Organization and Role-based access control
Organization and Role-based access control
https://blog.logto.io/organization-and-role-based-access-control
What is organization#
Organization definition#
The organization is a group of users(identities) and can represent the teams, business customers, and partner companies who can access your application.
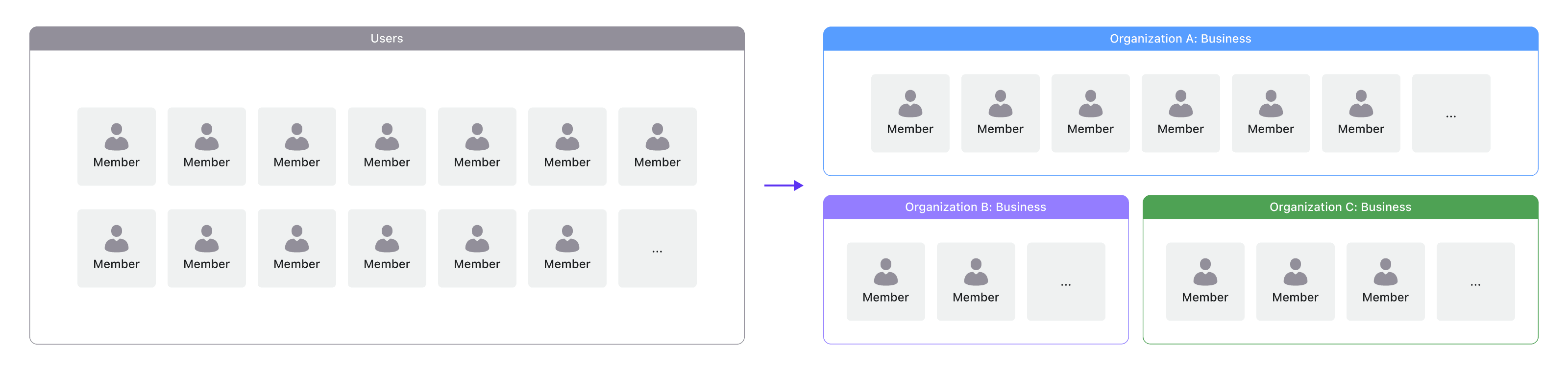
Organization is particularly effective in business-to-business (B2B) settings. In contrast to individual consumers, business clients often consist of teams, organizations, or entire companies, rather than just one person. The introduction of an organization as an entity is important, as it not only groups users but also provides a context for tenant isolation in multi-tenant apps.
Organization use cases#
With this fundamental element, you can now build the must-have features for your B2B products:
- Build a multi-tenant architecture to isolate clients’ data and resources.
- Application access levels are defined by roles assigned to organization members.
- Provisioning members on an invitation and just-in-time basis.
- Organizations can each have a single sign-on (SSO) authentication experience.
ROBAC: Scalable Role and Organization Based Access Control
https://profsandhu.com/zhang/pub/roac.pdf
權限設計OBAC模型
https://github.com/aitec-cn/obac/
-
模型
- 組織(organization)多層次組織。每個用戶屬于一個組織,每一個資源屬于一個組織,一個用戶可以訪問同一個組織內的資源,并根據角色確定訪問范圍等級
- 資源(resource) resource為數據資源, 如:訂單信息、客戶信息等,通過組織ID實現在不同組織層級的數據隔離。
- 動作(action) action為對resource的操作權限,通過web路徑來區分resource+action,如:創建、查看、修改、刪除等。
- 角色(role) role為組織下的角色,不同的user屬于不同的role,role又是不同層級下的role,一個role可以覆蓋多個resource,role可以對應多個action。
- 作用域(scope) tenant、group、company、individual(user)等均為不同層級的組織作用域,組織的關系為樹形結構。
-
實現
- 創建一個action、resource、role、scope 四元組表,用于存儲和判別某動作所需的組織角色和作用域(組織層級)。(對于簡單的應用,把role加入到url path里,實現通過路徑提取該action對應的四元組)
- 默認所有action,在數據庫操作層面都加入對應層級的org_id,以實現數據隔離。
- 同一組織下,管理員可以忽略低層級的orgID,以實現對其他普通成員的數據操作。
- 每一個請求的token里都需要攜帶多層級的org id(如tenantId GroupID companyId UsrId 等),role,userid 等,以確認是否滿足權限判別。
