單元測試框架pytest
1、什么是pytest
pytest是一個非常成熟的全功能的Python測試框架,主要有以下特點:
- 簡單靈活,容易上手,文檔豐富
- 支持參數化,可以細粒度地控制要測試的測試用例
- 能夠支持簡單的單元測試和復雜的功能測試,還可以用來做 selenium/appium 等自動化測試、接口自動化測試(pytest+request)
- pytest有很多第三方插件,可以自定義擴展
- 測試用例的skip和xfail處理
- 可以很好的和CI工具結合,例如Jenkins
安裝pytest 版本
pip3 install pytest==4.0.2
2、pytest的用例編寫規(guī)則
- 測試文件以test_開頭(以_test結尾也可以),注意:pytest 文件名.py不受此規(guī)則限制。
- 測試類以Test開頭,并且不能帶有 __init__ 方法
- 測試函數以test_開頭
- 斷言使用基本的assert即可
3、為什么使用pytest:可以通過命令行來對測試用例進行控制
舉例:test_a.py
import pytest def test_case1(): print("--- test_a ---") assert True def test_case2(): print("--- test_b ---") assert True
執(zhí)行1:pytest #會執(zhí)行所有test_ 開頭的文件
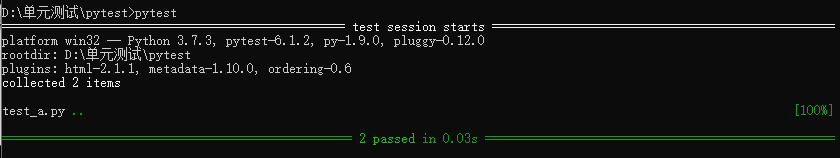
執(zhí)行2:pytest -v -s # -v顯示運行的函數,-s運行顯示內部的打印信息
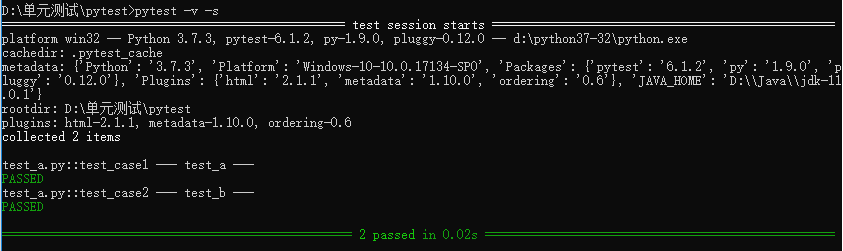
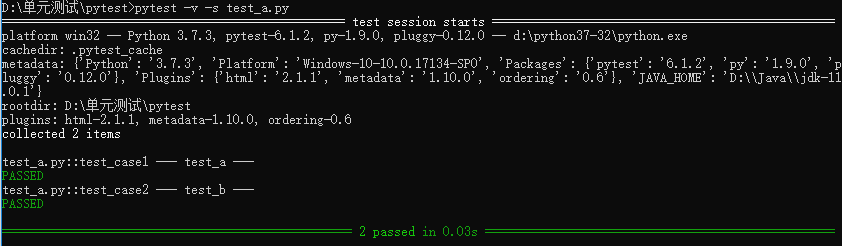
執(zhí)行3:pytest -v -s test_a.py
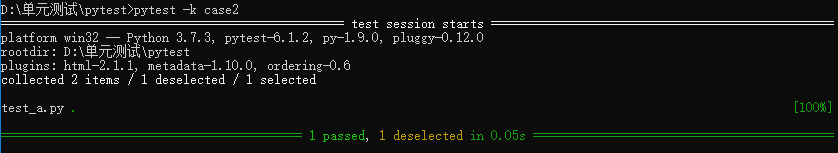
執(zhí)行4: pytest -k case2 #case2 是關鍵字,篩選測試文件、測試類名、測試方法中包含關鍵字的,均可被執(zhí)行
執(zhí)行5:pytest test_a.py::test_case1 -s -v #執(zhí)行指定的測試方法

4、執(zhí)行某個測試方法
代碼舉例:
