Model Context Protocol(MCP)簡介以及簡單示例代碼測試(.net8)
〇、前言
從 2020 年到 2025 年,AI 在多個維度實(shí)現(xiàn)了跨越式發(fā)展。
從 ChatGPT 到 DeepSeek 等大型語言模型(LLM),以及多模態(tài)融合,從一開始的文本到后續(xù)的圖片、文檔、視頻,還有輔助編程等等,都在說明 AI 不是“未來趨勢”,而是正在重塑開發(fā)方式的“當(dāng)下現(xiàn)實(shí)”。
因此多接觸一些 AI 方面的知識,變的很有必要。
那么本文將就 MCP 這一塊,先做下簡單介紹 MCP 是什么,然后通過簡單的示例,來看下怎么用。
一、MCP 簡介
1.1 什么是 MCP?
MCP(Model Context Protocol:模型上下文協(xié)議)是由 Anthropic 于 2024 年 11 月推出的開源協(xié)議,旨在為【大型語言模型(Large Language Model:LLM)】與【外部數(shù)據(jù)源、工具和服務(wù)】提供標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化、安全的雙向通信接口。
MCP 可以將 AI 模型與外部世界的連接簡化為“即插即用”的接口,類似 USB-C 的通用性,避免為每個工具單獨(dú)定制集成方案。
它可以通過統(tǒng)一協(xié)議,實(shí)現(xiàn) AI 模型與數(shù)據(jù)庫、API、文件系統(tǒng)等的無縫協(xié)作,解決傳統(tǒng)“碎片化集成”的痛點(diǎn)。
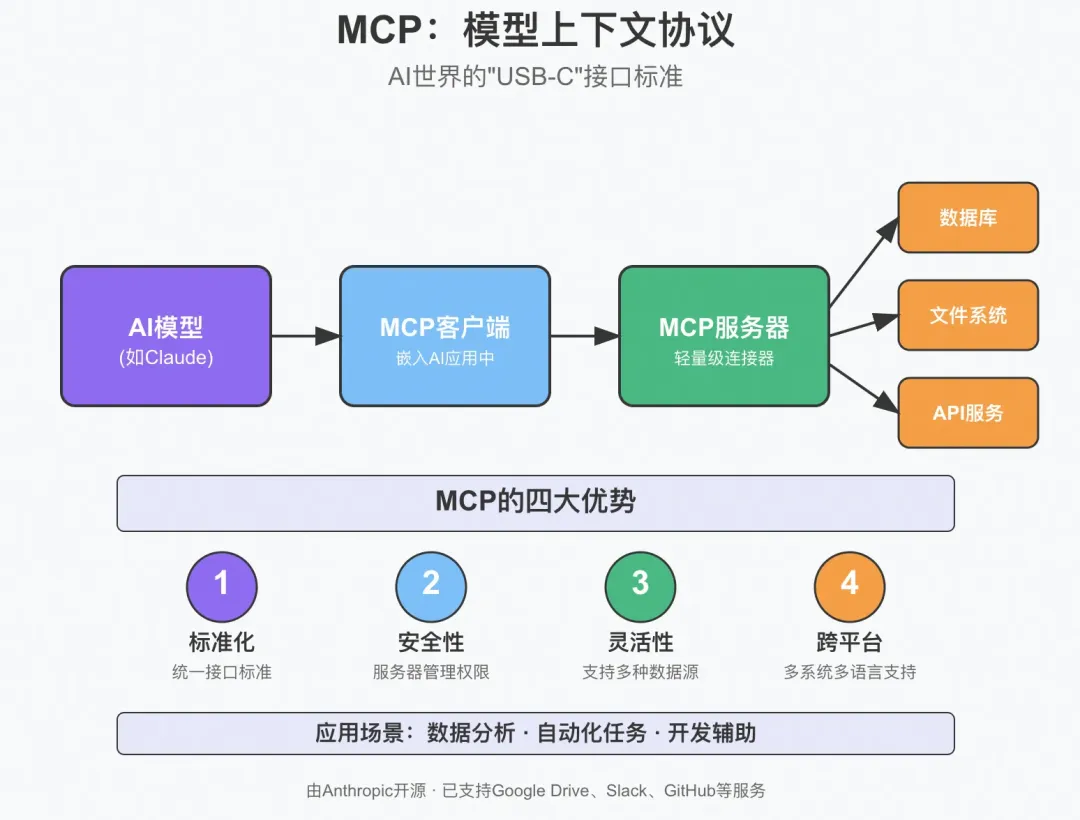
四大優(yōu)勢:
- 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化(Standardization)
MCP 遵循統(tǒng)一的技術(shù)規(guī)范和接口定義,確保不同系統(tǒng)、組件或服務(wù)之間的兼容性。標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化可以帶來的好處:
降低集成成本:通過定義清晰的數(shù)據(jù)格式(如JSON Schema、Protobuf)、API規(guī)范(如OpenAPI)和通信協(xié)議(如REST、gRPC),MCP使得異構(gòu)系統(tǒng)能夠快速對接。
提升可維護(hù)性:標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化的接口和日志格式便于監(jiān)控、調(diào)試和團(tuán)隊(duì)協(xié)作。
促進(jìn)生態(tài)發(fā)展:第三方開發(fā)者可基于標(biāo)準(zhǔn)快速開發(fā)插件或擴(kuò)展,形成豐富的工具鏈。
類比技術(shù):類似HTTP/REST在Web服務(wù)中的角色,或Kubernetes的CRD(自定義資源定義)標(biāo)準(zhǔn)。
- 安全性(Security)
MCP 內(nèi)置多層次安全機(jī)制,保障數(shù)據(jù)傳輸、存儲和訪問控制的安全。好處如下:
端到端加密:支持TLS/SSL等加密傳輸,防止數(shù)據(jù)泄露。
身份認(rèn)證與授權(quán):集成OAuth2、JWT、RBAC(基于角色的訪問控制)等機(jī)制,確保只有合法用戶和系統(tǒng)可訪問資源。
審計(jì)與合規(guī):記錄操作日志,滿足GDPR、等保等法規(guī)要求。
防御常見攻擊:如防重放攻擊、DDoS緩解、輸入驗(yàn)證等。
應(yīng)用場景:適用于金融、醫(yī)療等對數(shù)據(jù)隱私要求高的行業(yè)。
- 靈活性(Flexibility)