常見的訪問控制模型
https://blog.csdn.net/www_tlj/article/details/138140098
本文介紹了五種常見的訪問控制模型,包括自主訪問控制(DAC)、強制訪問控制(MAC)、基于角色的訪問控制(RBAC)、基于屬性的訪問控制(ABAC)以及組織基于訪問控制(OrBAC)。這些模型在不同場景下應用,是信息安全和合規性管理的關鍵組成部分。
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/1897600877277202401
四種訪問控制模型的比較
1. 關注點比較

2. 靈活性與復雜度比較
3. 典型應用場景對比

4. 優缺點總結
OBAC:
- 優點:對象中心化設計,支持細粒度控制,適合對象頻繁變化的環境
- 缺點:不易擴展到大量用戶,對象數量增加時管理復雜
RBAC:
- 優點:簡單易理解,管理成本低,與組織結構契合度高
- 缺點:缺乏靈活性,難以處理特例,不支持上下文敏感的決策
TBAC:
- 優點:支持動態權限管理,上下文感知,適合工作流系統
- 缺點:實現復雜,僅適用于有明確任務流程的系統
ABAC:
- 優點:極高的靈活性和精細度,適應動態環境,支持復雜的訪問策略
- 缺點:策略管理復雜,性能開銷大,實現和維護成本高
七、混合模式與演進趨勢
在實際應用中,很少有系統僅采用單一的訪問控制模型。更常見的是將多種模型組合使用,以平衡安全性、靈活性和可管理性。
1. 常見混合模式
- RBAC+ABAC混合模式:使用RBAC作為基礎框架,再通過ABAC提供細粒度的上下文控制
- RBAC+TBAC混合模式:角色定義基本權限集,任務狀態決定權限的動態變化
- 多層次訪問控制:不同安全級別的資源采用不同的訪問控制模型
Implementing Organization-Based Access Control with Keycloak
https://dev.to/devaaai/implementing-organization-based-access-control-with-keycloak-42km
Summary of Recommended Approach
| Component | Recommended Practice | Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Realm | Single-realm | Simplified administration |
| Organizations | Groups (/orgs/{org_name}) |
Clear hierarchical organization |
| Roles | Scoped with org-prefix (acme_user) |
Avoid role conflicts |
| Token Mappers | Group Membership & Script Mapper | Clear organization claims in tokens |
| Application Logic | JWT-based organization checks | Secure, clear authorization logic |
| Automation | Keycloak Admin API | Efficient onboarding and maintenance |
Groups vs. Roles
https://wjw465150.gitbooks.io/keycloak-documentation/content/server_admin/topics/groups.html
In the IT world the concepts of Group and Role are often blurred and interchangeable. In Keycloak, Groups are just a collection of users that you can apply roles and attributes to in one place. Roles define a type of user and applications assign permission and access control to roles
