Spring BeanFactory 接口
[[Spring IOC 源碼學(xué)習(xí)總筆記](méi)]
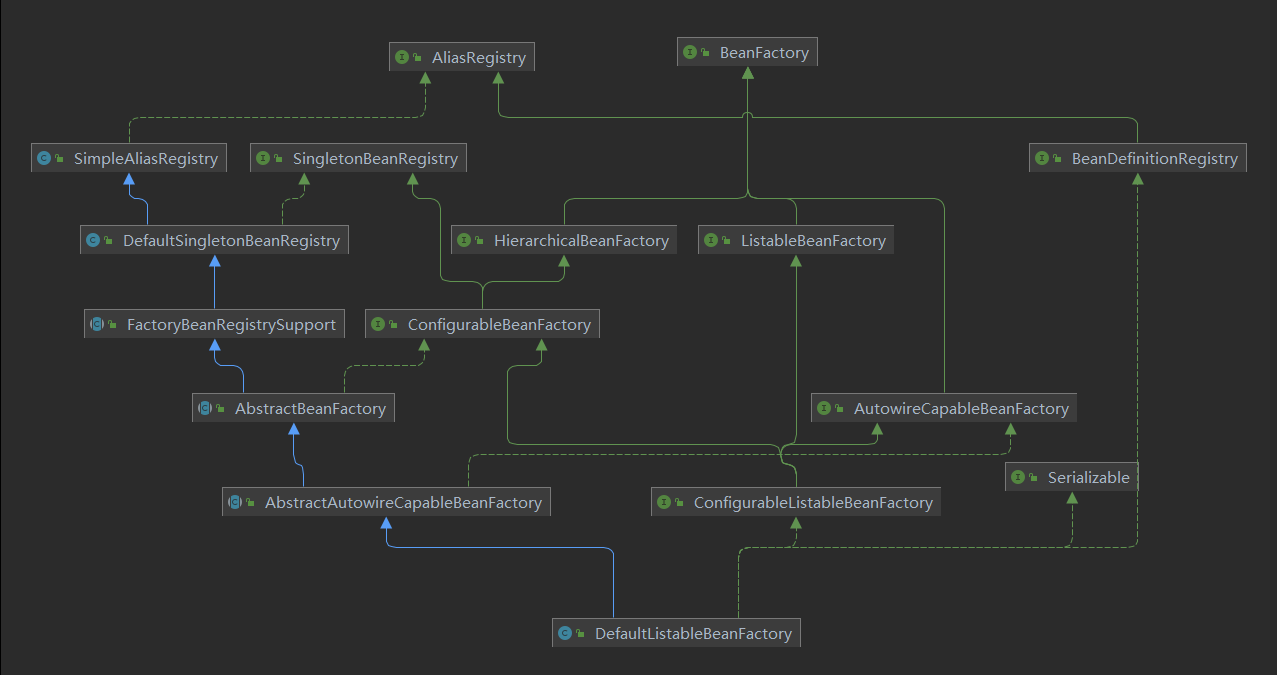
BeanFactory 的子接口
Spring BeanFactory 的設(shè)計(jì), 基于接口隔離原則(Interface Segregation Principle), 將具有不同細(xì)分的功能定義為接口, 增加擴(kuò)展性, 支持不同功能的 BeanFactory 再實(shí)現(xiàn)其接口即可
上圖:
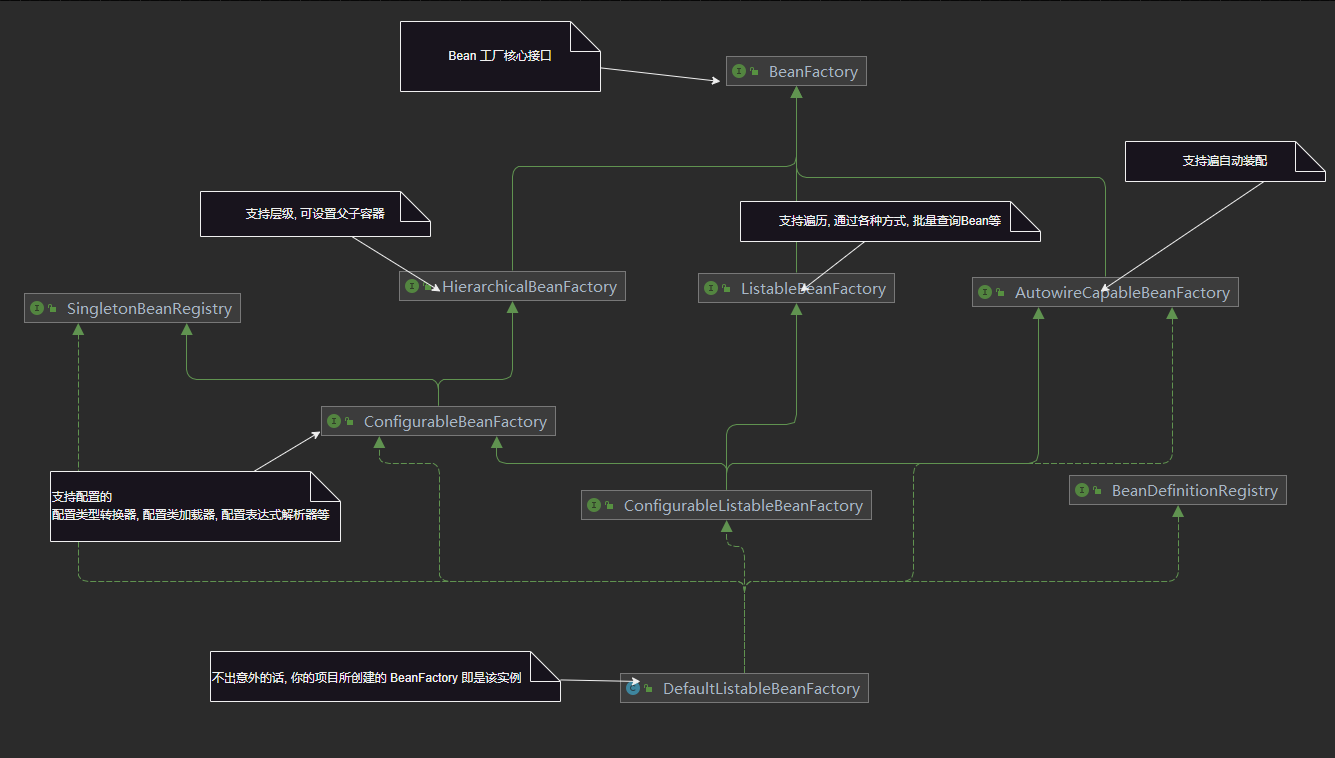
HierarchicalBeanFactory
支持層次的BeanFactory, 可以通過(guò)getParentBeanFactory()方法獲取父級(jí)BeanFactory,實(shí)現(xiàn)了容器之間的層次關(guān)系。
org.springframework.beans.factory.HierarchicalBeanFactory
package org.springframework.beans.factory;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Sub-interface implemented by bean factories that can be part
* of a hierarchy.
*
* <p>The corresponding {@code setParentBeanFactory} method for bean
* factories that allow setting the parent in a configurable
* fashion can be found in the ConfigurableBeanFactory interface.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 07.07.2003
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory#setParentBeanFactory
*/
public interface HierarchicalBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
/**
* Return the parent bean factory, or {@code null} if there is none.
*/
@Nullable
BeanFactory getParentBeanFactory();
/**
* Return whether the local bean factory contains a bean of the given name,
* ignoring beans defined in ancestor contexts.
