AQS原理分析
什么是AQS
java.util.concurrent包中的大多數(shù)同步器實(shí)現(xiàn)都是圍繞著共同的基礎(chǔ)行為,比如等待隊(duì)列、條件隊(duì)列、獨(dú)占獲取、共享獲取等,而這些行為的抽象就是基于AbstractQueuedSynchronizer(簡(jiǎn)稱AQS)實(shí)現(xiàn)的,AQS是一個(gè)抽象同步框架,可以用來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)依賴狀態(tài)的同步器。
JDK中提供的大多數(shù)的同步器如Lock, Latch, Barrier等,都是基于AQS框架來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)的
- 一般是通過(guò)一個(gè)內(nèi)部類Sync繼承 AQS
- 將同步器所有調(diào)用都映射到Sync對(duì)應(yīng)的方法
AQS具備的特性:
- 阻塞等待隊(duì)列
- 共享/獨(dú)占
- 公平/非公平
- 可重入
- 允許中斷
AQS內(nèi)部維護(hù)屬性volatile int state
- state表示資源的可用狀態(tài)
State三種訪問(wèn)方式:
- getState()
- setState()
- compareAndSetState()
AQS定義兩種資源共享方式
- Exclusive-獨(dú)占,只有一個(gè)線程能執(zhí)行,如ReentrantLock
- Share-共享,多個(gè)線程可以同時(shí)執(zhí)行,如Semaphore/CountDownLatch
AQS定義兩種隊(duì)列
- 同步等待隊(duì)列: 主要用于維護(hù)獲取鎖失敗時(shí)入隊(duì)的線程
- 條件等待隊(duì)列: 調(diào)用await()的時(shí)候會(huì)釋放鎖,然后線程會(huì)加入到條件隊(duì)列,調(diào)用signal()喚醒的時(shí)候會(huì)把條件隊(duì)列中的線程節(jié)點(diǎn)移動(dòng)到同步隊(duì)列中,等待再次獲得鎖
AQS 定義了5個(gè)隊(duì)列中節(jié)點(diǎn)狀態(tài):
- 值為0,初始化狀態(tài),表示當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)在sync隊(duì)列中,等待著獲取鎖。
- CANCELLED,值為1,表示當(dāng)前的線程被取消;
- SIGNAL,值為-1,表示當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)的后繼節(jié)點(diǎn)包含的線程需要運(yùn)行,也就是unpark;
- CONDITION,值為-2,表示當(dāng)前節(jié)點(diǎn)在等待condition,也就是在condition隊(duì)列中;
- PROPAGATE,值為-3,表示當(dāng)前場(chǎng)景下后續(xù)的acquireShared能夠得以執(zhí)行;
不同的自定義同步器競(jìng)爭(zhēng)共享資源的方式也不同。自定義同步器在實(shí)現(xiàn)時(shí)只需要實(shí)現(xiàn)共享資源state的獲取與釋放方式即可,至于具體線程等待隊(duì)列的維護(hù)(如獲取資源失敗入隊(duì)/喚醒出隊(duì)等),AQS已經(jīng)在頂層實(shí)現(xiàn)好了。自定義同步器實(shí)現(xiàn)時(shí)主要實(shí)現(xiàn)以下幾種方法:
- isHeldExclusively():該線程是否正在獨(dú)占資源。只有用到condition才需要去實(shí)現(xiàn)它。
- tryAcquire(int):獨(dú)占方式。嘗試獲取資源,成功則返回true,失敗則返回false。
- tryRelease(int):獨(dú)占方式。嘗試釋放資源,成功則返回true,失敗則返回false。
- tryAcquireShared(int):共享方式。嘗試獲取資源。負(fù)數(shù)表示失敗;0表示成功,但沒(méi)有剩余可用資源;正數(shù)表示成功,且有剩余資源。
- tryReleaseShared(int):共享方式。嘗試釋放資源,如果釋放后允許喚醒后續(xù)等待結(jié)點(diǎn)返回true,否則返回false。
同步等待隊(duì)列
AQS當(dāng)中的同步等待隊(duì)列也稱CLH隊(duì)列,CLH隊(duì)列是Craig、Landin、Hagersten三人發(fā)明的一種基于雙向鏈表數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)的隊(duì)列,是FIFO先進(jìn)先出線程等待隊(duì)列,Java中的CLH隊(duì)列是原CLH隊(duì)列的一個(gè)變種,線程由原自旋機(jī)制改為阻塞機(jī)制。
AQS 依賴CLH同步隊(duì)列來(lái)完成同步狀態(tài)的管理:
- 當(dāng)前線程如果獲取同步狀態(tài)失敗時(shí),AQS則會(huì)將當(dāng)前線程已經(jīng)等待狀態(tài)等信息構(gòu)造成一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)(Node)并將其加入到CLH同步隊(duì)列,同時(shí)會(huì)阻塞當(dāng)前線程
