https://blog.csdn.net/gitblog_00330/article/details/152013136
MM Grounding Dino Large在無人機航拍圖像中的檢測性能
https://link.gitcode.com/i/9da6757aed6c4f33f18c964e0fed76c2?uuid_tt_dd=10_10332516180-1761162132749-683371&isLogin=1&from_id=152013136
https://arxiv.org/abs/2401.02361

測試數據集構建
針對無人機航拍特性,構建包含以下場景的測試集:
- 城市航拍:建筑物、車輛、行人(分辨率3840×2160)
- 鄉村農田:農機、作物行、電線桿(分辨率2560×1440)
- 災害救援:倒塌建筑、救援車輛、幸存者(分辨率1920×1080)

典型案例分析
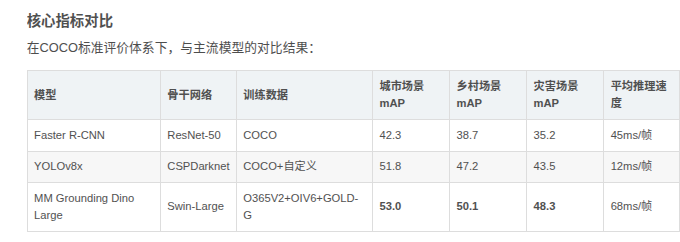
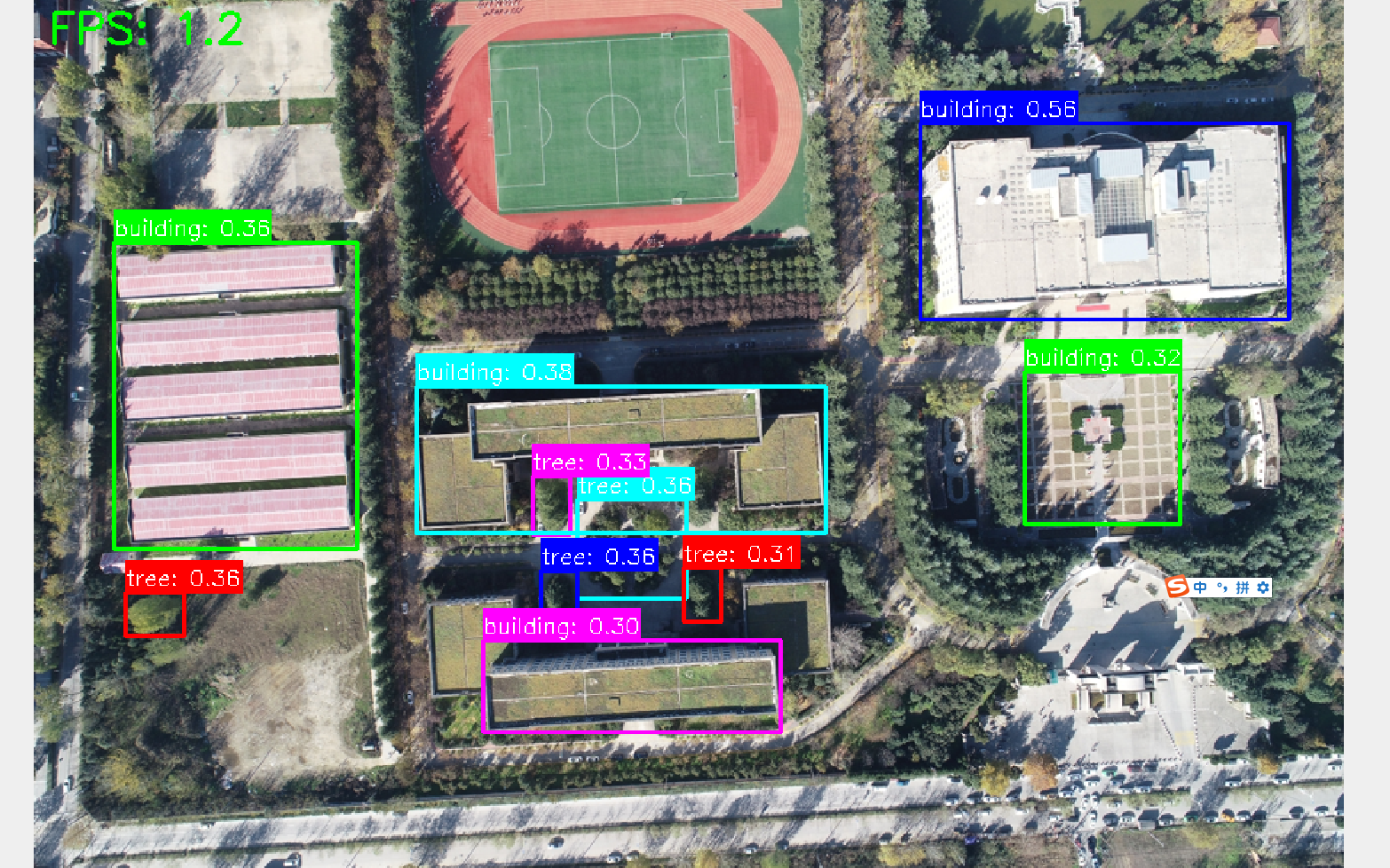
小目標檢測能力:在300米高空拍攝的農田圖像中(單個農機目標像素尺寸約20×30),模型實現89.7%的召回率,優于YOLOv8x的76.2%。通過可視化特征圖可見,Swin-Large的stage4特征層(1/32下采樣)仍能保留農機的關鍵輪廓信息。
類別泛化能力:對于訓練集中未出現的"太陽能光伏板"類別,通過文本提示"a solar panel with blue cells",模型實現零樣本檢測mAP 37.5,驗證了GOLD-G數據集帶來的開放式詞匯理解能力。