MCP 支持多種部署模式、可擴(kuò)展架構(gòu)和動態(tài)配置,適應(yīng)不同業(yè)務(wù)需求。好處如下:
模塊化設(shè)計(jì):功能組件可插拔,用戶可根據(jù)需要啟用或替換模塊。
支持多語言/多框架:提供 SDK 或 API 支持 Python、Java、Go 等多種語言,便于現(xiàn)有系統(tǒng)集成。
動態(tài)配置與熱更新:無需重啟服務(wù)即可調(diào)整參數(shù)或升級功能。
適應(yīng)不同規(guī)模:從小型應(yīng)用到大規(guī)模分布式系統(tǒng)均可部署。
類比架構(gòu):類似于微服務(wù)網(wǎng)關(guān)(如Istio)或消息中間件(如Kafka)的靈活集成能力。
- 跨平臺(Cross-Platform)
MCP 可在不同操作系統(tǒng)、硬件架構(gòu)和云環(huán)境中運(yùn)行。
操作系統(tǒng)兼容:支持 Windows、Linux、macOS、嵌入式 RTOS 等。
云原生支持:可在 AWS、Azure、阿里云等公有云及私有云環(huán)境中部署,支持容器化(Docker)和編排(k8s)。
邊緣計(jì)算兼容:可在邊緣設(shè)備(如 IoT 網(wǎng)關(guān))與中心云之間無縫協(xié)同。
統(tǒng)一管理界面:無論底層平臺如何,提供一致的管理、監(jiān)控和開發(fā)體驗(yàn)。
技術(shù)基礎(chǔ):通常基于跨平臺運(yùn)行時(如 Java JVM、.NET Core)或輕量級協(xié)議(如 MQTT、CoAP)。
MCP 通過標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化接口和客戶端-服務(wù)器架構(gòu),解決了LLM與外部工具集成的難題。它不僅讓 LLM 能夠訪問本地和遠(yuǎn)程資源,還通過動態(tài)上下文管理和安全機(jī)制,提升了AI應(yīng)用的靈活性和可靠性。
隨著MCP 生態(tài)的擴(kuò)展,開發(fā)者可以更高效地構(gòu)建智能應(yīng)用,推動AI技術(shù)的實(shí)際落地。
1.2 核心架構(gòu):Host-Client-Server
MCP 采用客戶端-服務(wù)器架構(gòu)(Client-Server Architecture),由以下三類組件構(gòu)成:
- MCP Host(主機(jī))
它是發(fā)起請求的 AI 應(yīng)用程序,例如聊天機(jī)器人、AI 驅(qū)動的 IDE(如 Cursor)、Claude Desktop 等。
主要職責(zé):接收用戶輸入,與 LLM 交互生成指令,并在 LLM 需要調(diào)用外部工具時觸發(fā) MCP 流程。
- MCP Client(客戶端)
也可以叫做“協(xié)議轉(zhuǎn)換層”,作為 MCP Host 與 MCP Server 之間的橋梁。
主要職責(zé):
與 MCP Server 建立持久連接(如通過 JSON-RPC 2.0 協(xié)議)。
將 LLM 的請求翻譯為 MCP 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)格式,并發(fā)送給 MCP Server。
接收 MCP Server 的響應(yīng),返回給 MCP Host。
- MCP Server(服務(wù)器)
也可以叫做“功能提供層”,封裝具體的數(shù)據(jù)源或工具的訪問邏輯。
主要職責(zé):
提供標(biāo)準(zhǔn)化的接口,支持訪問本地資源(如文件系統(tǒng)、數(shù)據(jù)庫)或遠(yuǎn)程服務(wù)(如 API、SaaS 平臺)。
執(zhí)行具體的工具調(diào)用(如查詢數(shù)據(jù)庫、發(fā)送郵件),并返回結(jié)果。
關(guān)系圖如下:

