【數據結構】 字典樹trie詳解
定義:
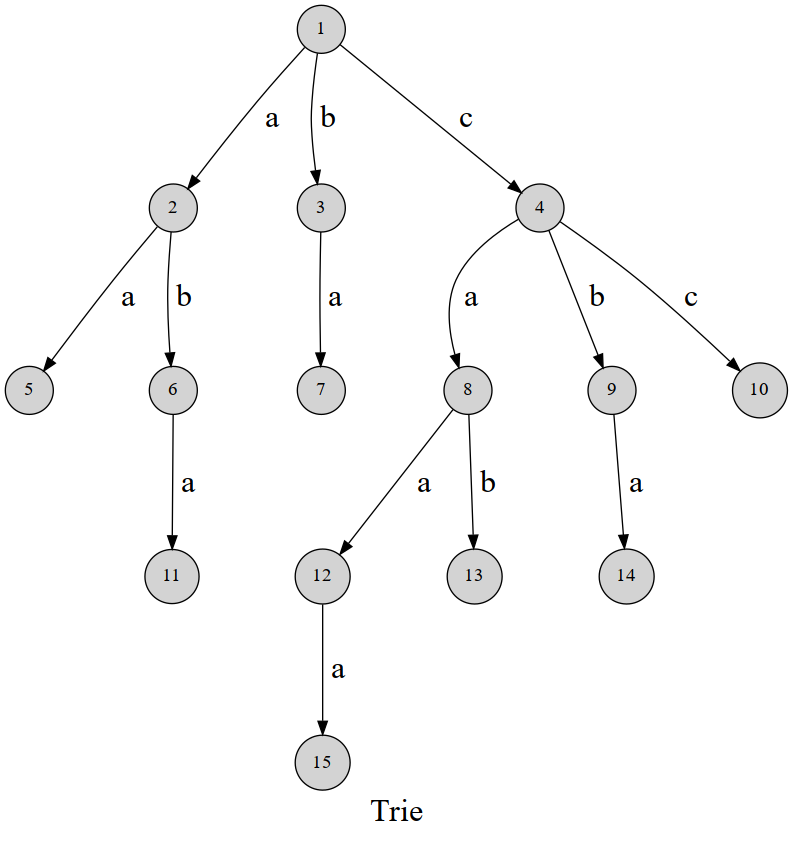
將多個字符串以樹的方式存儲即為字典樹,如圖,\(1,4,3,12\) 表示 \(cca\) ,我么用 \(ch[i][j]\) 來表示第 \(i\) 個節點的 \(j\) 字符所指向的下一個節點,\(tag[u]\) 表示節點 \(u\) 是否代表一個字符串的結尾,如果是的話,\(tag[u]=1\)。
模板CODE
添加字符串
//n表示即將要向字典樹插入n個字符串
const N 100005;
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
char s[N];
scanf("%s",s+1);
int u=1;
for (int j=1;s[j];j++){
int c=s[j]-'a';
if (!ch[u][c]) ch[u][c]=++tot;
u=ch[u][c];
}
tag[u]=1;
}
字符串查找
//查看字符串s是否在字典樹當中,如果在輸出OK,否則輸出WRONG
char s[N];
scanf("%s",s+1);
int u=1;
for (int i=1;s[i];i++){
int c=s[i]-'a';
u=ch[u][c];
if (!u) break;
}
if (tag[u]==1){
puts("OK");
continue;
}
else {
puts("WRONG");
continue;
}
例題
P2580 于是他錯誤的點名開始了
例題代碼:
點擊查看代碼
#include<cstdio>
using namespace std;
const int N=500010;
int n,m;
int ch[N][30];
int tag[N];
int tot=0;
char s[N];
int main(){
freopen("test_point/input.in","r",stdin);
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
scanf("%s",s+1);
int u=1;
for (int j=1;s[j];j++){
int c=s[j]-'a';
if (!ch[u][c]) ch[u][c]=++tot;
u=ch[u][c];
}
tag[u]=1;
}
scanf("%d",&m);
while (m--){
scanf("%s",s+1);
int u=1;
for (int i=1;s[i];i++){
int c=s[i]-'a';
u=ch[u][c];
if (!u) break;
}
if (tag[u]==2){
puts("REPEAT");
continue;
}
else if (tag[u]==1){
puts("OK");
tag[u]=2;
continue;
}
else {
puts("WRONG");
continue;
}
}
return 0;
}
維護異或極值
01-trie:01-trie 是指字符集為 {0,1} 的 trie。01-trie 可以用來維護一些數字的異或和,支持修改(刪除 + 重新插入),和全局加一
維護異或路徑:此類問題會給定一棵樹,讓你求出這棵樹最長的異或路徑,對于此類問題,我們需要先明白異或運算的性質
模板題目: https://www.luogu.com.cn/problem/P4551
- 交換律: \(a \oplus b=b \oplus a\)
- 結合律:\((a \oplus b) \oplus c=a \oplus (b \oplus c)\)
- 自反性:\(a \oplus a=0\)
- 與 \(0\) 異或:\(a \oplus 0=a\)
