面試題|線程池里有幾個線程在運行
??本文主要改編自文獻1,最大改進是以dubbo EagerThreadPoolExecutor源碼分析其實現機制。下面從一道面試題引入本文主題~~
面試官:"假設有一個空的線程池,配置的核心線程數為10,最大線程數為20,任務隊列長度為100。如果現在來了100個任務,那么線程池里有幾個線程在運行?"
粉絲豪:"應該是10吧!"
面試官:"你確定?"
粉絲豪:"確定啊!就是10…"
??于是乎,漂亮的HR小姐姐讓粉絲豪回去等通知了~
??大家如果看出來了此題的陷阱,就不用看本文了!其實,這道題正確的答案是"不一定!"因為并沒指明是哪一種線程池機制,帶著這個疑問繼續往下看!我們基于jdk 8,以兩類線程池機制——先放隊列再創建線程和先創建線程再放入隊列——來剖析這道面試題。
先放隊列再創建線程
??針對線程數為0的空線程池,來了任務之后,先創建核心線程,核心線程數用完后,新來的任務先進隊列,在隊列滿的時候,再創建線程。這種情況是大家最容易想到的情況,因為JDK中的線程池,也就是ThreadPoolExecutor就是這種機制!OK,我們先來看一下ThreadPoolExecutor的void execute(Runnable command)方法源碼,如下圖所示:

??在int c = ctl.get()代碼上方,折疊了如下所示的一段英文注釋,解釋了上述截圖中的三步流程:
/*
* Proceed in 3 steps:
*
* 1. If fewer than corePoolSize threads are running, try to
* start a new thread with the given command as its first
* task. The call to addWorker atomically checks runState and
* workerCount, and so prevents false alarms that would add
* threads when it shouldn't, by returning false.
*
* 2. If a task can be successfully queued, then we still need
* to double-check whether we should have added a thread
* (because existing ones died since last checking) or that
* the pool shut down since entry into this method. So we
* recheck state and if necessary roll back the enqueuing if
* stopped, or start a new thread if there are none.
*
* 3. If we cannot queue task, then we try to add a new
* thread. If it fails, we know we are shut down or saturated
* and so reject the task.
*/
??如果對英文不感冒,請參考下面的中文翻譯:
- 判斷當前活躍線程數是否小于corePoolSize,如果小于,則調用addWorker創建線程執行任務;
- 如果不小于corePoolSize,則將任務添加到workQueue隊列;
- 如果放入workQueue失敗,則創建線程執行任務,如果這時創建線程失敗(當前線程數不小于maximumPoolSize時),就會調用函數reject拒絕接受任務。
??用一張流程圖來解釋,如下:
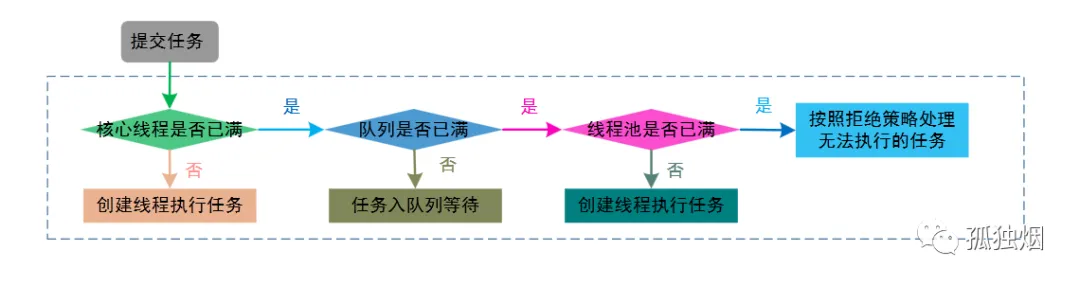
??如圖所示,默認的機制為線程池里的核心線程數不夠了,后面進來的任務會先丟隊列,當隊列滿了,才起新線程。
??因此,按照這套機制!粉絲豪的回答是正確的,當有100個任務添加進來時,先創建10個核心線程,剩下90個任務都丟進阻塞隊列,因此線程池里只有10個線程在執行任務!
