力扣刷題筆記
有序數組的平方:
我的錯誤解法:
public class Test { public static void main(String[] args) { Solution s = new Solution(); int[] nums = {-5,-3,-2,-1}; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s.removeElement(nums)));; } } class Solution { public int[] removeElement(int[] nums) { int min = 0; int max = nums.length-1; while (min != max){ if(Math.abs(nums[min]) > Math.abs(nums[max])){ int temp = nums[max]; nums[max] = (int)Math.pow(nums[min],2); nums[min] = temp; max --; }else{ nums[max] = (int)Math.pow(nums[max],2); max --; } } nums[min] = (int)Math.pow(nums[min],2); return nums; } }
在我自己的這種解法中,在一些數組中并不適用。比如這里的例子-5,-3,-2,-1.
第一輪nums[3]=25,nums[0]=-1。而第二輪直接用-1和-2比較,中間的-3其實才是最大的數,所以錯誤。
這也是為什么解答答案中必須用一個新數組去記錄的原因!
移除鏈表元素
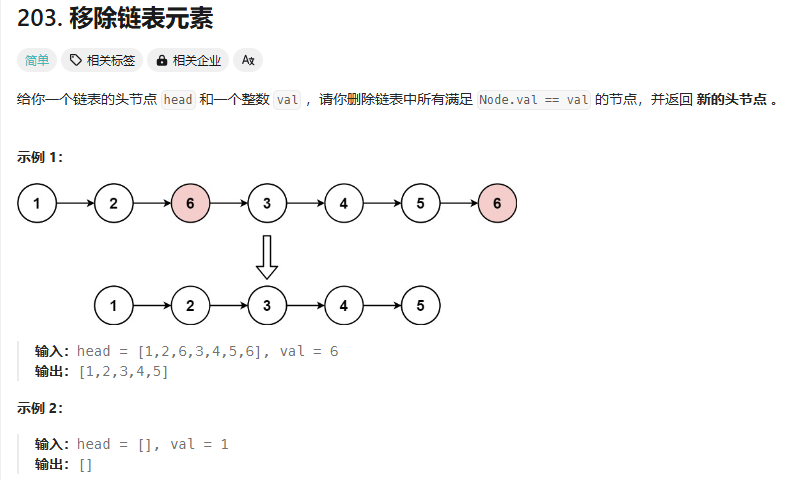
這里有兩個地方要注意
1.怎么處理頭節點,如果不加入虛擬頭節點那么就要分兩種情況去刪除元素:判斷是否為頭節點
2.空指針異常的警告問題
我的錯誤代碼:

在這里 我們應該寫:
class Solution { public ListNode removeElements(ListNode head, int val) { while (head != null && head.val == val ){ head = head.next; } ListNode temp = head; while(temp != null && temp.next != null){ if (temp.next.val == val){ temp.next = temp.next.next; }else{ temp = temp.next; } } return head; } }
還一種帶虛擬頭節點的
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(); dummy.next = head; ListNode temp = dummy; while (temp.next != null){ if (temp.next.val == val){ temp.next = temp.next.next; }else{ temp = temp.next; } } return dummy.next;
反轉鏈表
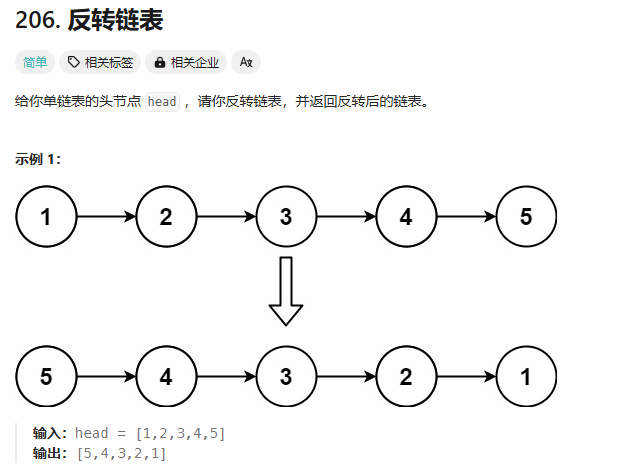
雙指針的方法:
首先兩個需要注意的點:
① 在最開始初始化的時候pre的賦值,這里應該是賦值null,因為最開始的頭結點應該變成尾結點指向空
② 在改變了next指向的時候,需要增加一個temp來保留原先的next指向的結點,避免在改變了指向之后找不到原先的下一結點。
我寫的代碼:
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; ListNode temp = cur.next; while (cur != null){ cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; if (temp.next != null){ temp = temp.next; } } return pre; } }
但這里我本來寫的
cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; temp = temp.next;
這其實是有錯誤的,當我的temp本來指向的就是null之后,我是沒有辦法遍歷它的next的,會出現空指針異常
需要更改的話,其實我可以將temp指針的賦值操作提到最前面,就不會有這個問題了。
正確寫法如下:
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) { ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; ListNode temp; while (cur != null){ temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; pre = cur; cur = temp; } return pre; } }
還有一種寫法是寫成遞歸的形式:
這一種形式最好是在寫了雙指針的解法之后去更改
這里也要注意一點就是空指針異常
temp的賦值要是在if判斷之前就會出現空指針異常的問題,我們如果放在了下面就避免了我們去訪問null的next的問題了。
class Solution { public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head){ ListNode pre = null; ListNode cur = head; return reverse(cur,pre); } public ListNode reverse(ListNode cur, ListNode pre){ if (cur == null){ return pre; } ListNode temp = cur.next; cur.next = pre; return reverse(temp,cur); } }
鏈表相交

