Android復習(二)應用資源——>字符串
轉自:https://developer.android.google.cn/guide/topics/resources/string-resource#kotlin
字符串資源為您的應用提供具有可選文本樣式和格式設置的文本字符串。共有三種類型的資源可為您的應用提供字符串:
- String
- 提供單個字符串的 XML 資源。
- String Array
- 提供字符串數組的 XML 資源。
- Quantity Strings (Plurals)
- 帶有用于多元化的不同字符串的 XML 資源。
所有字符串都能應用某些樣式設置標記和格式設置參數。如需了解有關樣式和格式設置字符串的信息,請參閱格式和樣式設置部分。
String
可從應用或其他資源文件(如 XML 布局)引用的單個字符串。
請注意:字符串是一種簡單資源,您可以使用 name 屬性(并非 XML 文件的名稱)中提供的值對其進行引用。因此,您可以在一個 <resources> 元素下,將字符串資源與其他簡單資源合并到一個 XML 文件中。
- 文件位置:
res/values/filename.xml
filename 是任意值。<string>元素的name用作資源 ID。- 編譯資源的數據類型:
- 指向
String的資源指針。 - 資源引用:
- 在 Java 中:
R.string.string_name
在 XML 中:@string/string_name - 語法:
-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="string_name" >text_string</string> </resources> - 元素:
- 示例:
- 保存在
res/values/strings.xml的 XML 文件:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string name="hello">Hello!</string> </resources>該布局 XML 會對視圖應用一個字符串:
<TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="@string/hello" />以下應用代碼用于檢索字符串:
java代碼: String string = getString(R.string.hello); kotlin代碼: val string: String = getString(R.string.hello)
您可以使用
getString(int)或getText(int)檢索字符串。getText(int)會保留所有應用于字符串的富文本樣式。
String Array
可從應用引用的字符串數組。
請注意:字符串數組是一種簡單資源,您可以使用 name 屬性(并非 XML 文件的名稱)中提供的值對其進行引用。因此,您可以在一個 <resources> 元素下,將字符串數組資源與其他簡單資源合并到一個 XML 文件中。
- 文件位置:
res/values/filename.xml
filename 是任意值。<string-array>元素的name用作資源 ID。- 編譯資源的數據類型:
- 指向
String數組的資源指針。 - 資源引用:
- 在 Java 中:
R.array.string_array_name - 語法:
-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string-array name="string_array_name"> <item >text_string</item> </string-array> </resources> - 元素:
- 示例:
- 保存在
res/values/strings.xml的 XML 文件:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <string-array name="planets_array"> <item>Mercury</item> <item>Venus</item> <item>Earth</item> <item>Mars</item> </string-array> </resources>以下應用代碼用于檢索字符串數組:
java代碼: Resources res = getResources(); String[] planets = res.getStringArray(R.array.planets_array); kotlin代碼: val array: Array = resources.getStringArray(R.array.planets_array)
Quantity Strings (Plurals)
針對語法數量的一致性,不同語言有不同規則。例如,在英語中,數量 1 是一種特殊情況。我們會寫成“1 book”,但如果是任何其他數量,則會寫成“n books”。這種對單復數的區分很常見,但其他語言擁有更細致的區分。Android 支持以下完整集合:zero、one、two、few、many 和 other。
決定為給定語言和數量使用哪種情況的規則可能非常復雜,因此 Android 為您提供 getQuantityString() 等方法來選擇合適資源。
雖然 Quantity Strings 過去稱作“Quantity Strings”(并且 API 中仍采用此名稱),但其只應用于表示復數。例如,類似使用 Quantity Strings 實現 Gmail 的“Inbox”這類情況便屬于錯誤行為,正確的做法是用其實現“Inbox (12)”這種存在未讀郵件的情況。使用 Quantity Strings 來替代 if 語句似乎很方便,但必須注意的是,某些語言(如中文)根本不做這些語法區分,因此您獲取的始終是 other 字符串。
選擇使用哪一個字符串完全取決于語法上的必要性。在英語中,即使數量為 0,表示 zero 的字符串也會被忽略,因為在語法上,0 與 2 或除 1 以外的任何其他數字并無區別(“zero books”、“one book”、“two books”等)。相反,韓語中僅使用過 other 字符串。
請勿被某些事實誤導,例如 two 聽起來僅適用于數量 2:某種語言可能規定,對 2、12、102(依此類推)等數量進行相同處理,但對其他數量進行特殊處理。您可以依靠翻譯人員來了解其語言的實際區分要求。
通常,您可以利用“Books: 1”等無需考慮數量的表示,從而避免使用 Quantity Strings。如果您的應用可接受此樣式,則您和翻譯人員的工作都會更輕松。
請注意:Plurals 集合是一種簡單資源,您可以使用 name 屬性(并非 XML 文件的名稱)中提供的值對其進行引用。因此,您可以在一個 <resources> 元素下,將 plurals 資源與其他簡單資源合并到一個 XML 文件中。
