一文讀懂Spring的SPI機制
一. 從類加載說起
Java中的類加載器負載加載來自文件系統、網絡或者其他來源的類文件。jvm的類加載器默認使用的是雙親委派模式。三種默認的類加載器Bootstrap ClassLoader、Extension ClassLoader和System ClassLoader(Application ClassLoader)每一個中類加載器都確定了從哪一些位置加載文件。于此同時我們也可以通過繼承 java.lang.classloader 實現自己的類加載器。
Bootstrap ClassLoader:負責加載JDK自帶的rt.jar包中的類文件,是所有類加載的父類
Extension ClassLoader:負責加載java的擴展類庫從jre/lib/ect目錄或者java.ext.dirs系統屬性指定的目錄下加載類,是System ClassLoader的父類加載器
System ClassLoader:負責從classpath環境變量中加載類文件
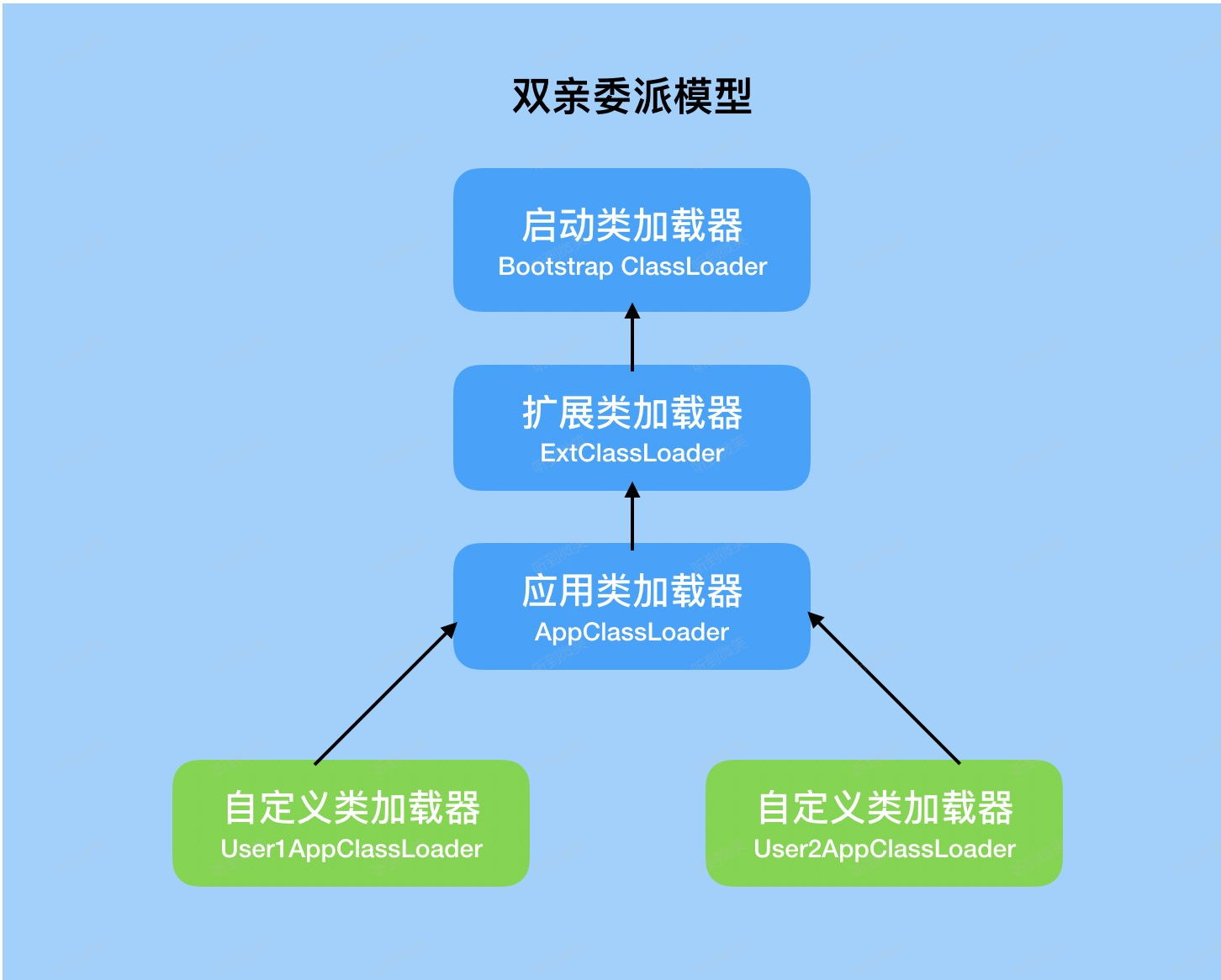
1.1 雙親委派
當一個類加載器收到類加載任務時,會先交給自己的父加載器去完成,因此最終加載任務都會傳遞到最頂層的BootstrapClassLoader,只有當父加載器無法完成加載任務時,才會嘗試自己來加載。
根據雙親委派模式,在加載類文件的時候,子類加載器首先將加載請求委托給它的父加載器,父加載器會檢測自己是否已經加載過類,如果已經加載則加載過程結束,如果沒有加載的話則請求繼續向上傳遞直Bootstrap ClassLoader。如果請求向上委托過程中,如果始終沒有檢測到該類已經加載,則Bootstrap ClassLoader開始嘗試從其對應路勁中加載該類文件,如果失敗則由子類加載器繼續嘗試加載,直至發起加載請求的子加載器為止。
采用雙親委派模式可以保證類型加載的安全性,不管是哪個加載器加載這個類,最終都是委托給頂層的BootstrapClassLoader來加載的,只有父類無法加載自己猜嘗試加載,這樣就可以保證任何的類加載器最終得到的都是同樣一個Object對象。
protected Class<?> loadClass(String name, boolean resolve) {
synchronized (getClassLoadingLock(name)) {
// 首先,檢查該類是否已經被加載,如果從JVM緩存中找到該類,則直接返回
Class<?> c = findLoadedClass(name);
if (c == null) {
try {
// 遵循雙親委派的模型,首先會通過遞歸從父加載器開始找,