- 當(dāng)同步狀態(tài)釋放時(shí),會(huì)把首節(jié)點(diǎn)喚醒(公平鎖),使其再次嘗試獲取同步狀態(tài)。
- 通過(guò)signal或signalAll將條件隊(duì)列中的節(jié)點(diǎn)轉(zhuǎn)移到同步隊(duì)列。(由條件隊(duì)列轉(zhuǎn)化為同步隊(duì)列)
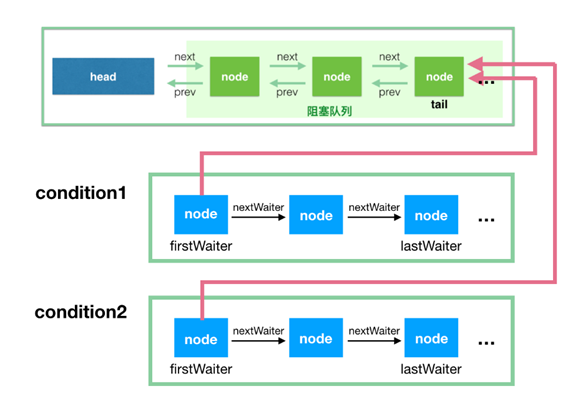
條件等待隊(duì)列
AQS中條件隊(duì)列是使用單向列表保存的,用nextWaiter來(lái)連接:
- 調(diào)用await方法阻塞線程;
- 當(dāng)前線程存在于同步隊(duì)列的頭結(jié)點(diǎn),調(diào)用await方法進(jìn)行阻塞(從同步隊(duì)列轉(zhuǎn)化到條件隊(duì)列)
Condition接口詳解
- 調(diào)用Condition#await方法會(huì)釋放當(dāng)前持有的鎖,然后阻塞當(dāng)前線程,同時(shí)向Condition隊(duì)列尾部添加一個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn),所以調(diào)用Condition#await方法的時(shí)候必須持有鎖。
- 調(diào)用Condition#signal方法會(huì)將Condition隊(duì)列的首節(jié)點(diǎn)移動(dòng)到阻塞隊(duì)列尾部,然后喚醒因調(diào)用Condition#await方法而阻塞的線程(喚醒之后這個(gè)線程就可以去競(jìng)爭(zhēng)鎖了),所以調(diào)用Condition#signal方法的時(shí)候必須持有鎖,持有鎖的線程喚醒被因調(diào)用Condition#await方法而阻塞的線程。
等待喚醒機(jī)制之a(chǎn)wait/signal測(cè)試
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Condition;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 等待喚醒機(jī)制 await/signal測(cè)試
*/
@Slf4j
public class ConditionTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 開(kāi)始處理任務(wù)");
//會(huì)釋放當(dāng)前持有的鎖,然后阻塞當(dāng)前線程
condition.await();
log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 結(jié)束處理任務(wù)");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 開(kāi)始處理任務(wù)");
Thread.sleep(2000);
//喚醒因調(diào)用Condition#await方法而阻塞的線程
condition.signal();
log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 結(jié)束處理任務(wù)");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}).start();
}
}
結(jié)果
18:55:50.720 [Thread-0] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ConditionTest - Thread-0 開(kāi)始處理任務(wù)
18:55:50.722 [Thread-1] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ConditionTest - Thread-1 開(kāi)始處理任務(wù)
18:55:52.737 [Thread-1] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ConditionTest - Thread-1 結(jié)束處理任務(wù)
18:55:52.737 [Thread-0] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ConditionTest - Thread-0 結(jié)束處理任務(wù)
ReentrantLock詳解
ReentrantLock是一種基于AQS框架的應(yīng)用實(shí)現(xiàn),是JDK中的一種線程并發(fā)訪問(wèn)的同步手段,它的功能類似于synchronized是一種互斥鎖,可以保證線程安全。
相對(duì)于 synchronized, ReentrantLock具備如下特點(diǎn):
- 可中斷
- 可以設(shè)置超時(shí)時(shí)間
- 可以設(shè)置為公平鎖
- 支持多個(gè)條件變量
- 與 synchronized 一樣,都支持可重入
?