- 文件位置:
res/values/filename.xml
filename 是任意值。<plurals>元素的name用作資源 ID。- 資源引用:
- 在 Java 中:
R.plurals.plural_name - 語法:
-
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <plurals name="plural_name"> <item quantity=["zero" | "one" | "two" | "few" | "many" | "other"] >text_string</item> </plurals> </resources> - 元素:
- 示例:
- 保存在
res/values/strings.xml的 XML 文件:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <plurals name="numberOfSongsAvailable"> <!-- As a developer, you should always supply "one" and "other" strings. Your translators will know which strings are actually needed for their language. Always include %d in "one" because translators will need to use %d for languages where "one" doesn't mean 1 (as explained above). --> <item quantity="one">%d song found.</item> <item quantity="other">%d songs found.</item> </plurals> </resources>保存在
res/values-pl/strings.xml中的 XML 文件:<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <resources> <plurals name="numberOfSongsAvailable"> <item quantity="one">Znaleziono %d piosenk?.</item> <item quantity="few">Znaleziono %d piosenki.</item> <item quantity="other">Znaleziono %d piosenek.</item> </plurals> </resources>用法:
java代碼: int count = getNumberOfSongsAvailable(); Resources res = getResources(); String songsFound = res.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count, count); kotlin代碼: val count = getNumberOfSongsAvailable() val songsFound = resources.getQuantityString(R.plurals.numberOfSongsAvailable, count, count)
使用
getQuantityString()方法時,如果您的字符串包含帶有數字的字符串格式設置,則您需要傳遞兩次count。例如,對于字符串%d songs found,第一個count參數會選擇相應的復數字符串,第二個count參數會被插入%d占位符內。如果您的復數字符串沒有字符串格式設置,則無需向getQuantityString傳遞第三個參數。
格式和樣式
關于如何正確設置字符串資源的格式和樣式,您應了解以下幾個要點。
處理特殊字符
如果 XML 或 Android 中的字符串包含有特殊用法的字符,則必須轉義這些字符。您可以使用前導反斜杠轉義某些字符,但其他字符需使用 XML 轉義。您也可以通過在雙引號中包括整個字符串,處理撇號和單引號。以下為部分示例:
| 字符 | 轉義形式 |
|---|---|
| @ | \@ |
| ? | \? |
| < | < |
| & | & |
單引號 (') |
以下任意字符:
|
雙引號 (") |
以下任意字符:
請注意,您必須轉義雙引號。在單引號中包括字符串沒有任何作用。 |
設置字符串格式
如需設置字符串的格式,您可以在字符串資源中放入格式參數(如以下示例資源所示)。
<string name="welcome_messages">Hello, %1$s! You have %2$d new messages.</string>
在本例中,格式字符串有兩個參數:%1$s 為字符串,而 %2$d 為十進制數字。然后,您可通過調用 getString(int, Object...) 來設置字符串格式。例如:
使用 HTML 標記設置樣式
您可以使用 HTML 標記為字符串添加樣式設置。例如:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<resources>
<string name="welcome">Welcome to <b>Android</b>!</string>
</resources>
支持以下 HTML 元素:
- 粗體:<b>、<em>
- 斜體:<i>、<cite>、<dfn>
- 文本放大 25%:<big>
- 文本縮小 20%:<small>
- 設置字體屬性:<font face=”font_family“ color=”hex_color”>。可能的字體系列示例包括
monospace、serif和sans_serif。 - 設置等寬字體系列:<tt>
- 刪除線:<s>、<strike>、<del>
- 下劃線:<u>
- 上標:<sup>
- 下標:<sub>
- 列表標記:<ul>、<li>
- 換行符:<br>
- 區隔標記:<div>
- CSS 樣式:<span style=”color|background_color|text-decoration”>
- 段落:<p dir=”rtl | ltr” style=”…”>
如果您沒有應用格式設置,則可通過調用 setText(java.lang.CharSequence) 直接設置 TextView 文本。但在某些情況下,您可能想創建帶樣式的文本資源,并將其用作格式字符串。您通常無法實現此目標,因為 format(String, Object...) 和 getString(int, Object...) 方法會刪除字符串中的所有樣式信息。解決方法是編寫帶轉義實體的 HTML 標記,并在完成格式設置后通過 fromHtml(String) 恢復這些實體。例如:
