[MoE] Deepseek的All-to-all通信: DeepEP代碼解讀
[MoE] Deepseek的All-to-all通信: DeepEP代碼解讀
前言
最近,Deepseek開源了一系列MoE的優(yōu)化技術(shù),讓我們看到了AI infra的強大之處。其中,第二天發(fā)布的DeepEP則是針對MoE中EP的all-to-all通信進(jìn)行了優(yōu)化。
我最近也在關(guān)注MoE和all-to-all,之前的MoE普遍使用NCCL的p2p通信進(jìn)行all-to-all,結(jié)果紛紛吐槽all-to-all性能差,帶寬利用率低。但是,很少有人真的去分析all-to-all性能差的原因,并嘗試去改進(jìn)。而DeepEP的出現(xiàn),可以說徹底解決了all-to-all打不滿帶寬的問題。DeepEP直接放棄了NCCL,轉(zhuǎn)而使用更底層的NVSHMEM進(jìn)行通信,結(jié)果基本用滿了NVLink和IB的帶寬。
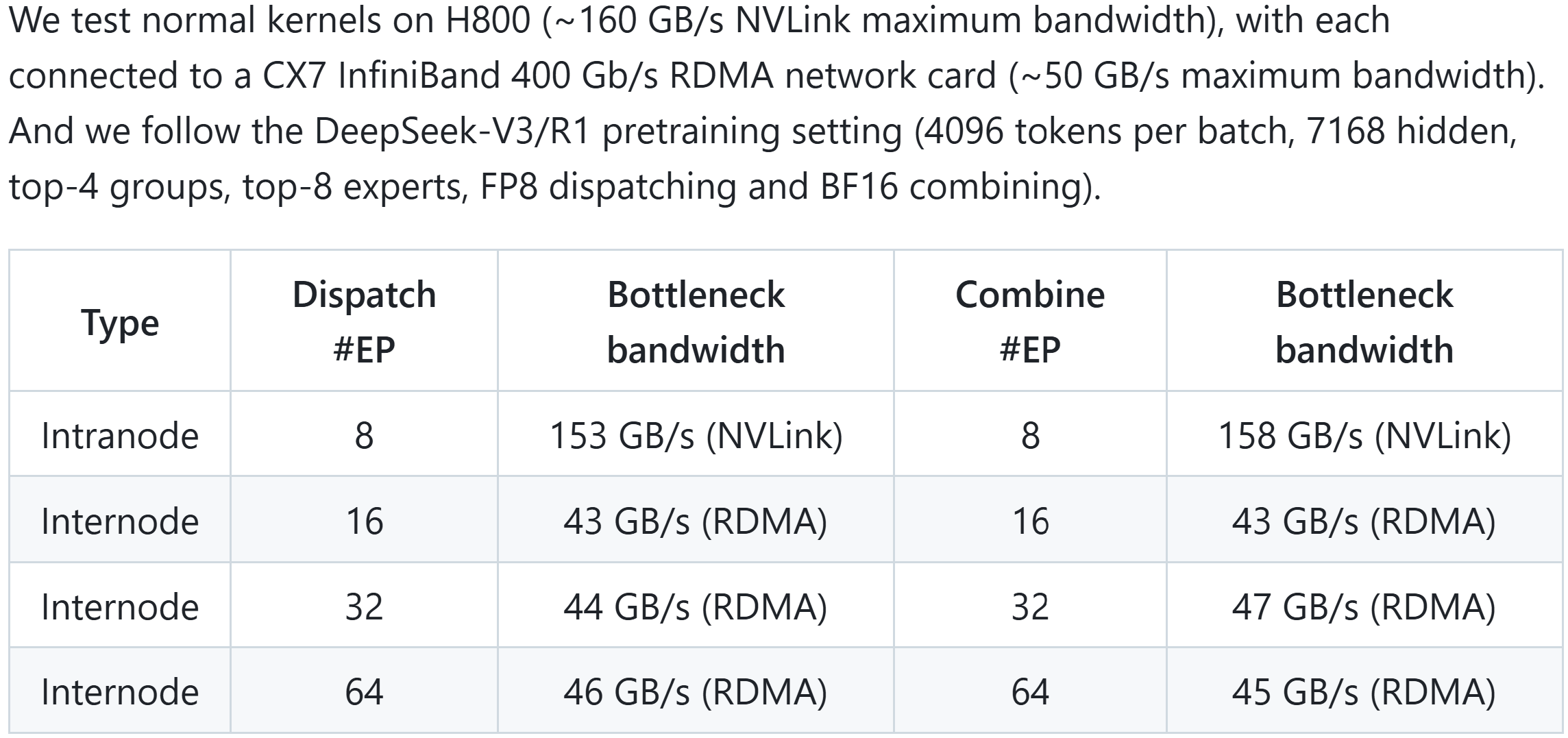
參考:
- deepseek-ai/DeepEP: DeepEP: an efficient expert-parallel communication library
- NVIDIA OpenSHMEM Library (NVSHMEM) Documentation — NVSHMEM 3.2.5 documentation
DeepEP的機內(nèi)通信使用IPC接口,走NVLink。機間通信使用NVSHMEM接口,走IB RDMA。
下面我們沿著README.md里的例子,分析一下DeepEP的源碼,看看它究竟是如何做到這么快的。這里為了便于理解,我們先不考慮low_latency模式。
初始化
我們省略一些配置的代碼。初始化中,最重要部分是創(chuàng)建Buffer。
_buffer = Buffer(group, num_nvl_bytes, num_rdma_bytes)
Buffer是DeepEP的核心數(shù)據(jù)結(jié)構(gòu),位于deep_ep/buffer.py,我們來看看它的注釋和構(gòu)造函數(shù)。
class Buffer:
"""
The core expert-parallel (EP) communication buffers for Mixture of Experts (MoE) model, which supports:
- high-throughput intranode all-to-all (dispatch and combine, using NVLink)
- high-throughput internode all-to-all (dispatch and combine, using RDMA without AR)
- low-latency all-to-all (dispatch and combine, using RDMA, AR supported)
Attributes:
num_sms: the SMs used in high-throughput kernels.
rank: the local rank number.
group_size: the number of ranks in the group.
group: the communication group.
num_nvl_bytes: the buffer size for intranode NVLink communication.
num_rdma_bytes: the buffer size for internode (also for intranode with low-latency mode) RDMA communication.
runtime: the C++ runtime.
"""
def __init__(self, group: dist.ProcessGroup,
num_nvl_bytes: int = 0, num_rdma_bytes: int = 0,
low_latency_mode: bool = False, num_qps_per_rank: int = 1) -> None:
"""
Initialize the communication buffer.
Arguments:
group: the communication group.
num_nvl_bytes: the buffer size for intranode NVLink communication.
num_rdma_bytes: the buffer size for internode (also for intranode with low-latency mode) RDMA communication.
low_latency_mode: whether to enable low-latency mode.
num_qps_per_rank: the number of QPs for RDMA, the low-latency mode requires that this number equals
to the number of local experts.