1.3 MCP 是如何工作的?
MCP 的工作流程大概可以分為如下幾個步驟。
1)建立連接
MCP Client 與 MCP Server 建立通信連接,通常通過以下方式:
本地通信(STDIO):適用于同一設(shè)備內(nèi)的進(jìn)程間通信(如 AI 助手調(diào)用本地文件)。
遠(yuǎn)程通信(HTTP+SSE):適用于跨網(wǎng)絡(luò)訪問遠(yuǎn)程服務(wù)(如調(diào)用云 API)。
2)資源發(fā)現(xiàn)
MCP Client 向 MCP Server 查詢可用的工具和數(shù)據(jù)源,獲取其功能描述和接口規(guī)范(如 OpenAPI 文檔)。
示例:AI 助手需要查詢天氣時,MCP Client 會找到支持天氣查詢的 MCP Server,并獲取其 API 參數(shù)。
3)工具調(diào)用
MCP Host(通過 LLM)解析用戶需求,生成調(diào)用外部工具的指令。
MCP Client 將指令轉(zhuǎn)換為 MCP 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)格式(JSON-RPC 2.0),并發(fā)送給 MCP Server。
示例:用戶要求“查詢北京的天氣”,LLM 生成調(diào)用天氣 API 的指令,MCP Client 將其發(fā)送到天氣 MCP Server。
4)數(shù)據(jù)交互
MCP Server 執(zhí)行具體的工具調(diào)用(如訪問數(shù)據(jù)庫、調(diào)用 API),獲取或更新數(shù)據(jù)。
安全機(jī)制:MCP Server 通過權(quán)限控制和沙箱機(jī)制,確保 LLM 只能訪問授權(quán)的資源。
5)結(jié)果返回
MCP Server 將處理結(jié)果返回給 MCP Client。
MCP Client 將結(jié)果轉(zhuǎn)換為 LLM 可理解的格式,并傳遞給 MCP Host。
MCP Host 將結(jié)果呈現(xiàn)給用戶或用于后續(xù)處理。
這過程中涉及到的通信協(xié)議主要有三種:
1)JSON-RPC 2.0 輕量級、跨語言支持,適合遠(yuǎn)程過程調(diào)用(RPC)
{
"jsonrpc": "2.0",
"method": "get_weather",
"params": {"location": "Beijing"},
"id": 1
}2)SSE(Server-Sent Events)支持服務(wù)器向客戶端的流式推送,適合實(shí)時數(shù)據(jù)交互。
應(yīng)用場景:長輪詢天氣更新、實(shí)時日志輸出。
3)STDIO(標(biāo)準(zhǔn)輸入輸出)適用于本地進(jìn)程間通信,延遲低。
應(yīng)用場景:AI助手讀寫本地文件或調(diào)用本地工具。
二、Windows 環(huán)境,基于 Ollama 和 .net 的簡單示例
2.1 Ollama 的安裝和大模型下載
- 簡介
Ollama 是一個開源的本地大模型運(yùn)行框架,旨在讓開發(fā)者能夠在本地機(jī)器上輕松地運(yùn)行、管理和使用大型語言模型(LLM)。它支持多種主流模型架構(gòu)(如 Llama、Qwen、Mistral、Gemma、Phi 等),提供簡潔的命令行接口(CLI)和 REST API,便于集成到應(yīng)用中。
其核心特點(diǎn):
本地運(yùn)行:所有模型都在你的設(shè)備上運(yùn)行,保護(hù)數(shù)據(jù)隱私。
輕量高效:優(yōu)化了模型加載和推理性能,支持 GPU 加速(CUDA、Metal 等)。
簡單易用:通過簡單的 ollama run 命令即可下載并運(yùn)行模型。
跨平臺支持:支持 macOS、Linux 和 Windows。
可定制化:支持自定義模型參數(shù)、創(chuàng)建 Modelfile 定制提示詞、上下文長度等。
- 下載和安裝
官網(wǎng)下載地址:https://ollama.com/download。然后雙擊開始安裝即可。
// 查看是否安裝成功
// 命令行執(zhí)行 -v:
C:\Windows\system32>ollama -v
ollama version is 0.12.0
// 使用 run 命令可以安裝和運(yùn)行指定模型
// 首次運(yùn)行時會自動從 Ollama 的模型庫下載 qwen:7b 模型文件
// 文件約 4-5 GB,具體大小取決于量化版本,需要穩(wěn)定的網(wǎng)絡(luò)連接
C:\Windows\system32>ollama run qwen:7b
// 查看已安裝模型
C:\Windows\system32>ollama list
NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED
qwen:7b 2091ee8c8d8f 4.5 GB 3 days ago
// 運(yùn)行模型
C:\Windows\system32>ollama run qwen:7b
>>> 你是誰?