先創建線程再放入隊列
??當核心線程數用完后,如果來了新任務,則先創建線程,直至達到最大線程數,再把新任務放入阻塞隊列。在dubbo中,有一種這種機制的線程池叫EagerThreadPoolExecutor線程池;在Tomcat里面也有類似的線程池。
??來看一下EagerThreadPoolExecutor源碼:
public class EagerThreadPoolExecutor extends ThreadPoolExecutor {
/**
* task count
*/
private final AtomicInteger submittedTaskCount = new AtomicInteger(0);
public EagerThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize,
int maximumPoolSize,
long keepAliveTime,
TimeUnit unit, TaskQueue<Runnable> workQueue,
ThreadFactory threadFactory,
RejectedExecutionHandler handler) {
super(corePoolSize, maximumPoolSize, keepAliveTime, unit, workQueue, threadFactory, handler);
}
/**
* @return current tasks which are executed
*/
public int getSubmittedTaskCount() {
return submittedTaskCount.get();
}
@Override
protected void afterExecute(Runnable r, Throwable t) {
submittedTaskCount.decrementAndGet();
}
@Override
public void execute(Runnable command) {
if (command == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// do not increment in method beforeExecute!
submittedTaskCount.incrementAndGet();
try {
super.execute(command);
} catch (RejectedExecutionException rx) {
// retry to offer the task into queue.
final TaskQueue queue = (TaskQueue) super.getQueue();
try {
//將任務提交到隊列中
if (!queue.retryOffer(command, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)) {
submittedTaskCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Queue capacity is full.", rx);
}
} catch (InterruptedException x) {
submittedTaskCount.decrementAndGet();
throw new RejectedExecutionException(x);
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
// decrease any way
submittedTaskCount.decrementAndGet();
throw t;
}
}
}
??主要重寫了ThreadPoolExecutor的函數void execute(Runnable command),如果觸發拒絕策略,那么將任務提交到TaskQueue阻塞隊列中,再看TaskQueue源碼:
??
public class TaskQueue<R extends Runnable> extends LinkedBlockingQueue<Runnable> {
private static final long serialVersionUID = -2635853580887179627L;
private EagerThreadPoolExecutor executor;
public TaskQueue(int capacity) {
super(capacity);
}
public void setExecutor(EagerThreadPoolExecutor exec) {
executor = exec;
}
@Override
public boolean offer(Runnable runnable) {
if (executor == null) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("The task queue does not have executor!");
}
int currentPoolThreadSize = executor.getPoolSize();
// have free worker. put task into queue to let the worker deal with task.
//如果提交任務數小于當前工作線程數,說明當前工作線程足夠處理任務,將提交的任務插入到工作隊列
if (executor.getSubmittedTaskCount() < currentPoolThreadSize) {
return super.offer(runnable);
}
// return false to let executor create new worker.
//重寫代碼的精髓之處:如果提交任務數大于當前工作線程數并且小于最大線程數,說明提交的任務量線程已經處理不過來,那么需要增加線程數,返回false
if (currentPoolThreadSize < executor.getMaximumPoolSize()) {
return false;
}
// currentPoolThreadSize >= max
//工作線程數到達最大線程數,插入到workqueue
return super.offer(runnable);
}
/**
* retry offer task
*
* @param o task
* @return offer success or not
* @throws RejectedExecutionException if executor is terminated.
*/
public boolean retryOffer(Runnable o, long timeout, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
if (executor.isShutdown()) {
throw new RejectedExecutionException("Executor is shutdown!");
}
return super.offer(o, timeout, unit);
}
}
??主要重寫了LinkedBlockingQueue的offer方法,而if (!queue.retryOffer(command, 0, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS))則調用offer,保證在當前線程數小于最大線程數時,直接新增線程。
??因此,如果按照這么一套機制,粉絲豪的答案就不正確了。線程池啟動完畢后進來100個任務時,直接會起20個線程,剩下的80個任務都會被丟進阻塞隊列,綜上所述,現在線程池里有20個線程在運行。
Reference
 Buy me a coffee. ?Get red packets.
Buy me a coffee. ?Get red packets.

 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號