8.13信息學(xué)集訓(xùn)_數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu)
預(yù)習(xí)筆記
鏈表、棧、隊(duì)列
B3631 單向鏈表
實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),維護(hù)一張表(最初只有一個(gè)元素 \(1\))。需要支持下面的操作,其中 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 都是 \(1\) 到 \(10^6\) 范圍內(nèi)的正整數(shù),且保證任何時(shí)間表中所有數(shù)字均不相同,操作數(shù)量不多于 \(10^5\):
1 x y:將元素 \(y\) 插入到 \(x\) 后面;2 x:詢問 \(x\) 后面的元素是什么。如果 \(x\) 是最后一個(gè)元素,則輸出 \(0\);3 x:從表中刪除元素 \(x\) 后面的那個(gè)元素,不改變其他元素的先后順序。
輸入格式:第一行一個(gè)整數(shù) \(q\) 表示操作次數(shù);接下來 \(q\) 行,每行表示一次操作,操作具體間題目描述。
輸出格式:對于每個(gè)操作 2,輸出一個(gè)數(shù)字,用換行隔開。
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
6 1 1 99 1 99 50 1 99 75 2 99 3 75 2 1 |
75 99 |
【分析】模擬一個(gè)鏈表,但是需要支持 \(O(1)\) 的查詢,因?yàn)?\(x,y\in [1,10^6]\),所以使用 \(h[x]=idx\) 來記錄 \(x\) 是那個(gè)節(jié)點(diǎn)。
單向鏈表的實(shí)現(xiàn)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
struct Node {
int r, v;
} e[N];
int h[N], idx;
// h[x] 表示 x 所在節(jié)點(diǎn)下標(biāo)
void insert(int x, int y) {
h[y] = ++idx;
e[h[y]] = {e[h[x]].r, y};
e[h[x]].r = h[y];
}
int find(int x) {
if (e[h[x]].r == 0) return 0;
return e[e[h[x]].r].v;
}
void del(int x) {
if (e[h[x]].r == 0) return;
e[h[x]].r = e[e[h[x]].r].r;
}
int main() {
int q, op, x, y; cin >> q, insert(0, 1);
while (q--) {
cin >> op >> x;
switch (op) {
case 1: cin >> y, insert(x, y); break;
case 2: cout << find(x) << endl; break;
case 3: del(x); break;
}
}
return 0;
}
以下是雙向鏈表的實(shí)現(xiàn)
struct Node {
int l, r, v;
} e[N];
int h[N], idx;
// h[x] 表示 x 所在節(jié)點(diǎn)下標(biāo)
void insert(int x, int y) {
h[y] = ++idx;
e[h[y]] = {h[x], e[h[x]].r, y};
e[e[h[x]].r].l = e[h[x]].r = h[y];
}
int find(int x) {
if (e[h[x]].r == 0) return 0;
return e[e[h[x]].r].v;
}
void del(int x) {
e[e[h[x]].r].l = h[x];
e[h[x]].r = e[e[h[x]].r].r;
}
P1981 [NOIP2013 普及組] 表達(dá)式求值
給定一個(gè)只包含加法和乘法的算術(shù)表達(dá)式,請你編程計(jì)算表達(dá)式的值。
輸入一行需要計(jì)算的表達(dá)式,表達(dá)式中只包含數(shù)字、加法運(yùn)算符‘+’和乘法運(yùn)算符‘×’,且沒有括號,所有參與運(yùn)算的數(shù)字均為 0 到 pow(2,31)-1之間的整數(shù)。輸入數(shù)據(jù)保證這一行只有 0-9、+、× 這12種字符。
輸出一個(gè)整數(shù),表示這個(gè)表達(dá)式的值,當(dāng)答案長度多于4位時(shí),請只輸出最后4位,前導(dǎo)0不輸出。
輸入樣例:1+1*3+4
輸出樣例:8
【分析】模擬/棧
先觀察輸入數(shù)據(jù)的格式,一定是:a+b+b+b...