"""
# 省略一些不太重要的部分
self.runtime = deep_ep_cpp.Buffer(self.rank, self.group_size, num_nvl_bytes, num_rdma_bytes, low_latency_mode)
這里創(chuàng)建runtime調(diào)用的是csrc/deep_ep.cpp里的Buffer的構(gòu)造函數(shù),其內(nèi)部主要是初始化了一些成員變量
這里列幾個重點變量
int device_id:來自cudaGetDeviceint* task_fifo_ptrs[NUM_MAX_NVL_PEERS]:任務(wù)隊列,用于機內(nèi)IPC通信。在后面notify_dispatch會用到,dispatch不會用到。cudaIpcMemHandle_t ipc_handles[NUM_MAX_NVL_PEERS]:來自cudaIpcGetMemHandle,用于建立機內(nèi)IPC通信,創(chuàng)建buffer_ptrs。void* buffer_ptrs[NUM_MAX_NVL_PEERS]:NVLink Buffer,用于機內(nèi)IPC通信。
繼續(xù)看buffer.py
class Buffer:
def __init__(...):
# 使用dist來同步device_id
# 即cudaGetDevice獲得的device_id
# Synchronize device IDs
device_ids = [None, ] * self.group_size
local_device_id = self.runtime.get_local_device_id()
dist.all_gather_object(device_ids, local_device_id, group)
# 同步ipc_handle,由前面的cudaIpcGetMemHandle獲得
# Synchronize IPC handles
ipc_handles = [None, ] * self.group_size
local_ipc_handle = self.runtime.get_local_ipc_handle()
dist.all_gather_object(ipc_handles, local_ipc_handle, group)
# Synchronize NVSHMEM unique IDs
# 獲取root的NVSHMEM的unique_id,然后同步它
root_unique_id = None
if self.runtime.get_num_rdma_ranks() > 1 or low_latency_mode:
# 省略掉一些關(guān)于low_latency_mode的代碼
# NOTES: make sure AR (Adaptive Routing) is turned off while running normal kernels, as we cannot verify AR status in the code
# Synchronize using the root ID
nvshmem_unique_ids = [None, ] * self.group_size
if (low_latency_mode and self.rank == 0) or (not low_latency_mode and self.runtime.get_rdma_rank() == 0):
# 內(nèi)部調(diào)用nvshmemx_get_uniqueid
root_unique_id = self.runtime.get_local_nvshmem_unique_id()
dist.all_gather_object(nvshmem_unique_ids, root_unique_id, group)
root_unique_id = nvshmem_unique_ids[0 if low_latency_mode else self.runtime.get_root_rdma_rank(True)]
# 現(xiàn)在已經(jīng)獲取了所有對端的信息。接下來創(chuàng)建IPC和NVSHMEM的結(jié)構(gòu)
# Make CPP runtime available
self.runtime.sync(device_ids, ipc_handles, root_unique_id)
assert self.runtime.is_available()
這里最后會進(jìn)入self.runtime.sync,即csrcs/deep_ep.cpp里的sync函數(shù),其內(nèi)容如下:
對每一個機內(nèi)的peer,都執(zhí)行:
-
打開IPC handle
-
cudaIpcOpenMemHandle(&buffer_ptrs[i], ipc_handles[i], cudaIpcMemLazyEnablePeerAccess);
-
-
創(chuàng)建任務(wù)隊列
task_fifo_ptrs -
將相關(guān)的變量同步到GPU上。
如果需要機間通信,則
-
初始化nvshmem:
internode::init(...),內(nèi)部調(diào)用-
nvshmemx_set_attr_uniqueid_args(rank, num_ranks, &root_unique_id, &attr); nvshmemx_init_attr(NVSHMEMX_INIT_WITH_UNIQUEID, &attr); -
這里對于非low_latency模式,每個nvshmem的通信組是所有rdma rank上nvk rank相同的GPU,即通信組數(shù)量為nvl rank數(shù)量,每個通信組的大小為rdma rank的數(shù)量,每個通信組的root位于rdma rank=0的節(jié)點上。
-
-
創(chuàng)建NVSHMEM的共享內(nèi)存指針
rdma_buffer_ptr,內(nèi)部是-
nvshmem_align(alignment, size); -
此后,所有GPU可以用
rdma_buffer_ptr來創(chuàng)建共享的buffer,然后使用nvshmem進(jìn)行通信
-
至此初始化部分就完成了。
Dispatch
回到README.md中的例子,接下來告訴我們怎么調(diào)用dispatch。
def dispatch_forward(x: Union[torch.Tensor, Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]],
topk_idx: torch.Tensor, topk_weights: torch.Tensor,
num_experts: int, previous_event: Optional[EventOverlap] = None) -> \
Tuple[Union[torch.Tensor, Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]], torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, List, Tuple, EventOverlap]:
# NOTES: an optional `previous_event` means a CUDA event captured that you want to make it as a dependency
# of the dispatch kernel, it may be useful with communication-computation overlap. For more information, please
# refer to the docs of `Buffer.dispatch`
global _buffer
# Calculate layout before actual dispatch
num_tokens_per_rank, num_tokens_per_rdma_rank, num_tokens_per_expert, is_token_in_rank, previous_event = \
_buffer.get_dispatch_layout(topk_idx, num_experts,
previous_event=previous_event, async_finish=True,
allocate_on_comm_stream=previous_event is not None)
# Do MoE dispatch
# NOTES: the CPU will wait for GPU's signal to arrive, so this is not compatible with CUDA graph
# For more advanced usages, please refer to the docs of the `dispatch` function
recv_x, recv_topk_idx, recv_topk_weights, num_recv_tokens_per_expert_list, handle, event = \
_buffer.dispatch(x, topk_idx=topk_idx, topk_weights=topk_weights,
num_tokens_per_rank=num_tokens_per_rank, num_tokens_per_rdma_rank=num_tokens_per_rdma_rank,
is_token_in_rank=is_token_in_rank, num_tokens_per_expert=num_tokens_per_expert,
previous_event=previous_event, async_finish=True,
allocate_on_comm_stream=True)
# For event management, please refer to the docs of the `EventOverlap` class
return recv_x, recv_topk_idx, recv_topk_weights, num_recv_tokens_per_expert_list, handle, event
我們來看其中兩個具體的函數(shù):get_dispatch_layout和dispatch。
get_dispatch_layout的API如下,建議閱讀一下其中每個參數(shù)的解釋。
class Buffer:
def get_dispatch_layout(self, topk_idx: torch.Tensor, num_experts: int,
previous_event: Optional[EventOverlap] = None, async_finish: bool = False,
allocate_on_comm_stream: bool = False) -> \
Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, EventOverlap]:
"""
Calculate the layout required for later communication.
Arguments:
topk_idx: `[num_tokens, num_topk]`, dtype must be `torch.int64`, the expert indices selected by each token,
`-1` means no selections.
num_experts: the number of experts.
previous_event: 如果不是None,則需要等待這個事件結(jié)束才會執(zhí)行kernel。這個參數(shù)可以用于描繪流水線并行中的依賴關(guān)系。
previous_event: the event to wait before actually executing the kernel.
async_finish: the current stream will not wait for the communication kernels to be finished if set.
allocate_on_comm_stream: control whether all the allocated tensors' ownership to be on the communication stream.
Returns:
num_tokens_per_rank: `[num_ranks]` with `torch.int`, the number of tokens to be sent to each rank.
num_tokens_per_rdma_rank: `[num_rdma_ranks]` with `torch.int`, the number of tokens to be sent to each RDMA
rank (with the same GPU index), return `None` for intranode settings.
num_tokens_per_expert: `[num_experts]` with `torch.int`, the number of tokens to be sent to each expert.
is_token_in_rank: 每個token是否發(fā)往每個rank
is_token_in_rank: `[num_tokens, num_ranks]` with `torch.bool`, whether a token be sent to a rank.
event: the event after executing the kernel (valid only if `async_finish` is set).