import pytest class Calc(object): @classmethod def add(cls, x, y, *d): # 加法計算 result = x + y for i in d: result += i return result @classmethod def sub(cls, x, y, *d): # 減法計算 result = x - y for i in d: result -= i return result @classmethod def mul(cls, x, y, *d): # 乘法計算 result = x * y for i in d: result *= i return result @staticmethod def div(x, y, *d): # 除法計算 if y != 0: result = x / y else: return -1 for i in d: if i != 0: result /= i else: return -1 return result def test_add(): assert Calc.add(1, 2, 3) == 6 def test_sub(): assert Calc.sub(100, 20, 30) == 50 class TestCalc(): def test_mul(self): assert Calc.mul(2, 3, 4) == 24 def test_div(self): assert Calc.div(32, 8, 4) == 2
執(zhí)行1:pytest test_c.py::TestCalc::test_mul -s -v #執(zhí)行指定的函數

執(zhí)行2:pytest test_c.py::TestCalc -s -v #執(zhí)行指定的類
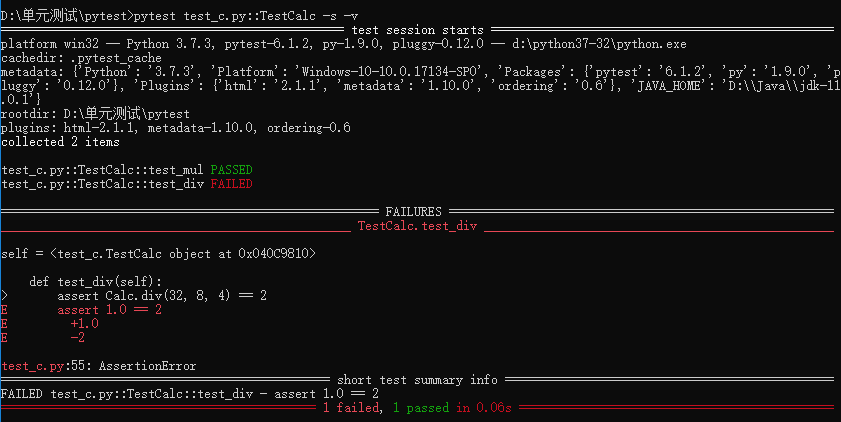
執(zhí)行3:pytest test_c.py::TestCalc -s -v --reruns 3 #3表示重跑3次

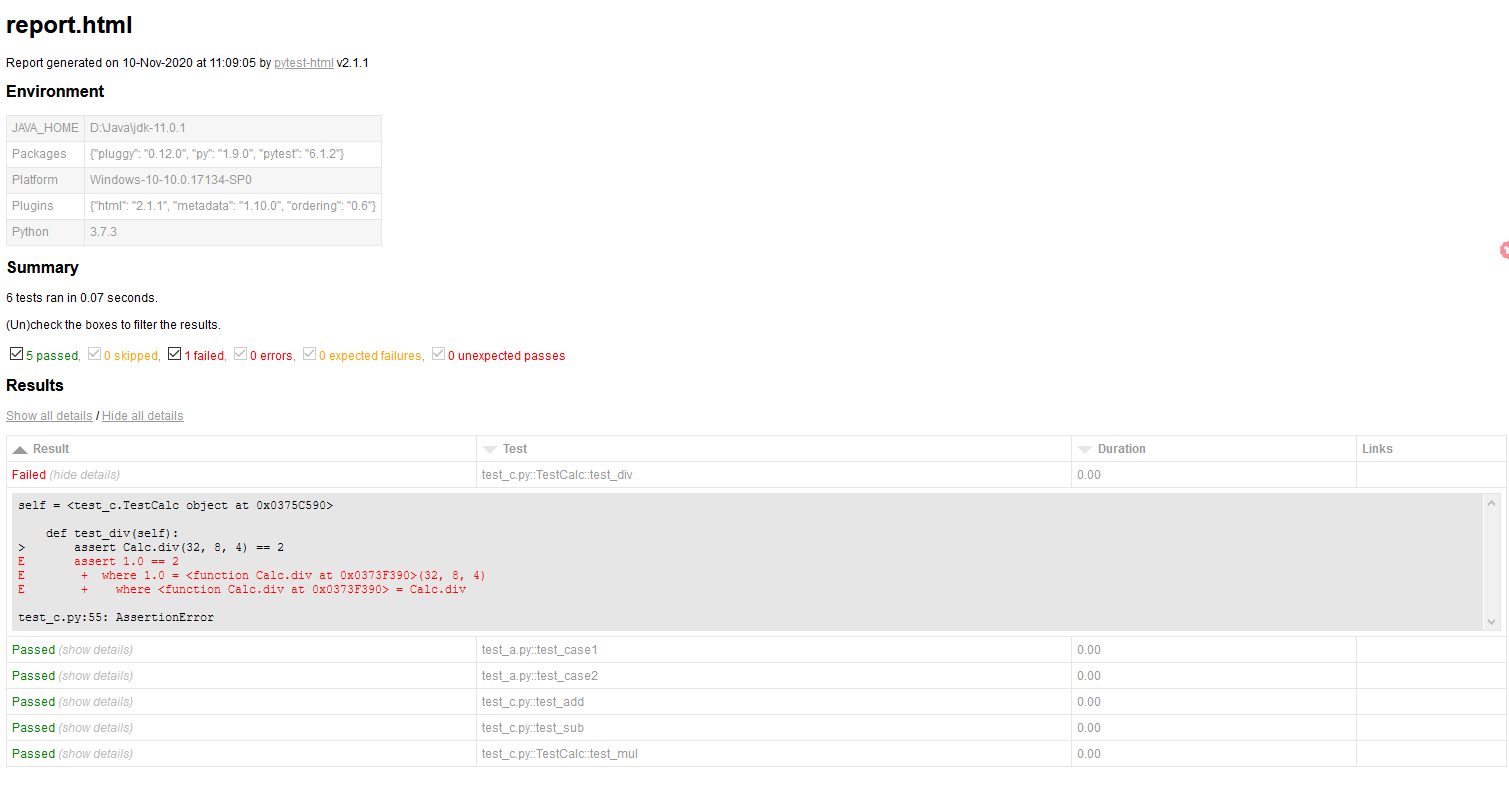
5、生成pytest測試報告
- 安裝包:pip install pytest-html
- 執(zhí)行命令:pytest --html=report.html
-
生成report.html 測試報告
![]() 6、setup 和 teardown 函數
6、setup 和 teardown 函數