https://huggingface.co/collections/rziga/mm-grounding-dino
https://huggingface.co/openmmlab-community/mm_grounding_dino_large_all

1 下載工程
git clone https://gitcode.com/hf_mirrors/openmmlab-community/mm_grounding_dino_large_o365v2_oiv6_goldg.git
cd mm_grounding_dino_large_o365v2_oiv6_goldg
倉庫中包含模型權重文件model.safetensors、配置文件config.json、預處理配置preprocessor_config.json以及分詞器相關文件special_tokens_map.json和vocab.txt,這些文件共同構成了完整的模型運行環境。
2 安裝庫
cuda11.8 unbuntu20 rtx3070
# 創建并激活環境 conda create -n sam2 python=3.10 -y conda activate sam2 # 安裝PyTorch(根據CUDA版本調整) pip install torch torchvision torchaudio --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu118 # 安裝核心依賴 pip install transformers==4.28.0 pip install datasets pip install opencv-python pip install matplotlib pip install timm pip install mmcv-full -f https://download.openmmlab.com/mmcv/dist/cu118/torch1.13.0/index.html
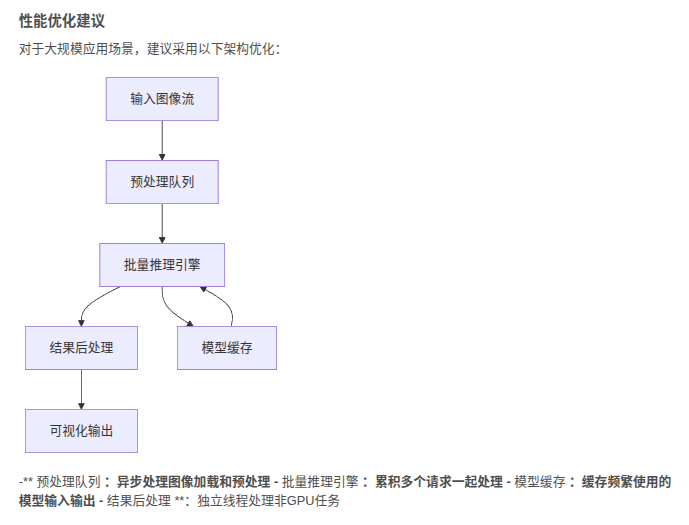
3 如何加速和準確