"""
num_tokens_per_rank, num_tokens_per_rdma_rank, num_tokens_per_expert, is_token_in_rank, event = \
self.runtime.get_dispatch_layout(topk_idx, num_experts, getattr(previous_event, 'event', None),
async_finish, allocate_on_comm_stream)
return num_tokens_per_rank, num_tokens_per_rdma_rank, num_tokens_per_expert, is_token_in_rank, EventOverlap(event)
簡單來說,get_dispatch_layout根據(jù)本地的topk_idx,來計算本地要發(fā)往每個rank和每個expert的token數(shù)量。其內(nèi)部使用了GPU來加速計算,具體的kernel代碼我們略過。
接下來是Buffer的dispatch函數(shù)。下面的注釋解釋了它的API
class Buffer:
def dispatch(self, x: Union[torch.Tensor, Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor]],
handle: Optional[Tuple] = None,
num_tokens_per_rank: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, num_tokens_per_rdma_rank: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
is_token_in_rank: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, num_tokens_per_expert: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
topk_idx: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, topk_weights: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None, expert_alignment: int = 1,
config: Optional[Config] = None,
previous_event: Optional[EventOverlap] = None, async_finish: bool = False,
allocate_on_comm_stream: bool = False) -> \
Tuple[Union[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor], Optional[torch.Tensor],
Optional[torch.Tensor], List[int], Tuple, EventOverlap]:
"""
Dispatch tokens to different ranks, both intranode and internode settings are supported.
Intranode kernels require all the ranks should be visible via NVLink.
Internode kernels require the ranks in a node should be visible via NVLink, while the ranks with the same GPU
index should be visible via RDMA. AR must be disabled.
Arguments:
x: token的數(shù)據(jù)
x: `torch.Tensor` or tuple of `torch.Tensor`, for the first type, the shape must be `[num_tokens, hidden]`,
and type must be `torch.bfloat16`; for the second type, the first element of the tuple must be shaped as
`[num_tokens, hidden]` with type `torch.float8_e4m3fn`, the second must be `[num_tokens, hidden // 128]`
(requiring divisible) with type `torch.float`.
handle: 如果設(shè)置了handle,則會重用之前計算過的layout信息。這個可用于backward的combine(本質(zhì)上是dispatch)
handle: an optional communication handle, if set, the CPU will reuse the layout information to save some time.
num_tokens_per_rank: `[num_ranks]` with `torch.int`, the number of tokens to be sent to each rank.
num_tokens_per_rdma_rank: `[num_rdma_ranks]` with `torch.int`, the number of tokens to be sent to each RDMA
rank (with the same GPU index), return `None` for intranode settings.
is_token_in_rank: `[num_tokens, num_ranks]` with `torch.bool`, whether a token be sent to a rank.
num_tokens_per_expert: `[num_experts]` with `torch.int`, the number of tokens to be sent to each expert.
topk_idx: `[num_tokens, num_topk]` with `torch.int64`, the expert indices selected by each token,
`-1` means no selections.
topk_weights: `[num_tokens, num_topk]` with `torch.float`, the expert weights of each token to dispatch.
expert_alignment: align the number of tokens received by each local expert to this variable.
config: the performance tuning config.
previous_event: the event to wait before actually executing the kernel.
async_finish: the current stream will not wait for the communication kernels to be finished if set.
allocate_on_comm_stream: control whether all the allocated tensors' ownership to be on the communication stream.
Returns:
recv_x: received tokens, the same type and tuple as the input `x`, but the number of tokens equals to the
received token count.
recv_topk_idx: received expert indices.
recv_topk_weights: received expert weights.
num_recv_tokens_per_expert_list: Python list shaped `[num_local_experts]`, the received token count by
each local expert, aligned to the input `expert_alignment`.
handle: the returned communication handle.
event: the event after executing the kernel (valid only if `async_finish` is set).
"""