那么可以考慮先讀入 a,后面死循環(huán)讀入 +b,這樣就可以輕松完成數(shù)據(jù)分割。
由于有 *+,可以將 * 先處理了,后面對于 + 直接累加即可。
構(gòu)建一個(gè)數(shù)字棧,遍歷字符串,數(shù)字直接入棧;如果是運(yùn)算符,將當(dāng)前棧頂元素 a 與 b進(jìn)行計(jì)算,同時(shí)pop,計(jì)算的結(jié)果push。
最后累加棧內(nèi)全部元素即可。
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack<long long> sta;
int a,b,ans=0, mod=10000; char ch;
int main() {
cin>>a; a %= mod; sta.push(a);
while(cin>>ch>>b) {
b %= mod;
if(ch=='*') {
a = sta.top(); sta.pop();
sta.push(a*b%mod);
} else if(ch=='+') { sta.push(b); }
}
while(!sta.empty()) {
ans += sta.top(), sta.pop();
ans %= mod;
}
cout<<ans%mod; return 0;
}
P1449 后綴表達(dá)式
所謂后綴表達(dá)式是指這樣的一個(gè)表達(dá)式:式中不再引用括號,運(yùn)算符號放在兩個(gè)運(yùn)算對象之后,所有計(jì)算按運(yùn)算符號出現(xiàn)的順序,嚴(yán)格地由左而右新進(jìn)行(不用考慮運(yùn)算符的優(yōu)先級)。
如:3*(5–2)+7 對應(yīng)的后綴表達(dá)式為:3.5.2.-*7.+@。
'@'為表達(dá)式的結(jié)束符號,'.'為操作數(shù)的結(jié)束符號。字符串長度在1000內(nèi)。
輸入格式:后綴表達(dá)式
輸出格式:表達(dá)式的值
輸入樣例:3.5.2.-*7.+@
輸出樣例:16
【分析】模擬/棧
先觀察輸入數(shù)據(jù)的格式,一定是:a.a.+@
每個(gè)數(shù)字后面有一個(gè) .,可以據(jù)此進(jìn)行數(shù)據(jù)分割。
構(gòu)建一個(gè)數(shù)字棧,遍歷字符串,數(shù)字直接入棧;
如果是運(yùn)算符,將順序取出兩個(gè)棧頂元素 a,b 進(jìn)行計(jì)算,計(jì)算的結(jié)果push。
最后棧頂元素就是答案。
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
stack<int> sta; int a,b,c; char ch;
int main(){
while((ch=getchar())!='@'){
if(ch<='9' && ch>='0'){
a=a*10+ch-'0';
}else if(ch=='.'){
sta.push(a); a=0;
}else {
a=sta.top(),sta.pop();
b=sta.top(),sta.pop();
if(ch=='+'){ c = b+a; }
else if(ch=='-'){ c = b-a; }
else if(ch=='*'){ c = b*a; }
else if(ch=='/'){ c = b/a; }
sta.push(c); a=b=0;
}
}
cout<<c<<endl; return 0;
}
P5788 【模板】單調(diào)棧
給出項(xiàng)數(shù)為 \(n\) 的整數(shù)數(shù)列 \(a_{1 \dots n}\)。
定義函數(shù) \(f(i)\) 代表數(shù)列中第 \(i\) 個(gè)元素之后第一個(gè)大于 \(a_i\) 的元素的下標(biāo),即 \(f(i)=\min_{i<j\leq n, a_j > a_i} \{j\}\)。若不存在,則 \(f(i)=0\)。
試求出 \(f(1\dots n)\)。
輸入格式:第一行一個(gè)正整數(shù) \(n\)。第二行 \(n\) 個(gè)正整數(shù) \(a_{1\dots n}\)。
輸出格式:一行 \(n\) 個(gè)整數(shù) \(f(1\dots n)\) 的值。
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
5 1 4 2 3 5 |
2 5 4 5 0 |
【數(shù)據(jù)范圍】對于 \(100\%\) 的數(shù)據(jù),\(1 \le n\leq 3\times 10^6\),\(1\leq a_i\leq 10^9\)。
【分析】
- 求每個(gè)元素右邊第一個(gè)大于該元素的值的下標(biāo)。
- 維護(hù)一個(gè)單調(diào)棧,可以畫一下下面這個(gè)圖。

上圖是從左向右遍歷的單調(diào)遞減棧,也可以維護(hù)一個(gè)從右向左遍歷的單調(diào)遞增棧。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 3e6 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, a[N], st[N], hh, ans[N];
