【Ray Tracing in One Weekend 超詳解】 光線追蹤1-10
《Ray Tracing in One Weekend》完結篇
最近課程上機實驗,封面圖渲染時間也超長,所以寫東西就落下了,見諒
這篇之后,我會繼續《Ray Tracing The Next Week》,還請多多關注
這幾天我在渲染這本書的封面圖,封面圖還沒出,不算結束,剛好安排了10節
今天呢,有兩件事:
1.闡述整個工程的文件組織即內容
2.闡述封面,完結
12.1工程文件組織
試過很多方法,問過很多老師,無奈,子類繼承實現的父類純虛函數實在無法和類聲明分成兩個文件(即聲明放于.h,其他實現放在.cpp中),室友說,純虛函數繼承實現和模板很類似
所以,我們在合適的時候使用hpp
在學習過程中,我們遇到了諸如反射、折射之類的函數,它們并不應該屬于某個具體子類,或者抽象基類
所以,我把它們寫在了泛型3D數學庫里面了
C++泛型3D數學庫是我們學光線追蹤的數學專用庫了吧算是
在回頭看我們的光線追蹤的項目代碼
1.工程定義文件
我們之前是在ray這個最基本的類中定義了一些基本的命名,爾后,發現,所有的東西都要用ray::val_type諸如此類的代碼去描述光線追蹤所用到的一些普遍類型,這個非常麻煩,代碼也長,后來,我們將它們移出了ray-class,放在了namespace rt中,但是,仍然放在ray文件中,這個很不合理,所以我們定義了一個RTdef.h,專門用于定義一些光線追蹤的常量和命名
/// RTdef.h // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1.1 // [brief ] the basic concept of rt // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once #include <lvgm\type_vec\type_vec.h> //http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10163085.html #include <lvgm\opticsfunc.hpp> //http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10241904.html #include <lvgm\randfunc.hpp> //http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10241904.html namespace rt { using rtvar = lvgm::precision; using rtvec = lvgm::vec3<rtvar>; constexpr static rtvar rtInf() { return static_cast<rtvar>(0x3f3f3f3f); } //最大值 constexpr rtvar π = 3.1415926; }
2.光線類
/// ray.h // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] the ray-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once #include "RTdef.h" namespace rt { class ray { public: ray() :_a{ rtvec() } , _b{ rtvec() } { } ray(const rtvec& a, const rtvec& b) :_a(a) , _b(b) { } ray(const ray& r) :_a(r._a) , _b(r._b) { } inline rtvec origin()const { return _a; } inline rtvec direction()const { return _b; } inline rtvec go(const rtvar t)const { return _a + t * _b; } private: rtvec _a; rtvec _b; }; }
3.相機類
/// camera.h //http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10221058.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1 // [brief ] the camera-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once #include "ray.h" namespace rt { class camera { public: camera(rtvec lookfrom, rtvec lookat, rtvec vup, rtvar vfov, rtvar aspect, rtvar aperture, rtvar focus) :_eye(lookfrom) , _lens_radius(aperture / 2) { rtvar theta = vfov * π / 180; rtvar half_height = tan(theta / 2) * focus; //tan(theta/2) = (height/2) / 焦距 rtvar half_width = aspect * half_height; _w = (lookfrom - lookat).ret_unitization(); _u = cross(vup, _w).ret_unitization(); _v = cross(_w, _u); //向量運算 _start = _eye - half_width * _u - half_height * _v - focus * _w;//高和寬都乘了焦距,w也要乘,不然公式是錯的 _horizontal = 2 * half_width * _u; _vertical = 2 * half_height * _v; } const ray get_ray(const rtvar u, const rtvar v)const { rtvec rd = rtvec(_lens_radius * lvgm::random_unit_plane()); rtvec offset = _u * rd.x() + _v * rd.y(); return ray{ _eye + offset, _start + u*_horizontal + v*_vertical - (_eye + offset) }; } const ray get_ray(const lvgm::vec2<rtvar>& para)const { return get_ray(para.u(), para.v()); } inline const rtvec& eye()const { return _eye; } inline const rtvec& start()const { return _start; } inline const rtvec& horizontal()const { return _horizontal; } inline const rtvec& vertical()const { return _vertical; } inline const rtvec& u()const { return _u; } inline const rtvec& v()const { return _v; } inline const rtvec& w()const { return _w; } inline const rtvar lens_r()const { return _lens_radius; } private: rtvec _u; rtvec _v; rtvec _w; rtvec _eye; rtvec _start; //left-bottom rtvec _horizontal; rtvec _vertical; rtvar _lens_radius; //the radius of lens }; }
4.碰撞相交部分
有一個碰撞相交基類