# Internode
if self.runtime.get_num_rdma_ranks() > 1:
return self.internode_dispatch(x, handle, num_tokens_per_rank, num_tokens_per_rdma_rank, is_token_in_rank, num_tokens_per_expert,
topk_idx, topk_weights, expert_alignment, config, previous_event, async_finish, allocate_on_comm_stream)
# 我們略過intranode_dispatch的情況
如果需要機間通信,則調(diào)用internode_dispatch。因為DeepEP主要就是對機間通信進(jìn)行了很大的優(yōu)化,因此我們來看其內(nèi)部是怎么實現(xiàn)的。
Buffer的 self.internode_dispatch直接調(diào)用了self.runtime.internode_dispatch,代碼位于csrc/deep_ep.cpp
std::tuple<torch::Tensor, ...>
Buffer::internode_dispatch(const torch::Tensor& x, ...) {
bool cached_mode = cached_rank_prefix_matrix.has_value();
// 1個channel對應(yīng)2個SM
const int num_channels = config.num_sms / 2;
// 設(shè)置comm_stream
// Allocate all tensors on comm stream if set
// NOTES: do not allocate tensors upfront!
auto compute_stream = at::cuda::getCurrentCUDAStream();
if (allocate_on_comm_stream) {
EP_HOST_ASSERT(previous_event.has_value() and async);
at::cuda::setCurrentCUDAStream(comm_stream);
}
// 等待前置任務(wù)完成
// Wait previous tasks to be finished
if (previous_event.has_value()) {
stream_wait(comm_stream, previous_event.value());
} else {
stream_wait(comm_stream, compute_stream);
}
if (cached_mode) {
// 如果之前進(jìn)行過dispatch,則可以重用之前的結(jié)果
internode::cached_notify(...);
}
else {
// 否則,需要進(jìn)行計算
internode::notify_dispatch(...);
}
// 等待notify_dispatch完成
}
notify_dispatch在使用NVSHMEM在所有rank之間進(jìn)行通信,計算互相發(fā)送的token數(shù)量以及負(fù)責(zé)的token區(qū)域,具體包括如下內(nèi)容:
-
rdma_channel_prefix_matrix:形狀(num_rdma_ranks, num_channels),每個channel要發(fā)往每個RDMA節(jié)點token數(shù)量的前綴和 -
recv_rdma_rank_prefix_sum:形狀(num_rdma_ranks),每個RDMA節(jié)點要接收的token數(shù)量 -
gbl_channel_prefix_matrix:形狀(num_ranks, num_channels),每個channel要發(fā)往每個GPU的token數(shù)量的前綴和 -
recv_gbl_rank_prefix_sum:形狀(num_ranks),每個GPU要接收的token數(shù)量 -
moe_recv_counter:int,總共要接收的token數(shù)量 -
moe_recv_expert_counter:int[NUM_MAX_LOCAL_EXPERTS],每個本地的expert要接收的token數(shù)量
然后,創(chuàng)建接收數(shù)據(jù)的tensor。
最后,正式進(jìn)行dispatch
// Launch data dispatch
internode::dispatch(...);
dispatch的核心代碼位于csrc/kernels/internode.cu,由于代碼非常長,我們這里用文字來講解它的流程。
在MoE里,一個token可能會發(fā)往多個GPU,這些GPU可能位于多個節(jié)點上(Deepseek-V3規(guī)定了一個token最多發(fā)往4個節(jié)點)。對于一個token,它首先經(jīng)過rdma channel,從本地傳輸?shù)剿械倪h(yuǎn)端節(jié)點上編號相同的GPU。然后再經(jīng)過nvl_channel,傳輸遠(yuǎn)端節(jié)點中所有的目標(biāo)GPU上。
DeepEP使用多個channel發(fā)送數(shù)據(jù)。DeepEP將每個GPU上的數(shù)據(jù)劃分為num_channels個連續(xù)的段,每一段用一個channel發(fā)送。其中每個channel包含一個rdma_channel和一個nvl_channel。rdma_channel和nvl_channel本質(zhì)上都是環(huán)形隊列。
下面這張圖展示了整體的工作流程,注意:為了方便,這里只展示了一個token發(fā)往一個目標(biāo)GPU的過程。實際上,每個token至多發(fā)往4個dst rdma rank,8個dst nvl rank。圖中的黃框代表GPU,實線代表數(shù)據(jù)流經(jīng)的路徑,虛線代表控制信息。
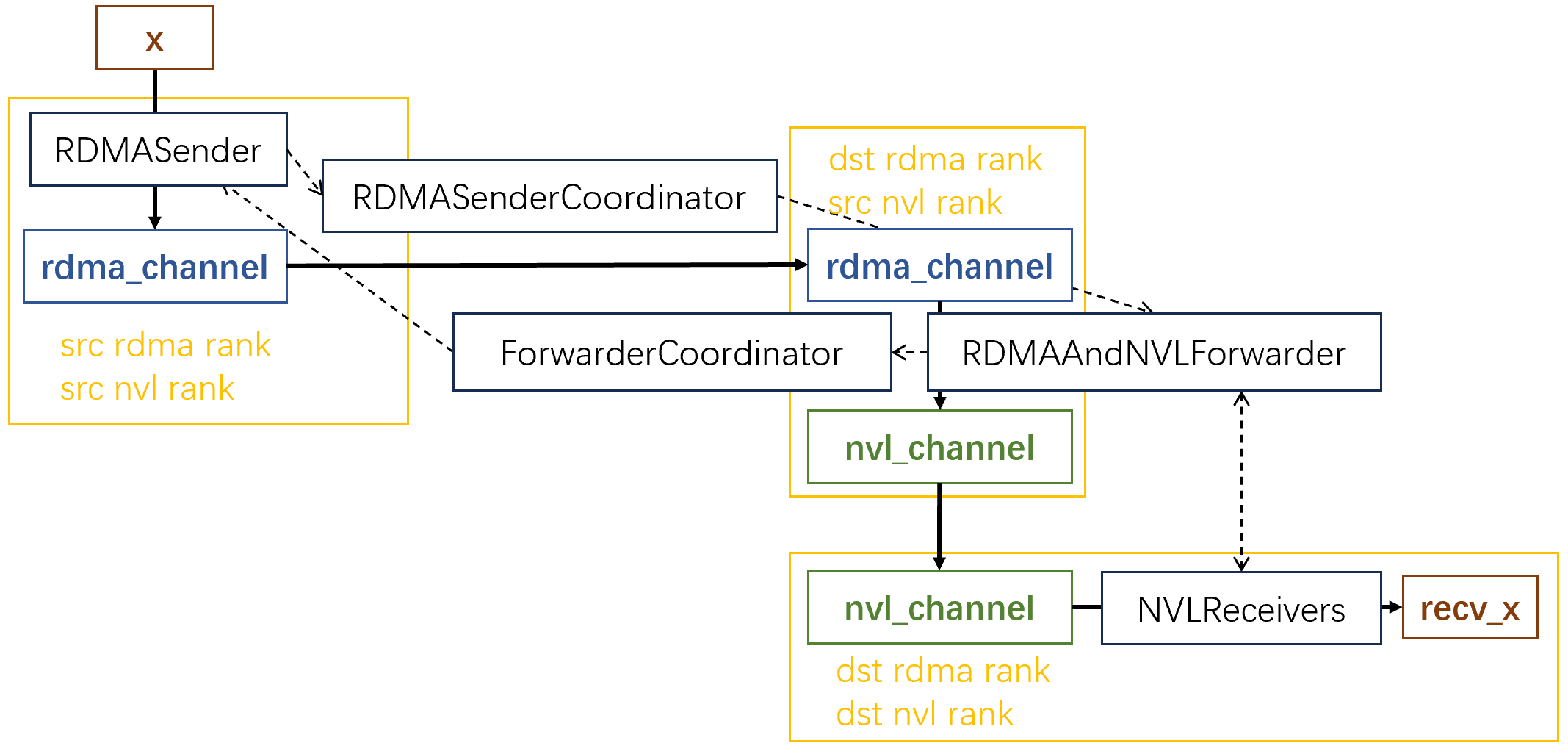
我們看看在這個過程中,kernel是如何分工的
關(guān)于kernel的啟動:
- dispatch會啟動
num_channels * 2個SM,其中每兩個SM對應(yīng)一個channel - 每個SM有
kNumDispatchRDMASenderWarps + 1 + NUM_MAX_NVL_PEERS個warp(默認(rèn)kNumDispatchRDMASenderWarps = 7,NUM_MAX_NVL_PEERS = 8,所以每個SM有16個warp) - H800中每個warp有32個線程
在每個channel內(nèi)部,線程的分工如下:
- 對于第一個SM
- 前8個warp為
RDMAAndNVLForwarder,負(fù)責(zé)將數(shù)據(jù)從RDMA傳輸?shù)絅VL - 1個warp為
ForwarderCoordinator,負(fù)責(zé)協(xié)調(diào)RDMAAndNVLForwarder
- 前8個warp為
- 對于第二個SM
- 前7個warp為
RDMASender,負(fù)責(zé)將數(shù)據(jù)拷貝到RDMA channel - 第8個warp為
RDMASenderCoordinator,負(fù)責(zé)協(xié)調(diào)RDMASender - 剩余8個warp為
NVLReceivers
- 前7個warp為
前面提到rdma_channel和nvl_channel都是隊列。下面兩張圖解釋了這些隊列的頭尾指針是什么,以及它們是如何維護(hù)的。
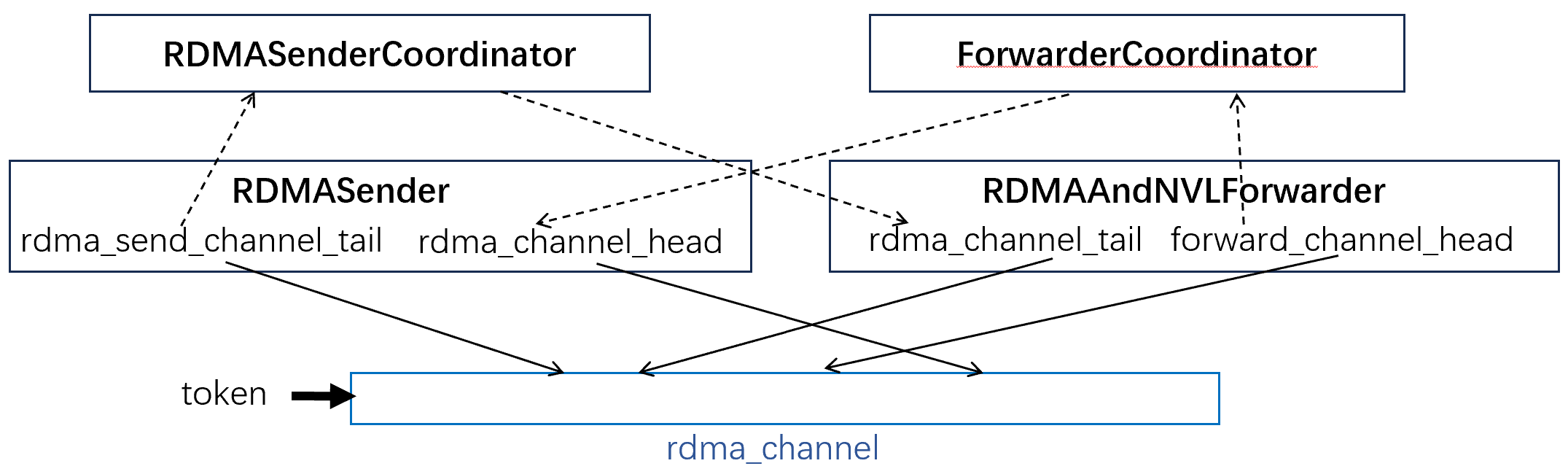
對于rdma_channel來說
- src rdma rank和dst rdma rank各自維護(hù)了隊列的頭尾指針,這些指針需要進(jìn)行同步
- src將數(shù)據(jù)放入send_buffer,使用nvshmem發(fā)往dst的recv_buffer
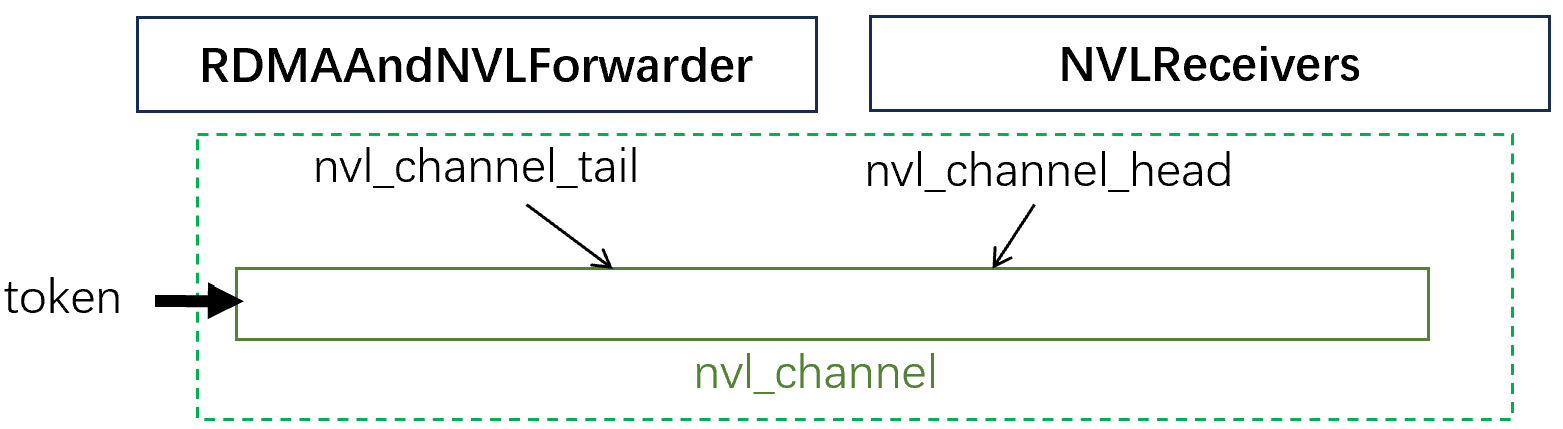
而對于nvl_channel來說,其頭尾指針和數(shù)據(jù)都放在機內(nèi)的IPC共享內(nèi)存中,因此不需要特別的進(jìn)行同步
在了解了這些channel以及線程的分工之后,我們回到代碼,具體地看一下這些warp的職責(zé)
RDMASender- 7個
RDMASender輪流取token,每個warp一次取一個token:- 在warp內(nèi)部,每個lane(線程)對應(yīng)一個dst rdma rank
- 如果當(dāng)前l(fā)ane對應(yīng)的rank屬于token要發(fā)往的rdma rank,則推進(jìn)
rdma_send_channel_tail,并等待遠(yuǎn)端發(fā)來的rdma_channel_head,要求tail-head<隊列大小num_max_rdma_chunked_recv_tokens - 將token放入