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
// 從左向右 : 維護(hù)一個(gè)單減棧
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (hh && a[st[hh]] < a[i]) {
ans[st[hh]] = i;
hh--;
}
st[++hh] = i;
}
// 從右向左 : 維護(hù)一個(gè)單增棧
/*hh = 0;
for (int i = n; i >= 1; i--) {
while (hh && a[st[hh]] <= a[i])
hh--;
ans[i] = st[hh];
st[++hh] = i;
}*/
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == n];
return 0;
}
P1886 滑動窗口 /【模板】單調(diào)隊(duì)列
有一個(gè)長為 \(n\) 的序列 \(a\),以及一個(gè)大小為 \(k\) 的窗口。現(xiàn)在這個(gè)從左邊開始向右滑動,每次滑動一個(gè)單位,求出每次滑動后窗口中的最大值和最小值。
例如:The array is \([1,3,-1,-3,5,3,6,7]\), and \(k = 3\)。
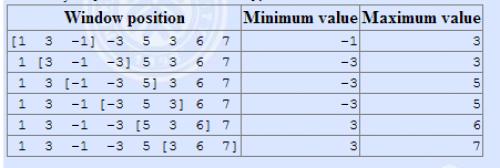
輸入格式: 輸入一共有兩行,第一行有兩個(gè)正整數(shù) \(n,k\)。第二行 \(n\) 個(gè)整數(shù),表示序列 \(a\)
輸出格式:輸出共兩行,第一行為每次窗口滑動的最小值;第二行為每次窗口滑動的最大值
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
8 3 1 3 -1 -3 5 3 6 7 |
-1 -3 -3 -3 3 3 3 3 5 5 6 7 |
【數(shù)據(jù)范圍】\(1\le k \le n \le 10^6\),\(a_i \in [-2^{31},2^{31})\)。
【分析】考慮兩個(gè)問題
- 如何確定窗口大小:可以通過下標(biāo)求差完成
- 如何確定窗口內(nèi)的最值:可以利用單調(diào)隊(duì)列完成
這里為了便于理解,我們畫一個(gè)樣例圖

#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, a[N], q[N], ans[N];
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i];
// 最小值 - 維護(hù)一個(gè)單調(diào)遞增隊(duì)列
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i]) tt--;
while (hh <= tt && i - q[hh] + 1 > m) hh++;
q[++tt] = i;
if (i >= m)
cout << a[q[hh]] << " \n"[i == n];
}
// 最大值 - 維護(hù)一個(gè)單調(diào)遞減隊(duì)列
hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] <= a[i]) tt--;
while (hh <= tt && i - q[hh] + 1 > m) hh++;
q[++tt] = i;
if (i >= m)
cout << a[q[hh]] << " \n"[i == n];
}
return 0;
}
P1901 發(fā)射站
某地有 \(N\) 個(gè)能量發(fā)射站排成一行,每個(gè)發(fā)射站 \(i\) 都有不相同的高度 \(H_i\),并能向兩邊(兩端的發(fā)射站只能向一邊)同時(shí)發(fā)射能量值為 \(V_i\) 的能量,發(fā)出的能量只被兩邊最近的且比它高的發(fā)射站接收。顯然,每個(gè)發(fā)射站發(fā)來的能量有可能被 \(0\) 或 \(1\) 或 \(2\) 個(gè)其他發(fā)射站所接受。
請計(jì)算出接收最多能量的發(fā)射站接收的能量是多少。
輸入格式:第 \(1\) 行一個(gè)整數(shù) \(N\)。第 \(2\) 到 \(N+1\) 行,第 \(i+1\) 行有兩個(gè)整數(shù) \(H_i\) 和 \(V_i\),表示第 \(i\) 個(gè)人發(fā)射站的高度和發(fā)射的能量值。
輸出格式:輸出僅一行,表示接收最多能量的發(fā)射站接收到的能量值。答案不超過 32 位帶符號整數(shù)的表示范圍。
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
3 4 2 3 5 6 10 |
7 |
【數(shù)據(jù)范圍】\(1\le N\le 10^6,1\le H_i\le 2\times 10^9,1\le V_i\le 10^4\)。
【分析】
- 法1:直接暴力模擬,左右查找合適的值,可以過 40%,會 TLE。
- 法2:維護(hù)單調(diào)棧(單調(diào)遞減棧:棧底到棧頂元素單調(diào)遞減)
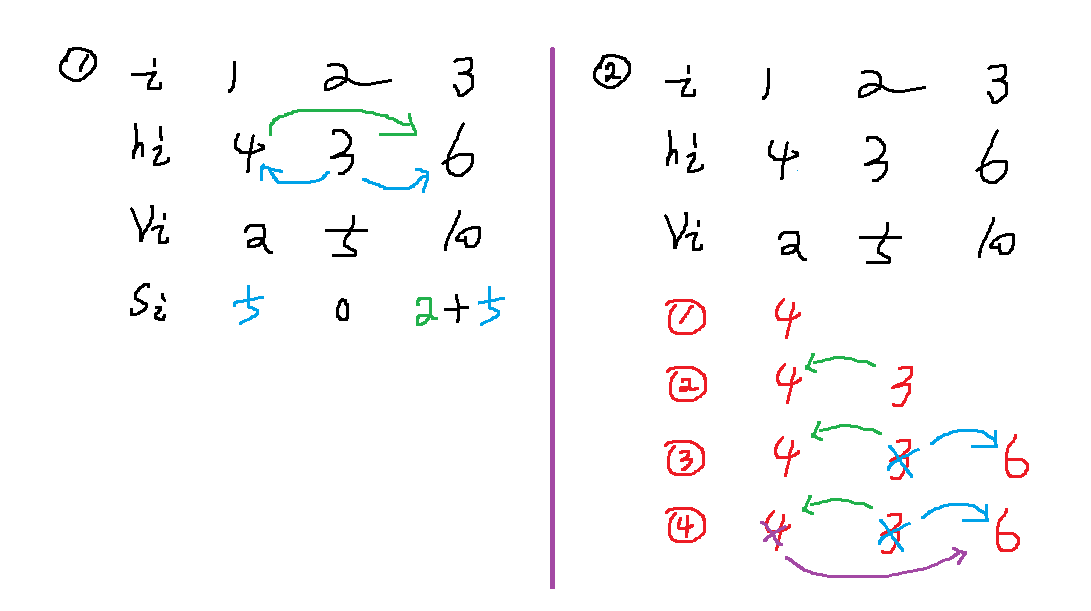