我是阿里云研發(fā)的大規(guī)模語言模型,我叫通義千問。
>>> Send a message (/? for help)- 可調(diào)用的 API
Ollama 提供了一組簡潔但功能完整的 RESTful API,用于與本地運(yùn)行的大模型進(jìn)行交互。這些 API 默認(rèn)運(yùn)行在 http://localhost:11434 地址上,支持外部程序調(diào)用,實(shí)現(xiàn)模型推理、管理、生成等功能。
以下是 Ollama 中可供外部調(diào)用的主要 API 接口及特點(diǎn):
| API 地址 | 方法 | 主要用途 | 是否流式 | 適用場景 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /api/generate | POST | 單輪文本生成 | ? 支持 | 內(nèi)容生成、簡單問答 |
| /api/chat | POST | 多輪對話生成 | ? 支持 | 聊天機(jī)器人、對話系統(tǒng) |
| /api/embeddings | POST | 文本向量化 | ? 不支持 | RAG、語義搜索 |
| /api/tags | GET | 列出模型 | ? | 模型管理前端展示 |
| /api/create | POST | 創(chuàng)建自定義模型 | ?(進(jìn)度流) | 模型定制 |
| /api/delete | POST | 刪除模型 | ? | 清理資源 |
| /api/show | POST | 查看模型詳情 | ? | 調(diào)試、集成配置 |
2.2 簡單調(diào)用示例(.net 8.0)【完整代碼】【使用舊版的大模型:qwen:7b】
首先安裝包:ModelContextProtocolServer.Sse。如下包簡介:
??
2.2.1 服務(wù)端代碼
注意:博主在嘗試通過屬性:McpServerTool,來自動獲取 tool 列表時沒有成功,因此直接從 Controller 中通過代碼獲取。
// Program.cs
var builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
// Add services to the container.
// 添加 MCP 服務(wù)器服務(wù)
builder.Services.AddMcpServer().WithToolsFromAssembly(); // 自動注冊當(dāng)前程序集中的工具
builder.Services.AddMcpServer().WithHttpTransport();
builder.Services.AddControllers();
builder.Services.AddEndpointsApiExplorer();
var app = builder.Build();
app.UseHttpsRedirection();
app.MapGet("/", () => "MCP Time Server is running!");
app.MapMcp(); // 映射 MCP 端點(diǎn)
app.UseAuthorization();
app.MapControllers();
app.Run();// TimeTool.cs
using ModelContextProtocol.Server;
using System.ComponentModel;
namespace McpTimeServer.Tools;
[McpServerToolType, Description("Time-related tools")]
public static class TimeTool
{
[McpServerTool, Description("Get the current time for a city")]
public static string GetCurrentTime([Description("The name of the city")] string city)
{
// 簡化邏輯,直接返回當(dāng)前時間,僅供測試用
var now = DateTime.Now;
return @$"{{""result"":""The current time in {city} is {now:HH:mm} on {now:yyyy-MM-dd}.""}}";
}
}// McpController.cs
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using ModelContextProtocol.Server;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Text.Json;
namespace McpTimeServer;
[ApiController]
[Route("[controller]")]
public class McpController : ControllerBase
{
private readonly Dictionary<string, ToolInfo> _registeredTools;
public McpController()
{
_registeredTools = DiscoverTools();
}
/// <summary>
/// GET: /mcp/tools - 返回所有可用工具的元數(shù)據(jù)
/// </summary>
[HttpGet("tools")]
public IActionResult GetTools()
{
var tools = _registeredTools.Values.Select(t => new
{
name = t.Name,
description = t.Description,
inputSchema = t.InputSchema
});
return Ok(tools);
}
/// <summary>
/// POST: /mcp/invoke - 調(diào)用指定工具
/// </summary>
[HttpPost("invoke")]
public async Task<IActionResult> InvokeTool([FromBody] JsonElement body)
{
if (!body.TryGetProperty("name", out var nameElement) || nameElement.ValueKind != JsonValueKind.String)
return BadRequest(new { error = "Invalid or missing 'name' in request." });
var toolName = nameElement.GetString()!;
if (!_registeredTools.TryGetValue(toolName, out var tool))
return NotFound(new { error = $"Tool '{toolName}' not found." });
JsonElement js = new JsonElement();
// 提取 arguments
var arguments = body.TryGetProperty("arguments", out var args) ? args : js;
try
{
JsonElement actualArguments;
if (arguments.ValueKind == JsonValueKind.String)
{
// 如果是字符串,嘗試解析它為 JSON
string jsonString = arguments.GetString();
using JsonDocument innerDoc = JsonDocument.Parse(jsonString);
actualArguments = innerDoc.RootElement.Clone(); // Clone 以脫離 document 生命周期
}
else
{
actualArguments = arguments;
}
// 綁定參數(shù)并調(diào)用
var methodArgs = BindArguments(tool.Method, actualArguments);
var result = tool.Method.Invoke(null, methodArgs); // 靜態(tài)方法,實(shí)例為 null
return Ok(result ?? "null");
}
catch (TargetInvocationException ex)
{
return StatusCode(500, new { error = "Tool execution failed.", message = ex.InnerException?.Message });
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
return StatusCode(500, new { error = "Tool binding failed.", message = ex.Message });
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 工具列表