send_buffer中 - 更新
rdma_channel_tail
- 7個
RDMASenderCoordinator- 每個lane負(fù)責(zé)一個dst rdma rank
- 如果還有未發(fā)送的數(shù)據(jù),則輪訓(xùn)所有rdma rank:
- 如果某個rdma_channel中,待發(fā)送的數(shù)據(jù)超過
num_max_rdma_chunked_send_tokens,則從send_buffer發(fā)送這些數(shù)量的token到遠(yuǎn)端的recv_buffer中 - 更新遠(yuǎn)端的
rdma_channel_tail+=發(fā)送的token數(shù)
- 如果某個rdma_channel中,待發(fā)送的數(shù)據(jù)超過
RDMAAndNVLForwarder- 每個warp負(fù)責(zé)一個機內(nèi)的nvl rank(編號從自身的開始),這些warp同時處理來自rdma_channel的數(shù)據(jù)
- 若有未轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)的數(shù)據(jù)
- 等待nvl channel的剩余空間達(dá)到
num_max_nvl_chunked_send_tokens - 輪訓(xùn)所有src rdma rank,檢查其
rdma_channel_tail,看看有沒有新來的token - 若找到了一個有token的src rdma rank,枚舉收到的所有token,看它是否應(yīng)發(fā)給當(dāng)前warp對應(yīng)的nvl rank
- 若是,則將token從rdma_channel的
recv_buffer拷貝到nvl_channel
- 等待nvl channel的剩余空間達(dá)到
- 更新
forward_channel_head=rdma_channel_tail;nvl_channel_tail+=處理的數(shù)據(jù)
ForwarderCoordinator- 每個lane負(fù)責(zé)一個src rdma rank
- 若有
RDMAAndNVLForwarder還沒結(jié)束- 輪訓(xùn)rdma rank中的每個nvl rank,如果所有的8個
RDMAAndNVLForwarder的forward_channel_head都更新了,則更新遠(yuǎn)端的rdma_channel_head
- 輪訓(xùn)rdma rank中的每個nvl rank,如果所有的8個
NVLReceivers- 每個warp負(fù)責(zé)一個機內(nèi)的nvl rank(從自身的下一個rank開始)
- 若
nvl_channel_tail更新了,則- 枚舉所有收到的token,從nvl_channel中拷貝到recv_x中
- 更新
nvl_channel_head
最后回到deep_ep.cpp,看一看dispatch完成之后的部分:
std::tuple<torch::Tensor, ...>
Buffer::internode_dispatch(const torch::Tensor& x, ...) {
// internode::dispatch之后
// 如果是同步模式,則等待dispatch結(jié)束
// 如果是異步,則記錄事件到comm_stream上
// Wait streams
std::optional<EventHandle> event;
if (async) {
event = EventHandle(comm_stream);
for (auto& t: {x, is_token_in_rank, rank_prefix_matrix, channel_prefix_matrix, recv_x, recv_src_idx, recv_channel_prefix_matrix, send_head}) {
t.record_stream(comm_stream);
if (allocate_on_comm_stream)
t.record_stream(compute_stream);
}
// 再對其他一些tensor也執(zhí)行record_stream
} else {
stream_wait(compute_stream, comm_stream);
}
// Switch back compute stream
if (allocate_on_comm_stream)
at::cuda::setCurrentCUDAStream(compute_stream);
// Return values
return {recv_x, recv_x_scales, recv_topk_idx, recv_topk_weights, num_recv_tokens_per_expert_list, rank_prefix_matrix, channel_prefix_matrix, recv_channel_prefix_matrix, recv_src_idx, send_head, event};
}
至此,DeepEP的dispatch就全部完成了。
Combine
combine的流程和dispatch差不多,我們還是先從API開始看
class Buffer:
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
def combine(self, x: torch.Tensor, handle: Tuple,
topk_weights: Optional[torch.Tensor] = None,
config: Optional[Config] = None,
previous_event: Optional[EventOverlap] = None, async_finish: bool = False,
allocate_on_comm_stream: bool = False) -> \
Tuple[torch.Tensor, Optional[torch.Tensor], EventOverlap]:
"""
Combine (reduce) tokens (addition **without** weights) from different ranks, both intranode and internode
settings are supported.
Intranode kernels require all the ranks should be visible via NVLink.
Internode kernels require the ranks in a node should be visible via NVLink, while the ranks with the same GPU
index should be visible via RDMA. AR must be disabled.
Arguments:
x: `[num_tokens, hidden]` with `torch.bfloat16`, the tokens to send for reducing to its original ranks.
handle: 必須由dispatch取得
handle: a must-set communication handle, you can obtain this from the dispatch function.
topk_weights: `[num_tokens, num_topk]` with `torch.float`, the tokens' top-k weights for reducing to its original ranks.
config: the performance tuning config.
previous_event: the event to wait before actually executing the kernel.
async_finish: the current stream will not wait for the communication kernels to be finished if set.
allocate_on_comm_stream: control whether all the allocated tensors' ownership to be on the communication stream.
Returns:
recv_x: the reduced token from its dispatched ranks.
recv_topk_weights: the reduced top-k weights from its dispatch ranks.
event: the event after executing the kernel (valid only if `async_finish` is set).