/// intersect.h //http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10190092.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] the intersect-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class material; struct hitInfo { lvgm::precision _t; //ray 中的系數t rtvec _p; //相交點、撞擊點 rtvec _n; //_p點的表面法線 material* materialp; //材質 }; class intersect { public: intersect() { } /* @brief: 撞擊函數,求取撞擊點相關記錄信息 @param: sight->視線 系數t的上下界->篩選撞擊點 rec->返回撞擊點信息 @retur: 是否存在合法撞擊點 */ virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& rec)const = 0; virtual ~intersect() { } }; }
后面有一個子類intersections是用于處理一組碰撞相交的類,類比于容器
/// intersections.h // http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10190092.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] the intersections-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class intersections :public intersect { public: intersections() { } intersections(intersect** list, size_t n) :_list(list), _size(n) { } virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& rec)const override; private: intersect** _list; size_t _size; }; bool intersections::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& rec)const { hitInfo t_rec; bool hitSomething = false; rtvar far = t_max; //剛開始可以看到無限遠 for (int i = 0; i < _size; ++i) { if (_list[i]->hit(sight, t_min, far, t_rec)) { hitSomething = true; far = t_rec._t; //將上一次的最近撞擊點作為視線可達最遠處 rec = t_rec; } } return hitSomething; } }
還有一個子類sphere是一種幾何體用來做自身的碰撞檢測的,之后,我們可能還會加入心形幾何體類
/// sphere.h // http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10190092.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.1.1 // [brief ] the sphere-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class sphere :public intersect { public: sphere() { } /* @para1: 球心坐標 @para2: 球半徑 @para3: 材質 */ sphere(const rtvec& h, rtvar r, material* ma) :_heart(h), _radius(r), _materialp(ma) { } ~sphere() { if (_materialp) delete _materialp; } virtual bool hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& rec)const override; inline const rtvar r()const { return _radius; } inline const rtvec& heart()const { return _heart; } inline rtvar& r() { return _radius; } inline rtvec& heart() { return _heart; } private: rtvec _heart; rtvar _radius; material* _materialp; }; bool sphere::hit(const ray& sight, rtvar t_min, rtvar t_max, hitInfo& rec)const { rtvec trace = sight.origin() - _heart; rtvar a = dot(sight.direction(), sight.direction()); rtvar b = 2.0 * dot(trace, sight.direction()); rtvar c = dot(trace, trace) - _radius * _radius; rtvar delt = b*b - 4.0*a*c; if (delt > 0) { rec.materialp = _materialp; rtvar x = (-b - sqrt(delt)) / (2.0*a); if (x < t_max && x > t_min) { rec._t = x; rec._p = sight.go(rec._t); rec._n = (rec._p - _heart) / _radius; return true; } x = (-b + sqrt(delt)) / (2.0*a); if (x < t_max && x > t_min) { rec._t = x; rec._p = sight.go(x); rec._n = (rec._p - _heart) / _radius; return true; } } return false; } }
一個總文件
/// RThit.h // http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10190092.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1 // [brief ] some intersects // intersections // sphere // heart // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once #include "ray.h" #include "intersect.h" #include "sphere.hpp" #include "intersections.hpp"
5.材質類
材質有一個基類和三個子類