// 直到父類加載器是BootstrapClassLoader為止
if (parent != null) {
c = parent.loadClass(name, false);
} else {
c = findBootstrapClassOrNull(name);
}
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {}
if (c == null) {
// 如果還找不到,嘗試通過findClass方法去尋找
// findClass是留給開發者自己實現的,也就是說
// 自定義類加載器時,重寫此方法即可
c = findClass(name);
}
}
if (resolve) {
resolveClass(c);
}
return c;
}
}
1.2 雙親委派模型的缺陷
在雙親委派模型中,子類加載器可以使用父類加載器已經加載的類,而父類加載器無法使用子類加載器已經加載的。這就導致了雙親委派模型并不能解決所有的類加載器問題。
案例:Java 提供了很多服務提供者接口(Service Provider Interface,SPI),允許第三方為這些接口提供實現。常見的 SPI 有 JDBC、JNDI、JAXP 等,這些SPI的接口由核心類庫提供,卻由第三方實現,這樣就存在一個問題:SPI 的接口是 Java 核心庫的一部分,是由BootstrapClassLoader加載的;SPI實現的Java類一般是由AppClassLoader來加載的。BootstrapClassLoader是無法找到 SPI 的實現類的,因為它只加載Java的核心庫。它也不能代理給AppClassLoader,因為它是最頂層的類加載器。也就是說,雙親委派模型并不能解決這個問題
1.3 使用線程上下文類加載器(ContextClassLoader)加載
如果不做任何的設置,Java應用的線程的上下文類加載器默認就是AppClassLoader。在核心類庫使用SPI接口時,傳遞的類加載器使用線程上下文類加載器,就可以成功的加載到SPI實現的類。線程上下文類加載器在很多SPI的實現中都會用到。
通常我們可以通過Thread.currentThread().getClassLoader()和Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader()獲取線程上下文類加載器。
1.4 使用類加載器加載資源文件,比如jar包
類加載器除了加載class外,還有一個非常重要功能,就是加載資源,它可以從jar包中讀取任何資源文件,比如,ClassLoader.getResources(String name)方法就是用于讀取jar包中的資源文件
