25Java基礎之IO(二)
IO流-字符流
FileReader(文件字符輸入流)
- 作用:以內存為基準,可以把文件中的數據以字符的形式讀入到內存中去。
![image]()
案例:讀取一個字符
//目標:文件字符輸入流的使用,每次讀取一個字符。
public class FileReaderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args){
//1. 創建字符輸入流管道與源文件接通
try(Reader reader = new FileReader("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest.txt");
){
//2. 讀取一個字符,返回編號,沒有字符可讀時返回-1。
int c;
while((c = reader.read()) != -1) {
char ch = (char) c;
System.out.print(ch);
}
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//拓展:解決了亂碼的問題,2.性能較差。
}
}
案例:讀取多個字符
//目標:文件字符輸入流的使用:每次讀取多個字符
public class FileReaderDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 創建字符輸入流管道與源文件接通
try(Reader reader = new FileReader("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest.txt");
){
//2. 定義一個字符數組
char[] buf = new char[3];
int len;
while((len = reader.read(buf)) != -1) {
String str = new String(buf, 0, len);
System.out.print(str);
}
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
//拓展:解決了亂碼的問題,2.性能挺好。這是目前來說學到過的讀取文本文件的最好的方式。
}
}
FileWriter(文件字符輸出流)
- 作用:以內存為基準,把內存中的數據以字符的形式寫出到文件中去。
![image]()
案例
//目標:文件字符輸出流的使用
public class FileReaderDemo03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 創建字符輸出流管道與源文件接通
try(//Writer rt = new FileWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest1.txt");//覆蓋管道
Writer rt = new FileWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest1.txt", true);//追加管道
){
//2. 寫一個字符出去
rt.write(98);
rt.write("\r\n");
rt.write('王');
rt.write("我是中國人,我愛我的祖國!",3 ,6);
rt.write("\r\n");
// //3. 刷新
// rt.flush();
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符輸出流使用的注意事項
- 字符輸出流寫出數據后,必須刷新流,或者關閉流,寫出去的數據才能生效。
![image]()
字節流、字符流的使用場景小結:
- 字節流適合做一切文件數據的拷貝(音視頻、文本);字節流不適合讀取中文內容輸出。
- 字符流適合做文本文件的操作(讀、寫)。
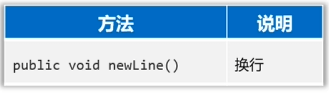
IO流-緩沖流
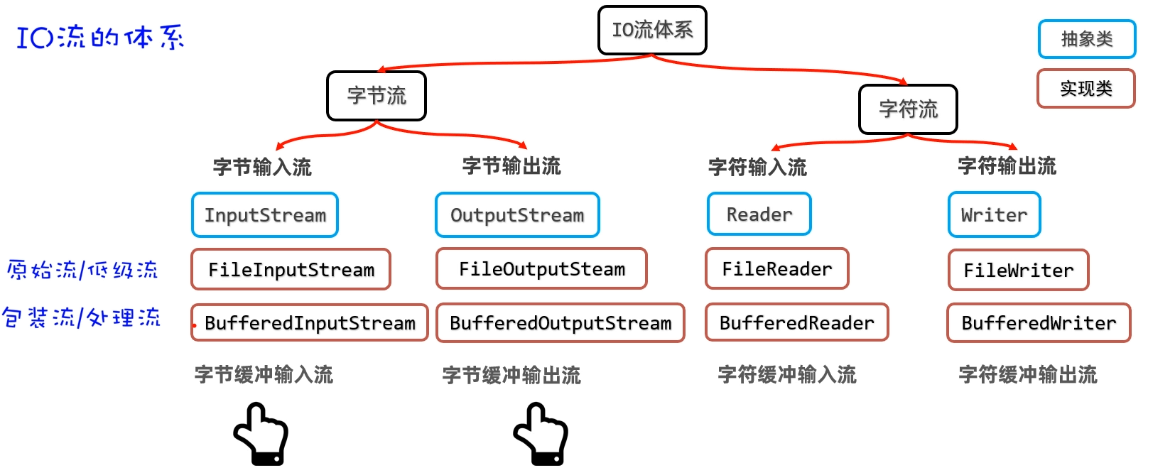
字節緩沖流的作用
- 提高字節流讀寫數據的性能。
- 原理:字節緩沖輸入流自帶了8KB緩沖池;字節緩沖輸出流也自帶了8KB緩沖池。
![image]()
案例
//目標:使用字節緩沖流提升原始字節流讀寫數據的性能。
public class BufferedInputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 創建字節流輸入流管道與源文件接通
try(InputStream in = new FileInputStream("F:\\360安全瀏覽器下載\\4b60c2c15cad30091caa0940e15fadb4.jpeg");
//2. 使用高級的緩沖流包裝低級的字節輸入流
InputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("F:\\360安全瀏覽器下載\\4b60c2c15cad30091caa0940e15fadb4_bak.jpeg");
//3. 使用高級的緩沖流包裝低級的字節輸出流
OutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