順便總結(jié)了幾點(diǎn)synchronized和ReentrantLock的區(qū)別:
- synchronized是JVM層次的鎖實(shí)現(xiàn),ReentrantLock是JDK層次的鎖實(shí)現(xiàn);
- synchronized的鎖狀態(tài)是無(wú)法在代碼中直接判斷的,但是ReentrantLock可以通過(guò)ReentrantLock#isLocked判斷;
- synchronized是非公平鎖,ReentrantLock是可以是公平也可以是非公平的;
- synchronized是不可以被中斷的,而ReentrantLock#lockInterruptibly方法是可以被中斷的;
- 在發(fā)生異常時(shí)synchronized會(huì)自動(dòng)釋放鎖,而ReentrantLock需要開(kāi)發(fā)者在finally塊中顯示釋放鎖;
- ReentrantLock獲取鎖的形式有多種:如立即返回是否成功的tryLock(),以及等待指定時(shí)長(zhǎng)的獲取,更加靈活;
- synchronized在特定的情況下對(duì)于已經(jīng)在等待的線程是后來(lái)的線程先獲得鎖(回顧一下sychronized的喚醒策略),而ReentrantLock對(duì)于已經(jīng)在等待的線程是先來(lái)的線程先獲得鎖;
ReentrantLock的使用
同步執(zhí)行,類似于synchronized
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(); //參數(shù)默認(rèn)false,不公平鎖
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); //公平鎖
//加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
//臨界區(qū)
} finally {
// 解鎖
lock.unlock();
}
測(cè)試
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
/**
* 同步執(zhí)行
*/
public class ReentrantLockDemo {
private static int sum = 0;
private static Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Thread thread = new Thread(()->{
//加鎖
lock.lock();
try {
// 臨界區(qū)代碼
// TODO 業(yè)務(wù)邏輯:讀寫操作不能保證線程安全
for (int j = 0; j < 10000; j++) {
sum++;
}
} finally {
// 解鎖
lock.unlock();
}
});
thread.start();
}
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
可重入
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 可重入
*/
@Slf4j
public class ReentrantLockDemo2 {
public static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1();
}
public static void method1() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("execute method1");
method2();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void method2() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("execute method2");
method3();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void method3() {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("execute method3");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
可中斷
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 可中斷
*/
@Slf4j
public class ReentrantLockDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("t1啟動(dòng)...");
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
log.debug("t1獲得了鎖");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("t1等鎖的過(guò)程中被中斷");
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("main線程獲得了鎖");
t1.start();
//先讓線程t1執(zhí)行
Thread.sleep(1000);
t1.interrupt();
log.debug("線程t1執(zhí)行中斷");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 可中斷
*/
@Slf4j
public class ReentrantLockDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("t1啟動(dòng)...");
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
log.debug("t1獲得了鎖");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("t1等鎖的過(guò)程中被中斷");
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("main線程獲得了鎖");
t1.start();
//先讓線程t1執(zhí)行
Thread.sleep(1000);
t1.interrupt();
log.debug("線程t1執(zhí)行中斷");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 可中斷
*/
@Slf4j
public class ReentrantLockDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("t1啟動(dòng)...");
try {
lock.lockInterruptibly();
try {
log.debug("t1獲得了鎖");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
log.debug("t1等鎖的過(guò)程中被中斷");
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("main線程獲得了鎖");
t1.start();
//先讓線程t1執(zhí)行
Thread.sleep(1000);
t1.interrupt();
log.debug("線程t1執(zhí)行中斷");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
結(jié)果
19:05:14.930 [main] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ReentrantLockDemo3 - main線程獲得了鎖
19:05:14.934 [t1] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ReentrantLockDemo3 - t1啟動(dòng)...