我的思路是算兩個鏈表的長度之差mins,長度更長的鏈表先往前走mius步,然后再共同移動,每一步比較一下所指的節點是否一致。
還有一種看起來更快速的思路:

環形鏈表
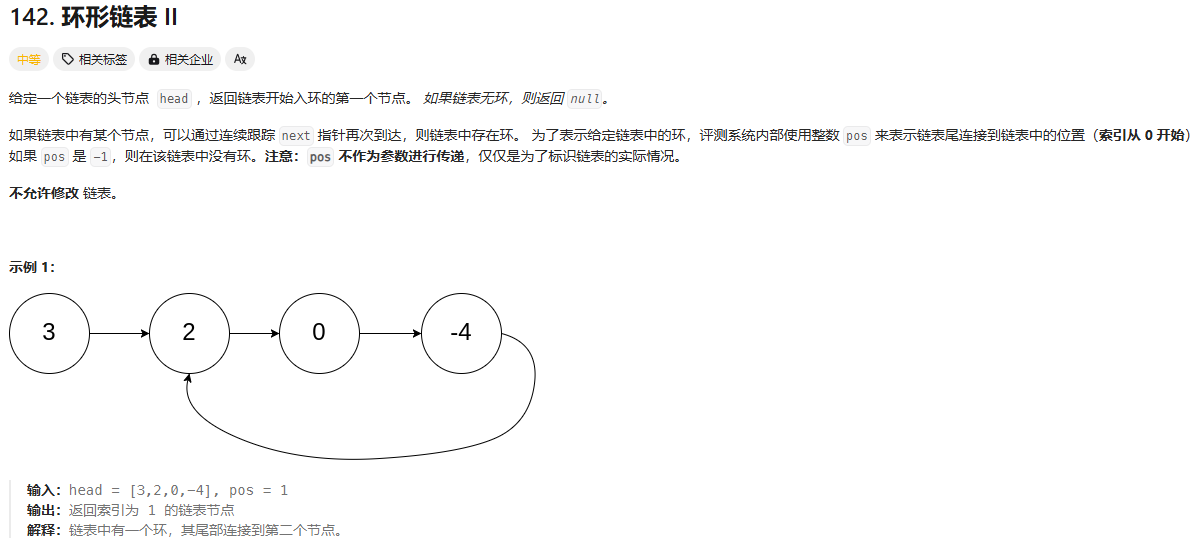
這個題目沒寫出來

我按照這個思路的代碼是這樣寫的:
class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; next = null; } } public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != slow){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == null || fast.next == null){ return null; } } ListNode temp = head; while (slow != temp){ slow = slow.next; temp = temp.next; } return temp; } }
但其實這里有一個很嚴重的錯誤,在最開始我想要找到相遇結點時的程序是不正確的,最開始fast == slow就已經滿足了,所以判斷條件不能這樣寫
正確寫法:
class ListNode { int val; ListNode next; ListNode(int x) { val = x; next = null; } } public class Solution { public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) { ListNode fast = head; ListNode slow = head; while (fast != null && fast.next != null){ fast = fast.next.next; slow = slow.next; if (fast == slow){ ListNode temp = head; while (slow != temp){ slow = slow.next; temp = temp.next; } return temp; } } return null; } }
兩個數組的交集