){
//準備一個字節數組
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len = bin.read(buf)) != -1){
bout.write(buf, 0, len);
}
}
catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
字符緩沖輸入流(BufferReader)
- 作用:自帶8K(8192)的字符緩沖池,可以提高字符輸入流讀取字符數據的性能。
![image]()
字符緩沖輸入流新增的功能:按照行讀取字符

案例
public class BufferedReaderDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 創建字符輸入流管道與源文件接通
try(Reader fr = new FileReader("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest2.txt");
// 把低級的字符輸入流包裝成一個高級的緩沖字符輸入流
BufferedReader fr2 = new BufferedReader(fr);
){
//2. 定義一個字符數組用于讀取多個字符
/* char[] buf = new char[1024];
int len;
while((len = fr2.read(buf)) != -1){
String rs = new String(buf, 0, len);
System.out.print(rs);
}*/
//3. 緩沖字符輸入流多了一個按照行讀取內容的方式功能。
String ln;
while((ln = fr2.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(ln);
}
}
catch (IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符緩沖輸出流(BufferedWriter)
- 作用:自帶8K的字符緩沖池,可以提高字符輸出流寫字符數據的性能。
![image]()
字符緩沖輸出流新增的功能:換行
案例
//目標:掌握緩沖字符流的使用
public class BufferedWirterDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
//1. 創建一個文件字符輸出流管道與源文件接通
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\chartest2.txt");
BufferedWriter br = new BufferedWriter(fw);
){
//2. 寫一個字符出去
br.write(98);
br.write('c');
br.newLine();
br.write("我是中國人,我愛我的祖國!");
br.newLine();
}
catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
案例:原始流、緩沖流的性能分析
測試用例:
- 分別使用原始的字節流,以及字節緩沖流復制一個很大視頻。
測試步驟:
- 使用低級的字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件。
- 使用低級的字節流按照字節數組的形式復制文件。
- 使用高級的緩沖字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件。
- 使用高級的緩沖字節流按照字節數組的形式復制文件。
//目標:原始流和緩沖流的性能分析
//1. 使用低級的字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件。
//2. 使用低級的字節流按照字節數組的形式復制文件。
//3. 使用高級的緩沖字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件。
//4. 使用高級的緩沖字節流按照字節數組的形式復制文件。
public class TimeTest05 {
public static final String SRC_VIDEO = "F:\\BaiduNetdiskDownload\\0412 天才的學習方法\\0412 天才的學習方法.mp4";
public static final String DEST_VIDEO = "D:\\WEMedia\\";
public static void main(String[] args) {
// copy01(); //使用低級的字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件:速度非常慢,禁止使用,直接淘汰!
copy02(); //使用低級的字節流按照字節數組的形式復制文件:速度還可以,相對來說比較慢。
// copy03(); //使用高級的緩沖字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件:特別慢,不推薦使用。
copy04(); //使用高級的緩沖字節流按照字節數組的形式復制文件:極快,推薦使用!