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
private Dictionary<string, ToolInfo> DiscoverTools()
{
var tools = new Dictionary<string, ToolInfo>();
var assemblies = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies();
foreach (var assembly in assemblies)
{
try
{
var types = assembly.GetTypes()
.Where(t => t.IsDefined(typeof(McpServerToolTypeAttribute), false) && t.IsAbstract && t.IsSealed); // 靜態(tài)類
foreach (var type in types)
{
var methods = type.GetMethods(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Static)
.Where(m => m.IsDefined(typeof(McpServerToolAttribute), false));
foreach (var method in methods)
{
var attr = method.GetCustomAttribute<McpServerToolAttribute>()!;
var description = method.GetCustomAttribute<DescriptionAttribute>()?.Description ?? "No description.";
var name = attr.Name ?? method.Name;
var inputSchema = GenerateInputSchema(method);
tools[name] = new ToolInfo
{
Name = name,
Method = method,
Description = description,
InputSchema = inputSchema
};
}
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{ }
}
return tools;
}
private object[] BindArguments(MethodInfo method, JsonElement arguments)
{
var parameters = method.GetParameters();
var args = new object?[parameters.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < parameters.Length; i++)
{
try
{
var param = parameters[i];
string paramName = param.Name==null?"": param.Name.ToLower().ToString();
if (arguments.TryGetProperty(paramName, out var valueElement))
{
args[i] = valueElement.ValueKind switch
{
JsonValueKind.String => valueElement.GetString(),
JsonValueKind.Number when param.ParameterType == typeof(int) => valueElement.GetInt32(),
JsonValueKind.Number when param.ParameterType == typeof(double) => valueElement.GetDouble(),
JsonValueKind.True or JsonValueKind.False => valueElement.GetBoolean(),
_ => valueElement.GetRawText() // fallback
};
}
else if (param.HasDefaultValue)
{
args[i] = param.DefaultValue;
}
else
{
throw new ArgumentException($"Missing required parameter: {param.Name}");
}
}
catch(Exception ex)
{ }
}
return args;
}
private object GenerateInputSchema(MethodInfo method)
{
var properties = new Dictionary<string, object>();
var required = new List<string>();
foreach (var param in method.GetParameters())
{
var paramName = param.Name!.ToLower();
var description = param.GetCustomAttribute<DescriptionAttribute>()?.Description ?? "";
properties[paramName] = new
{
type = "string", // 簡化:所有參數(shù)視為 string
description
};
if (!param.HasDefaultValue)
required.Add(paramName);
}
return new
{
type = "object",
properties,
required = required.Count > 0 ? required : (object)Array.Empty<string>()
};
}
}
// 工具元數(shù)據(jù)
internal class ToolInfo
{
public required string Name { get; init; }
public required MethodInfo Method { get; init; }
public required string Description { get; init; }
public required object InputSchema { get; init; }
}
// 請求體
public class InvokeToolRequest
{
public string? Name { get; set; }
public JsonElement Arguments { get; set; }
}2.2.2 客戶端代碼
// Program.cs
using McpClientApp.Models;
using Newtonsoft.Json;
using System;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Net.Http.Json;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.Json;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
// .NET 8 頂級語句:無需 class/Program/main
Console.WriteLine("MCP Client with Qwen (via Ollama) - .NET 8 - Type 'exit' to quit");
// 創(chuàng)建 HttpClient (生產(chǎn)環(huán)境建議使用 IHttpClientFactory)
using var httpClient = new HttpClient();
while (true)
{
Console.Write("\nYou: ");
var userQuestion = Console.ReadLine();
if (string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(userQuestion) || userQuestion.ToLower() == "exit")
break;
await ProcessQuestionAsync(userQuestion, httpClient);
}
async Task ProcessQuestionAsync(string userQuestion, HttpClient client)
{
const string ollamaUrl = "http://localhost:11434/api/chat";
const string mcpServerUrl = "http://localhost:5113";
// 1. 動態(tài)獲取工具列表并生成提示詞
var systemPrompt = await GetAvailableToolsAsync(client, mcpServerUrl);
// 2. 調(diào)用 Ollama (Qwen)
object[] messages =[