- 將您帶樣式的文本資源存儲為 HTML 轉義字符串:
<resources> <string name="welcome_messages">Hello, %1$s! You have <b>%2$d new messages</b>.</string> </resources>
如上所示,帶格式的字符串中添加了
<b>元素。請注意,開括號使用<符號實現了 HTML 轉義。 - 然后照常設置字符串格式,但還需調用
fromHtml(String),以將 HTML 文本轉換成帶樣式的文本:java代碼: String text = getString(R.string.welcome_messages, username, mailCount); Spanned styledText = Html.fromHtml(text, FROM_HTML_MODE_LEGACY); kotlin代碼: val text: String = getString(R.string.welcome_messages, username, mailCount) val styledText: Spanned = Html.fromHtml(text, FROM_HTML_MODE_LEGACY)
由于 fromHtml(String) 方法會設置所有 HTML 實體的格式,因此請務必使用 htmlEncode(String) 轉義帶格式文本的字符串中任何可能存在的 HTML 字符。例如,如果您打算對包含“<”或“&”等字符的字符串進行格式設置,則在設置格式前必須先轉義這類字符。如此一來,當通過 fromHtml(String) 傳遞帶格式的字符串時,字符才會以最初的編寫形式顯示。例如:
java代碼: String escapedUsername = TextUtils.htmlEncode(username); String text = getString(R.string.welcome_messages, escapedUsername, mailCount); Spanned styledText = Html.fromHtml(text); kotlin代碼: val escapedUsername: String = TextUtils.htmlEncode(username) val text: String = getString(R.string.welcome_messages, escapedUsername, mailCount) val styledText: Spanned = Html.fromHtml(text, FROM_HTML_MODE_LEGACY)
使用 Spannable 設置樣式
Spannable 是一種文本對象,您可使用顏色和字體粗細等字體屬性對其進行樣式設置。您可以使用 SpannableStringBuilder 生成文本,然后對文本應用 android.text.style 軟件包中定義的樣式。
您可以使用以下輔助方法設置創建 spannable 文本的大量工作:
java代碼
/**
* Returns a CharSequence that concatenates the specified array of CharSequence
* objects and then applies a list of zero or more tags to the entire range.
*
* @param content an array of character sequences to apply a style to
* @param tags the styled span objects to apply to the content
* such as android.text.style.StyleSpan
*
*/
private static CharSequence applyStyles(CharSequence[] content, Object[] tags) {
SpannableStringBuilder text = new SpannableStringBuilder();
openTags(text, tags);
for (CharSequence item : content) {
text.append(item);
}
closeTags(text, tags);
return text;
}
/**
* Iterates over an array of tags and applies them to the beginning of the specified
* Spannable object so that future text appended to the text will have the styling
* applied to it. Do not call this method directly.
*/
private static void openTags(Spannable text, Object[] tags) {
for (Object tag : tags) {
text.setSpan(tag, 0, 0, Spannable.SPAN_MARK_MARK);
}
}
/**
* "Closes" the specified tags on a Spannable by updating the spans to be
* endpoint-exclusive so that future text appended to the end will not take
* on the same styling. Do not call this method directly.
*/
private static void closeTags(Spannable text, Object[] tags) {
int len = text.length();
for (Object tag : tags) {
if (len > 0) {
text.setSpan(tag, 0, len, Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE);
} else {
text.removeSpan(tag);
}
}
}
kotlin 代碼:
/**
* Returns a CharSequence that concatenates the specified array of CharSequence
* objects and then applies a list of zero or more tags to the entire range.