//獲取資源的方法
public Enumeration<URL> getResources(String name) throws IOException {
Enumeration<URL>[] tmp = (Enumeration<URL>[]) new Enumeration<?>[2];
if (parent != null) {
tmp[0] = parent.getResources(name);
} else {
tmp[0] = getBootstrapResources(name);
}
tmp[1] = findResources(name);
return new CompoundEnumeration<>(tmp);
}
它的邏輯其實跟類加載的邏輯是一樣的,首先判斷父類加載器是否為空,不為空則委托父類加載器執行資源查找任務,直到BootstrapClassLoader,最后才輪到自己查找。而不同的類加載器負責掃描不同路徑下的jar包,就如同加載class一樣,最后會掃描所有的jar包,找到符合條件的資源文件。
// 使用線程上下文類加載器加載資源
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
// Array.class的完整路徑
String name = "java/sql/Array.class";
Enumeration<URL> urls = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResources(name);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
System.out.println(url.toString());
}
}
二. Spring中的SPI機制
2.1 Spring中SPI的使用
在Spring中提供了SPI機制,我們只需要在 META-INF/spring.factories 中配置接口實現類名,即可通過服務發現機制,在運行時加載接口的實現類:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.admin.SpringApplicationAdminJmxAutoConfiguration
在 spring-boot-autoconfigure 模塊下,SpringBoot默認就配置了很多接口的服務實現:
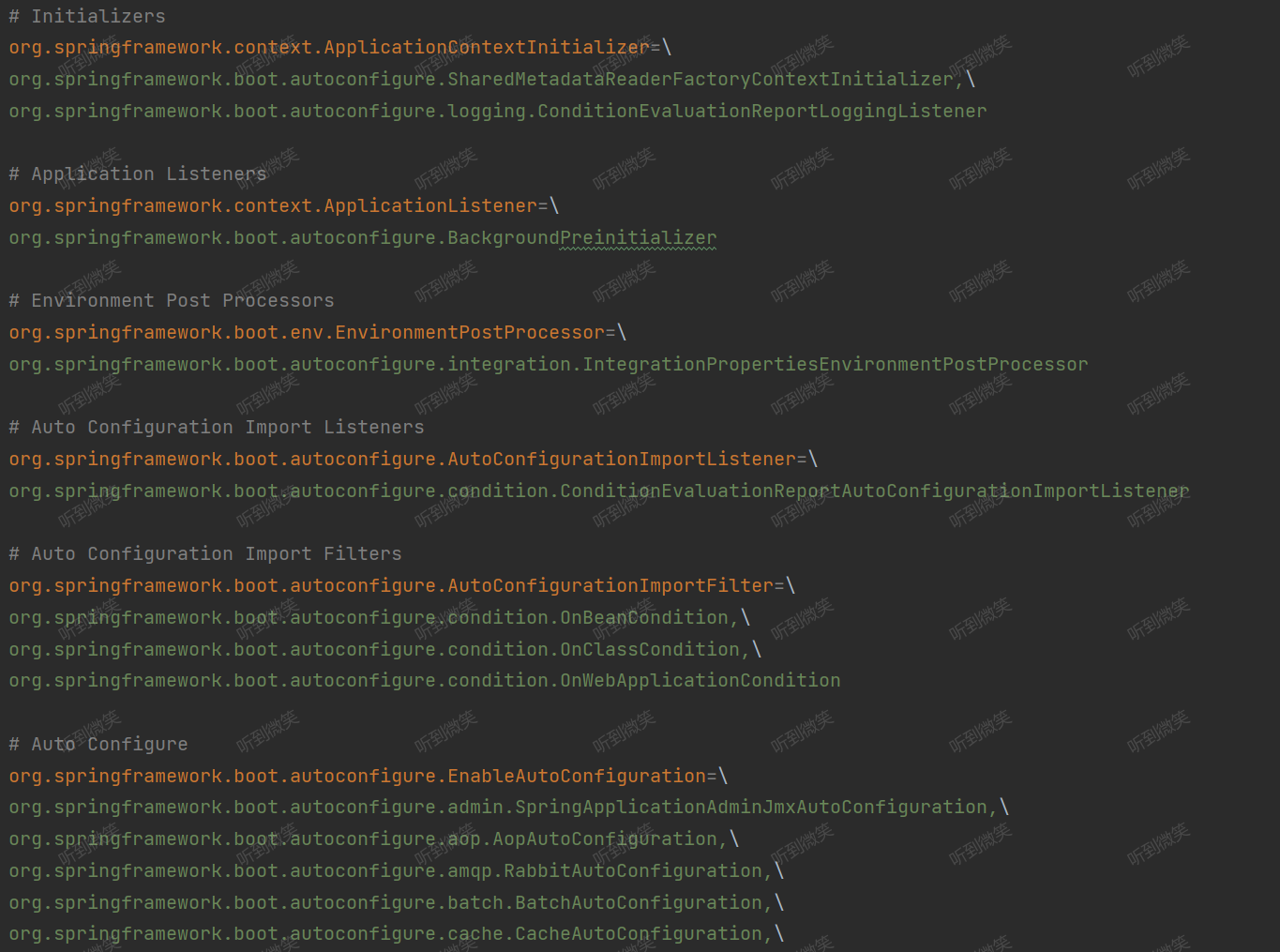
