【單調棧】
單調棧
采取的是空間換時間的方式。將歷史信息保存在具有自己定義出入棧規則的棧中,來達到記憶的效果,實現了空間換時間。
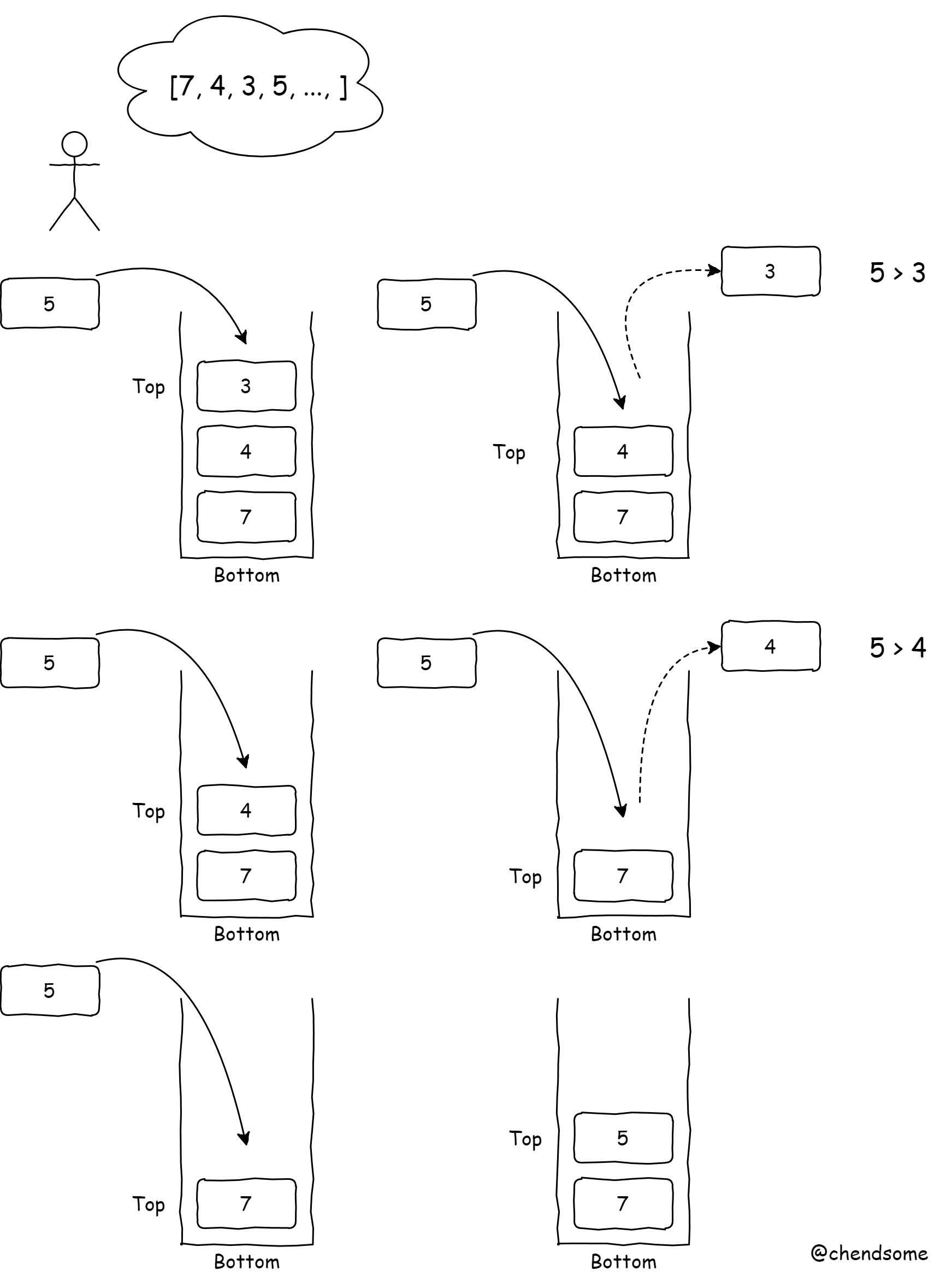
自己定義的出入棧規則,從棧頂到棧底單調遞增來舉例:在這就是指棧內的順序只能是自頂向底,依次遞增才可以入棧。如果當前待入棧的元素大于棧頂,就需要把這個棧頂元素彈出,并循環比較下一個棧頂元素,直至棧頂元素大于當前待入棧元素才可以。
什么時候用單調棧呢?