/// material.h // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] the material-class for the ray-tracing project // from the 《ray tracing in one week》 // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { //abstract basic class class material { public: /* @brief: produce a scattered ray @param: InRay -> Incident light info -> the information of intersect-point(hit-point) attenuation -> when scattered, how much the ray should be attenuated by tis reflectance R scattered -> as we talk, it is a new sight; or it is the scattered ray with the intersect-point @retur: the function calculate a scattered ray or not */ virtual bool scatter(const ray& InRay, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered)const = 0; }; }
/// diffuse.hpp // http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10198423.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] one of the materials // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { //diffuse material class lambertian : public material { public: lambertian(const rtvec& a) :_albedo(a) { } bool scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered)const override { rtvec target = info._p + info._n + lvgm::random_unit_sphere(); scattered = ray{ info._p, target - info._p }; attenuation = _albedo; return true; } protected: rtvec _albedo; }; }
/// metal.hpp // http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10206773.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2018.12 // [brief ] one of the materials // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { //metal material class metal :public material { public: metal(const rtvec& a, const rtvar f = 0.) :_albedo(a) { if (f < 1 && f >= 0)_fuzz = f; else _fuzz = 1; } virtual bool scatter(const ray& rIn, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered)const { rtvec target = reflect(rIn.direction().ret_unitization(), info._n); scattered = ray{ info._p, target + _fuzz * lvgm::random_unit_sphere() }; attenuation = _albedo; return dot(scattered.direction(), info._n) != 0; } inline static rtvec reflect(const rtvec& in, const rtvec& n) { return in - 2 * dot(in, n)*n; } protected: rtvec _albedo; rtvar _fuzz; }; }
/// dielectric.hpp // http://www.rzrgm.cn/lv-anchoret/p/10217719.html // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1 // [brief ] one of the materials // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once namespace rt { class dielectric :public material { public: dielectric(const rtvar RI) :_RI(RI) { } virtual bool scatter(const ray& InRay, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered)const override; protected: rtvar _RI; inline rtvar schlick(const rtvar cosine)const; }; bool dielectric::scatter(const ray& InRay, const hitInfo& info, rtvec& attenuation, ray& scattered)const { rtvec outward_normal; rtvec refracted; rtvec reflected = reflect(InRay.direction(), info._n); rtvar eta; rtvar reflect_prob; rtvar cos; attenuation = rtvec(1., 1., 1.); if (dot(InRay.direction(), info._n) > 0) { outward_normal = -info._n; eta = _RI; cos = _RI * dot(InRay.direction(), info._n) / InRay.direction().normal(); } else { outward_normal = info._n; eta = 1.0 / _RI; cos = -dot(InRay.direction(), info._n) / InRay.direction().normal(); } if (refract(InRay.direction(), outward_normal, eta, refracted)) reflect_prob = schlick(cos); //如果有折射,計算反射系數 else reflect_prob = 1.0; //如果沒有折射,那么為全反射 if (lvgm::rand01() < reflect_prob) scattered = ray(info._p, reflected); else scattered = ray(info._p, refracted); return true; } inline rtvar dielectric::schlick(const rtvar cosine)const { rtvar r0 = (1. - _RI) / (1. + _RI); r0 *= r0; return r0 + (1 - r0)*pow((1 - cosine), 5); } }
總文件
/// RTmaterial.h // ----------------------------------------------------- // [author] lv // [begin ] 2019.1 // [brief ] some materials // diffuse // metal // dielectric // ----------------------------------------------------- #pragma once #include "ray.h" #include "intersect.h" #include "material.h" #include "diffuse.hpp" #include "metal.hpp" #include "dielectric.hpp"