配置好 spring.factories 文件后,我們就可以通過 SpringFactoriesLoader 動態加載接口實現類了,代碼如下:
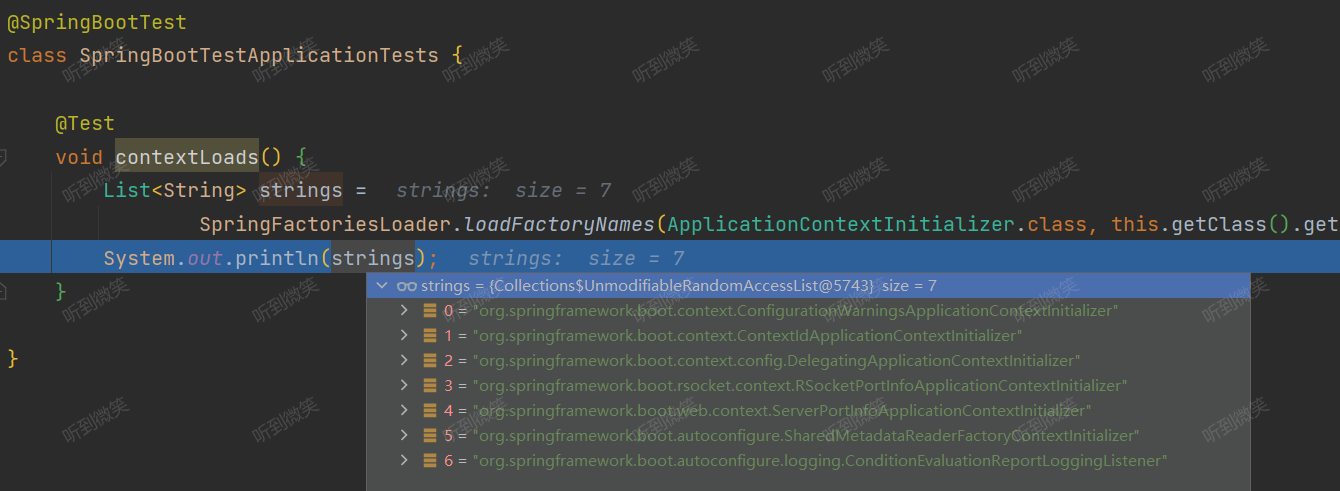
List<String> strings = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(ApplicationContextInitializer.class, this.getClass().getClassLoader());
System.out.println(strings);
我們在引入 spring-boot-starter-web 模塊時,應用環境就配置了6個 ApplicationContextInitializer接口實現類:
2.2 SpringFactoriesLoader API
org.springframework.core.io.support.SpringFactoriesLoader就是Spring框架中的“ServiceLoader”,該類提供了下列功能:
-
類靜態成員常量
final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories"
此常量定義了該工具類要從每個jar包中提取的工廠類定義屬性文件的相對路徑。 -
類靜態方法
<T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader)
此方法會讀取classpath上所有的jar包中的所有META-INF/spring.factories屬性文件,找出其中定義的匹配類型 factoryClass 的工廠類,然后創建每個工廠類的對象/實例,并返回這些工廠類對象/實例的列表。 -
類靜態方法
List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, ClassLoader classLoader)
此方法會讀取classpath上所有的jar包中的所有META-INF/spring.factories屬性文件,找出其中定義的匹配類型 factoryClass 的工廠類,然后并返回這些工廠類的名字列表,注意是包含包名的全限定名。
2.3 SpringFactoriesLoader 源碼
本源碼基于 spring-framework 5.3.10 版本分析:
/**
* General purpose factory loading mechanism for internal use within the framework.