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=1e6+10,INF=0x3f3f3f3f;
int n,h[N],v[N],st[N],head=0;
LL ans[N];
void slove1() { // 預(yù)計(jì) TLE
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
int l=i-1, r=i+1;
while(l>0 && h[l]<=h[i]) l--;
while(r<=n && h[r]<=h[i]) r++;
ans[l]+=v[i], ans[r]+=v[i];
}
}
void slove2() { // 維護(hù)一個(gè)單調(diào)棧
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
while(head && h[st[head]] < h[i]) {
ans[i] += v[st[head]], head--;
}
ans[st[head]] += v[i];
st[++head] = i;
}
}
int main() {
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) scanf("%d%d",&h[i],&v[i]);
slove1();
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) ans[1]=max(ans[1],ans[i]);
printf("%lld\n",ans[1]);
return 0;
}
P1540 [NOIP2010 提高組] 機(jī)器翻譯
翻譯軟件從頭到尾,依次將每個(gè)英文單詞用對應(yīng)的中文含義來替換。對于每個(gè)英文單詞,軟件會先在內(nèi)存中查找這個(gè)單詞的中文含義,如果內(nèi)存中有,軟件就會用它進(jìn)行翻譯;如果內(nèi)存中沒有,軟件就會在外存中的詞典內(nèi)查找,查出單詞的中文含義然后翻譯,并將這個(gè)單詞和譯義放入內(nèi)存,以備后續(xù)的查找和翻譯。
假設(shè)內(nèi)存中有 \(M\) 個(gè)單元,每單元能存放一個(gè)單詞和譯義。每當(dāng)軟件將一個(gè)新單詞存入內(nèi)存前,如果當(dāng)前內(nèi)存中已存入的單詞數(shù)不超過 \(M-1\),軟件會將新單詞存入一個(gè)未使用的內(nèi)存單元;若內(nèi)存中已存入 \(M\) 個(gè)單詞,軟件會清空最早進(jìn)入內(nèi)存的那個(gè)單詞,騰出單元來,存放新單詞。
假設(shè)一篇英語文章的長度為 \(N\) 個(gè)單詞。給定這篇待譯文章,翻譯軟件需要去外存查找多少次詞典?假設(shè)在翻譯開始前,內(nèi)存中沒有任何單詞。
輸入格式:共 \(2\) 行。每行中兩個(gè)數(shù)之間用一個(gè)空格隔開。
第一行為兩個(gè)正整數(shù) \(M,N\),代表內(nèi)存容量和文章的長度。
第二行為 \(N\) 個(gè)非負(fù)整數(shù),按照文章的順序,每個(gè)數(shù)(大小不超過 \(1000\))代表一個(gè)英文單詞。文章中兩個(gè)單詞是同一個(gè)單詞,當(dāng)且僅當(dāng)它們對應(yīng)的非負(fù)整數(shù)相同。
輸出格式:一個(gè)整數(shù),為軟件需要查詞典的次數(shù)。
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
3 7 1 2 1 5 4 4 1 |
5 |
【數(shù)據(jù)范圍】\(1 \leq M \leq 100\),\(1 \leq N \leq 1000\)。
數(shù)組模擬隊(duì)列
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, a[N], st[N], q[N], hh, tt = -1, ans;
int main() {
cin >> m >> n;
for (int i = 1, x; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> x, a[i] = x;
if (!st[x]) {
while (tt - hh + 1 >= m) st[q[hh++]] = 0;
q[++tt] = x, ans++, st[x] = 1;
}
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}
使用STL
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int m, n, v, ans; bool st[N];
queue<int> q;
int main() {
scanf("%d%d", &m, &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &v);
if (st[v]) continue;
q.push(v), ans++, st[v] = 1;
while (q.size() > m)
st[q.front()] = 0, q.pop();
}
printf("%d\n", ans);