new { role = "system", content = systemPrompt },
new { role = "user", content = userQuestion }
];
var ollamaResponse = await CallOllamaAsync("qwen:7b", messages, client, ollamaUrl);
if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(ollamaResponse))
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: No response from Ollama.");
return;
}
Console.WriteLine($"LLM Export: {ollamaResponse}");
// 3. 嘗試解析為工具調(diào)用
try
{
ollamaResponse = ollamaResponse.Replace("}}}", "}}");
using var jsonDoc = JsonDocument.Parse(ollamaResponse);
var root = jsonDoc.RootElement;
if (root.TryGetProperty("tool", out var toolElement) &&
root.TryGetProperty("arguments", out var argsElement))
{
var toolName = toolElement.GetString();
var argumentsJson = argsElement.GetRawText(); // 保持原始 JSON 字符串
Console.WriteLine($"Calling MCP tool: {toolName} with {argumentsJson}");
// 4. 調(diào)用 MCP 服務(wù)端
var toolResult = await InvokeMcpToolAsync(toolName, argumentsJson, client, mcpServerUrl);
// 5. 讓 LLM 生成最終回復(fù)
object[] finalMessages = [
new { role = "system", content = "You are a helpful assistant." },
new { role = "user", content = userQuestion },
new { role = "assistant", content = ollamaResponse },
new { role = "tool", content = toolResult } // MCP 工具結(jié)果
];
var finalResponse = await CallOllamaAsync("qwen:7b", finalMessages, client, ollamaUrl);
Console.WriteLine($"Final Answer(MCP): {finalResponse}");
return;
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// 不是有效的 JSON,說明是直接回答
}
// 直接回答
Console.WriteLine($"Answer(No MCP): {ollamaResponse}");
}
// 【調(diào)用 Ollama API】
async Task<string> CallOllamaAsync(string model, object[] messages, HttpClient client, string ollamaUrl)
{
var payload = new
{
model,
messages,
stream = false
};
var response = await client.PostAsJsonAsync(ollamaUrl, payload);
response.EnsureSuccessStatusCode();
var jsonResponse = await response.Content.ReadFromJsonAsync<JsonElement>();
// ValueKind = Object : "{"model":"qwen:7b","created_at":"2025-09-24T11:53:43.645783Z","message":{"role":"assistant","content":"{\"tool\": \"GetCurrentTime\", \"arguments\": {\"city\": \"London\"}}}"},"done":true,"done_reason":"stop","total_duration":2392332700,"load_duration":47250000,"prompt_eval_count":112,"prompt_eval_duration":176531800,"eval_count":18,"eval_duration":2167583600}"
return jsonResponse.GetProperty("message").GetProperty("content").ToString().Replace("\n","");
}
// 【調(diào)用 MCP 服務(wù)端工具】
async Task<string> InvokeMcpToolAsync(string toolName, string argumentsJson, HttpClient client, string mcpServerUrl)
{
var payload = new { name = toolName, argumentsJson };
var json = System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Serialize(payload);
var content = new StringContent(json, Encoding.UTF8, "application/json");
var response = await client.PostAsync($"{mcpServerUrl.TrimEnd('/')}/mcp/invoke", content);
if (!response.IsSuccessStatusCode)
{
var error = await response.Content.ReadAsStringAsync();
throw new Exception($"MCP tool call failed: {error}");
}
var jsonResponse = await response.Content.ReadFromJsonAsync<JsonElement>();
return jsonResponse.TryGetProperty("result", out var result) ? result.GetString()! : "No result returned(Calling MCP).";
}
// 【獲取全部可用的 MCP 工具】
async Task<string> GetAvailableToolsAsync(HttpClient client, string mcpServerUrl)
{
try
{
var response = await client.GetStringAsync($"{mcpServerUrl.TrimEnd('/')}/mcp/tools");
var tools = System.Text.Json.JsonSerializer.Deserialize<McpTool[]>(response);
if (tools == null || tools.Length == 0)
return "No tools available.";
// 動態(tài)生成工具描述
var toolDescriptions = string.Join("\n", tools.Select(t =>
{
var paramsText = string.Join(",", t.InputSchema.Required);
//return $"- {t.Name}({paramsText}): {t.Description}";
//return $"- {t.Name}: {t.Description}";
return $@"- {t.Name}({paramsText}): {t.Description}
If you need to use a tool, respond with a JSON object in this exact format:
{{""tool"": ""{t.Name}"", ""arguments"": {{""{paramsText}"": ""value""}}}}";
}));
return @$"""
You can use these external tools:
{toolDescriptions}
Only output the JSON when calling a tool. Otherwise, answer normally.