* 用于框架內部使用的通用工廠加載機制。
*
* <p>{@code SpringFactoriesLoader} {@linkplain #loadFactories loads} and instantiates
* factories of a given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION} files which
* may be present in multiple JAR files in the classpath. The {@code spring.factories}
* file must be in {@link Properties} format, where the key is the fully qualified
* name of the interface or abstract class, and the value is a comma-separated list of
* implementation class names. For example:
*
* SpringFactoriesLoader#loadFactories設計用于加載和實例化指定類型的工廠,這些工廠類型的定義
* 來自classpath中多個JAR包內常量FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION所指定的那些spring.factories文件。
* spring.factories文件的格式必須是{@link Properties}格式,每條屬性的key必須是接口或者抽象類的全限定名,
* 而屬性值value是一個逗號分割的實現類的名稱。
*
* <pre class="code">example.MyService=example.MyServiceImpl1,example.MyServiceImpl2</pre>
*
* where {@code example.MyService} is the name of the interface, and {@code MyServiceImpl1}
* and {@code MyServiceImpl2} are two implementations.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 3.2
*/
public final class SpringFactoriesLoader {
/**
* The location to look for factories.
* <p>Can be present in multiple JAR files.
*
* 在classpath中的多個JAR中要掃描的工廠配置文件的在本JAR包中的路徑。
* 實際上,Springboot的每個 autoconfigure包都包含一個這樣的文件。
*/
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
private static final Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(SpringFactoriesLoader.class);
/**
* 緩存,在 loadFactoryNames 首次被調用時,所有jar包中的 META-INF/spring.factories
* 文件內容都會被加載,然后緩存在 cache 中, 注意 cache Map 的 key 是 loadFactoryNames
* 調用時的參數 classLoader, 而 value 是另外一個 Map,其 key 是工廠類的名稱,
* 也就是每個 META-INF/spring.factories 屬性文件中屬性名部分
*/
static final Map<ClassLoader, Map<String, List<String>>> cache = new ConcurrentReferenceHashMap<>();
private SpringFactoriesLoader() {
}
/**
* Load and instantiate the factory implementations of the given type from
* {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given class loader.
* <p>The returned factories are sorted through {@link AnnotationAwareOrderComparator}.
* <p>If a custom instantiation strategy is required, use {@link #loadFactoryNames}
* to obtain all registered factory names.
* <p>As of Spring Framework 5.3, if duplicate implementation class names are
* discovered for a given factory type, only one instance of the duplicated
* implementation type will be instantiated.
* @param factoryType the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading (can be {@code null} to use the default)
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if any factory implementation class cannot
* be loaded or if an error occurs while instantiating any factory
* @see #loadFactoryNames
*/
public static <T> List<T> loadFactories(Class<T> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
Assert.notNull(factoryType, "'factoryType' must not be null");
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
// 加載類型為factoryClass的工廠的名稱,其實是一個個的全限定類名,使用指定的classloader:
List<String> factoryImplementationNames = loadFactoryNames(factoryType, classLoaderToUse);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Loaded [" + factoryType.getName() + "] names: " + factoryImplementationNames);
}
List<T> result = new ArrayList<>(factoryImplementationNames.size());
// 實例化所加載的每個工廠類
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
result.add(instantiateFactory(factoryImplementationName, factoryType, classLoaderToUse));
}
// 排序
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(result);
return result;
}
/**
* Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the
* given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given
* class loader.