19:05:15.949 [main] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ReentrantLockDemo3 - 線程t1執(zhí)行中斷
19:05:15.950 [t1] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ReentrantLockDemo3 - t1等鎖的過(guò)程中被中斷
java.lang.InterruptedException
at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.doAcquireInterruptibly(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:898)
at java.util.concurrent.locks.AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.acquireInterruptibly(AbstractQueuedSynchronizer.java:1222)
at java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock.lockInterruptibly(ReentrantLock.java:335)
at com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ReentrantLockDemo3.lambda$main$0(ReentrantLockDemo3.java:22)
at java.lang.Thread.run(Thread.java:748)
鎖超時(shí)
立即失敗
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
/**
* 鎖超時(shí)
*/
@Slf4j
public class ReentrantLockDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("t1啟動(dòng)...");
// 注意: 即使是設(shè)置的公平鎖,此方法也會(huì)立即返回獲取鎖成功或失敗,公平策略不生效
// if (!lock.tryLock()) {
// log.debug("t1獲取鎖失敗,立即返回false");
// return;
// }
//超時(shí)
try {
if (!lock.tryLock(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
log.debug("等待 1s 后獲取鎖失敗,返回");
return;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
try {
log.debug("t1獲得了鎖");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("main線程獲得了鎖");
t1.start();
//先讓線程t1執(zhí)行
Thread.sleep(1000);
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
結(jié)果
19:07:39.080 [main] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ReentrantLockDemo4 - main線程獲得了鎖
19:07:39.082 [t1] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ReentrantLockDemo4 - t1啟動(dòng)...
19:07:40.084 [t1] DEBUG com.yoocar.jucdemo.lock.ReentrantLockDemo4 - 等待 1s 后獲取鎖失敗,返回
超時(shí)失敗
@Slf4j
public class ReentrantLockDemo4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Thread t1 = new Thread(() -> {
log.debug("t1啟動(dòng)...");
//超時(shí)
try {
if (!lock.tryLock(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS)) {
log.debug("等待 1s 后獲取鎖失敗,返回");
return;
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
try {
log.debug("t1獲得了鎖");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t1");
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug("main線程獲得了鎖");
t1.start();
//先讓線程t1執(zhí)行
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
結(jié)果
公平鎖

ReentrantLock 默認(rèn)是不公平的
@Slf4j
public class ReentrantLockDemo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock(true); //公平鎖
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running...");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "t" + i).start();
}
// 1s 之后去爭(zhēng)搶鎖
Thread.sleep(1000);
for (int i = 0; i < 500; i++) {
new Thread(() -> {
lock.lock();
try {
log.debug(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " running...");
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}, "強(qiáng)行插入" + i).start();
}
}
}
結(jié)果
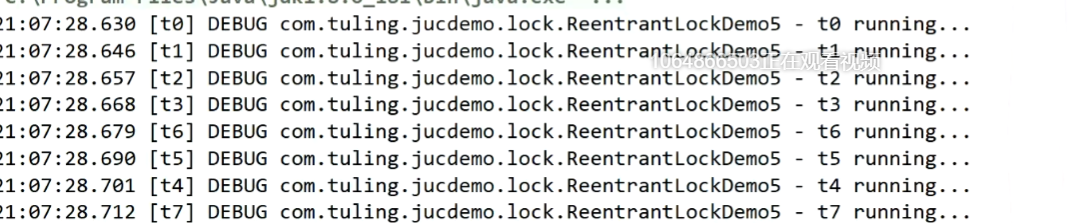
思考:ReentrantLock公平鎖和非公平鎖的性能誰(shuí)更高?