我們所有的文件就寫完了
12.2封面完結
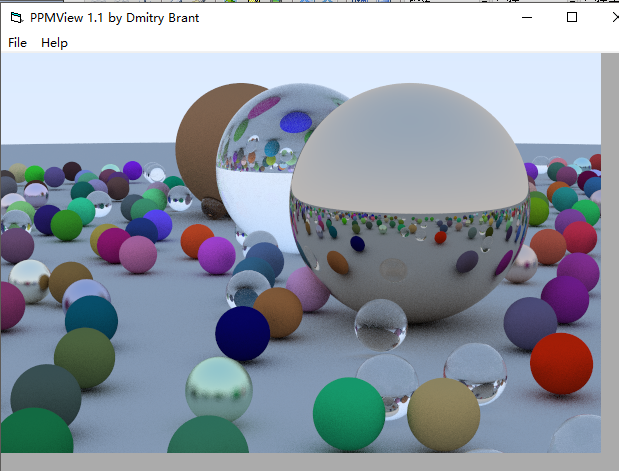
這個圖讓我學會了分段渲染。。。
這個圖非常好看,于是乎,整了一個600*400的,整整渲染了兩天(....),內心是崩潰的
我試過并發編程,結果效果不好(自己也不怎么會上鎖。。。)
所以,就只能單線程處理,時間超過十個小時左右吧,VS那個時間過程診斷框就壞死了。。。
有時候,不能一直渲染,這個時候,被迫結束后,只需要讀取已有文件的行數,然后計算出渲染了多少個點了,然后在渲染的雙重for循環中從下一個點開始渲染寫入文件即可,就可以隨時隨地想停就停,想渲染就渲染,因為圖像本事就是一個一個像素點,我們只需要24w個點的文件數據即可,你也可以并發寫入多個文件,最后拼在一起
我們采用的相機參數是這樣的
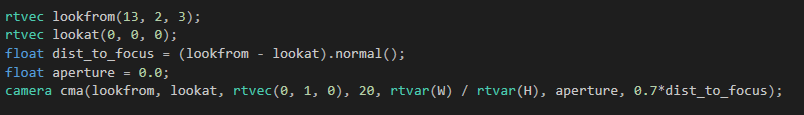
據說是官方的,我也不清楚
還有一個文章寫得非常好,是寫相機的參數測試的,大家可以閱讀一下,對相機的參數有一個更直觀深入的了解
因為這個圖實在是渲染了好久,所以也沒有出一些其他的效果圖,可能之后會更,大家可以自己設置球體以及相機,歡迎在評論區發出你的渲染圖~
下面是代碼:
#define LOWPRECISION #include <fstream> #include "RTmaterial.h" #include "RThit.h" #include "camera.h" #define stds std:: using namespace rt; rtvec lerp(const ray& sight, intersect* world, int depth) { hitInfo info; if (world->hit(sight, (rtvar)0.001, rtInf(), info)) { ray scattered; rtvec attenuation; if (depth < 50 && info.materialp->scatter(sight, info, attenuation, scattered)) return attenuation * lerp(scattered, world, depth + 1); else return rtvec(0, 0, 0); } else { rtvec unit_dir = sight.direction().ret_unitization(); rtvar t = 0.5*(unit_dir.y() + 1.); return (1. - t)*rtvec(1., 1., 1.) + t*rtvec(0.5, 0.7, 1.0); } } intersect* random_sphere() { int cnt = 500; intersect **list = new intersect*[cnt + 1]; list[0] = new sphere(rtvec(0, -1000, 0), 1000, new lambertian(rtvec(0.5, 0.5, 0.5))); int size = 1; for (int a = -11; a < 11; ++a) for (int b = -11; b < 11; ++b) { rtvar choose_mat = lvgm::rand01(); rtvec center(a + 0.9 * lvgm::rand01(), 0.2, b + 0.9*lvgm::rand01()); if ((center - rtvec(4, 0.2, 0)).normal()>0.9) { if (choose_mat < 0.75) { list[size++] = new sphere(center, 0.2, new lambertian(rtvec(lvgm::rand01()*lvgm::rand01(), lvgm::rand01()*lvgm::rand01(), lvgm::rand01()*lvgm::rand01()))); } else if (choose_mat < 0.9) { list[size++] = new sphere(center, 0.2, new metal(rtvec(0.5*(1 + lvgm::rand01()), 0.5*(1 + lvgm::rand01()), 0.5*(1 + lvgm::rand01())), 0.5*lvgm::rand01())); } else { list[size++] = new sphere(center, 0.2, new dielectric(1.5)); } } } list[size++] = new sphere(rtvec(0, 1, 0), 1.0, new dielectric(1.5)); list[size++] = new sphere(rtvec(-4, 1, 0), 1.0, new lambertian(rtvec(0.4, 0.2, 0.1))); list[size++] = new sphere(rtvec(4, 1, 0), 1.0, new metal(rtvec(0.7, 0.6, 0.5), 0.)); return new intersections(list, size); } void build_12_1() { stds ofstream file("graph12-1.ppm"); size_t W = 200, H = 120, sample = 100; if (file.is_open()) { file << "P3\n" << W << " " << H << "\n255\n" << stds endl; intersect* world = random_sphere(); rtvec lookfrom(13, 2, 3); rtvec lookat(0, 0, 0); float dist_to_focus = (lookfrom - lookat).normal(); float aperture = 0.0; camera cma(lookfrom, lookat, rtvec(0, 1, 0), 20, rtvar(W) / rtvar(H), aperture, 0.7*dist_to_focus); for (int y = H - 1; y >= 0; --y) for (int x = 0; x < W; ++x) { rtvec color; for (int cnt = 0; cnt < sample; ++cnt) { lvgm::vec2<rtvar> para{ (lvgm::rand01() + x) / W, (lvgm::rand01() + y) / H }; color += lerp(cma.get_ray(para), world, 0); } color /= sample; color = rtvec(sqrt(color.r()), sqrt(color.g()), sqrt(color.b())); //gamma 校正 int r = int(255.99 * color.r()); int g = int(255.99 * color.g()); int b = int(255.99 * color.b()); file << r << " " << g << " " << b << stds endl; } file.close(); if (world)delete world; stds cout << "complished" << stds endl; } else stds cerr << "open file error" << stds endl; } int main() { build_12_1(); }
感謝您的閱讀,生活愉快~


 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號