解法一:
import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; class Solution { public int[] intersection(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) { Set<Integer> arr = new HashSet<Integer>(); Set<Integer> rearr = new HashSet<Integer>(); for(int i = 0; i < nums1.length; i ++){ arr.add(nums1[i]); } for (int j = 0 ; j<nums2.length; j++){ if (arr.contains(nums2[j])){ rearr.add(nums2[j]); } } return rearr.stream().mapToInt(x -> x).toArray(); } }
快樂數

這道題目我開始想的是使用map,但是后來看答案我發現不用map,直接set判斷這個數在不在里面就行了。我自己想的方法有一步特別麻煩的就是在計算一個數的各位平方之和的情況下,我還用了一個數組專門存放各個位上的數字,后來發現完全不需要這么復雜。
所以這道題很需要學習這種求各個位上平方之和的方法。
import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Set; class Solution { public boolean isHappy(int n) { Set <Integer> hashset = new HashSet<Integer>(); while (!hashset.contains(n)){ if (n == 1){ return true; } hashset.add(n); n = getnext(n); } return false; } public int getnext (int n){ int next = 0; while(n != 0){ next += (n%10) * (n%10); n = n / 10; } return next; } }
兩數之和

這道題目我是用數組做的,借鑒了冒泡法的思想,我需要兩層for循環去遍歷,但其實這樣時間復雜度會比較高一點。
這道題目也可以去用哈希法。我們可以用一個map存儲數組中我們遍歷過的元素,然后直接用contains判斷我們需要的元素在不在map里面即可。這里的map可以存儲key和value,正好滿足了我們需要得到數組下標的需求。
我們遍歷一遍數組中的元素,將遍歷過的元素存儲在map中,后續遍歷后面的元素,我們通過target - nums[i]得到我們需要的數temp,然后直接搜索是否存在map中即可。
但需要注意的一點是,我們的key存放的是數,value存放的是下標。因為map只能通過key返回value,我們后續要的是下標值,所以應該吧下標值放在value中。
import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int[] twoSum(int[] nums, int target) { HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashmap = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); int[] arr = new int[2]; for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i ++){ int temp = target - nums[i]; while (hashmap.containsKey(temp)){ arr[0] = hashmap.get(temp); arr[1] = i; return arr; } hashmap.put(nums[i],i); } return null; } }
四數相加

我最開始的想法:
import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) { HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap1 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap2 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); int num = 0; int member = 0; int n = nums1.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++){ hashMap1.put(++num,nums1[i]+nums2[j]); } } num = 0; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++){ hashMap2.put(++num,nums3[i]+nums4[j]); } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n*n; i ++){ for(int j = 0 ; j < n*n ;j ++){ if (hashMap1.get(i+1)+hashMap2.get(j+1)==0){ member++; } } } return member; } }
先將兩個數組的兩兩之和用一個hashmap存儲起來
key可以反應我獲取和變來的下標(比如說1:00 ; 2:01; 3:10; 4:11)
但是后來我發現并不需要得到具體的數組的下標值。而且我這算法超出了時間限制,我發現最后的兩層for循環去遍歷其實是不需要的,我可以直接使用hashmap里自帶的contains函數就可以找到hashmap2是否有-hashmap1的值就好。
但此時又有一個問題就是hashmap不能查找value值,我是將所有的存儲在hashmap2的value里。如果我需要遍歷一遍我的value我也沒有辦法獲得這個value對應的次數,所以這個問題要換紅方法解決。
那么我只能夠將這些計算得到的和存儲在key中,把這個值出現的次數放在value中,每當這個數字出現了一次,我的value值+1。
這里使用了一個很好用的函數getOrDefault。這個函數可以查找我需要的key值,此時我如果把所求的和存放在key里面,value就存放這個和出現的次數即可。
import java.util.HashMap; class Solution { public int fourSumCount(int[] nums1, int[] nums2, int[] nums3, int[] nums4) { HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap1 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); HashMap<Integer,Integer> hashMap2 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>(); int member = 0; int n = nums1.length; for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++){ for ( int j = 0; j < n; j ++){ if (hashMap1.containsKey(nums1[i]+nums2[j])){ int num = hashMap1.get(nums1[i]+nums2[j]); hashMap1.put((nums1[i]+nums2[j]),++num); }else { hashMap1.put(nums1[i] + nums2[j], 1); } } } for (int i = 0 ; i < n; i ++) { for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) { member += hashMap1.getOrDefault((-nums3[i] - nums4[j]), 0); } } return member; } }
四數之和