*
* @param content an array of character sequences to apply a style to
* @param tags the styled span objects to apply to the content
* such as android.text.style.StyleSpan
*/
private fun apply(content: Array<out CharSequence>, vararg tags: Any): CharSequence {
return SpannableStringBuilder().apply {
openTags(tags)
content.forEach { charSequence ->
append(charSequence)
}
closeTags(tags)
}
}
/**
* Iterates over an array of tags and applies them to the beginning of the specified
* Spannable object so that future text appended to the text will have the styling
* applied to it. Do not call this method directly.
*/
private fun Spannable.openTags(tags: Array<out Any>) {
tags.forEach { tag ->
setSpan(tag, 0, 0, Spannable.SPAN_MARK_MARK)
}
}
/**
* "Closes" the specified tags on a Spannable by updating the spans to be
* endpoint-exclusive so that future text appended to the end will not take
* on the same styling. Do not call this method directly.
*/
private fun Spannable.closeTags(tags: Array<out Any>) {
tags.forEach { tag ->
if (length > 0) {
setSpan(tag, 0, length, Spanned.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE)
} else {
removeSpan(tag)
}
}
}
以下 bold、italic 和 color 方法包含上述輔助方法,并展示應用 android.text.style 軟件包中所定義樣式的具體示例。通過創建類似的方法,您也可對其他類型的文本進行樣式設置。
java代碼:
/**
* Returns a CharSequence that applies boldface to the concatenation
* of the specified CharSequence objects.
*/
public static CharSequence bold(CharSequence... content) {
return apply(content, new StyleSpan(Typeface.BOLD));
}
/**
* Returns a CharSequence that applies italics to the concatenation
* of the specified CharSequence objects.
*/
public static CharSequence italic(CharSequence... content) {
return apply(content, new StyleSpan(Typeface.ITALIC));
}
/**
* Returns a CharSequence that applies a foreground color to the
* concatenation of the specified CharSequence objects.
*/
public static CharSequence color(int color, CharSequence... content) {
return apply(content, new ForegroundColorSpan(color));
}
kotlin代碼:
/**
* Returns a CharSequence that applies boldface to the concatenation
* of the specified CharSequence objects.
*/
fun bold(vararg content: CharSequence): CharSequence = apply(content, StyleSpan(Typeface.BOLD))
/**
* Returns a CharSequence that applies italics to the concatenation
* of the specified CharSequence objects.
*/
fun italic(vararg content: CharSequence): CharSequence = apply(content, StyleSpan(Typeface.ITALIC))
/**
* Returns a CharSequence that applies a foreground color to the
* concatenation of the specified CharSequence objects.
*/
fun color(color: Int, vararg content: CharSequence): CharSequence =
apply(content, ForegroundColorSpan(color))
以下示例展示如何通過結合這些方法,向短語中的單個字詞應用各種樣式:
Java代碼:
// Create an italic "hello, " a red "world",
// and bold the entire sequence.
var text = bold(italic(getString(R.string.hello)),
color(Color.RED, getString(R.string.world)))
</pre>
</section><section><h3 id="java">Java</h3>
<pre class="prettyprint lang-java">
// Create an italic "hello, " a red "world",
// and bold the entire sequence.
CharSequence text = bold(italic(getString(R.string.hello)),
color(Color.RED, getString(R.string.world)));
kotlin代碼:
// Create an italic "hello, " a red "world",
// and bold the entire sequence.