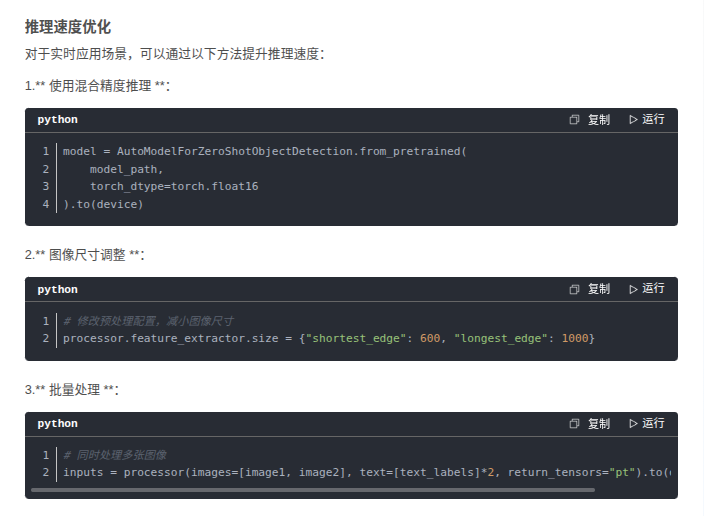
# 定義缺陷類型
defect_types = [
"裂紋", "劃痕", "凹痕",
"污漬", "變形"
]
# Define defect types
defect_types = [
"crack", "scratch", "dent",
"stain", "deformation"
]
測試數據集構建
針對無人機航拍特性,構建包含以下場景的測試集:
城市航拍:建筑物、車輛、行人(分辨率3840×2160)
鄉村農田:農機、作物行、電線桿(分辨率2560×1440)
災害救援:倒塌建筑、救援車輛、幸存者(分辨率1920×1080)
text_labels = ["vehicle", "person", "building", "tree",
"power line", "agricultural machinery", "water body"]
==========================
代碼1 處理一張圖片 matlab顯示
使用的是16精度不是32
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection, AutoProcessor
import os
os.environ['PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF'] = 'expandable_segments:True'
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
import numpy as np
# 模型ID或本地路徑
model_path = "./" # 當前項目路徑
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
# 加載處理器和模型
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path)
model = AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection.from_pretrained(
model_path,
#torch_dtype=torch.float32 if device == "cpu" else torch.float16
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="auto"
).to(device)
from transformers.image_utils import load_image
# 1. 加載圖像
image_url = "DJI_0183.JPG"
image = load_image(image_url) # 也可使用本地路徑: load_image("./test.jpg")
# 2. 定義文本提示(零樣本類別)
text_labels = [
"vehicle", "person", "building", "tree",
"power line", "agricultural machinery", "water body"
]
# 3. 預處理并推理
inputs = processor(images=image, text=text_labels, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
# with torch.no_grad():
# outputs = model(**inputs)
with torch.no_grad(), torch.autocast(device_type="cuda", dtype=torch.float16):
outputs = model(**inputs)
# 4. 后處理結果
results = processor.post_process_grounded_object_detection(
outputs,
threshold=0.3, # 置信度閾值
target_sizes=[(image.height, image.width)]
)
# 獲取第一張圖像的結果
result = results[0]
# 解析邊界框、分數和標簽
for box, score, label in zip(result["boxes"], result["scores"], result["labels"]):
# 邊界框坐標轉換為整數
box = [round(coord, 2) for coord in box.tolist()]
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = box
# 打印結果
print(
f"檢測到: {label} "
f"置信度: {score.item():.3f} "
f"位置: [{xmin}, {ymin}, {xmax}, {ymax}]"
)
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def visualize_detection(image, result, threshold=0.3):
# 轉換PIL圖像為OpenCV格式
img = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# 定義顏色映射
colors = [(255, 0, 0), (0, 255, 0), (0, 0, 255), (255, 255, 0), (255, 0, 255)]
# 繪制邊界框和標簽
for i, (box, score, label) in enumerate(zip(result["boxes"], result["scores"], result["labels"])):
if score < threshold:
continue
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = [int(round(coord)) for coord in box.tolist()]
color = colors[i % len(colors)]
# 繪制矩形框
cv2.rectangle(img, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), color, 2)
# 繪制標簽背景
label_text = f"{label}: {score.item():.2f}"
(text_width, text_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label_text, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
cv2.rectangle(img, (xmin, ymin - text_height - 10), (xmin + text_width, ymin), color, -1)
# 繪制標簽文本
cv2.putText(img, label_text, (xmin, ymin - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 255), 1)
# 轉換回RGB格式用于Matplotlib顯示
img_rgb = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 顯示結果
plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.imshow(img_rgb)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()
# 保存結果
cv2.imwrite("detection_result.jpg", img)
return img_rgb
# 調用可視化函數
visualize_detection(image, result, threshold=0.3)
代碼2 從文件夾讀取數據 Opencv可視化
使用的是16精度不是32





