CH04_程序流程結構
程序流程結構
C/C++支持最基本的三種程序運行結構:
- 順序結構:程序按順序執行,不發生挑戰
- 選擇結構:依據條件是否滿足,有選擇的執行相應的功能
- 循環結構:依據條件是否滿足,循環多次執行某段代碼
選擇結構
if語句
作用:執行滿足條件的語句
單行格式if語句:if(條件){語句塊}

示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score = 72;
//判斷條件是否滿足
if (score >= 60) {
cout << "及格了" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
多行格式if語句:if(條件){語句塊}else{語句塊}

示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score = 72;
//判斷條件是否滿足
if (score >= 60) {
cout << "及格了" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "繼續努力" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
多條件的if語句:if(條件){語句塊}else if(條件){語句塊}...else{語句塊}
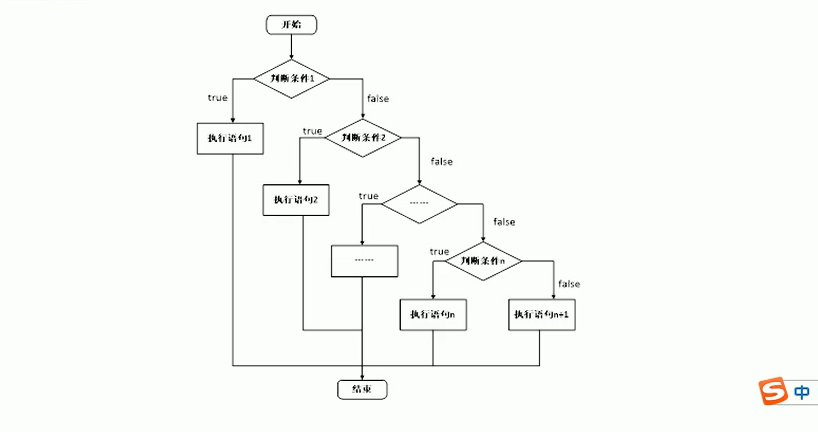
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score = 0;
cout << "請輸入你的考試成績:" << endl;
cin >> score;
//判斷條件
if (score >= 80) {
cout << "優秀" << endl;
}
else if (score >= 70) {
cout << "良好" << endl;
}
else if (score >= 60) {
cout << "及格" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "差" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
嵌套if語句:在if語句中,可以嵌套使用if語句,達到更精準的條件判斷
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//學校組建校籃球隊,面向全校招募隊員,要求身高不低于1.75米
char flag = 'n';
double height = 0;
cout << "你是本校學生嗎?(y/n):" << endl;
cin >> flag;
cout << "你身高多少(cm):" << endl;
cin >> height;
if (flag == 'y') {
if (height >= 175) {
cout << "恭喜你,報名成功!" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "很遺憾,身高不滿足要求!" << endl;
}
}
else {
cout << "非本校學生,禁止報名!" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
三目運算符
作用:通過三目運算符實現簡單的判斷
語法:表達式1?表達式2:表達式3;
描述:
如果表達式1為真,則執行表達式2,并返回表達式2的結果;
如果表達式1為假,則執行表達式3,并返回表達式3的結果.