return 0;
}
優(yōu)先隊(duì)列、堆
P2085 最小函數(shù)值
有 \(n\) 個(gè)函數(shù),分別為 \(F_1,F_2,\dots,F_n\)。定義 \(F_i(x)=A_ix^2+B_ix+C_i(x\in\mathbb N*)\)。給定這些 \(A_i\)、\(B_i\) 和 \(C_i\),請求出所有函數(shù)的所有函數(shù)值中最小的 \(m\) 個(gè)(如有重復(fù)的要輸出多個(gè))。
輸入格式:第一行輸入兩個(gè)正整數(shù) \(n\) 和 \(m\),以下 \(n\) 行每行三個(gè)正整數(shù),其中第 \(i\) 行的三個(gè)數(shù)分別為 \(A_i\)、\(B_i\) 和 \(C_i\)。
輸出格式:輸出將這 \(n\) 個(gè)函數(shù)所有可以生成的函數(shù)值排序后的前 \(m\) 個(gè)元素。這 \(m\) 個(gè)數(shù)應(yīng)該輸出到一行,用空格隔開。
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
3 10 4 5 3 3 4 5 1 7 1 |
9 12 12 19 25 29 31 44 45 54 |
【數(shù)據(jù)范圍】 \(1 \leq n,m\le10000\),\(1 \leq A_i\le10,B_i\le100,C_i\le10^4\)。
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e6 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, a[N], b[N], c[N];
namespace BF {
void solve() {
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q; // down
for (int x = 1; x <= m; x++)
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int t = a[i] * x * x + b[i] * x + c[i];
q.push(t);
}
while (m--) {
cout << q.top() << " ";
q.pop();
}
}
}; // namespace BF
namespace BF2 {
struct T {
int a, b, c, x;
int cal() const { return a * x * x + b * x + c; }
bool operator<(const T& t) const { return cal() > t.cal(); }
};
void solve() {
priority_queue<T> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
q.push({a[i], b[i], c[i], 1});
while (m--) {
T t = q.top();
cout << t.cal() << " ";
t.x++, q.push(t), q.pop();
}
}
}; // namespace BF2
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cin >> a[i] >> b[i] >> c[i];
BF2::solve();
return 0;
}
P1090 [NOIP2004 提高組] 合并果子 / [USACO06NOV] Fence Repair G
\(n\) 堆果子經(jīng)過 \(n-1\) 次合并后, 剩下一堆,把兩堆果子合并到一起,消耗的體力等于兩堆果子的重量之和。求最小消耗體力。
輸入格式:第一行是一個(gè)整數(shù) n ,表示果子的種類數(shù)。
第二行包含 n個(gè)整數(shù),第 i 個(gè)整數(shù) \(a_i\) 是第 i 種果子的數(shù)目。
輸出格式:最小的體力耗費(fèi)值。輸入數(shù)據(jù)保證這個(gè)值小于 \(2^{31}\)。
說明/提示:\(1 ≤ n ≤ 10000, 1 ≤ a_i ≤ 20000\)。
【分析】貪心策略:每次選擇最小的兩個(gè)元素進(jìn)行合并。
P6033 [NOIP2004 提高組] 合并果子 加強(qiáng)版
【數(shù)據(jù)規(guī)模與約定】
- Subtask 1(10 points):\(1 \leq n \leq 8\)。
- Subtask 2(20 points):\(1 \leq n \leq 10^3\)。
- Subtask 3(30 points):\(1 \leq n \leq 10^5\)。
- Subtask 4(40 points):\(1 \leq n \leq 10^7\)。
對于全部的測試點(diǎn),保證 \(1 \leq a_i \leq 10^5\)。
【分析】\(10^7\),使用堆排序 \(O(nlog)\) 無法通過,考慮 \(O(n)\)
切入點(diǎn):\(1 \leq a_i \leq 10^5\) ,單個(gè)元素大小較小,可以使用計(jì)數(shù)排序進(jìn)行第一次處理,但是后續(xù)的還需要插入 \(n-1\) 怎么排序呢?