* <p>This is an alternative to {@code containsBean}, ignoring a bean
* of the given name from an ancestor bean factory.
* @param name the name of the bean to query
* @return whether a bean with the given name is defined in the local factory
* @see BeanFactory#containsBean
*/
boolean containsLocalBean(String name);
}
ListableBeanFactory
支持通過(guò)名稱獲取所有的bean定義,而不是只獲取一個(gè)bean。提供幾種遍歷查找的方法, 主要是:
getBeanDefinitionNames返回 BeanFactory 定義的所有 bean 名稱getBeansOfType根據(jù)類型 獲取獲取 查找 beangetBeanNamesForAnnotation獲取被注解修飾過(guò)的 bean
in short 它提供可以遍歷 查找 bean 的一系列方法, 而不是只能一個(gè)一個(gè)獲取
org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory 部分源碼
/**
* Extension of the {@link BeanFactory} interface to be implemented by bean factories
* that can enumerate all their bean instances, rather than attempting bean lookup
* by name one by one as requested by clients. BeanFactory implementations that
* preload all their bean definitions (such as XML-based factories) may implement
* this interface.
*
* <p>If this is a {@link HierarchicalBeanFactory}, the return values will <i>not</i>
* take any BeanFactory hierarchy into account, but will relate only to the beans
* defined in the current factory. Use the {@link BeanFactoryUtils} helper class
* to consider beans in ancestor factories too.
*
* <p>The methods in this interface will just respect bean definitions of this factory.