這道題目最難的地方我覺得就是不能重復的四元組,你要保證你所獲取的所有的元組是之前沒有取到的,就需要一個去重的操作。
上一道題目是三數之和,思想有部分是一樣的:

import java.util.*; class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) { List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>(); Arrays.sort(nums); for ( int i = 0 ; i < nums.length; i++){ if (nums[i] > 0){ return lists; }else if( i >0 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]){ continue; } int left = i + 1; int right = nums.length-1; while (left < right){ int sum = nums[i] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum > 0){ right --; }else if(sum < 0){ left++; }else{ lists.add(new LinkedList<>(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[left],nums[right]))); while (left < right && nums[left] == nums[left+1]) left++; while (left < right && nums[right] == nums[right-1]) right--; left++;right--; } } } return lists; } }
為了后續的操作,這里一定第一步就是進行數組排序操作。
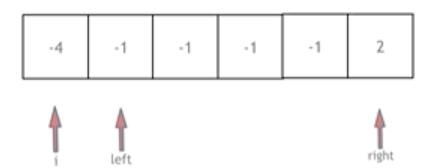

這中間比較重要的就是去重操作。首先對外層的i,當nums[i]和前一個位置的數相等時,我們就要向后移動一位,這里不能夠和后一位去判斷,我們時要防止和前面的取到的元組一樣,所以和前面一位去判斷。
四數之和就是外層再增加了一層循環。但是外層要注意的一點就是nums[k]>target并不能作為break的判斷語句,大于了目標值并不代表后續移動中沒有滿足的條件了,如果時-4,-1,0,0.那么nums[k]= -4, nums[i]= -1。這個時候我們倆個負數相加其實變小了,所以仍然可能滿足條件。
import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Arrays; import java.util.List; class Solution { public List<List<Integer>> fourSum(int[] nums, int target) { Arrays.sort(nums); List<List<Integer>> lists = new ArrayList<>(); for (int k = 0; k < nums.length; k++){ if (nums[k] >= 0 && nums[k] > target){break;} if (k > 0 && nums[k] == nums[k-1]){continue;} for ( int i = k + 1; i < nums.length; i++){ if (i > k+1 && nums[i] == nums[i-1]){continue;} if (nums[k]+nums[i]>target && nums[k]+nums[i]>=0){break; } int left = i + 1; int right = nums.length-1; while (left<right){ long sum =(long) nums[i] + nums[k] + nums[left] + nums[right]; if (sum<target){ left++; }else if(sum>target){ right--; }else { lists.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i],nums[k],nums[left],nums[right])); while (left < right && nums[left]==nums[left+1]){left++;} while (right> left && nums[right]==nums[right-1]){right--;} right--; left++; } } } } return lists; } }
反轉字符串

這里我想到的就是a=a+b;b=a-b;a=a-b;
給出的答案里面有一種異或運算的方法:
class Solution { public void reverseString(char[] s) { int l = 0; int r = s.length - 1; while (l < r) { s[l] ^= s[r]; //構造 a ^ b 的結果,并放在 a 中 s[r] ^= s[l]; //將 a ^ b 這一結果再 ^ b ,存入b中,此時 b = a, a = a ^ b s[l] ^= s[r]; //a ^ b 的結果再 ^ a ,存入 a 中,此時 b = a, a = b 完成交換 l++; r--; } } } // 第二種方法用temp來交換數值更多人容易理解些 class Solution { public void reverseString(char[] s) { int l = 0; int r = s.length - 1; while(l < r){ char temp = s[l]; s[l] = s[r]; s[r] = temp; l++; r--; } } }