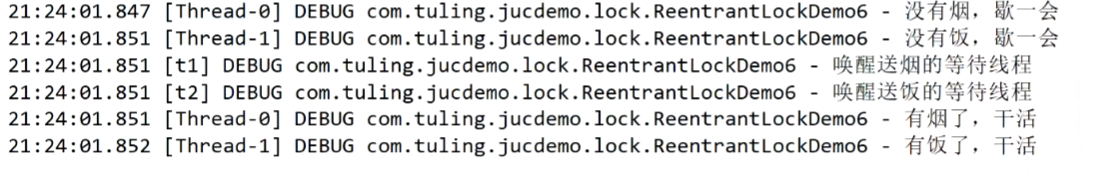
條件變量
java.util.concurrent類庫(kù)中提供Condition類來(lái)實(shí)現(xiàn)線程之間的協(xié)調(diào)。調(diào)用Condition.await() 方法使線程等待,其他線程調(diào)用Condition.signal() 或 Condition.signalAll() 方法喚醒等待的線程。
注意:調(diào)用Condition的await()和signal()方法,都必須在lock保護(hù)之內(nèi)。
@Slf4j
public class ReentrantLockDemo6 {
private static ReentrantLock lock = new ReentrantLock();
private static Condition cigCon = lock.newCondition();
private static Condition takeCon = lock.newCondition();
private static boolean hashcig = false;
private static boolean hastakeout = false;
//送煙
public void cigratee(){
lock.lock();
try {
while(!hashcig){
try {
log.debug("沒(méi)有煙,歇一會(huì)");
cigCon.await();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("有煙了,干活");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
//送外賣
public void takeout(){
lock.lock();
try {
while(!hastakeout){
try {
log.debug("沒(méi)有飯,歇一會(huì)");
takeCon.await();
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
log.debug("有飯了,干活");