-
思路1:整體有序,插入一個(gè)新生成的數(shù)據(jù),可以考慮插入排序優(yōu)化,但是還是會TLE。
-
思路2:原數(shù)據(jù)排序后升序,新生成的數(shù)據(jù)一定是遞增的,考慮分別維護(hù)單調(diào)遞增隊(duì)列1、2,每次選擇隊(duì)首最小的2個(gè)元素,進(jìn)行合并,之后在插入隊(duì)列2。復(fù)雜度分析:計(jì)數(shù)排序 \(O(n)\),維護(hù)兩個(gè)隊(duì)列 \(O(n)\),整體復(fù)雜度 \(O(n)\)。
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 1e7 + 5, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, a[N];
namespace IO {
ll read() {
ll v = 0, f = 1; char c = getchar();
while (c < '0' || c > '9') {
if (c == '-') f = -1;
c = getchar();
}
while (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
v = v * 10 + c - '0', c = getchar();
return v * f;
}
}; // namespace IO
namespace Heap {
void solve() {
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) q.push(a[i]);
int ans = 0, a, b;
while (q.size() > 1) {
a = q.top(), q.pop();
b = q.top(), q.pop();
q.push(a + b), ans += a + b;
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
}; // namespace Heap
namespace Queue {
void solve() {
vector<int> st(1e5 + 5, 0);
queue<ll> q1, q2;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) st[a[i]]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= 1e5; i++)
while (st[i]--) q1.push(i);
ll ans = 0, x, y;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
if (q2.empty() || q1.size() && q1.front() < q2.front())
x = q1.front(), q1.pop();
else x = q2.front(), q2.pop();
if (q2.empty() || q1.size() && q1.front() < q2.front())
y = q1.front(), q1.pop();
else y = q2.front(), q2.pop();
ans += x + y, q2.push(x + y);
}
cout << ans << endl;
}
}; // namespace Queue
int main() {
// using namespace IO;
// n = read();
// for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
// a[i] = read();
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf("%d", &a[i]);
// Heap::solve();
Queue::solve();
return 0;
}
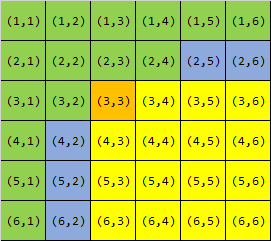
P1631 序列合并
有兩個(gè)長度為 \(N\) 的單調(diào)不降序列 \(A,B\),在 \(A,B\) 中各取一個(gè)數(shù)相加可以得到 \(N^2\) 個(gè)和,求這 \(N^2\) 個(gè)和中最小的 \(N\) 個(gè)。
輸入格式:第一行一個(gè)正整數(shù) \(N\),第二行 \(N\) 個(gè)整數(shù) \(A_{1\dots N}\),第三行 \(N\) 個(gè)整數(shù) \(B_{1\dots N}\)。
輸出格式:一行 \(N\) 個(gè)整數(shù),從小到大表示這 \(N\) 個(gè)最小的和。
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
3 2 6 6 1 4 8 |
3 6 7 |
【數(shù)據(jù)范圍】\(1 \le N \le 10^5\),\(1 \le a_i,b_i \le 10^9\)。
【分析】看圖說話,哪里存在答案?