}
public static void copy01(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//1. 使用低級的字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件。
try (
//1. 創建字節流輸入流管道與源文件接通
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(SRC_VIDEO);
//2. 創建字節輸出流管道與目標文件接通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(DEST_VIDEO + "01.mp4");
) {
int len;
while ((len = in.read()) != -1) {
out.write(len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("1.使用低級的字節流總耗時:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void copy02(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//2. 使用低級的字節流按照字節數組的形式復制文件。
try (
//1. 創建字節流輸入流管道與源文件接通
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(SRC_VIDEO);
//2. 創建字節輸出流管道與目標文件接通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(DEST_VIDEO + "02.mp4");
) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = in.read(buf)) != -1) {
out.write(len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("2.使用低級的字節流按照字符數組的形式,總耗時:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void copy03(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//3. 使用高級的緩沖字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件。
try (
//1. 創建字節流輸入流管道與源文件接通
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(SRC_VIDEO);
InputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
//2. 創建字節輸出流管道與目標文件接通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(DEST_VIDEO + "03.mp4");
OutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
) {
int len;
while ((len = bin.read()) != -1) {
bout.write(len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("3.使用高級的緩沖字節流總耗時:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void copy04(){
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
//3. 使用高級的緩沖字節流按照一個一個字節的形式復制文件。
try (
//1. 創建字節流輸入流管道與源文件接通
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(SRC_VIDEO);
InputStream bin = new BufferedInputStream(in);
//2. 創建字節輸出流管道與目標文件接通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(DEST_VIDEO + "04.mp4");
OutputStream bout = new BufferedOutputStream(out);
) {
byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bin.read(buf)) != -1) {
bout.write(len);
}
long end = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("3.使用高級的緩沖字節流總耗時:" + (end - start) / 1000.0 + "s");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
IO流-轉換流
不同編碼讀取出現亂碼的問題
- 如果代碼編碼和被讀取的文本文件的編碼是一致的,使用字符流讀取文本文件時不會出現亂碼!
- 如果代碼編碼和被讀取的文本文件的編碼是不一致的,使用字符流讀取文本文件就會出現亂碼!
字符輸入轉換流(InputStreamReader)
- 解決不同編碼時,字符流讀取文本內容亂碼的問題。
- 解決思路:先獲取文件的原始字節流,再將其按照真實的字符集編碼轉成字符輸入流,這樣字符輸入流中的字符就不會亂碼了。
![image]()
案例
//目標:字符輸入轉換流
public class Test01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(//1. 得到GBK文件的原始字節輸入流
InputStream in = new FileInputStream("D:\\java_project\\resource\\ds.txt");
//2. 通過字符輸入轉換流把原始字節流按照指定編碼轉換成字符輸入流。
Reader ir = new InputStreamReader(in, "GBK");
//3. 把字符輸入流包裝成高級的緩沖字符輸入流
BufferedReader isr = new BufferedReader(ir);
){
//4. 按照行讀取
String ln ;
while((ln = isr.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(ln);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符輸出轉換流(OutputStreamWriter)
-
需要控制寫出去的字符使用什么字符集編碼該怎么辦?