通常是一維數組,要尋找任一個元素的右邊或者左邊第一個比自己大或者小的元素的位置,此時我們就要想到可以用單調棧了
以leetcode的一道題為例
給定一個整數數組 temperatures ,表示每天的溫度,返回一個數組 answer ,其中 answer[i] 是指對于第 i 天,下一個更高溫度出現在幾天后。如果氣溫在這之后都不會升高,請在該位置用 0 來代替。
輸入: temperatures = [73,74,75,71,69,72,76,73]
輸出: [1,1,4,2,1,1,0,0]
如果當前待入棧元素大于棧頂,說明當前元素就是第一個比棧頂大的元素,此時就需要把棧頂元素彈出,并比較下一個棧頂元素。
class Solution {
public int[] dailyTemperatures(int[] temperatures) {
int n = temperatures.length;
int[] result = new int[n];
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
stack.push(0);
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
// 隊列不為空,且 當前帶入棧元素 大于 當前棧頂元素 執行 出棧, 并計算棧頂元素的任務
while (!stack.isEmpty() && temperatures[i] > temperatures[stack.peek()]) {
result[stack.peek()] = i - stack.pop();
}
// 隊列空了,或者是已經比較完了,準備入棧了,入棧
stack.push(i);
}
return result;
}
}
84.柱狀圖中最大的矩形
class Solution {
public int largestRectangleArea(int[] heights) {
int res = 0;
Deque<Integer> stack = new LinkedList<>();
// 數組擴容,在頭和尾各加入一個元素
int [] newHeights = new int[heights.length + 2];
newHeights[0] = 0;
newHeights[newHeights.length - 1] = 0;
for (int index = 0; index < heights.length; index++){
newHeights[index + 1] = heights[index];
}
heights = newHeights;
stack.push(0);
for (int i = 1; i < heights.length; i++){
if(heights[i] > heights[stack.peek()]){
stack.push(i);
} else if( heights[i] == heights[stack.peek()]){
stack.pop();
stack.push(i);
}else {
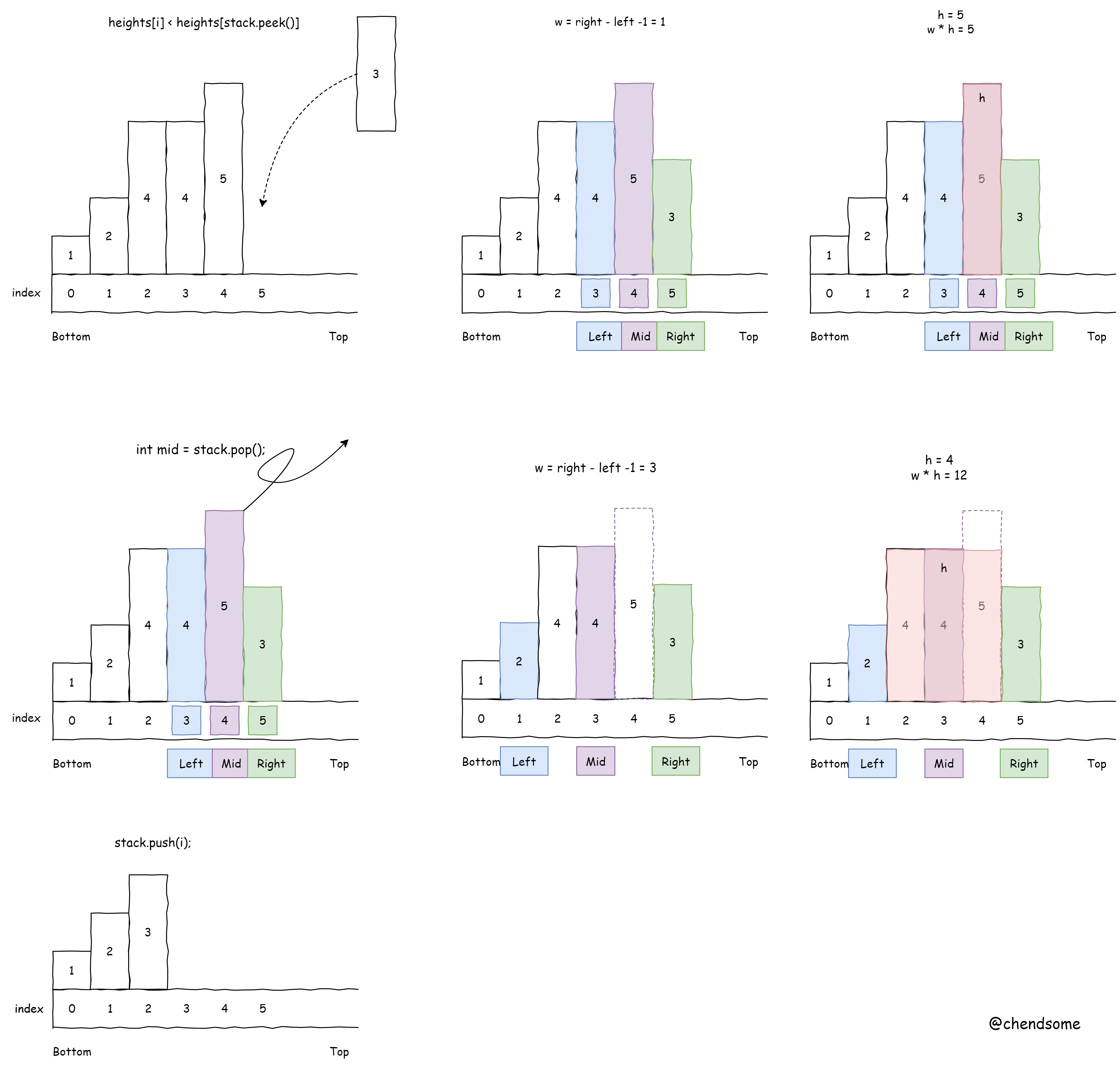
while (!stack.isEmpty() && heights[i] < heights[stack.peek()]){
int mid = stack.pop();
if (!stack.isEmpty()){
int left = stack.peek();
int right = i;
int w = right - left - 1;
int h = heights[mid];
res = Math.max(res, w * h);
}
}
stack.push(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}
本文來自博客園,作者:chendsome,轉載請注明原文鏈接:http://www.rzrgm.cn/chendsome/p/18576216



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號