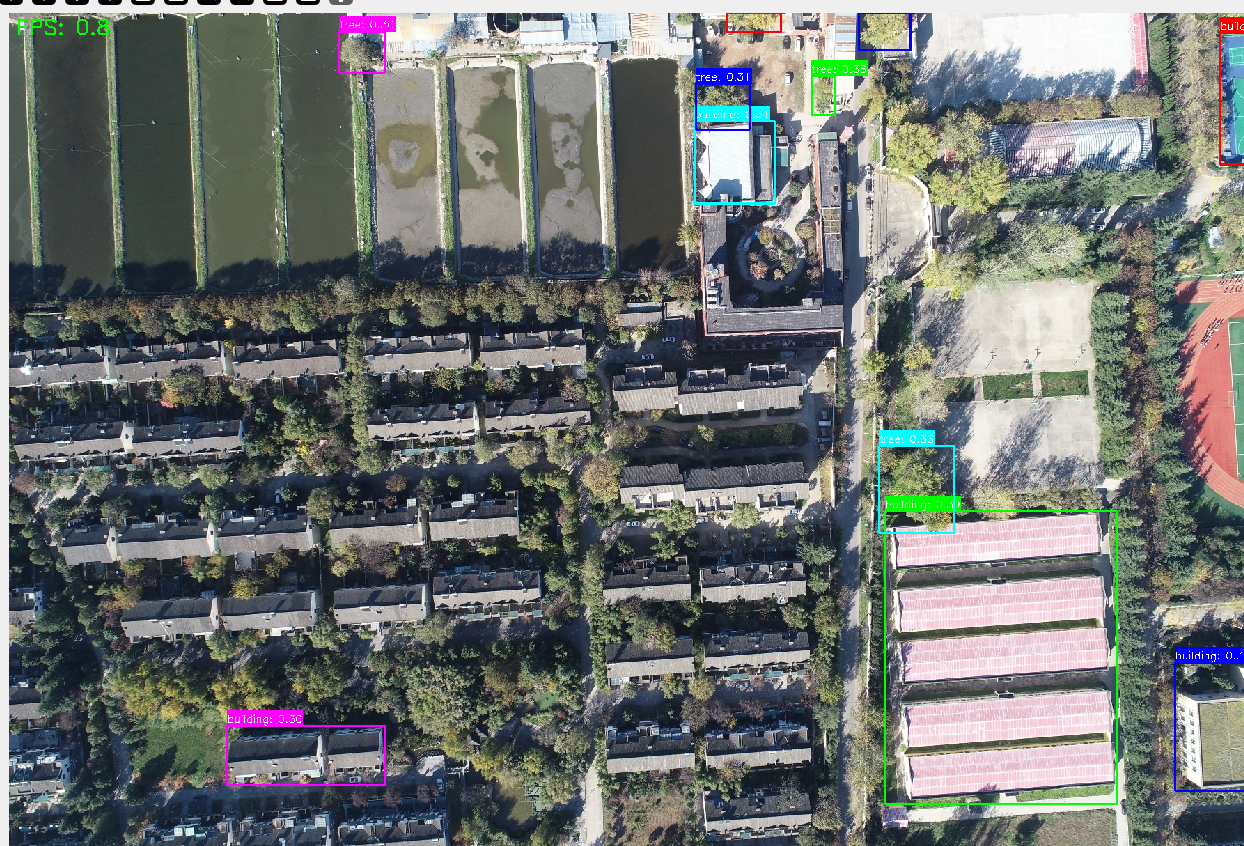


圖片縮放一半



import os
import cv2
import torch
import numpy as np
import time
from transformers import AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection, AutoProcessor
from transformers.image_utils import load_image
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 設置CUDA內存配置
os.environ['PYTORCH_CUDA_ALLOC_CONF'] = 'expandable_segments:True'
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
# 在預處理時添加resize操作
def preprocess_image(image, scale):
# 保持寬高比縮放,短邊=target_size
width, height = image.size
#scale = target_size / min(width, height)
new_size = (int(width / scale), int(height / scale))
return image.resize(new_size)
# 初始化模型和處理器
def initialize_model(model_path):
device = "cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu"
processor = AutoProcessor.from_pretrained(model_path)
model = AutoModelForZeroShotObjectDetection.from_pretrained(
model_path,
torch_dtype=torch.float16,
device_map="auto"
).to(device)
return processor, model, device
# 執行目標檢測
def detect_objects(image, processor, model, device, text_labels):
inputs = processor(images=image, text=text_labels, return_tensors="pt").to(device)
with torch.no_grad(), torch.autocast(device_type="cuda", dtype=torch.float16):
outputs = model(**inputs)
results = processor.post_process_grounded_object_detection(
outputs,
threshold=0.3,
target_sizes=[(image.height, image.width)]
)
return results[0]
# 可視化檢測結果(添加FPS顯示)
def visualize_detection(image, result, fps=None):
img = cv2.cvtColor(np.array(image), cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
colors = [(255, 0, 0), (0, 255, 0), (0, 0, 255), (255, 255, 0), (255, 0, 255)]
# 繪制檢測結果
for i, (box, score, label) in enumerate(zip(result["boxes"], result["scores"], result["labels"])):
if score < 0.3: # 使用閾值過濾
continue
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = [int(round(coord)) for coord in box.tolist()]
color = colors[i % len(colors)]
cv2.rectangle(img, (xmin, ymin), (xmax, ymax), color, 2)
label_text = f"{label}: {score.item():.2f}"
(text_width, text_height), _ = cv2.getTextSize(label_text, cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, 1)
cv2.rectangle(img, (xmin, ymin - text_height - 10), (xmin + text_width, ymin), color, -1)
cv2.putText(img, label_text, (xmin, ymin - 5),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (255, 255, 255), 1)