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ReentrantLockDemo6 test = new ReentrantLockDemo6();
new Thread(() ->{
test.cigratee();
}).start();
new Thread(() -> {
test.takeout();
}).start();
new Thread(() ->{
lock.lock();
try {
//有煙了
hashcig = true;
//喚醒送煙的等待線程
cigCon.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t1").start();
new Thread(() ->{
lock.lock();
try {
//有飯了
hastakeout = true;
//喚醒送飯的等待線程
takeCon.signal();
}finally {
lock.unlock();
}
},"t2").start();
}
}
結(jié)果
ReentrantLock源碼分析
關(guān)注點(diǎn):
- ReentrantLock加鎖解鎖的邏輯
- 公平和非公平,可重入鎖的實(shí)現(xiàn)
- 線程競(jìng)爭(zhēng)鎖失敗入隊(duì)阻塞邏輯和獲取鎖的線程釋放鎖喚醒阻塞線程競(jìng)爭(zhēng)鎖的邏輯實(shí)現(xiàn) ( 設(shè)計(jì)的精髓:并發(fā)場(chǎng)景下入隊(duì)和出隊(duì)操作)
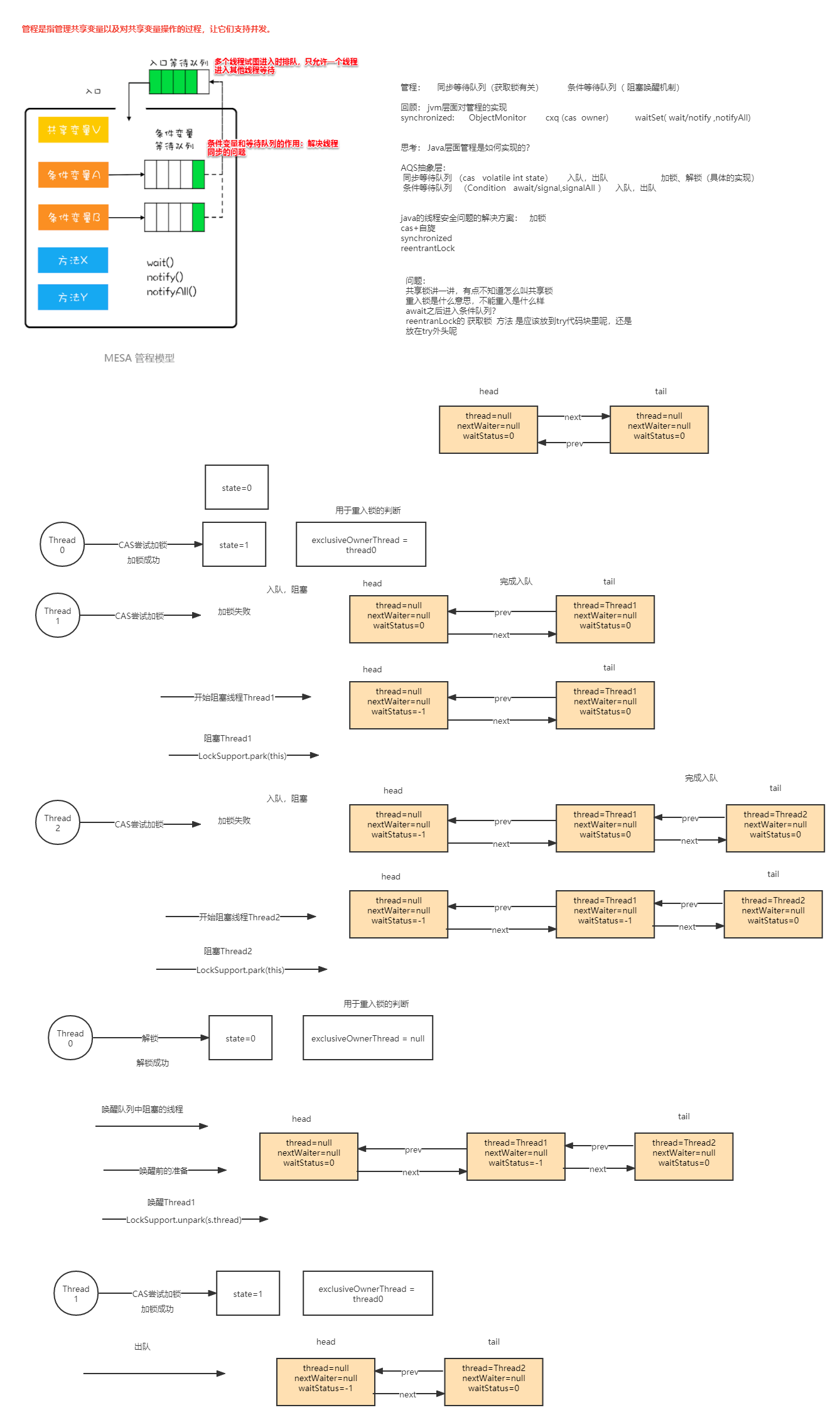
ReentrantLock加鎖邏輯
ReentrantLock reentrantLock=new ReentrantLock();
reentrantLock.lock();
非公平鎖的實(shí)現(xiàn)
CAS嘗試加鎖,加鎖成功,將State=1
static final class NonfairSync extends Sync {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 7316153563782823691L;
/**
* Performs lock. Try immediate barge, backing up to normal
* acquire on failure.