"""
# Default config
config = self.get_combine_config(self.group_size) if config is None else config
# Internode
if self.runtime.get_num_rdma_ranks() > 1:
return self.internode_combine(x, handle, topk_weights, config, previous_event, async_finish, allocate_on_comm_stream)
# 省略intranode
可以看到,其內(nèi)部依然是internode_combine,大體上流程和internode_dispatch相近。不過internode_combine和internode_dispatch有一個區(qū)別:internode_combine必須依賴之前dispatch計算過的token數(shù)量信息,也就是沒有notify_dispatch的過程,必須要進(jìn)行internode::cached_notify。
既然combine和dispatch的函數(shù)調(diào)用都差不多,我們直接看combine的核心kernel部分,這里依然是用文字講解。
啟動kernel
- combine會啟動
num_channels * 2個SM,其中每兩個SM對應(yīng)一個channel - 每個SM有
NUM_MAX_NVL_PEERS+kNumCombineForwarderWarps+1個warp(默認(rèn)NUM_MAX_NVL_PEERS = 8,kNumCombineForwarderWarps = 16,所以每個SM默認(rèn)有25個warp) - H800中每個warp有32個線程
在每個channel內(nèi)部,線程的分工如下
- 第一個SM負(fù)責(zé)發(fā)送
- 前8個warp為
NVLSender,負(fù)責(zé)NVL傳輸 - 然后16個warp為
NVLAndRDMAForwarder,負(fù)責(zé)將數(shù)據(jù)從NVL轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)到RDMA - 一個warp為
Coordinator (send)
- 前8個warp為
- 第二個SM負(fù)責(zé)接收
- 24個warp為
RDMAReceiver,負(fù)責(zé)接受RDMA數(shù)據(jù),將其寫入combined_x - 一個warp為
Coordinator (recv)
- 24個warp為
下圖展示了每個token的傳輸路徑,差不多就是把dispatch反過來。
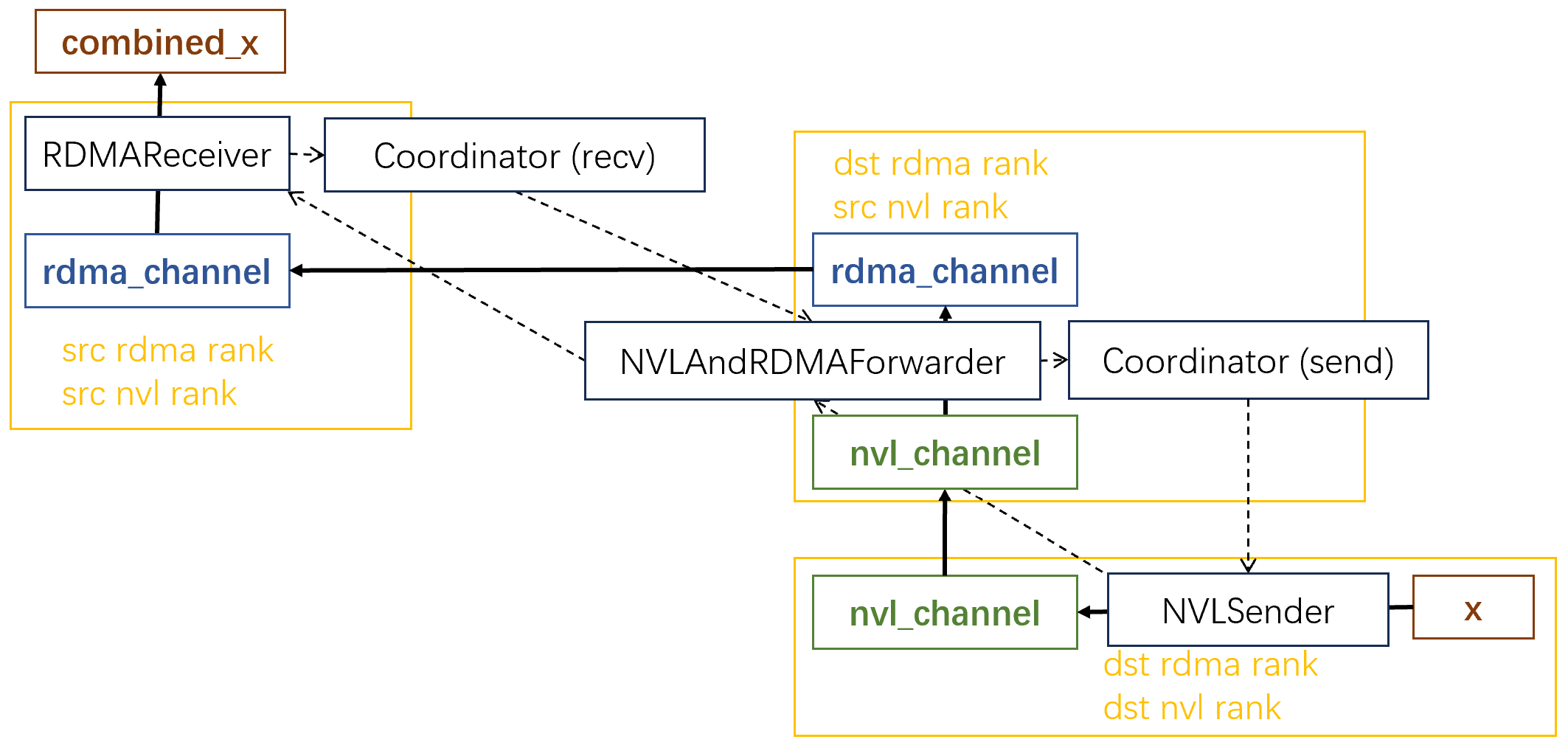
注意:為了方便理解,圖中我用的src和dst指dispatch時的src和dst,這與comine代碼中的src和dst正好相反。
注意:這里nvl_channel為每個RDMA rank都分別創(chuàng)建了nvl_buffer。
接下來講這些線程的具體職責(zé):
NVLSender- 每個warp負(fù)責(zé)一個遠(yuǎn)端的nvl rank(對應(yīng)dispatch的src nvl rank)
- 每個lane對應(yīng)一個遠(yuǎn)端的rdma rank(對應(yīng)dispatch的src rdma rank)
- 每個lane從
gbl_channel_prefix_matrix獲取到其負(fù)責(zé)的token范圍, - 若有l(wèi)ane有未發(fā)送的token,且nvl_channel的剩余空間大于
num_max_nvl_chunked_send_tokens,則- 每個符合條件的lane將至多
num_max_nvl_chunked_send_tokens個token放入nvl_channel
- 每個符合條件的lane將至多
- 更新
nvl_channel_tail
NVLAndRDMAForwarder- 所有warp平均分給每個遠(yuǎn)端的rdma rank(對應(yīng)dispatch的src nvl rank)。我們稱負(fù)責(zé)相同遠(yuǎn)端rdma rank的warp為一個warp組。
- 枚舉所有未轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)的token
- warp組中的第一個warp負(fù)責(zé)等待rdma_channel的剩余空間大于
num_max_rdma_chunked_send_tokens - warp組中的warp輪流枚舉待轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)的token
- 在dispatch階段,一個token會從(dst rdma rank, src nvl rank)轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)到多個(dst rdma rank, dst nvl rank)上;因此,在combine階段,這些不同dst nvl rank上的token要進(jìn)行reduce
- 這里
NVLAndRDMAForwarder枚舉的就是dispatch中(dst rdma rank, src nvl rank)要轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)的所有token。使用之前dispatch留下的信息(combined_nvl_head),我們可以知道每個token位于哪些dst nvl rank上。在等待這些nvl rank把所需的token發(fā)過來后,就可以對它們進(jìn)行reduce。 - reduce后的結(jié)果寫入rdma_channel。
- 更新
forwarder_nvl_head
- 在token都reduce完成后,發(fā)送rdma_channel的數(shù)據(jù),并更新遠(yuǎn)端的
rdma_channel_tail
- warp組中的第一個warp負(fù)責(zé)等待rdma_channel的剩余空間大于
RDMAReceiver- 每個warp輪流枚舉待combine的token
- 這里跟
NVLAndRDMAForwarder其實差不多。在dispatch時,一個token會從(src rdma rank, src nvl rank)發(fā)往多個(dst rdma rank, src nvl rank);因此,在combine階段,這些不同dst rdma rank上的token要進(jìn)行reduce。 RDMAReceiver枚舉的就是dispatch中一開始位于(src rdma rank, src nvl rank)的所有token。使用之前dispatch留下的信息(combined_rdma_head),我們可以知道每個token位于哪些dst rdma rank上,然后就可以對它們進(jìn)行reduce。在等待這些rdma rank把所需的token發(fā)過來后,就可以對它們進(jìn)行reduce。- reduce的結(jié)果寫入