* They will ignore any singleton beans that have been registered by other means like
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory}'s
* {@code registerSingleton} method, with the exception of
* {@code getBeanNamesForType} and {@code getBeansOfType} which will check
* such manually registered singletons too. Of course, BeanFactory's {@code getBean}
* does allow transparent access to such special beans as well. However, in typical
* scenarios, all beans will be defined by external bean definitions anyway, so most
* applications don't need to worry about this differentiation.
*
* <p><b>NOTE:</b> With the exception of {@code getBeanDefinitionCount}
* and {@code containsBeanDefinition}, the methods in this interface
* are not designed for frequent invocation. Implementations may be slow.
*
* @author Rod Johnson
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 16 April 2001
* @see HierarchicalBeanFactory
* @see BeanFactoryUtils
*/
public interface ListableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
/**
* Return the names of all beans defined in this factory.
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in,
* and ignores any singleton beans that have been registered by
* other means than bean definitions.
* @return the names of all beans defined in this factory,
* or an empty array if none defined
*/
String[] getBeanDefinitionNames();
/**
* Return the bean instances that match the given object type (including
* subclasses), judging from either bean definitions or the value of
* {@code getObjectType} in the case of FactoryBeans.
* <p><b>NOTE: This method introspects top-level beans only.</b> It does <i>not</i>
* check nested beans which might match the specified type as well.
* <p>Does consider objects created by FactoryBeans, which means that FactoryBeans
* will get initialized. If the object created by the FactoryBean doesn't match,
* the raw FactoryBean itself will be matched against the type.
* <p>Does not consider any hierarchy this factory may participate in.
* Use BeanFactoryUtils' {@code beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors}
* to include beans in ancestor factories too.
* <p>Note: Does <i>not</i> ignore singleton beans that have been registered
* by other means than bean definitions.
* <p>This version of getBeansOfType matches all kinds of beans, be it
* singletons, prototypes, or FactoryBeans. In most implementations, the
* result will be the same as for {@code getBeansOfType(type, true, true)}.
* <p>The Map returned by this method should always return bean names and
* corresponding bean instances <i>in the order of definition</i> in the
* backend configuration, as far as possible.
* @param type the class or interface to match, or {@code null} for all concrete beans
* @return a Map with the matching beans, containing the bean names as
* keys and the corresponding bean instances as values
* @throws BeansException if a bean could not be created
* @since 1.1.2
* @see FactoryBean#getObjectType
* @see BeanFactoryUtils#beansOfTypeIncludingAncestors(ListableBeanFactory, Class)
*/
<T> Map<String, T> getBeansOfType(@Nullable Class<T> type) throws BeansException;
/**
* Find all names of beans which are annotated with the supplied {@link Annotation}
* type, without creating corresponding bean instances yet.
* <p>Note that this method considers objects created by FactoryBeans, which means
* that FactoryBeans will get initialized in order to determine their object type.
* @param annotationType the type of annotation to look for
* (at class, interface or factory method level of the specified bean)
* @return the names of all matching beans
* @since 4.0
* @see #getBeansWithAnnotation(Class)
* @see #findAnnotationOnBean(String, Class)
*/
String[] getBeanNamesForAnnotation(Class<? extends Annotation> annotationType);
AutowireCapableBeanFactory
支持自動(dòng)裝配。可以通過(guò)該接口的方法實(shí)現(xiàn)對(duì)bean的自動(dòng)裝配,包括構(gòu)造函數(shù)注入、屬性注入等。
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.AutowireCapableBeanFactory 部分源碼
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import java.util.Set;
import org.springframework.beans.BeansException;
import org.springframework.beans.TypeConverter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoUniqueBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
/**
* Extension of the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory}
* interface to be implemented by bean factories that are capable of
* autowiring, provided that they want to expose this functionality for
* existing bean instances.
*
* <p>This subinterface of BeanFactory is not meant to be used in normal
* application code: stick to {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory}
* or {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory} for
* typical use cases.
*
* <p>Integration code for other frameworks can leverage this interface to
* wire and populate existing bean instances that Spring does not control
* the lifecycle of. This is particularly useful for WebWork Actions and
* Tapestry Page objects, for example.
*
* <p>Note that this interface is not implemented by
* {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext} facades,
* as it is hardly ever used by application code. That said, it is available
* from an application context too, accessible through ApplicationContext's
* {@link org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext#getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()}
* method.