*/
final void lock() {
//直接CAS
if (compareAndSetState(0, 1))
setExclusiveOwnerThread(Thread.currentThread());
else
acquire(1);
}
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
}
CAS嘗試加鎖,加鎖失敗,入隊(duì),阻塞
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
//添加到等待隊(duì)列
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
tryAcquire
嘗試獲取鎖
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
return nonfairTryAcquire(acquires);
}
final boolean nonfairTryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
if (c == 0) {
if (compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
//重入鎖,每次+1
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0) // overflow
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
acquireQueued
Node
static final class Node {
//共享
static final Node SHARED = new Node();
//獨(dú)占
static final Node EXCLUSIVE = null;
//都是waitStatus的狀態(tài)
static final int CANCELLED = 1;
static final int SIGNAL = -1;
static final int CONDITION = -2;
static final int PROPAGATE = -3;
volatile int waitStatus;
//鏈表的前置節(jié)點(diǎn)
volatile Node prev;
//鏈表的后置節(jié)點(diǎn)
volatile Node next;
//當(dāng)前線程
volatile Thread thread;
Node nextWaiter;
final boolean isShared() {
return nextWaiter == SHARED;
}
final Node predecessor() throws NullPointerException {
Node p = prev;
if (p == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
else
return p;
}
Node() { // Used to establish initial head or SHARED marker
}
Node(Thread thread, Node mode) { // Used by addWaiter
this.nextWaiter = mode;
this.thread = thread;
}
Node(Thread thread, int waitStatus) { // Used by Condition
this.waitStatus = waitStatus;
this.thread = thread;
}
}
addWaiter
創(chuàng)建節(jié)點(diǎn)并入隊(duì)
/**
* Creates and enqueues node for current thread and given mode.
*
* @param mode Node.EXCLUSIVE for exclusive, Node.SHARED for shared
* @return the new node
*/
private Node addWaiter(Node mode) {
Node node = new Node(Thread.currentThread(), mode);
//第一次的時(shí)候tail=null
Node pred = tail=null;
if (pred != null) {
node.prev = pred;
if (compareAndSetTail(pred, node)) {
pred.next = node;
return node;
}
}
//將node初始化
enq(node);
return node;
}
enq
設(shè)置node鏈表,如果沒(méi)有鏈表,則將頭結(jié)點(diǎn)和尾結(jié)點(diǎn)都設(shè)置成node
private Node enq(final Node node) {
for (;;) {
Node t = tail;
//沒(méi)有尾結(jié)點(diǎn)
if (t == null) { // Must initialize
//初始化鏈表,將頭結(jié)點(diǎn)和尾結(jié)點(diǎn)都設(shè)置成node
if (compareAndSetHead(new Node()))
tail = head;
} else {
//將node設(shè)置到原鏈表的尾結(jié)點(diǎn)后面
node.prev = t;
if (compareAndSetTail(t, node)) {
t.next = node;
return t;
}
}
}
}
acquireQueued
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
//這里的for循環(huán)非常重要,確保node節(jié)點(diǎn)可以阻塞和可以中斷
for (;;) {
//取到head節(jié)點(diǎn)
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
//阻塞
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire
private static boolean shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(Node pred, Node node) {
int ws = pred.waitStatus;
//Status=-1是,返回true,表示可以阻塞
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL)
/*
* This node has already set status asking a release
* to signal it, so it can safely park.
*/
return true;
if (ws > 0) {
/*
* Predecessor was cancelled. Skip over predecessors and
* indicate retry.
*/
do {
node.prev = pred = pred.prev;
} while (pred.waitStatus > 0);
pred.next = node;
} else {
/*
* waitStatus must be 0 or PROPAGATE. Indicate that we
* need a signal, but don't park yet. Caller will need to
* retry to make sure it cannot acquire before parking.
*/
//將pred節(jié)點(diǎn)的Status設(shè)置成-1,表示可以阻塞
compareAndSetWaitStatus(pred, ws, Node.SIGNAL);
}
return false;
}
parkAndCheckInterrupt
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
//掛起當(dāng)前線程,阻塞線程,內(nèi)部可以識(shí)別中斷
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
ReentrantLock釋放鎖邏輯
ReentrantLock reentrantLock=new ReentrantLock();
....
reentrantLock.unlock();
unlock()
public void unlock() {
sync.release(1);
}
release
public final boolean release(int arg) {
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
tryRelease
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
//c=0
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
//用于重入鎖
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
//setState=0
setState(c);
return free;
}
unparkSuccessor
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
//喚醒線程
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
當(dāng)然其中還有很多鏈表的操作,后面有時(shí)間了再研究
https://www.processon.com/view/link/6191f070079129330ada1209



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)