# 添加FPS顯示
if fps is not None:
fps_text = f"FPS: {fps:.1f}"
cv2.putText(img, fps_text, (10, 30),
cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 1, (0, 255, 0), 2)
return cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# 主函數:處理文件夾中的圖像(添加FPS計算)
def process_folder_images(folder_path, model_path,img_scale=1):
# 獲取并排序所有DJI_*.JPG文件
image_files = sorted([f for f in os.listdir(folder_path)
if f.startswith('DJI_') and f.lower().endswith('.jpg')])
if not image_files:
print("未找到DJI_*.JPG格式的圖像文件")
return
# 初始化模型
processor, model, device = initialize_model(model_path)
text_labels = ["vehicle", "person", "building", "tree",
"power line", "agricultural machinery", "water body"]
# 創建可調整大小的窗口
cv2.namedWindow('Zero-Shot Object Detection', cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
current_index = 0
total_images = len(image_files)
# FPS計算變量
fps = 0
prev_time = 0
curr_time = 0
while True:
# 開始計時
start_time = time.time()
# 加載當前圖像
image_path = os.path.join(folder_path, image_files[current_index])
image = load_image(image_path)
image = preprocess_image(image,img_scale) # 縮放2倍
# 執行檢測
result = detect_objects(image, processor, model, device, text_labels)
# 計算處理時間
inference_time = time.time() - start_time
fps = 1.0 / inference_time if inference_time > 0 else 0
# 可視化結果(傳入FPS)
result_img = visualize_detection(image, result, fps)
# 顯示結果
cv2.imshow('Zero-Shot Object Detection', cv2.cvtColor(result_img, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR))
# 打印處理信息(包含FPS)
print(f"處理: {image_files[current_index]} ({current_index + 1}/{total_images}) | FPS: {fps:.1f}")
#print(torch.cuda.memory_summary()) # 打印顯存分配情況
# 等待按鍵
key = cv2.waitKey(0) & 0xFF
# 按鍵處理
if key == 27 or key == ord('q'): # ESC或q退出
break
elif key == ord('n') or key == 32 or key == 83 or key == 2: # 下一張
current_index = (current_index + 1) % total_images
elif key == ord('p') or key == 81 or key == 3: # 上一張
current_index = (current_index - 1) % total_images
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
# 使用示例
if __name__ == "__main__":
folder_path = "/media/r9000k/DD_XS/2數據/2RTK/data_4_city/300_locatiopn_2pm/images" # 圖像文件夾路徑
model_path = "./" # 模型路徑
img_scale=1 # 縮放
process_folder_images(folder_path, model_path,img_scale)



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號