combined_x。 - 更新
rdma_receiver_rdma_head
- 這里跟
- 每個warp輪流枚舉待combine的token
Coordinator (send)- 枚舉每個dispatch時的dst rdma rank,每個lane負(fù)責(zé)一個dispatch時的src nvl rank
- 枚舉所有
NVLAndRDMAForwarder的warp組,如果當(dāng)前warp組中所有NVLAndRDMAForwarder的forwarder_nvl_head都推進(jìn)了,則推進(jìn)對應(yīng)NVLSender的nvl_channel_head
- 枚舉所有
- 枚舉每個dispatch時的dst rdma rank,每個lane負(fù)責(zé)一個dispatch時的src nvl rank
Coordinator (recv)- 每個lane負(fù)責(zé)一個dispatch時的dst rdma rank,協(xié)調(diào)它的所有
RDMAReceiver - 如果所有
RDMAReceiver的rdma_receiver_rdma_head都推進(jìn)了,則推進(jìn)遠(yuǎn)端NVLAndRDMAForwarder的rdma_channel_head
- 每個lane負(fù)責(zé)一個dispatch時的dst rdma rank,協(xié)調(diào)它的所有
至此combine也完成了。
low_latency模式
看完普通模式后,我們再看low_latency模式,它犧牲了一些帶寬,但是可以降低延遲,可用于對延遲敏感的推理任務(wù)。

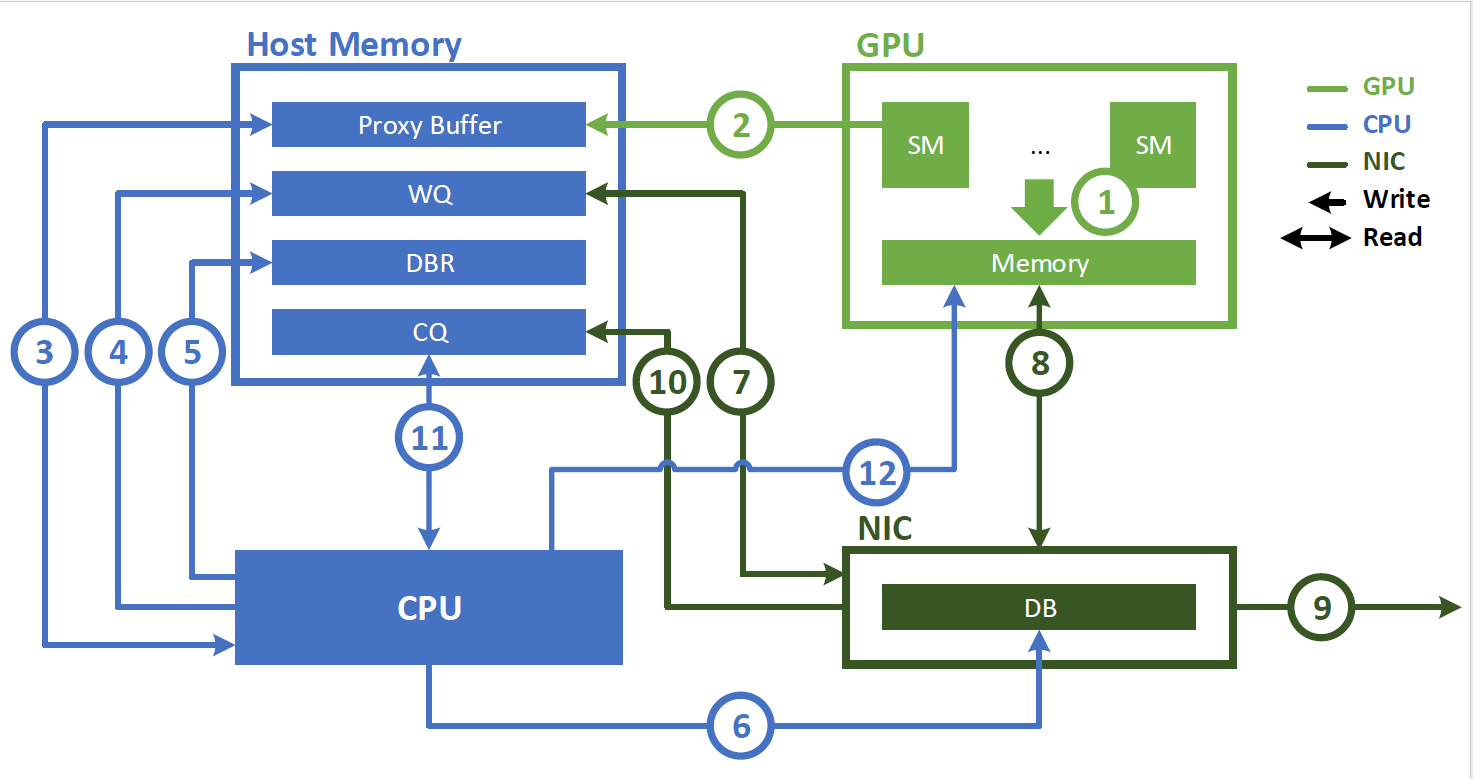
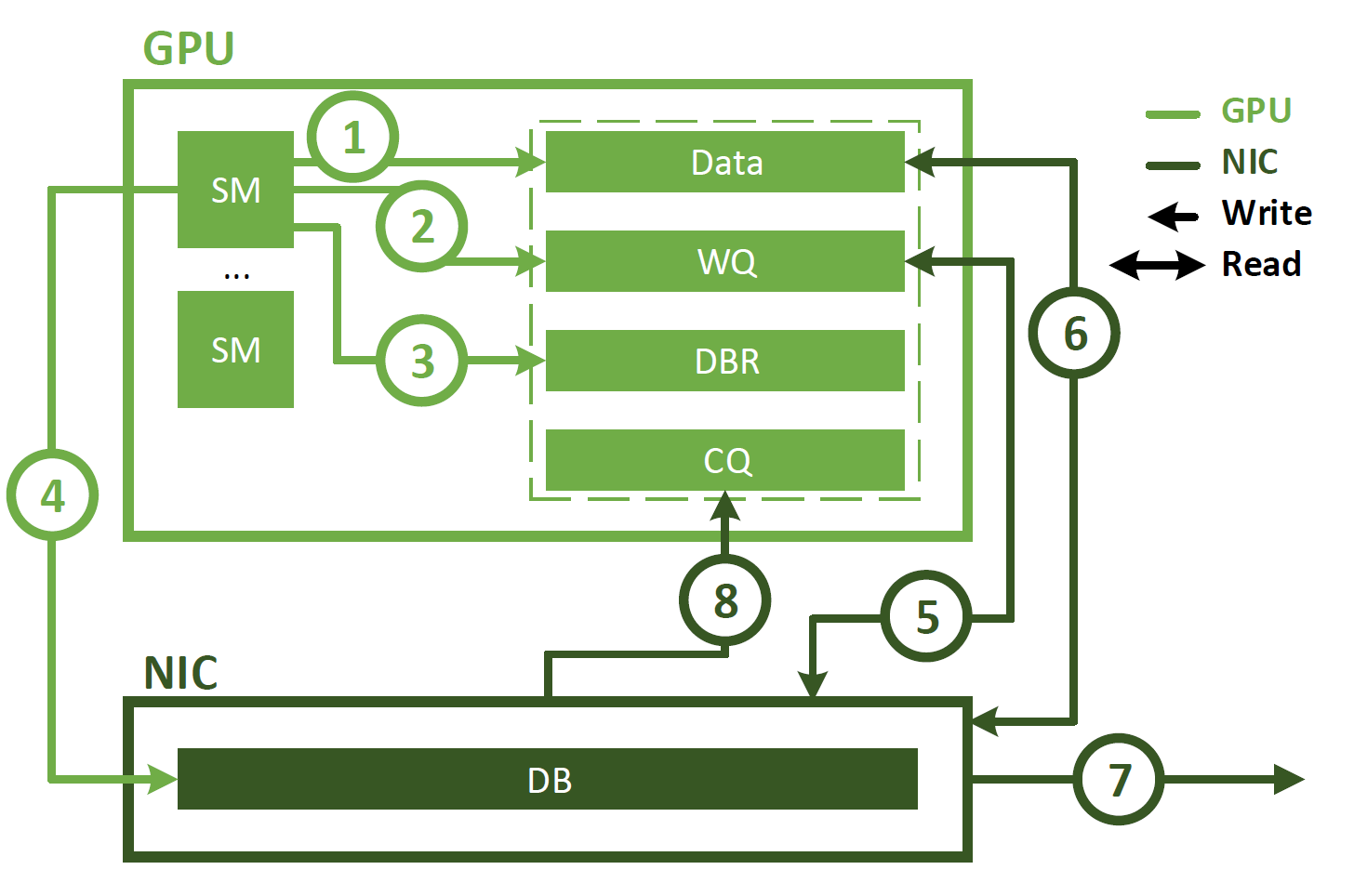
首先,對于NVSHMEM,普通模式使用IBRC,而low-latency模式會使用IBGDA,二者的區(qū)別可以參考這里。
簡單來說,普通的GPU-Direct RDMA使用CPU上的代理線程發(fā)起請求;而IBGDA直接從GPU發(fā)起請求,因此可以降低延遲。
使用代理線程的圖示如下:
IBGDA的圖示如下:
在初始化階段,low_latency會啟用IBGDA。相關(guān)代碼在deep_ep/buffer.py的構(gòu)造函數(shù)中:
class Buffer:
def __init__(...):
# Synchronize NVSHMEM unique IDs
root_unique_id = None
if self.runtime.get_num_rdma_ranks() > 1 or low_latency_mode:
# Enable IBGDA for the low latency mode, which refers to "no package forwarding between NVLink and RDMA"
if low_latency_mode:
assert num_qps_per_rank > 0
os.environ['NVSHMEM_DISABLE_P2P'] = '1'
os.environ['NVSHMEM_IB_ENABLE_IBGDA'] = '1'
os.environ['NVSHMEM_IBGDA_NIC_HANDLER'] = 'gpu'
os.environ['NVSHMEM_IBGDA_NUM_RC_PER_PE'] = f'{num_qps_per_rank}'
# Make sure QP depth is always larger than the number of on-flight WRs, so that we can skip WQ slot check
os.environ['NVSHMEM_QP_DEPTH'] = '1024'
# NOTES: NVSHMEM initialization requires at least 256 MiB
os.environ['NVSHMEM_CUMEM_GRANULARITY'] = f'{2 ** 29}'
if (low_latency_mode and self.rank == 0) or (not low_latency_mode and self.runtime.get_rdma_rank() == 0):
root_unique_id = self.runtime.get_local_nvshmem_unique_id()
low_latency的數(shù)據(jù)路徑也與普通模式不同。在普通模式中,token要先被發(fā)送到(dst rdma rank, src nvl rank)上,然后在被轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)到(dst rdma rank, dst nvl rank)。而low_latency省去了轉(zhuǎn)發(fā)的過程,直接把數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)往(dst rdma rank, dst nvl rank)上。因此,所有的GPU都屬于一個nvshmem通信組,root就是rank=0的GPU。
low_latency模式使用low_latency_dispatch函數(shù),我們看它的API:
class Buffer:
# noinspection PyTypeChecker
def low_latency_dispatch(self, x: torch.Tensor, topk_idx: torch.Tensor,
num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank: int, num_experts: int,
async_finish: bool = False, return_recv_hook: bool = False) -> \
Tuple[Tuple[torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor], torch.Tensor, Tuple, EventOverlap, Callable]:
"""
A low-latency implementation for dispatching with IBGDA **with implicit FP8 casting**.
This kernel requires all the ranks (no matter intranode or internode) should be visible via RDMA
(specifically, IBGDA must be enabled).