- 調用String提供的getBytes方法解決。
![image]()
- 使用“字符輸出轉換流”實現。
- 調用String提供的getBytes方法解決。
-
作用:可以控制寫出去的字符使用什么字符集編碼。
-
解決思路:獲取字節輸出流,在按照指定的字符集編碼將其轉換成字符輸出流,以后寫出去的字符就會用該字符集編碼了。
![image]()
案例
//目標:掌握字符輸出轉換流的使用
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
//1.創建一個輸出字節流于源文件連通
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream("D:\\java_project\\resource\\ds1.txt");
//2.創建一個字符輸出轉換流,把字節輸出流按照指定編碼轉換成字符輸出流
Writer ow = new OutputStreamWriter(out, "GBK");
//3.把字符輸出流包裝成高級的緩沖字符輸出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(ow);
){
bw.write("hello world!");
bw.newLine();
bw.write("我是中國人,我愛我的祖國!");
bw.newLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
IO流-打印流
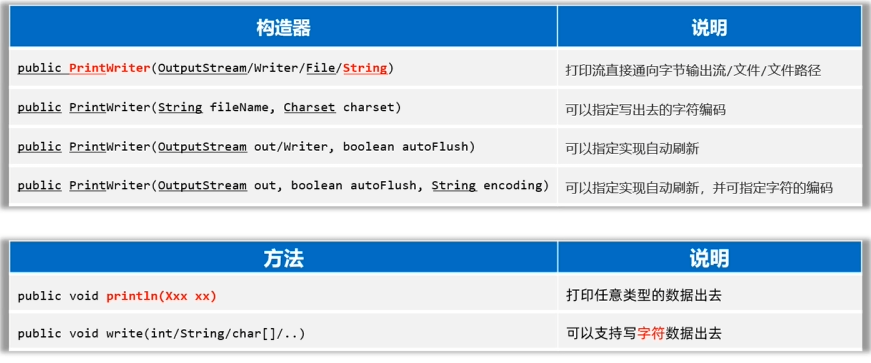
PrintStream/PrintWriter(打印流)
- 作用:打印流可以實現更方便、更高效的打印數據出去,能實現打印啥出去就是啥出去。
PrintStream提供的打印數據的方案
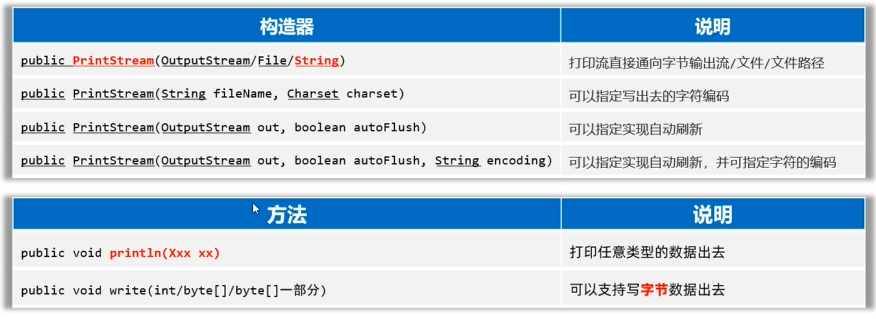
PrintWriter提供的打印數據的方案
//目標:打印流,方便,高效的寫數據出去
public class PrintStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("day10-io-code\\src\\ps.txt");
// PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\ps.txt");//默認是覆蓋
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(new FileWriter("day10-io-code\\src\\ps.txt",true));//追加
){
//寫數據出去
ps.println(97);
ps.println("2314asdf");
ps.println('A');
ps.println(16.5);
ps.println(true);
ps.println("------------------------------------");
pw.println(751);
pw.println('a');
pw.println("我是中國人,我愛我的祖國!");
pw.println(true);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
PrintStream和PrintWriter的區別
- 打印數據的功能上是一模一樣的:都是使用方便,性能高效(核心優勢)
- PrintStream繼承自字節輸出流OutputStream,因此支持寫字節數據的方法。
- PrintWriter繼承自字符輸出流Writer,因此支持寫字符數據出去。
打印流的一種應用:輸出語句的重定向。

案例
//目標:輸出語句的重定向
public class PrintStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
System.out.println("紅豆生南國");
System.out.println("春來發幾枝");
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(new FileOutputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\ps.txt", true));
System.setOut(ps); //把系統的打印流改成自己的打印流
System.out.println("愿君多采擷");
System.out.println("此物最相思");
}
}
IO特殊數據流---數據輸出流(DataOutputStream)
- 允許把數據和其類型一并寫出去。
![image]()
案例
public class DataOutputStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\dos.txt"));
){
//寫入數據
dos.writeByte(97);
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeInt(4232);
dos.writeChar('c');
dos.writeChars("zcvsadf55");
dos.writeUTF("我是中國人!");
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
DataInputStream(數據輸入流)
- 用于讀取數據輸出流寫出去的數據。
![image]()
案例
//特殊數據輸入流
public class DataInputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try(
