Vision-Language Models are Zero-Shot Reward Models for Reinforcement Learning
發表時間:2024(ICLR2024)
文章要點: 文章提出用預訓練的視覺語言模型作為zero-shot的reward model(VLM-RMs)。好處在于可以通過自然語言來給定一個具體的任務,通過VLM-RMs讓強化學習基于reward學習這個任務(using pretrained vision-language models (VLMs) as zero shot reward models (RMs) to specify tasks via natural language)。這樣的好處是不用人工設計reward,而且任務自定義擴大了強化的適用范圍。
具體的,作者用CLIP作為基礎模型,其中包括CLIP image encoder和CLIP language encoder。將圖片和任務描述編碼成embedding后計算余弦相似度得到reward。

方法基本上就這么簡單。
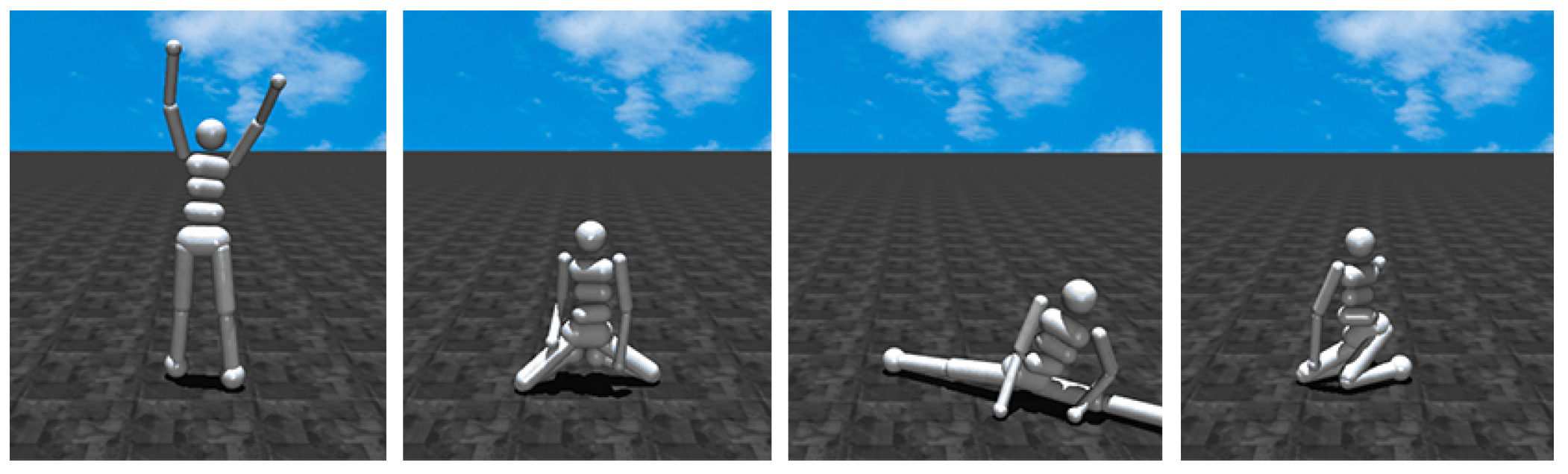
此外作者還設計了一個Goal-Baseline Regularization,不過在mujoco上沒效果。這個regularization的出發點是想講無關信息去掉,指保留和任務相關的信息來計算reward(projecting out irrelevant information about the observation)。具體的,除了任務描述外,還定義了一個baseline描述,比如任務描述是a humanoid robot kneeling,baseline描述是a humanoid robot。然后reward定義為
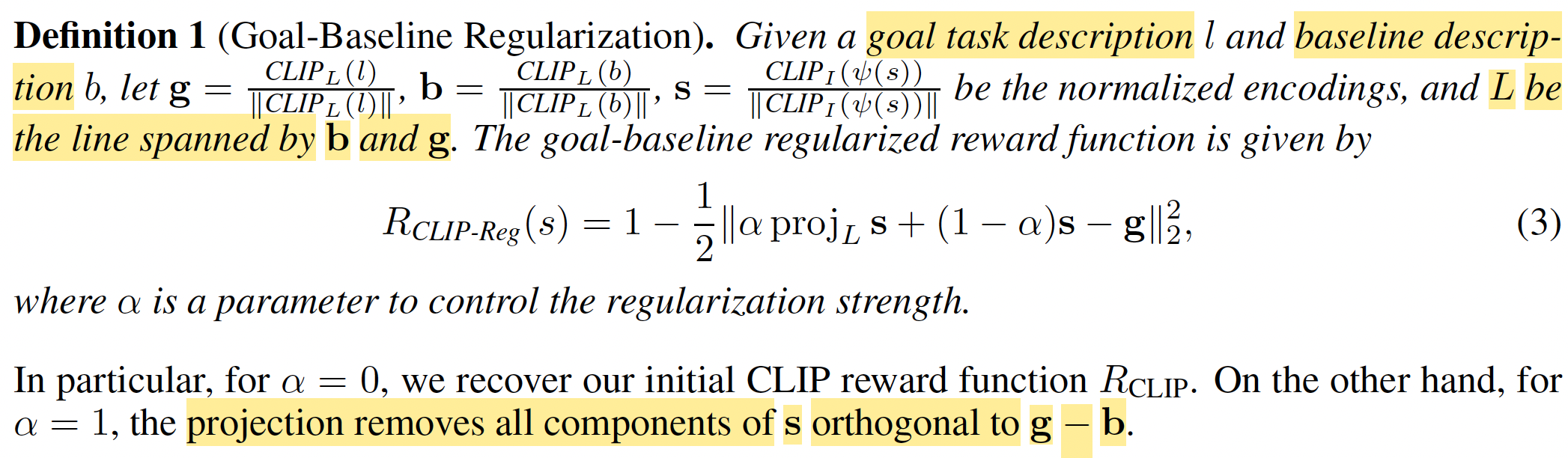
這個proj的目的是projecting our state embedding onto the line spanned by the baseline and task embeddings。不過作者也說了這個映射并不一定就正確,后面mujoco的實驗也表明不用其實效果更好。
還有個細節就是圖像的紋理,作者發現圖片更真實的話,reward更準確(zero-shot VLM-based rewards work better in environments that are more “photorealistic” because they are closer to the training distribution of the underlying VLM)。
總結:很有意思的工作,任務可以自己定義了,而且是圖像輸入。效果看起來還不算驚艷,不過方向應用面很廣。作者在附錄里也說了,這種方式主要還是focus on goal-based tasks,因為reward的計算是基于狀態和任務的相似度的,這種設計比較順理成章(because they are most straightforward to specify using image-text encoder VLMs.)。
不過文章確實方法上novelty有限,實驗也做的很少,有兩個reject也合理。不過架不住有人抬一手啊,換做我們肯定涼透了。
疑問:文章說alpha取0的時候就是不帶regularization的reward,沒看出來這兩式子一樣呢?



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號