*
* <p>You may also implement the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware}
* interface, which exposes the internal BeanFactory even when running in an
* ApplicationContext, to get access to an AutowireCapableBeanFactory:
* simply cast the passed-in BeanFactory to AutowireCapableBeanFactory.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 04.12.2003
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactoryAware
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext#getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()
*/
public interface AutowireCapableBeanFactory extends BeanFactory {
/**
* Constant that indicates no externally defined autowiring. Note that
* BeanFactoryAware etc and annotation-driven injection will still be applied.
* 未定義注入方式?
* @see #autowire
* @see #autowireBeanProperties
*/
int AUTOWIRE_NO = 0;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring bean properties by name
* (applying to all bean property setters).
* 通過(guò)名稱注入
* @see #autowire
* @see #autowireBeanProperties
*/
int AUTOWIRE_BY_NAME = 1;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring bean properties by type
* (applying to all bean property setters).
* 通過(guò)類型注入
* @see #autowire
* @see #autowireBeanProperties
*/
int AUTOWIRE_BY_TYPE = 2;
/**
* Constant that indicates autowiring the greediest constructor that
* can be satisfied (involves resolving the appropriate constructor).
* @see #autowire
* 通過(guò)構(gòu)造函數(shù)注入
*/
int AUTOWIRE_CONSTRUCTOR = 3;
/**
* Constant that indicates determining an appropriate autowire strategy
* through introspection of the bean class.
* @see #autowire
* @deprecated as of Spring 3.0: If you are using mixed autowiring strategies,
* prefer annotation-based autowiring for clearer demarcation of autowiring needs.
* 自動(dòng)選擇
*/
@Deprecated
int AUTOWIRE_AUTODETECT = 4;
/**
* Suffix for the "original instance" convention when initializing an existing
* bean instance: to be appended to the fully-qualified bean class name,
* e.g. "com.mypackage.MyClass.ORIGINAL", in order to enforce the given instance
* to be returned, i.e. no proxies etc.
* @since 5.1
* @see #initializeBean(Object, String)
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization(Object, String)
* @see #applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization(Object, String)
*/
String ORIGINAL_INSTANCE_SUFFIX = ".ORIGINAL";
ConfigurableBeanFactory
繼承自AutowireCapableBeanFactory接口,提供了配置BeanFactory的方法,如設(shè)置類加載器、屬性編輯器、BeanPostProcessors等。
org.springframework.beans.factory.config.ConfigurableBeanFactory 的部分源碼
package org.springframework.beans.factory.config;
import java.beans.PropertyEditor;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyEditorRegistrar;
import org.springframework.beans.PropertyEditorRegistry;
import org.springframework.beans.TypeConverter;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.HierarchicalBeanFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.NoSuchBeanDefinitionException;
import org.springframework.core.convert.ConversionService;
import org.springframework.core.metrics.ApplicationStartup;
import org.springframework.lang.Nullable;
import org.springframework.util.StringValueResolver;
/**
* Configuration interface to be implemented by most bean factories. Provides
* facilities to configure a bean factory, in addition to the bean factory
* client methods in the {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory}
* interface.
*
* 繼承自`AutowireCapableBeanFactory`接口,提供了配置`BeanFactory`的方法,如設(shè)置類加載器、屬性編輯器、BeanPostProcessors等。
*
* <p>This bean factory interface is not meant to be used in normal application
* code: Stick to {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory} or
* {@link org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory} for typical
* needs. This extended interface is just meant to allow for framework-internal
* plug'n'play and for special access to bean factory configuration methods.
*
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @since 03.11.2003
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanFactory
* @see org.springframework.beans.factory.ListableBeanFactory
* @see ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
*/
public interface ConfigurableBeanFactory extends HierarchicalBeanFactory, SingletonBeanRegistry {
/**
* 設(shè)置加載bean 的類加載器
* Set the class loader to use for loading bean classes.
* Default is the thread context class loader.
* <p>Note that this class loader will only apply to bean definitions
* that do not carry a resolved bean class yet. This is the case as of
* Spring 2.0 by default: Bean definitions only carry bean class names,
* to be resolved once the factory processes the bean definition.
* @param beanClassLoader the class loader to use,
* or {@code null} to suggest the default class loader
*/
void setBeanClassLoader(@Nullable ClassLoader beanClassLoader);
/**
* 設(shè)置解析表達(dá)式的 解釋器
* Specify the resolution strategy for expressions in bean definition values.
* <p>There is no expression support active in a BeanFactory by default.
* An ApplicationContext will typically set a standard expression strategy
* here, supporting "#{...}" expressions in a Unified EL compatible style.