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\dos.txt"));
){
System.out.println(dis.readByte());
System.out.println(dis.readBoolean());
System.out.println(dis.readInt());
System.out.println(dis.readChar());
System.out.println(dis.readUTF());
}
catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
注意:輸出流和輸入流的數據類型讀寫順序必須保持一致,否則會報錯。
IO流---序列化流
ObjectOutputStream(對象字節輸出流)
- 對象序列化:把java對象寫入到文件中去。
![image]()
注意:對象如果要參與序列化,必須實現序列化接口(java.io.Serializable)
案例
學生類:
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
//注意:如果學生對象要參與序列化,那么學生類必須實現Serializable接口,否則會拋出NotSerializableException異常。
public class Student implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
//transient:修飾的成員變量,不能參與序列化。
private transient String password;
private double height;
}
測試類:
//目標:完成對象的序列化:把java對象存儲到文件中去。
public class ObjectOutputStreamDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.創建一個Student對象
Student s1 = new Student("電驢", 18, "123456", 1.78);
//2.創建對象字節輸出流管道與目標文件接通
try(
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\obj.txt"));
){
//3. 開始寫對象出去
oos.writeObject(s1);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
- 對象反序列化:把文件里的java對象讀出來。
案例
//目標:完成對象的反序列化:把文件中的數據恢復成java對象。
public class ObjectInputStreamDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1;
try (
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("day10-io-code\\src\\obj.txt"));
){
s1 = (Student) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(s1);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
如果要一次序列多個對象,怎么辦?
- 用一個ArrayList集合存儲多個對象,然后直接對結合進行序列化即可。
- 注意:ArrayList集合已經實現了序列化接口。
IO框架
什么是框架?
- 解決某類問題,編寫的一套類、接口等,可以理解成一個半成品,大多數框架都是第三方開發的。
- 好處:在框架的基礎上開發,可以得到優秀的軟件架構,并能提高開發效率。
- 框架的形式:一般是把類、接口等編譯成class形式,再壓縮成一個.jar結尾的文件發行出去。
![image]()
什么是IO框架?
- 封裝了Java提供的對文件、數據進行操作的代碼,對外提供了更簡單的方式來對文件進行操作,對數據進行讀寫等。
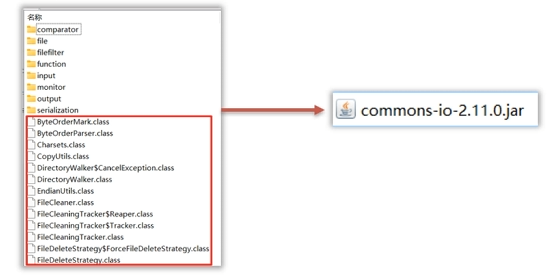
commons-io-2.11.0.jar框架
導入commons-io-2.11.0.jar框架到項目中去。
- 在項目中創建一個文件夾:lib
- 將commons-io-2.6.jar文件復制到lib文件夾
- 在jar文件上點右鍵,選擇Add as Library->點擊OK
- 在類中導包使用
下載地址:https://commons.apache.org/io/download_io.cgi
- Commons-io是apache開源基金組織提供的一組有關IO操作的小框架,目的是提高IO流的開發效率。
![image]()
![image]()
案例
//目標:使用Commons IO框架進行IO操作
public class CommonsIODemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
FileUtils.copyFile(new File("day10-io-code\\src\\dos.txt"), new File("day10-io-code\\src\\dos1.txt"));
// FileUtils.copyDirectory(new File("D:\\java_project\\resource\\b"), new File("D:\\java_project\\resource\\b1"));
// FileUtils.deleteDirectory(new File("D:\\java_project\\resource\\b"));
//JDK7開始也新增了單行復制相關的技術