* <p>As of Spring Framework 5.3, if a particular implementation class name
* is discovered more than once for the given factory type, duplicates will
* be ignored.
* @param factoryType the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading resources; can be
* {@code null} to use the default
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an error occurs while loading factory names
* @see #loadFactories
*/
public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryType, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
ClassLoader classLoaderToUse = classLoader;
if (classLoaderToUse == null) {
classLoaderToUse = SpringFactoriesLoader.class.getClassLoader();
}
String factoryTypeName = factoryType.getName();
// 1. 使用指定的classloader掃描classpath上所有的JAR包中的文件META-INF/spring.factories,加載其中的多值
// 工廠屬性定義,使用多值Map的形式返回,
// 2. 返回多值Map中key為factoryClassName的工廠名稱列表,如果沒有相應的entry,返回空列表而不是返回null
return loadSpringFactories(classLoaderToUse).getOrDefault(factoryTypeName, Collections.emptyList());
}
/**
* 使用指定的classloader掃描classpath上所有的JAR包中的文件META-INF/spring.factories,加載其中的多值
* 工廠屬性定義,使用多值Map的形式返回
**/
private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(ClassLoader classLoader) {
Map<String, List<String>> result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
result = new HashMap<>();
try {
// 掃描classpath上所有JAR中的文件META-INF/spring.factories
Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION);
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
// 找到的每個META-INF/spring.factories文件都是一個Properties文件,將其內容
// 加載到一個 Properties 對象然后處理其中的每個屬性
URL url = urls.nextElement();
// url 對應某個 META-INF/spring.factories 配置文件資源
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
// properties 來自 url 對應某個 META-INF/spring.factories 配置文件資源
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry<?, ?> entry : properties.entrySet()) {
// 獲取工廠類名稱(接口或者抽象類的全限定名)
String factoryTypeName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
// 將逗號分割的屬性值逐個取出,然后放到多值Map結果result中去。
String[] factoryImplementationNames =
StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue());
for (String factoryImplementationName : factoryImplementationNames) {
// 放到 result 中 :
// key 使用 factoryClassName
// value 可能有多值, 使用 factoryName
result.computeIfAbsent(factoryTypeName, key -> new ArrayList<>())
.add(factoryImplementationName.trim());
}
}
}
// Replace all lists with unmodifiable lists containing unique elements
result.replaceAll((factoryType, implementations) -> implementations.stream().distinct()
.collect(Collectors.collectingAndThen(Collectors.toList(), Collections::unmodifiableList)));
// 放到緩存中,key 使用 classLoader
cache.put(classLoader, result);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
return result;
}
/**
* @param factoryImplementationName 工廠實現類全限定名稱
* @param factoryType 工廠所屬接口/抽象類全限定名稱
* @param classLoader 所要使用的類加載器
**/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private static <T> T instantiateFactory(String factoryImplementationName, Class<T> factoryType, ClassLoader classLoader) {
try {
Class<?> factoryImplementationClass = ClassUtils.forName(factoryImplementationName, classLoader);
if (!factoryType.isAssignableFrom(factoryImplementationClass)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Class [" + factoryImplementationName + "] is not assignable to factory type [" + factoryType.getName() + "]");