* @since 3.0
*/
void setBeanExpressionResolver(@Nullable BeanExpressionResolver resolver);
/**
* 設(shè)置屬性類型轉(zhuǎn)換的 轉(zhuǎn)換器
* Specify a {@link ConversionService} to use for converting
* property values, as an alternative to JavaBeans PropertyEditors.
* @since 3.0
*/
void setConversionService(@Nullable ConversionService conversionService);
/**
* 添加 屬性編輯器
* 在 屬性填充時(shí) 會(huì)用到的, 見[[Spring 中的屬性填充]]
* Add a PropertyEditorRegistrar to be applied to all bean creation processes.
* <p>Such a registrar creates new PropertyEditor instances and registers them
* on the given registry, fresh for each bean creation attempt. This avoids
* the need for synchronization on custom editors; hence, it is generally
* preferable to use this method instead of {@link #registerCustomEditor}.
* @param registrar the PropertyEditorRegistrar to register
*/
void addPropertyEditorRegistrar(PropertyEditorRegistrar registrar);
/**
* 添加 bean 的前置和后置處理器
* 在 bean 實(shí)例化, 填充完屬性后會(huì)回調(diào)的
* Add a new BeanPostProcessor that will get applied to beans created
* by this factory. To be invoked during factory configuration.
* <p>Note: Post-processors submitted here will be applied in the order of
* registration; any ordering semantics expressed through implementing the
* {@link org.springframework.core.Ordered} interface will be ignored. Note
* that autodetected post-processors (e.g. as beans in an ApplicationContext)
* will always be applied after programmatically registered ones.
* @param beanPostProcessor the post-processor to register
*/
void addBeanPostProcessor(BeanPostProcessor beanPostProcessor);
BeanFactory 的關(guān)鍵屬性
以 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 入口創(chuàng)建的 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory 為例:
三級(jí)緩存 Map
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry
/** Cache of singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
/**
* 一級(jí)緩存 這是最終緩存實(shí)例的地方,保存完全初始化并準(zhǔn)備好的Bean實(shí)例。
* 所屬: org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#singletonObjects
*/
private final Map<String, Object> singletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/**
* 二級(jí)緩存
* 里面存放的是提早曝光的單例對(duì)象,早期對(duì)象(earlySingletonObjects)。簡(jiǎn)而言之 就是剛new出來(lái)的對(duì)象,可是這個(gè)對(duì)象還沒(méi)填充屬性
* 所屬: org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#singletonFactories
*/
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
/** Cache of early singleton objects: bean name to bean instance. */
/**
* 二級(jí)緩存
* 存放早期暴露出來(lái)的Bean對(duì)象,實(shí)例化以后,就把對(duì)象放到這個(gè)Map中。(Bean可能只經(jīng)過(guò)實(shí)例化,屬性還未填充)
* 所屬: org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultSingletonBeanRegistry#earlySingletonObjects
*/
private final Map<String, Object> earlySingletonObjects = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
BeanDefinition 和 PropertyEditorRegistrar
/**
* 緩存容器中, 所有Bean的 RootBeanDefinition (RootBeanDefinition 可以理解為是Bean完整的描述元數(shù)據(jù))
* 所屬 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#mergedBeanDefinitions
**/
private final Map<String, RootBeanDefinition> mergedBeanDefinitions = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
/**
* 存儲(chǔ)所有屬性編輯的 PropertyEditorRegistry
* 見筆記: 擴(kuò)展 Bean 屬性填充時(shí)的邏輯
*/
//org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#propertyEditorRegistrars
private final Set<PropertyEditorRegistrar> propertyEditorRegistrars = new LinkedHashSet<>(4);
////////////////////// DefaultListableBeanFactory
/**
這個(gè)list 存儲(chǔ)所有的 bean definition 名稱
所屬 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.DefaultListableBeanFactory#beanDefinitionNames
*/
private volatile List<String> beanDefinitionNames = new ArrayList<>(256);
后置處理器
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory
/**
* 直接添加在 context 中的 BeanPostProcessor
* 所屬 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.AbstractBeanFactory#mergedBeanDefinitions
**/
private final List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new BeanPostProcessorCacheAwareList();
factoryBean 緩存
org.springframework.beans.factory.support.FactoryBeanRegistrySupport
/**
* 緩存 factoryBeans 的目標(biāo)對(duì)象, 注意是單例bean才會(huì)放進(jìn)去Map
* 所屬 org.springframework.beans.factory.support.FactoryBeanRegistrySupport#factoryBeanObjectCache
*/
private final Map<String, Object> factoryBeanObjectCache = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(16);
注意 是FactoryBean 不是 BeanFactory, 不要傻傻分不清



 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號(hào)