Files.copy(Path.of("day10-io-code\\src\\dos.txt"), Path.of("day10-io-code\\src\\dos2.txt"));
}
}
案例:復制文件夾
//目標:復制文件夾
//源文件夾:D:\java_project\resource\
//目標文件夾:E:\
public class CopyDirectoryDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
copyDirectory(new File("D:\\java_project\\resource\\"), new File("E:\\"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void copyDirectory(File srcDir, File destDir) throws Exception {
//1.判斷源文件夾是否存在
if(srcDir == null || destDir == null || !srcDir.exists()
|| !destDir.exists() || srcDir.isFile() || destDir.isFile()) {
return;
}
//2.開始拷貝之前,先在目標位置創建新的文件夾名和原文件夾名稱一樣。
File destNewDir = new File(destDir, srcDir.getName());
destNewDir.mkdirs();
//3. 提取原始目錄的一級文件對象
File[] files = srcDir.listFiles();
//4. 判斷這個目錄是否可以拿到一級文件對象
if(files == null || files.length==0) return;
//5. 遍歷全部一級文件對象,拷貝到新的目錄中
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
FileUtils.copyFile(file, new File(destNewDir, file.getName()));
}
else {
copyDirectory(file, destNewDir);
}
}
}
}
案例:刪除文件夾
//目標:刪除文件夾
public class DeleteDirDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
deleteDirectory(new File("e:\\resource\\"));
}
public static void deleteDirectory(File dir){
//1. 不刪除的情況
if(dir == null || !dir.exists()) return;
//2. 如果是文件,直接刪除
if(dir.isFile()) {
dir.delete();
return;
}
//3.文件夾
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
if(files == null) return;
if(files.length == 0){
dir.delete();
return;
}
//4.遍歷全部一級文件對象,刪除
for (File file : files) {
if(file.isFile()){
file.delete();
}
else {
deleteDirectory(file);
}
}
//5.刪除自己
dir.delete();
}
}
課外拓展案例:啤酒問題
- 需求:啤酒2元一瓶,4個蓋子可以換一瓶,2個空瓶可以換一瓶,10元可以買多少瓶?剩余多少個蓋子和空瓶?
代碼
//目標:啤酒問題:啤酒2元一瓶,4個蓋子可以換一瓶,2個空瓶可以換一瓶,10元可以買多少瓶?剩余多少個蓋子和空瓶?
public class BeerDemo03 {
public static int totalBeers;
public static int lastBottles;
public static int lastCovers;
public static void main(String[] args) {
buyBeers(10);
System.out.println("一共可以買"+ totalBeers + "瓶酒,"
+ "還剩" + lastBottles + "個空瓶子,還剩" + lastCovers + "個瓶蓋子!");
}
public static void buyBeers(int money) {
//1.拿錢買酒
int beers = money /2;
totalBeers += beers;
//2.計算出本輪總共的空瓶和蓋子數,換算成錢繼續遞歸買酒。
int totalBottles = lastBottles + beers;
int totalCovers = lastCovers + beers;
//3. 換算成錢,繼續買酒
int newMoney = 0;
if(totalBottles >= 2){
newMoney += (totalBottles / 2) * 2;
}
lastBottles = totalBottles % 2; //記錄剩余瓶子數
if(totalCovers >= 4){
newMoney += (totalCovers / 4) * 2;
}
lastCovers = totalCovers % 4; //記錄剩余蓋子數
if(newMoney >= 2){
buyBeers(newMoney);//遞歸
}
}
}
















 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號