import pytest class Test_ST(): def setup(self): print("------setup------") def teardown(self): print("------teardown------") def test_001(self): assert True def test_002(self): assert False
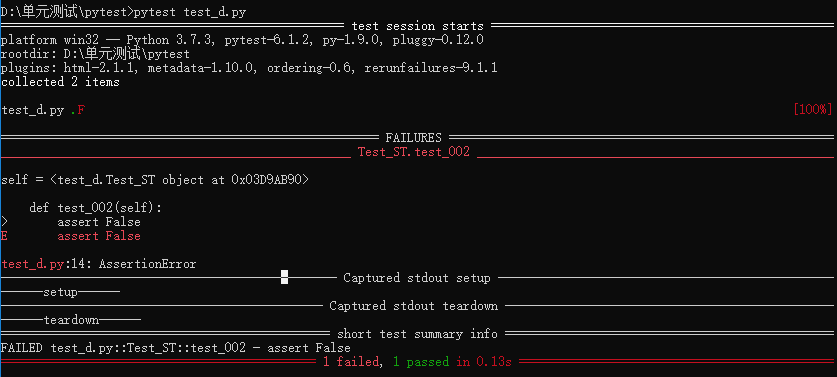
7、確定執(zhí)行順序
1)安裝包:
pip install pytest-ordering
2)使用 @pytest.mark.run(order=x) 標記被測試函數
3)運行的順序由order傳入的參數決定,order從小到大的順序執(zhí)行
import pytest class Test_ST(): @pytest.mark.run(order=3) #第三個被執(zhí)行 def test_001(self): print("001...") assert True @pytest.mark.run(order=2) #第二個被執(zhí)行 def test_002(self): print("002...") assert True @pytest.mark.run(order=1) #第一個被執(zhí)行 def test_003(self): print("003...") assert True
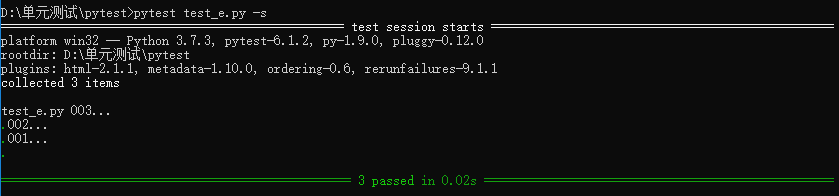
8、@pytest.fixture
pytest中加入fixture裝飾器來標記固定的工廠函數,使測試能夠可靠、重復地執(zhí)行,fixture函數可以在測試執(zhí)行前和執(zhí)行后進行必要的準備和清理工作,和unitest測試框架中的setup、teardown類似。但是pytest fixture和傳統風格的setuo/teardown函數相比,有了巨大的改進:
1)fixture具有明確的名稱,并且通過在測試函數、模塊、類或整個項目中申明它們的使用來激活。
2)fixture是以模塊化的方式實現的,因為每個fixture名稱都會觸發(fā)fixture函數,其本身也可以使用其他fixture、
3)fixture管理從簡單的單元擴展到復制的函數測試,允許根據配置和組件選項參數化fixture和測試,或者在函數、類、模塊或整個測試會話范圍內重復使用fixture。
fixture(scope='function',params=None,autouse=False,ids=None,name=None):
scope:被標記方法的作用域,有四個級別參數