第一步
a = a ^ b; 完成后 a變量的結果為a ^ b
第二步:
b = a ^ b; 此時賦值號右邊的a保存的是a ^ b的值,那么將賦值號右邊的a用a ^ b替換,
得到(a ^ b) ^ b=a ^ (b ^ b)=a ^0=a, 即經過第二步運算后b中的值為a,即b=a,將a換到了b里
第三步: a = a ^ b;
此時賦值號右邊的a保存的仍然是a ^ b的值,不變,而賦值號右邊的b已經是a 了,將賦值號右邊的a,b分別進行替換,
即此時賦值號右邊a ^ b=(a ^ b)^ a=a ^ b^ a=a ^ a^ b=0^ b=b, 該值賦值給a,即a=b
即經過第三步運算后a中的值為b,即a=b,將b換到了a里
實現strStr()

這里我的寫法是暴力搜索時間消耗很大,這個看到答案之后知道是KMP問題,可以通過找到next數組幫助。
我的寫法:
class Solution { public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { char[] a = haystack.toCharArray(); char[] b = needle.toCharArray(); int j = 0; for (int i = 0; i < a.length; i ++){ if (a[i] == b[0]){ int num = i; for(j =0 ; j < b.length; j++){ if (num + b.length > a.length){return -1;} if(a[i] != b[j]){ break; } i++; } if(j == b.length){ return i-b.length; }else{ i = num; } } } return -1; } }
首先學一下怎么獲得next數組
public void findNext(String s, int[] next){ next[0] = -1; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (int i =1, j = -1; i < s.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && chars[i] != chars[j +1]){j = next[j];} if ( chars[i] == chars[j + 1]){ j++;} next[i] = j; } }
不懂就自己去IDEA里遍歷一遍就知道啦,不太好說
class Solution { public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { int[] next = new int[needle.length()]; int j = -1; findNext(needle,next); for (int i = 0; i < haystack.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && haystack.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j + 1)){j = next[j];} if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j + 1)){ j ++; } if (j == needle.length() -1){ return (i - needle.length())+1; } } return -1; } public void findNext(String s, int[] next){ next[0] = -1; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (int i =1, j = -1; i < s.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && chars[i] != chars[j +1]){j = next[j];} if ( chars[i] == chars[j + 1]){ j++;} next[i] = j; } } }
這里我們算的是needle的next數組,因為我們借助needle的next數組可以幫助我們在haystack[i] != needle[j]的時候,不用從頭重新遍歷一次needle,這樣減少了復雜度!
class Solution { public int strStr(String haystack, String needle) { int[] next = new int[needle.length()]; int j = -1; findNext(needle,next); for (int i = 0; i < haystack.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && haystack.charAt(i) != needle.charAt(j + 1)){j = next[j];} if (haystack.charAt(i) == needle.charAt(j + 1)){ j ++; } if (j == needle.length() -1){ return (i - needle.length())+1; } } return -1; } public void findNext(String s, int[] next){ next[0] = -1; char[] chars = s.toCharArray(); for (int i =1, j = -1; i < s.length(); i++){ while (j >= 0 && chars[i] != chars[j +1]){j = next[j];} if ( chars[i] == chars[j + 1]){ j++;} next[i] = j; } } }
重復的子字符串

第一種想法是:
![]()
class Solution { public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) { String copy = s+s; copy = copy.substring(1,copy.length()-1); if (copy.contains(s)){return true;} return false; } }
這道題還是可以用上面的KMP來算,但是有一個要知道的規律:

class Solution { public boolean repeatedSubstringPattern(String s) { int len = s.length(); int[] next = new int[s.length()]; next[0] = -1; for ( int i = 1, j = -1; i < s.length(); i++){ while ( j >= 0 && s.charAt(i) != s.charAt(j + 1)){ j = next[j]; } if(s.charAt(i) == s.charAt(j + 1)){ j++; } next[i] = j; } if (next[len - 1] != -1 && len % (len - ((next[len - 1]) + 1)) == 0){ return true; } return false; } }
滑動窗口最大值