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 3e6 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, a[N], b[N];
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q;
int main() {
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> b[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n / i; j++)
q.push(a[i] + b[j]);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
cout << q.top() << " \n"[i == n], q.pop();
return 0;
}
P2251 質(zhì)量檢測
為了檢測生產(chǎn)流水線上總共 \(N\) 件產(chǎn)品的質(zhì)量,我們首先給每一件產(chǎn)品打一個(gè)分?jǐn)?shù) \(A\) 表示其品質(zhì),然后統(tǒng)計(jì)前 \(M\) 件產(chǎn)品中質(zhì)量最差的產(chǎn)品的分值 \(Q[m] = min\{A_1, A_2, ... A_m\}\),以及第 2 至第 \(M + 1\) 件的 $Q[m + 1], Q[m + 2] $... 最后統(tǒng)計(jì)第 \(N - M + 1\) 至第 \(N\) 件的 \(Q[n]\)。根據(jù) \(Q\) 再做進(jìn)一步評估。
請你盡快求出 \(Q\) 序列。
輸入格式:輸入共兩行,第一行共兩個(gè)數(shù) \(N\)、\(M\),由空格隔開,含義如前述;第二行共 \(N\) 個(gè)數(shù),表示 \(N\) 件產(chǎn)品的質(zhì)量。
輸出格式:輸出共 \(N - M + 1\) 行,第 1 至 \(N - M + 1\) 行每行一個(gè)數(shù),第 \(i\) 行的數(shù) \(Q[i + M - 1]\)。含義如前述。
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
10 4 16 5 6 9 5 13 14 20 8 12 |
5 5 5 5 5 8 8 |
【數(shù)據(jù)范圍】\(M \le N, A \le 1 000 000\)
【分析】滑動窗口裸題
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int N = 3e6 + 10, INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, a[N], q[N];
int main() {
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (hh <= tt && a[q[tt]] >= a[i]) tt--;
while (hh <= tt && i - q[hh] + 1 > m) hh++;
q[++tt] = i;
if (i >= m) cout << a[q[hh]] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
課后練習(xí)
P1739 表達(dá)式括號匹配
【數(shù)據(jù)范圍】
【分析】
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
P1996 約瑟夫問題
n 個(gè)人圍成一圈,從第一個(gè)人開始報(bào)數(shù),數(shù)到 m 的人出列,再由下一個(gè)人重新從 1 開始報(bào)數(shù),數(shù)到 m 的人再出圈,依次類推,直到所有的人都出圈,請輸出依次出圈人的編號。
輸入格式:輸入兩個(gè)整數(shù) n,m(1≤m,n≤100)。
輸出格式:輸出一行 n 個(gè)整數(shù),按順序輸出每個(gè)出圈人的編號。
輸入樣例:10 3
輸出樣例:3 6 9 2 7 1 8 5 10 4
使用STL
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
queue<int> que;
int main(){
int n,m,cnt=1; cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) que.push(i);
while(!que.empty()){
if(cnt<m){
que.push(que.front());
que.pop(); cnt++;
}else if(cnt==m){
cout<<que.front()<<" ";
que.pop(); cnt=1;
}
} return 0;
}
P1808 單詞分類
【題目描述】
兩個(gè)單詞可以分為一類當(dāng)且僅當(dāng)組成這兩個(gè)單詞的各個(gè)字母的數(shù)量均相等。
例如 "AABAC",它和 "CBAAA" 就可以歸為一類,而和 "AAABB" 就不是一類。
現(xiàn)在Oliver有N個(gè)單詞,所有單詞均由大寫字母組成,每個(gè)單詞的長度不超過100。
你要告訴Oliver這些單詞會被分成幾類。
【輸入格式】輸入文件的第一行為單詞個(gè)數(shù)N,以下N行每行為一個(gè)單詞。
【輸出格式】輸出文件僅包含一個(gè)數(shù),表示這N個(gè)單詞分成的類數(shù)
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
3 AABAC CBAAA AAABB |
2 |
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e4+1;
char s[N][101];
int main(){
int n; cin>>n;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
scanf("%s", s[i]);
sort(s[i], s[i]+strlen(s[i]));
}
map<string,int> m;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
m.insert(pair<string,int>(s[i],1));