根據以上性質我們可以得到一個推論:\(a \oplus b \oplus b=a \oplus (b \oplus b)=a \oplus 0=a\) ,因此,在樹或圖中,如果定義一條路徑的異或值為路徑上所有邊權的異或和,那么:
從節點 \(u\) 到節點 \(v\) 的路徑異或值等于從根節點到 \(u\) 的異或值 \(xor[u]\) 與從根節點到 \(v\) 的異或值 \(xor[v]\) 的異或,因此我們可以預處理所有節點到根節點的異或路徑,存在 \(xor[]\) 數組中,然后對 \(xor[]\) 數組構造字典樹,如下圖
 $\longrightarrow $
$\longrightarrow $ 
接著,我們存好后,用兩個指針在字典樹上遍歷,對于每次,對要盡可能選擇不一樣的兩位,這樣可以保證異或值最大,因為高位的 \(1\) 比他下面所有位的 \(1\) 加起來都大,但是如果存在兩種選擇都可以讓該為異或為 \(1\) ,則需要dfs一下
模板CODE:
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=100005;
int n;
int tr[2000000][2];
struct edge{
int v;
int w;
};
vector<edge> g[N];
int xr[N];
int cnt=1;
int h;
int res,ans;
void dfs(int u,int fa){
for (edge ed:g[u]){
int v=ed.v,w=ed.w;
if (v==fa) continue;
xr[v]=xr[u]^w;
dfs(v,u);
}
return ;
}
void dfs1(int i,int j,int k){
if (!k){
ans=max(ans,res);
return ;
}
if ((tr[i][0]&&tr[j][1])||(tr[i][1]&&tr[j][0])){
if (tr[i][0]&&tr[j][1]){
res+=(1<<(k-1));
dfs1(tr[i][0],tr[j][1],k-1);
res-=(1<<(k-1));
}
if (tr[i][1]&&tr[j][0]){
res+=(1<<(k-1));
dfs1(tr[i][1],tr[j][0],k-1);
res-=(1<<(k-1));
}
}
else{
if (tr[i][0]&&tr[j][0]) dfs1(tr[i][0],tr[j][0],k-1);
else if (tr[i][1]&&tr[j][1]) dfs1(tr[i][1],tr[j][1],k-1);
}
}
int main(){
scanf("%d",&n);
for (int i=1;i<=n-1;i++){
int u,v,w;
scanf("%d%d%d",&u,&v,&w);
g[u].push_back((edge){v,w});
g[v].push_back((edge){u,w});
}
dfs(1,-1);
int maxn=0;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) maxn=max(maxn,xr[i]);
while (maxn) maxn>>=1,h++;
if (h==0) h++;
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++){
int u=1;
for (int j=h-1;j>=0;j--){
int w=(xr[i]>>j)&1;
if (!tr[u][w]) tr[u][w]=++cnt;
u=tr[u][w];
}
}
dfs1(1,1,h);
printf("%d",ans);
return 0;
}



 浙公網安備 33010602011771號
浙公網安備 33010602011771號