1.雙端隊列維護窗口中的最大值:
使用雙端隊列(Deque)來高效維護滑動窗口中的元素:
- 隊列存儲下標,而不是直接存儲數值。這樣我們可以根據下標來判斷哪些元素已經滑出窗口。
- 隊列中的元素保持單調遞減,隊列頭部總是當前窗口的最大值。
2. 如何維護隊列:
在遍歷數組時,我們對每個元素做以下操作:
-
移除隊列頭部過期的下標:如果隊列頭部的元素不在當前窗口范圍內(即小于
i - k + 1),就將其從隊列中移除。 -
保持單調性:如果當前元素大于隊列尾部的元素,就將隊列尾部的元素移除,直到找到比當前元素大的或隊列為空。這樣可以保證隊列中的元素單調遞減。
-
將當前元素下標加入隊列:把當前下標放入隊列尾部。
-
記錄最大值:當
i >= k - 1時,窗口已經成型,隊列頭部的下標對應的元素就是當前窗口的最大值,將其加入結果數組。
3. 時間復雜度優化:
- 每個元素最多進隊和出隊一次,因此時間復雜度為
O(n),比暴力解法的O(n*k)更高效。
import java.util.ArrayDeque; class Solution { public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) { ArrayDeque<Integer> deque = new ArrayDeque<>(); int n = nums.length; int[] res = new int[n - k + 1]; int idx = 0; for ( int i =0; i< n; i++){ while (!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peek() < i-k+1){ // 當隊列的頭節點不在我們需要的[i - k + 1, i]范圍內,刪除 deque.poll(); } while (!deque.isEmpty() && nums[deque.peekLast()] < nums[i]){ // 當隊列的尾結點小于當前加入的值,刪除 deque.pollLast(); } deque.offer(i); // 加入下標 if(i >= k - 1){ // 說明一定構成了一個窗口 則可以取最大值記錄下來 res[idx ++] = nums[deque.peek()]; //不是彈出,是訪問 } } return res; } }
前K個高頻元素

這里利用了一個優先級隊列進行排序操作,使得頻率出現高的一直被保留在pq隊列里面。這里使用的是小頂堆。
PriorityQueue<int[]> pq
- 這是創建了一個存儲
int[]類型數組的優先隊列pq。 PriorityQueue是一個基于堆的優先隊列,默認是最小堆,也就是說它總是優先取出隊列中最小的元素。
2. new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1])
- 這里使用了一個自定義的比較器來定義優先級規則。
PriorityQueue默認按照自然順序進行排序(對于數值型,默認從小到大),但這里我們通過一個 lambda 表達式自定義了比較規則。
解釋比較器 (o1, o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1]:
o1和o2是優先隊列中的兩個int[]數組。- 比較器根據每個數組的第二個元素 (
o1[1]和o2[1]) 來比較兩個數組的大小。 - 如果
o1[1] - o2[1]的結果為負值,說明o1[1]小于o2[1],則o1的優先級更高(排在前面);如果結果為正值,o2的優先級更高。
如果要使用大頂堆:(o1,o2) -> o2[1] - o1[1];
import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Map; import java.util.PriorityQueue; class Solution { public int[] topKFrequent(int[] nums, int k) { PriorityQueue<int[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((o1, o2) -> o1[1] - o2[1]); //小頂堆 int[] res = new int[k]; //這里用來保留我們要選取的前k個高頻的結果 Map<Integer,Integer> map = new HashMap<>(); // key用來存儲值,value用來存儲出現的頻率 for(int num : nums){ map.put(num,map.getOrDefault(num,0)+1); //每次頻率+1 } for(var x : map.entrySet()){ //遍歷map里的每一個鍵值對 int[] temp = new int[2]; temp[0] = x.getKey(); temp[1] = x.getValue(); pq.offer(temp); if(pq.size() > k){ // 我們只保存前k個高頻率的值 pq.poll(); // 刪除隊頭頻率低的值 } } for(int i =0; i < k; i++){ res[i] = pq.poll()[0]; } return res; } }


 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號