val text: CharSequence = bold(italic(getString(R.string.hello)),
color(Color.RED, getString(R.string.world)))
core-ktx Kotlin 模塊還包含擴展函數,便于您更輕松地使用 span。您可以前往 GitHub 查看 android.text 軟件包文檔,了解詳情。
如需了解有關使用 span 的更多信息,請訪問以下鏈接:
使用注解設置樣式
您可以通過使用 strings.xml 資源文件中的 Annotation 類和 <annotation> 標記,應用復雜樣式或自定義樣式。借助注解標記,您可以通過在 XML 文件中定義自定義鍵值對來標記自定義樣式的部分字符串,框架隨后會將該 XML 文件轉換成 Annotation span。然后,您便可檢索這些注解,并使用鍵和值來應用樣式。
創建注解時,請務必為 strings.xml 文件中的所有字符串翻譯添加 <annotation> 標記。
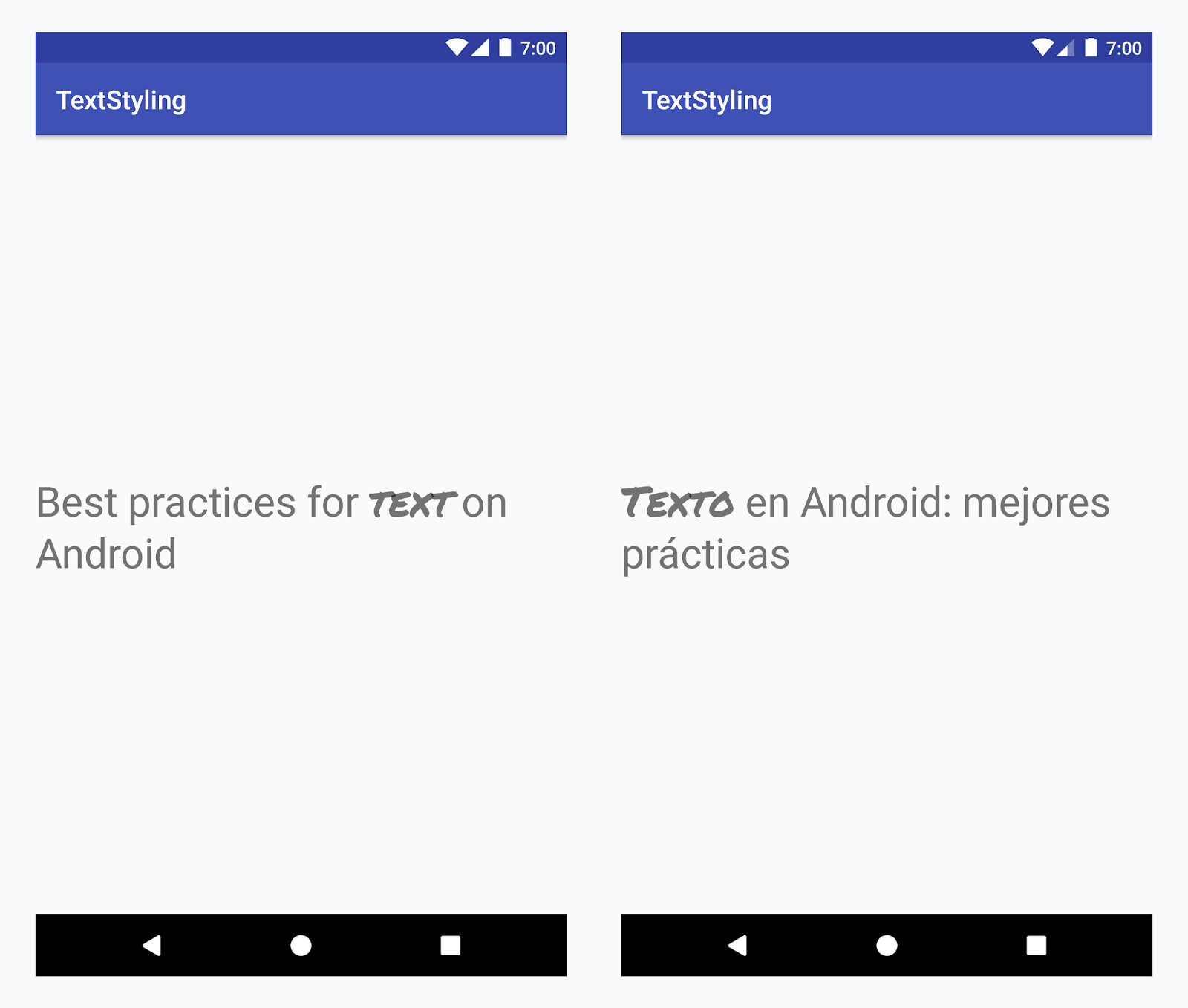
在所有語言中向“text”一詞應用自定義字體
示例 - 添加自定義字體
-
添加
<annotation>標記并定義鍵值對。在此情況下,鍵為 font,而值是我們要使用的字體類型:title_emphasis// values/strings.xml <string name="title">Best practices for <annotation font="title_emphasis">text</annotation> on Android</string> // values-es/strings.xml <string name="title"><annotation font="title_emphasis">Texto</annotation> en Android: mejores prácticas</string>
-
加載字符串資源并找到包含 font 鍵的注解。然后,創建一個自定義 span,并用其替換現有 span。
java代碼: // get the text as SpannedString so we can get the spans attached to the text SpannedString titleText = (SpannedString) getText(R.string.title_about); // get all the annotation spans from the text Annotation[] annotations = titleText.getSpans(0, titleText.length(), Annotation.class); // create a copy of the title text as a SpannableString. // the constructor copies both the text and the spans. so we can add and remove spans SpannableString spannableString = new SpannableString(titleText); // iterate through all the annotation spans for (Annotation annotation: annotations) { // look for the span with the key font if (annotation.getKey().equals("font")) { String fontName = annotation.getValue(); // check the value associated to the annotation key if (fontName.equals("title_emphasis")) { // create the typeface Typeface typeface = ResourcesCompat.getFont(this, R.font.roboto_mono); // set the span at the same indices as the annotation spannableString.setSpan(new CustomTypefaceSpan(typeface), titleText.getSpanStart(annotation), titleText.getSpanEnd(annotation), Spannable.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE); } } } // now, the spannableString contains both the annotation spans and the CustomTypefaceSpan styledText.text = spannableString; kotlin代碼: // get the text as SpannedString so we can get the spans attached to the text val titleText = getText(R.string.title) as SpannedString // get all the annotation spans from the text val annotations = titleText.getSpans(0, titleText.length, Annotation::class.java) // create a copy of the title text as a SpannableString. // the constructor copies both the text and the spans. so we can add and remove spans val spannableString = SpannableString(titleText) // iterate through all the annotation spans for (annotation in annotations) { // look for the span with the key font if (annotation.key == "font") { val fontName = annotation.value // check the value associated to the annotation key if (fontName == "title_emphasis") { // create the typeface val typeface = getFontCompat(R.font.permanent_marker) // set the span at the same indices as the annotation spannableString.setSpan(CustomTypefaceSpan(typeface), titleText.getSpanStart(annotation), titleText.getSpanEnd(annotation), Spannable.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE) } } } // now, the spannableString contains both the annotation spans and the CustomTypefaceSpan styledText.text = spannableString
如果您多次使用相同文本,則應構建一次 SpannableString 對象并根據需要重復使用該對象,以避免出現潛在的性能和內存問題。
如需了解注解用法的更多示例,請參閱在 Android 中設置國際化文本的樣式
注解 span 和文本打包
Annotation span 也是 ParcelableSpans,因此需對鍵值對進行打包和拆包。只要包的接收方了解如何解釋注解,您便可使用 Annotation span 向打包文本應用自定義樣式。
如要在向 Intent Bundle 傳遞文本時保留自定義樣式,您首先需在文本中添加 Annotation span。您可以使用 <annotation> 標記在 XML 資源中執行此操作(如上例所示),或通過創建新的 Annotation 并將其設置為 span,在代碼中執行此操作(如下所示):
java代碼:
SpannableString spannableString = new SpannableString("My spantastic text");
Annotation annotation = new Annotation("font", "title_emphasis");
spannableString.setSpan(annotation, 3, 7, 33);
// start Activity with text with spans
Intent intent = new Intent(this, MainActivity.class);
intent.putExtra(TEXT_EXTRA, spannableString);
this.startActivity(intent);
kotlin代碼:
val spannableString = SpannableString("My spantastic text")
val annotation = Annotation("font", "title_emphasis")
spannableString.setSpan(annotation, 3, 7, Spannable.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE)
// start Activity with text with spans
val intent = Intent(this, MainActivity::class.java)
intent.putExtra(TEXT_EXTRA, spannableString)
startActivity(intent)
以 SpannableString 的形式從 Bundle 中檢索文本,然后解析附加的注解(如上例所示)。
java代碼: // read text with Spans SpannableString intentCharSequence = (SpannableString)intent.getCharSequenceExtra(TEXT_EXTRA); kotlin代碼: // read text with Spans val intentCharSequence = intent.getCharSequenceExtra(TEXT_EXTRA) as SpannableString




 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號