Android IPC機制(一)開啟多進程
1. 為何要開啟多進程
為何開啟android應用要開啟多進程,主要有以下幾點:
單進程所分配的內存不夠,需要更多的內存。在早期android系統只為一個單進程的應用分配了16M的可用內存,隨著手機的硬件的提升和android系統的改進,雖然可分配內存越來越多,但仍舊可以通過開啟多進程來獲取更多的內存來處理自己App的業務
獨立運行的組件,比如個推,它的服務會另開一個進程。
運行一些”不可見人”的操作,比如獲取用戶的隱私數據,比如雙守護進程來防止被用戶殺掉
2. 開啟多進程
首先我們寫一個Activity并啟動一個service
public class MyProcessActivity extends AppCompatActivity {
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_my_process);
Intent myServiceIntent=new Intent(MyProcessActivity.this,MyService.class);
this.startService(myServiceIntent);
}
}
service的代碼:
public class MyService extends Service {
private static final String TAG = "wangshu";
@Override
public void onCreate() {
Log.i(TAG,"MyService is oncreate");
}
@Override
public int onStartCommand(Intent intent, int flags, int startId) {
Log.i(TAG, "MyProcessActivity is created: ");
return START_STICKY;
}
@Override
public void onDestroy() {
Log.i(TAG,"OnDestory");
}
@Override
public IBinder onBind(Intent arg0) {
return null;
}
}
最后我們只需要在AndroidManifest.xml中的配置 android:process就可以了
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.example.liuwangshu.myprogress" >
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:name=".MyApplication"
android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:supportsRtl="true"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity android:name=".MyProcessActivity" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<service
android:name=".MyService"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:process=":remote">
</service>
</application>
</manifest>
這里選擇“remote”這個名字是隨意主觀的,你也可以取其他的名字。冒號“:”則代替當前應用的包名,所以MyService跑在進程名為“com.example.liuwangshu.myprogress:remote”的進程中。我們也可以設置 android:process=”com.example.liuwangshu.myprogress.remote”,這樣MyService跑在進程名為“com.example.liuwangshu.myprogress.remote”的進程中。這兩種命名也是有區別的,如果被設置的進程名是以一個冒號開頭的,則這個新的進程對于這個應用來說是私有的,當它被需要或者這個服務需要在新進程中運行的時候,這個新進程將會被創建。如果這個進程的名字是以小寫字符開頭的,則這個服務將運行在一個以這個名字命名的全局的進程中,當然前提是它有相應的權限。這將允許在不同應用中的各種組件可以共享一個進程,從而減少資源的占用。
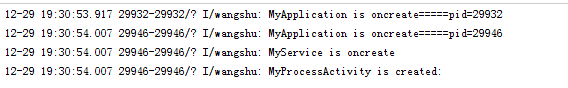
我們運行應用則發現:開啟了兩個進程
3. 開啟多進程引出的問題
開啟多進程會使Application運行兩次,我們繼承Application,在oncreate方法中打log并運行程序

public class MyApplication extends Application {
private static final String TAG = "wangshu";
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
int pid = android.os.Process.myPid();
Log.i(TAG, "MyApplication is oncreate====="+"pid="+pid);
}
在log中我們發現我們開啟的兩個進程都會執行oncreate方法。現在很多開發者都習慣在Application中做初始化操作以及數據的傳遞操作,這顯然是不妥當的,解決的方法就是得到每個進程的名稱,如果進程的名稱和我們應用的進程名稱相同則做我們應用的操作,如果不是則做其他進程的操作
public class MyApplication extends Application {
private static final String TAG = "wangshu";
@Override
public void onCreate() {
super.onCreate();
int pid = android.os.Process.myPid();
Log.i(TAG, "MyApplication is oncreate====="+"pid="+pid);
String processNameString = "";
ActivityManager mActivityManager = (ActivityManager)this.getSystemService(getApplicationContext().ACTIVITY_SERVICE);
for (ActivityManager.RunningAppProcessInfo appProcess : mActivityManager.getRunningAppProcesses()) {
if (appProcess.pid == pid) {
processNameString = appProcess.processName;
}
}
if("com.example.liuwangshu.myprogress".equals(processNameString)){
Log.i(TAG, "processName="+processNameString+"-----work");
}else{
Log.i(TAG, "processName="+processNameString+"-----work");
}
}
}
從Log中可以看到不同的進程執行了不同的操作




 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號