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int age = 0;
cout << "請輸入你的年齡:"<<endl;
cin >> age;
cout << "你是:" << (age >= 18 ? "成年人" : "未成年人") << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
switch語句
作用:執行等值多條件的分支語句
語法:
switch(表達式){
case 值1:
//語句塊
break;
case 值2:
//語句塊
break;
case 值3:
//語句塊
break;
default:
//語句塊
break;
}
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int mingCi = 0;
cout << "請輸入你的名次:" << endl;
cin >> mingCi;
switch (mingCi) {
case 1:
cout << "獎勵一個女朋友" << endl;
break;
case 2:
cout << "獎勵一個筆記本電腦" << endl;
break;
case 3:
cout << "獎勵一個移動硬盤" << endl;
break;
default:
cout << "什么獎勵都沒有" << endl;
break;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
循環結構
while循環
作用:滿足循環條件執行循環語句。
語法:while(循環條件){循環語句}
描述:只要循環條件的結果為真,就執行循環語句。
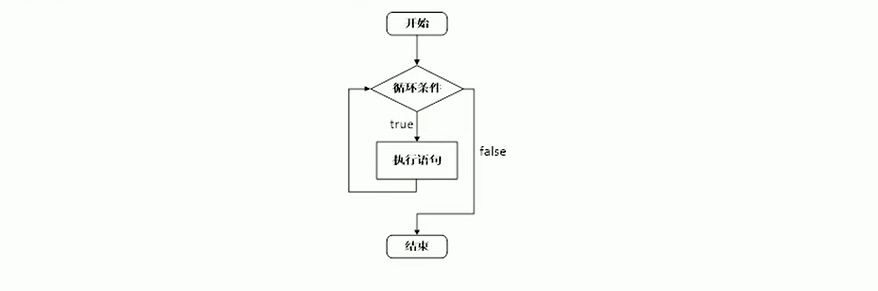
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
//產生的隨機數范圍為:1-100
//int num = rand() % 100 + 1;
int count = 0;
while (count < 10) {
cout << "好好學習,天天向上!" << endl;
count++;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
do-while循環
作用:滿足循環條件,執行循環語句。
語法:do{循環語句}while(循環條件);
描述:與while的區別在于do..while會先執行一次循環語句,再判斷循環條件。
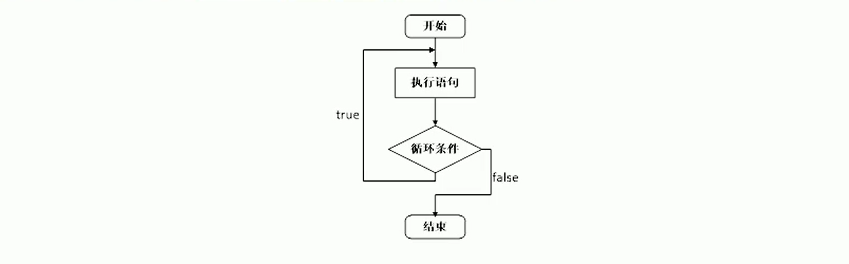
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score = 0;
do {
cout << "參加了一次考試,請輸入分數:" << endl;
cin >> score;
} while (score<60);
cout << "恭喜你,考試合格!" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
for循環
作用:滿足循環條件,執行循環語句。
語法:for(初始部分;條件部分;迭代部分){循環語句}
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
cout << "hello world" << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
嵌套循環
作用:在循環體中再嵌套一層循環,解決一些實際問題
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <=9; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= i; j++) {
cout << j<<"*"<<i<<"="<<(j*i)<<"\t";
}
cout << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
跳轉語句
break語句
作用:用于跳出選擇結構或循環結構。
描述:
1.出現在switch條件語句中,作用是終止case并跳出switch。
2.出現在循環語句中,作用是跳出當前的循環語句。
3.出現在嵌套循環中,跳出最近的內存循環結構。
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int score = 0;
for (int i = 0; i <10; i++) {
cout << "請輸入分數:" << endl;
cin >> score;
if (score < 0) {
cout << "分數輸入錯誤,終止錄入!" << endl;
break;
}
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
continue語句
作用:在循環語句中,結束本次循環,繼續下一次循環。
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
for (int i = 1; i <= 100; i++) {
if (i % 2 == 0)continue;
cout << i << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
goto語句
作用:可以無條件跳轉語句。
語法:goto 標記
描述:如果標記的名稱存在,則執行到goto語句時,會跳轉到標及的位置。
示例:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
cout << "1" << endl;
goto Flag;
cout << "2" << endl;
cout << "3" << endl;
cout << "4" << endl;
Flag:
cout << "5" << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號