, albedo, scattered, pdf)) return emitted + albedo *info._materialp->scatter_pdf(sight, info, scattered)*lerp(scattered, world, depth + 1) / pdf; else return emitted; } else return rtvec(); }
所以,它運行時間多了3min,新代碼的運算只增無減
解釋一些東西:
scatter_pdf函數里面的cosine值是散射光線和表面法線的夾角,所以大于90°無效,表示采樣失敗,上一篇說過
scatter函數還是原來的差不多
上述是基于上一本書的第一次修改
下面來進行第二次修改
我們嘗試一下不同的采樣策略,比如,我們選擇從表面的上半球部分隨機采樣(可以把物體放入球坐標系中,我們只取上半球部分),那么我們的p(direction) = 1/(2π)
因為球體的球面度是4πsr,所以半球就是2πsr,采取表面均勻采樣的話,就是一立體角對應的球面度量1sr,所以就是1/(2π)
bool lambertian::scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered, rtvar& pdf)const { rtvec direction; do{ direction = lvgm::random_unit_sphere(); } while (dot(direction, info._n) < 0); scattered = ray{ info._p,direction.ret_unitization(),rIn.time() }; attenuation = _albedo->value(info._u, info._v, info._p); pdf = 0.5 / π; return true; }
按理說應該得到同上述兩張圖片相同的圖片,但是可能事與愿違

書作者采用的是咱們2-7教程里面的如下圖左上角那張,而我們今天采用的是右下角那張,因為它讓問題看的更清楚

下面是書中的結尾

其實你看一下這張圖頂部的白光(這一變化更容易讓我們捕捉到),就可以驗證作者所提出的問題
本來是周六就寫了這篇的草稿的,但是因為抄錯代碼了,出不來效果,白天調了好久。。。可能不適合抄東西。。
感謝您的閱讀,生活愉快~



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號