Aren’t Composite Roles also similar to Groups? Logically they provide the same exact functionality, but the difference is conceptual. Composite roles should be used to apply the permission model to your set of services and applications. Groups should focus on collections of users and their roles in your organization. Use groups to manage users. Use composite roles to manage applications and services.
https://wjw465150.gitbooks.io/keycloak-documentation/content/server_admin/topics/roles/composite.html
Composite Roles
Any realm or client level role can be turned into a composite role. A composite role is a role that has one or more additional roles associated with it. When a composite role is mapped to the user, the user also gains the roles associated with that composite. This inheritance is recursive so any composite of composites also gets inherited.
To turn a regular role into a composite role, go to the role detail page and flip the Composite Role switch on.
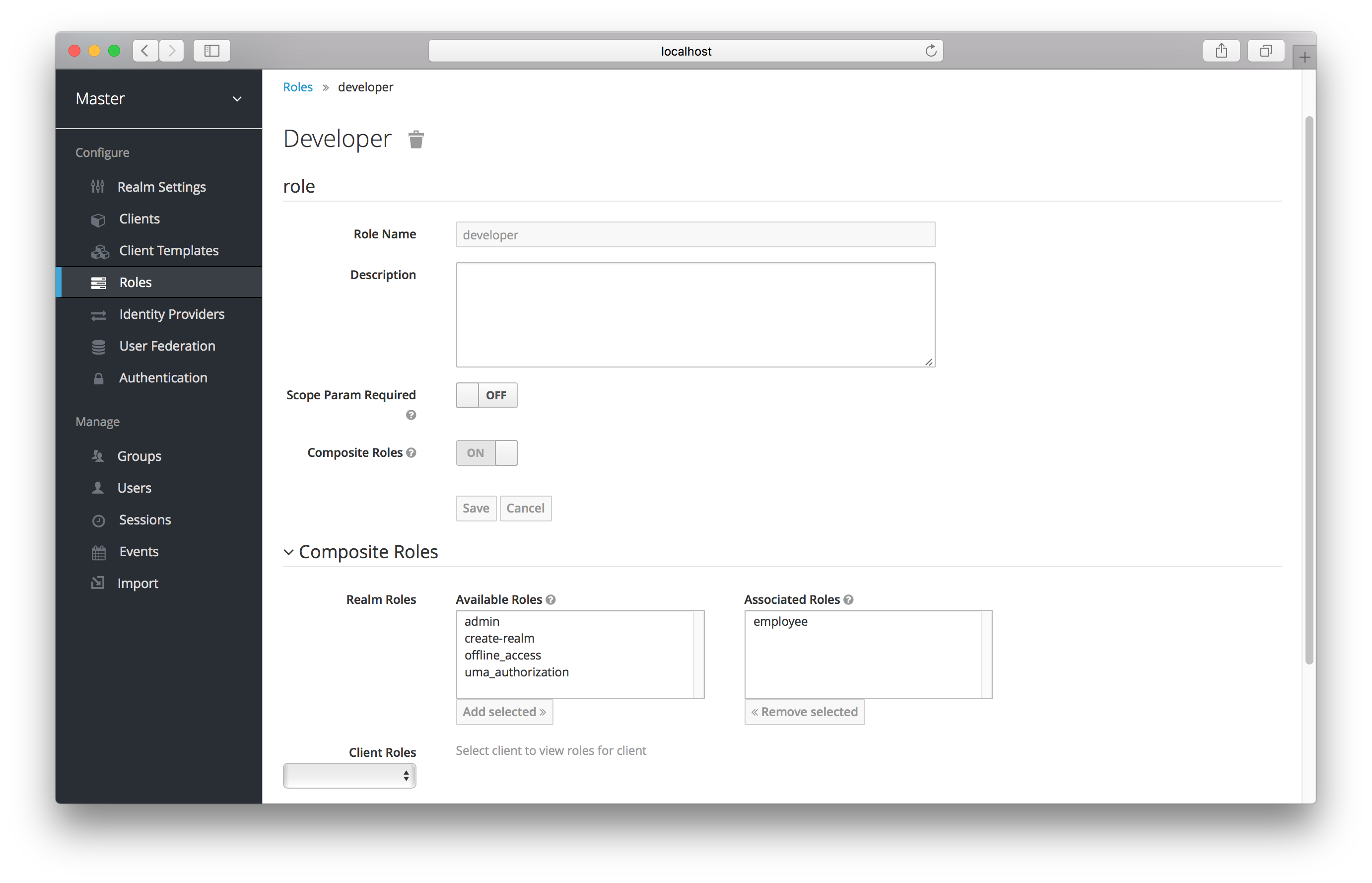
Once you flip this switch the role selection UI will be displayed lower on the page and you’ll be able to associate realm level and client level roles to the composite you are creating. In this example, the employee realm-level role was associated with the developer composite role. Any user with the developer role will now also inherit the employee role too.
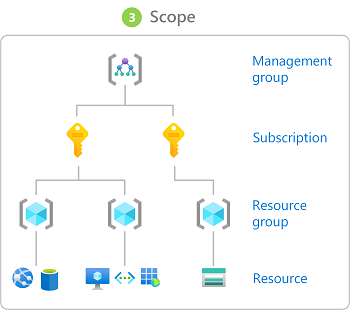
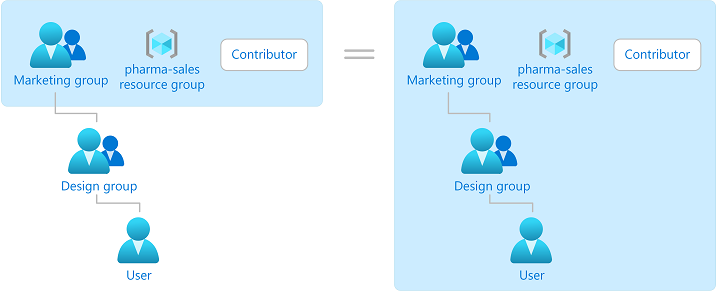
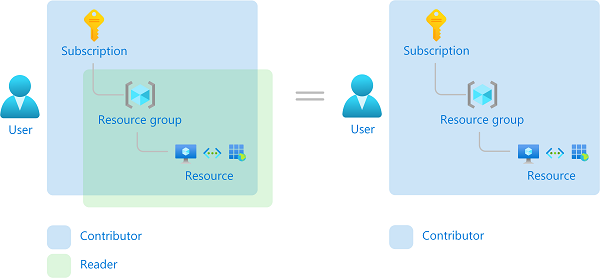
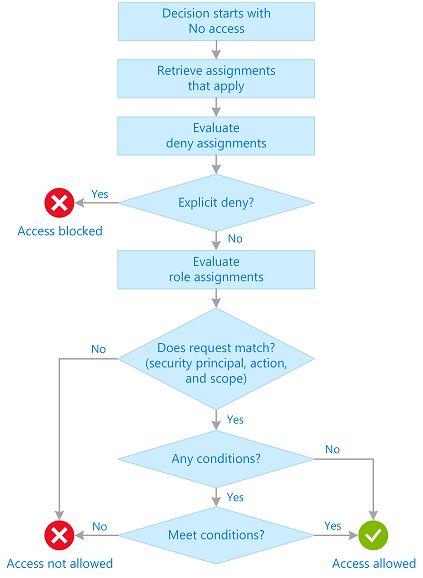
What is Azure role-based access control (Azure RBAC)?
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/role-based-access-control/overview
Here are some examples of what you can do with Azure RBAC:
- Allow one user to manage virtual machines in a subscription and another user to manage virtual networks
- Allow a DBA group to manage SQL databases in a subscription
- Allow a user to manage all resources in a resource group, such as virtual machines, websites, and subnets
- Allow an application to access all resources in a resource group



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號