}
return (T) ReflectionUtils.accessibleConstructor(factoryImplementationClass).newInstance();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Unable to instantiate factory class [" + factoryImplementationName + "] for factory type [" + factoryType.getName() + "]",
ex);
}
}
}
2.4 SpringFactoriesLoader 的應用
Spring Boot提供的一些JAR包,里面會帶有文件META-INF/spring.factories。Spring Boot應用啟動的時候,根據啟動階段不同的需求,框架就會調用SpringFactoriesLoader加載相應的工廠配置信息。
比如SpringBoot應用使用了注解@EnableAutoConfiguration時,就會觸發對SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()的調用。
除此之外,SpringBoot還會對外提供其它的擴展點,下面列舉了部分常見的擴展點
// SpringApplication.initialize
// => SpringApplication.getSpringFactoriesInstances()
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer)
// SpringApplication.initialize
// => SpringApplication.getSpringFactoriesInstances()
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(org.springframework.context.ApplicationListenr)
// SpringApplication.run
// => getRunListeners
// => SpringApplication.getSpringFactoriesInstances()
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener)
// SpringApplication.run
// => prepareEnvironment
// => SpringApplication.getSpringFactoriesInstances()
// => ConfigFileApplicationListener.onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent() //事件處理
// => loadPostProcessors()
SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor)
我們就以 ApplicationContextInitializer 為例,分析一下在SpringBoot中 ApplicationContextInitializer 擴展點的加載時機。
SpringBoot啟動是直接使用 main 方法啟動,程序入口一目了然,對源碼閱讀比較友好,下面是一個SpringBoot應用標準的啟動代碼:
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTestApplication.class, args);
我們從 run 方法入手:
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
// <1> 調用重載run方法
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
// <2> 創建,并初始化SpringApplication實例,并調用run方法,啟動容器
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
首先是連續兩個重載的靜態run方法,靜態run方法內部會調用構造方法實例化SpringApplication對象,再調用一個成員方法run()來正式啟動。
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
this.bootstrapRegistryInitializers = new ArrayList<>(
getSpringFactoriesInstances(BootstrapRegistryInitializer.class));
// <3> 通過SPI機制,加載classpath環境中配置的ApplicationContextInitializer實現類,并實例化
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
// <4> 通過SPI機制,加載classpath環境中配置的ApplicationListener實現類,并實例化
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
在調用構造器實例化SpringApplication時,會通過SPI機制,加載classpath環境中配置的ApplicationContextInitializer實現類,并實例化:
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
// 獲取當前線程的classLoader
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
// <1> 加載指定類型對應的,在 `META-INF/spring.factories` 里的類名的數組
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// <2> 創建對象
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
// <3> 排序對象
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
三. SpringBoot2.7.0 自動配置將不推薦使用spring.factories
SpringBoot 2.7 中,不再推薦使用/META-INF/spring.factories文件作為自動配置類的配置文件,所以對于有自定義Starter的開發者來說,有時間要抓緊把這一變化改起來了,因為在SpringBoot 3開始將移除對/META-INF/spring.factories的支持。
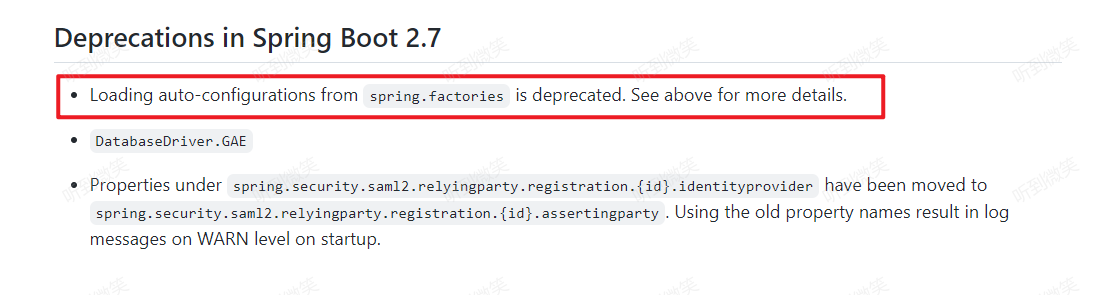
如果您已經創建了自動配置,那么應該將注冊從META-INF/spring.factories轉移到一個名為META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports的新文件。每一行都包含自動配置的完全限定名。請參考: the included auto-configurations
為了向后兼容,spring.factories 的功能仍將暫時支持。
本文參考至:


 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號