Sample-Efficient Deep Reinforcement Learning via Episodic Backward Update
發(fā)表時(shí)間:2019 (NeurIPS 2019)
文章要點(diǎn):這篇文章提出Episodic Backward Update (EBU)算法,采樣一整條軌跡,然后從后往前依次更新做experience replay,這種方法對(duì)稀疏和延遲回報(bào)的環(huán)境有很好的效果(allows sparse and delayed rewards to propagate directly through all transitions of the sampled episode.)。
作者的觀點(diǎn)是
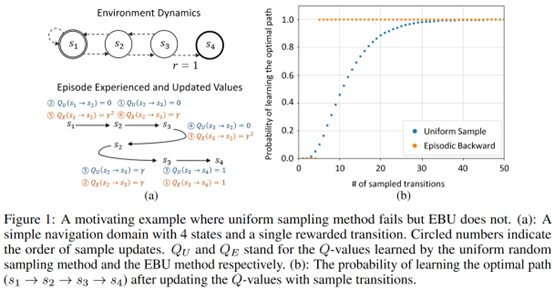
(1) We have a low chance of sampling a transition with a reward for its sparsity.
(2) there is no point in updating values of one-step transitions with zero rewards if the values of future transitions with nonzero rewards have not been updated yet.
作者的解決方法是
(1) by sampling transitions in an episodic manner.
(2) by updating the values of transitions in a backward manner
為了打破數(shù)據(jù)的相關(guān)性緩解overestimation,作者采用了一個(gè)diffusion factor \(\beta\)來做trade off。這個(gè)參數(shù)會(huì)在最新的估計(jì)和之前的估計(jì)之間做加權(quán),take a weighted sum of the new backpropagated value and the pre-existing value estimate
算法偽代碼如下

最后作者用多個(gè)learner設(shè)置不同的diffusion factor來學(xué)習(xí),最終選一個(gè)來輸出動(dòng)作。We generate K learner networks with different diffusion factors, and a single actor to output a policy. For each episode, the single actor selects one of the learner networks in a regular sequence.這些learner的參數(shù)隔一段時(shí)間同步一次。
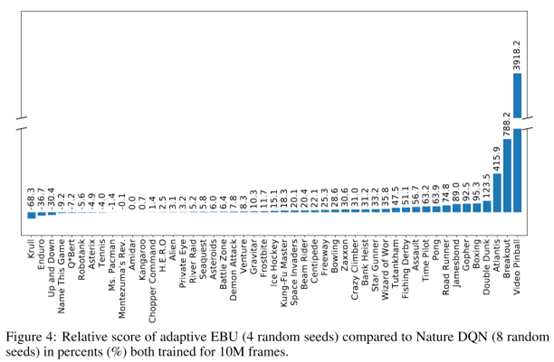
最終看起來有一定效果
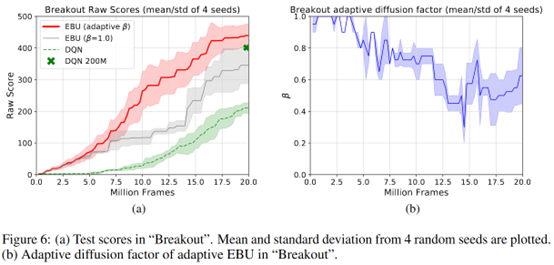
總結(jié):感覺依次更新問題應(yīng)該不少啊,可能trick有點(diǎn)多。另外作者強(qiáng)調(diào)achieves the same mean and median human normalized performance of DQN by using only 5% and 10% of samples,有點(diǎn)牽強(qiáng)了。明顯看出來訓(xùn)練一樣多的step,很多游戲提升也不大
疑問:里面這個(gè)diffusion factor好像也不能打亂數(shù)據(jù)之間的相關(guān)性吧,不知道會(huì)不會(huì)有問題。



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)