}
printf("%d", m.size());
return 0;
}
B3616 【模板】隊(duì)列
請你實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)隊(duì)列(queue),支持如下操作:
push(x):向隊(duì)列中加入一個(gè)數(shù) \(x\)。pop():將隊(duì)首彈出。如果此時(shí)隊(duì)列為空,則不進(jìn)行彈出操作,并輸出ERR_CANNOT_POP。query():輸出隊(duì)首元素。如果此時(shí)隊(duì)列為空,則輸出ERR_CANNOT_QUERY。size():輸出此時(shí)隊(duì)列內(nèi)元素個(gè)數(shù)。
輸入格式:第一行,一個(gè)整數(shù) \(n\),表示操作的次數(shù)。
接下來 \(n\) 行,每行表示一個(gè)操作。格式如下:
1 x,表示將元素x加入隊(duì)列。2,表示將隊(duì)首彈出隊(duì)列。3,表示查詢隊(duì)首。4,表示查詢隊(duì)列內(nèi)元素個(gè)數(shù)。
輸出格式:輸出若干行,對于每個(gè)操作,按「題目描述」輸出結(jié)果。每條輸出之間應(yīng)當(dāng)用空行隔開。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e4 + 10;
int que[N], head = 0, tol = 0;
void push(int x) {
que[tol++] = x;
}
void pop() {
if (head == tol) cout << "ERR_CANNOT_POP" << endl;
else ++head;
}
void query() {
if (head >= tol) cout << "ERR_CANNOT_QUERY" << endl;
else cout << que[head] << endl;
}
int size() {
return tol - head;
}
int main() {
int n, op, x; cin >> n;
while (n--) {
cin >> op;
switch (op) {
case 1: cin >> x, push(x); break;
case 2: pop(); break;
case 3: query(); break;
case 4: cout << size() << endl; break;
}
}
return 0;
}
P3378 【模板】堆
給定一個(gè)數(shù)列,初始為空,請支持下面三種操作:
- 給定一個(gè)整數(shù) x,請將 x 加入到數(shù)列中。
- 輸出數(shù)列中最小的數(shù)。
- 刪除數(shù)列中最小的數(shù)(如果有多個(gè)數(shù)最小,只刪除 1 個(gè))。
輸入格式:第一行是一個(gè)整數(shù),表示操作的次數(shù) n。
接下來 n 行,每行表示一次操作。每行首先有一個(gè)整數(shù) op 表示操作類型。
若 op=1,則后面有一個(gè)整數(shù) x,表示要將 x 加入數(shù)列。
若 op=2,則表示要求輸出數(shù)列中的最小數(shù)。
若 op=3,則表示刪除數(shù)列中的最小數(shù)。如果有多個(gè)數(shù)最小,只刪除 1 個(gè)。
輸出格式:對于每個(gè)操作 2,輸出一行一個(gè)整數(shù)表示答案。
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
5 1 2 1 5 2 3 2 |
2 5 |
【分析】
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int> > pq;
//priority_queue<int, vector<int>, less<int> > pq;
int main(){
int n; cin>>n;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++){
int f; cin>>f;
if(f==1){
int x; cin>>x; pq.push(x);
}else if(f==2){
cout<<pq.top()<<endl;
}else if(f==3){
pq.pop();
}
} return 0;
}
P4715 【深基16.例1】淘汰賽
有 2^n(n≤7) 個(gè)國家參加世界杯決賽圈且進(jìn)入淘汰賽環(huán)節(jié)。
我經(jīng)知道各個(gè)國家的能力值,且都不相等。能力值高的國家和能力值低的國家踢比賽時(shí)高者獲勝。
1 號國家和 2 號國家踢一場比賽,勝者晉級。3 號國家和 4 號國家也踢一場,勝者晉級……晉級后的國家用相同的方法繼續(xù)完成賽程,直到?jīng)Q出冠軍。
給出各個(gè)國家的能力值,請問亞軍是哪個(gè)國家?
| 輸入樣例 | 輸出樣例 |
|---|---|
3 4 2 3 1 10 5 9 7 |
1 |
點(diǎn)擊查看代碼
#include<iostream>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<map>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int n; cin>>n; n = pow(2, n); // n=1<<n;
queue<pair<int, int> > que;
for(int i=1; i<=n; i++) {
int a; cin>>a; que.push(make_pair(i, a));
}
while( que.size() > 2 ){
pair<int, int> x,y;
x = que.front(); que.pop();
y = que.front(); que.pop();
if(x.second > y.second) que.push(x);
else que.push(y);
}
pair<int, int> x,y;
x = que.front(); que.pop();
y = que.front(); que.pop();
if(x.second > y.second) cout<<y.first;
else cout<<x.first;
return 0;
}



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號