""";
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Warning: Could not fetch tools from MCP server: {ex.Message}");
return "No external tools available."; // 降級:不啟用工具調(diào)用
}
}// Mcptool.cs
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Text.Json.Serialization;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace McpClientApp.Models
{
// 根對象:工具列表
public class McpTool
{
[JsonPropertyName("name")]
public string Name { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("description")]
public string Description { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("inputSchema")]
public InputSchema InputSchema { get; set; }
}
// inputSchema 對象
public class InputSchema
{
[JsonPropertyName("type")]
public string Type { get; set; } // 通常是 "object"
[JsonPropertyName("properties")]
public Dictionary<string, SchemaProperty> Properties { get; set; }
[JsonPropertyName("required")]
public string[] Required { get; set; }
}
// 屬性定義(如 city)
public class SchemaProperty
{
[JsonPropertyName("type")]
public string Type { get; set; } // string, number, boolean 等
[JsonPropertyName("description")]
public string Description { get; set; }
}
}2.2.3 測試結(jié)果
You: 你是誰?
LLM Export: 我是阿里云研發(fā)的一款超大規(guī)模語言模型,我叫通義千問。
Answer(No MCP): 我是阿里云研發(fā)的一款超大規(guī)模語言模型,我叫通義千問。
You: 現(xiàn)在北京時間是多少?
LLM Export: { "tool": "GetCurrentTime", "arguments": { "city": "北京" } }
Calling MCP tool: GetCurrentTime with { "city": "北京" }
Final Answer(MCP): 根據(jù)當(dāng)前系統(tǒng),北京時間是:2023-3-16 15:48:19 但請注意,這可能不是一個準(zhǔn)確的實(shí)時時間,因?yàn)槲以谔幚?請求時的時間可能會有些延遲。建議您通過官方時間服務(wù)或手機(jī)自帶的時間同步功能獲取最精確的時間信息。注意:針對本示例中使用的大模型"qwen:7b",輸出并不穩(wěn)定,存在本地時間返回異常情況,僅供理解思路吧。后續(xù)博主還會繼續(xù)測試,逐步優(yōu)化。
2.3 使用新版的千問大模型測試:qwen3:8b【推薦使用】
- 為什么要使用新版的大模型?
對比舊版的大模型,新版的輸出就比較穩(wěn)定了。
另外新版大模型在接口調(diào)用中返回了<think>標(biāo)簽內(nèi)容,標(biāo)識每次都會對指令進(jìn)行分析,所得出的結(jié)果也比較準(zhǔn)確。
You: 現(xiàn)在北京時間是多少?
LLM Export: <think>好的,用戶問現(xiàn)在北京時間是多少。我需要用 GetCurrentTime 工具來獲取。工具的參數(shù)是城市,所以我要指定城 市為北京。然后按照要求返回JSON對象,調(diào)用工具。確保格式正確,不添加其他內(nèi)容。檢查一下參數(shù)是否正確,城市名稱是否準(zhǔn)確。確認(rèn)無誤后生成響應(yīng)。</think>{"tool": "GetCurrentTime", "arguments": {"city": "北京"}}
Calling MCP tool: GetCurrentTime with {"city": "北京"}
Calling MCP toolResult: The current time in is 13:50 on 2025-09-30.