"function"(默認),作用于每個測試方法,每個test都運行一次
"class",作用于整個類,每個class的所有test只運行一次
"module",作用于每個模塊,每個module的所有test只運行一次
"session",作用于整個session,每個session只運行一次
params:(list類型)提供參數數據,供調用標記方法的函數使用。
autouse:如果True,則為所有測試激活fixture func可以看到它。如果為False則顯示需要參考來激活fixture。
ids:每個字符串id的列表,每個字符串對應于params這樣他們就是測試ID的一部分。如果沒有提供ID它們將從params自動生成
name:fixture的名稱。這默認為裝飾函數的名稱。如果fixture在定義它的統一模塊中使用,夾具的功能名稱將被請求夾具的功能arg遮蔽,解決這個問題的一種方法時將裝飾函數命令"fixture_<fixturename>"然后使用"@pytest.fixture(name='<fixturename>')"。
使用場景:
-
作為參數引用
- 作為函數引用
- 設置自動執(zhí)行
-
設置作用域為function
- 設置作用域class
- 設置作用域module
-
設置作用域為 session
- 參數化
9、@pytest.mark
使用方法舉例:@pytest.mark.skipif(condition,reason=None)
參數:
condition:跳過的條件,True(跳過、不執(zhí)行)/False(不跳過、執(zhí)行),必傳參數
reason:標注原因
作用:
1)跳過測試函數:@pytest.mark.skipif(2>1,reason="故意的")
2)標記函數為失敗函數:@pytest.mark.xfail(True,reason="故意的")
3)傳參(要傳參數的名稱,且和參數化中定義的一致):
單個參數:@pytest.mark.parametrize('name', ["tom", "lisa", "lucy"])
多個參數:@pytest.mark.parametrize("username,password",[('wang','wang123'),('li','li23'),('zhao','zhao123')])

 6、setup 和 teardown 函數
6、setup 和 teardown 函數
 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號