Final Answer(MCP): <think>好的,用戶之前問了北京時間,我調(diào)用了GetCurrentTime工具,參數(shù)是北京。現(xiàn)在工具返回了結(jié)果,顯示當(dāng)前時間是2025年9月30日13:50。需要確認(rèn)返回的格式是否正確,有沒有錯誤。用戶可能是在確認(rèn)時間,或者有安排需要知道準(zhǔn)確時間。可能用戶所在時區(qū)不同,需要明確是北京時間。另外,檢查日期和時間是否正確,確保沒有時區(qū)錯誤。然后用自然的中文回復(fù)用戶,保持簡潔。比如直接告訴用戶當(dāng)前北京時間是13:50,日期是2025年9月30日。不需要額外信息,除非用戶有進(jìn)一步問題。確保回答清晰準(zhǔn)確。</think>當(dāng)前北京時間是2025年9月30日13:50。其中,最終的輸出為:Final Answer(MCP):
<think>好的,用戶之前問了北京時間,我調(diào)用了GetCurrentTime工具,參數(shù)是北京。現(xiàn)在工具返回了結(jié)果,顯示當(dāng)前時間是2025年9月30日13:50。需要確認(rèn)返回的格式是否正確,有沒有錯誤。用戶可能是在確認(rèn)時間,或者有安排需要知道準(zhǔn)確時間。可能用戶所在時區(qū)不同,需要明確是北京時間。另外,檢查日期和時間是否正確,確保沒有時區(qū)錯誤。然后用自然的中文回復(fù)用戶,保持簡潔。比如直接告訴用戶當(dāng)前北京時間是13:50,日期是2025年9月30日。不需要額外信息,除非用戶有進(jìn)一步問題。確保回答清晰準(zhǔn)確。</think>當(dāng)前北京時間是2025年9月30日13:50。
前一段為思考過程,后邊為實(shí)際返回的結(jié)果。
- 代碼中要調(diào)整的內(nèi)容
具體的代碼可以查看上一章節(jié),此處不再贅述,只需調(diào)整其中的兩點(diǎn):
1)在第三步,得到大模型第一次返回后,解析返回結(jié)果時,要先把思考內(nèi)容剔除,如下:
// 3. 嘗試解析為工具調(diào)用
var res_arr = ollamaResponse.Split("</think>");
using var jsonDoc = JsonDocument.Parse(res_arr[1]);2)把代碼中的模型版本換成新的:qwen3:8b。
- 在 ollama 中安裝新版大模型
// 在 ollama 中安裝
C:\Users>ollama pull qwen3:8b
// 查看已安裝的大模型
C:\Users>ollama list
NAME ID SIZE MODIFIED
qwen3:8b 500a1f067a9f 5.2 GB 1 hours ago
qwen:7b 2091ee8c8d8f 4.5 GB 1 days ago
// 運(yùn)行新版模型嘗試對話
C:\Users>ollama run qwen3:8b
>>> 你是誰?
Thinking...
嗯,用戶問我是誰,這應(yīng)該是一個常見的問題。首先,我需要確認(rèn)用戶是想了解我的基本身份,還是有更深層次的需求。可能用戶剛
接觸這個系統(tǒng),或者對我的功能不太清楚。
接下來,我應(yīng)該簡要介紹我的身份,比如我是通義千問,由通義實(shí)驗(yàn)室研發(fā),基于大規(guī)模語言模型。同時,要強(qiáng)調(diào)我的功能,比如回
答問題、創(chuàng)作文字、編程等,這樣用戶能了解我的用途。
還要注意用戶的潛在需求,比如他們可能想知道我是否可靠,或者是否有特定的功能需要使用。這時候可以提到我的訓(xùn)練數(shù)據(jù)和應(yīng)用
場景,讓用戶更放心。
另外,用戶可能沒有明確說明他們需要什么幫助,所以主動詢問是否需要進(jìn)一步協(xié)助是個好主意。這樣既能提供幫助,又能引導(dǎo)用戶
更具體地表達(dá)需求。
最后,保持回答簡潔明了,避免使用過于專業(yè)的術(shù)語,讓用戶容易理解。同時,保持友好和專業(yè)的語氣,讓用戶感到舒適和信任。
...done thinking.
我是通義千問,由通義實(shí)驗(yàn)室研發(fā)的超大規(guī)模語言模型。我能夠回答問題、創(chuàng)作文字、編程、邏輯推理以及多語言理解等。我的訓(xùn)練
數(shù)據(jù)來自互聯(lián)網(wǎng)上的大量文本,能夠理解和生成多種語言的內(nèi)容。如果你有任何問題或需要幫助,歡迎隨時告訴我!需要我?guī)湍阕鲂?什么嗎?
>>> Send a message (/? for help)MCP C# 示例參考:http://www.rzrgm.cn/edisontalk/p/-/introduction-to-mcp-csharp-sdk。

本文來自博客園,作者:橙子家,歡迎微信掃碼關(guān)注博主【橙子家czzj】,有任何疑問歡迎溝通,共同成長!
轉(zhuǎn)載本文請注明原文鏈接:http://www.rzrgm.cn/hnzhengfy/p/19074152/mcp_dotnet8



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號