Even for ranks in the same node, NVLink are fully disabled for simplicity.
Warning: as there are only two buffers, and the returned tensors reuse the buffer, you can not hold more than 2
low-latency kernels' result tensor at a single moment.
Arguments:
x: `torch.Tensor` with `torch.bfloat16`, shaped as `[num_tokens, hidden]`, only several hidden shapes are
supported. The number of tokens to be dispatched must be less than `num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank`.
topk_idx: `torch.Tensor` with `torch.int64`, shaped as `[num_tokens, num_topk]`, only several top-k shapes
are supported. `-1` indices (not selecting any expert) are supported.
num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank: the maximum number of tokens to dispatch, all the ranks must hold the same value.
num_experts: the number of all experts.
async_finish: the current stream will not wait for the communication kernels to be finished if set.
return_recv_hook: return a receiving hook if set. If set, the kernel will just do the RDMA request issues,
but **without actually receiving the data**. You must call the received hook to make sure the data's arrival.
If you not set this flag, the kernel will ensure the data's arrival.
Returns:
recv_x: a tuple with received tokens for each expert. The first element is a `torch.Tensor` shaped as
`[num_local_experts, num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank * num_ranks, hidden]` with `torch.float8_e4m3fn`.
The second tensor is the corresponding scales for the first element with shape
`[num_local_experts, num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank * num_ranks, hidden // 128]` with `torch.float`.
Notice that, the last-two-dimension of the scaling tensors are in column-major for TMA compatibility.
Moreover, not all tokens are valid, only some of the `num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank * num_ranks` are,
as we do not synchronize CPU received count with GPU (also not incompatible with CUDA graph).
recv_count: a tensor shaped `[num_local_experts]` with type `torch.int`, indicating how many tokens each
expert receive. As mentioned before, all not tokens are valid in `recv_x`.
handle: the communication handle to be used in the `low_latency_combine` function.
event: the event after executing the kernel (valid only if `async_finish` is set).
hook: the receiving hook function (valid only if `return_recv_hook` is set).
"""
packed_recv_x, packed_recv_x_scales, packed_recv_count, packed_recv_src_info, packed_recv_layout_range, event, hook = \
self.runtime.low_latency_dispatch(x, topk_idx,
num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank, num_experts,
async_finish, return_recv_hook)
handle = (packed_recv_src_info, packed_recv_layout_range, num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank, num_experts)
tensors_to_record = (x, topk_idx,
packed_recv_x, packed_recv_x_scales, packed_recv_count,
packed_recv_src_info, packed_recv_layout_range)
return (packed_recv_x, packed_recv_x_scales), packed_recv_count, handle, \
EventOverlap(event, tensors_to_record if async_finish else None), hook
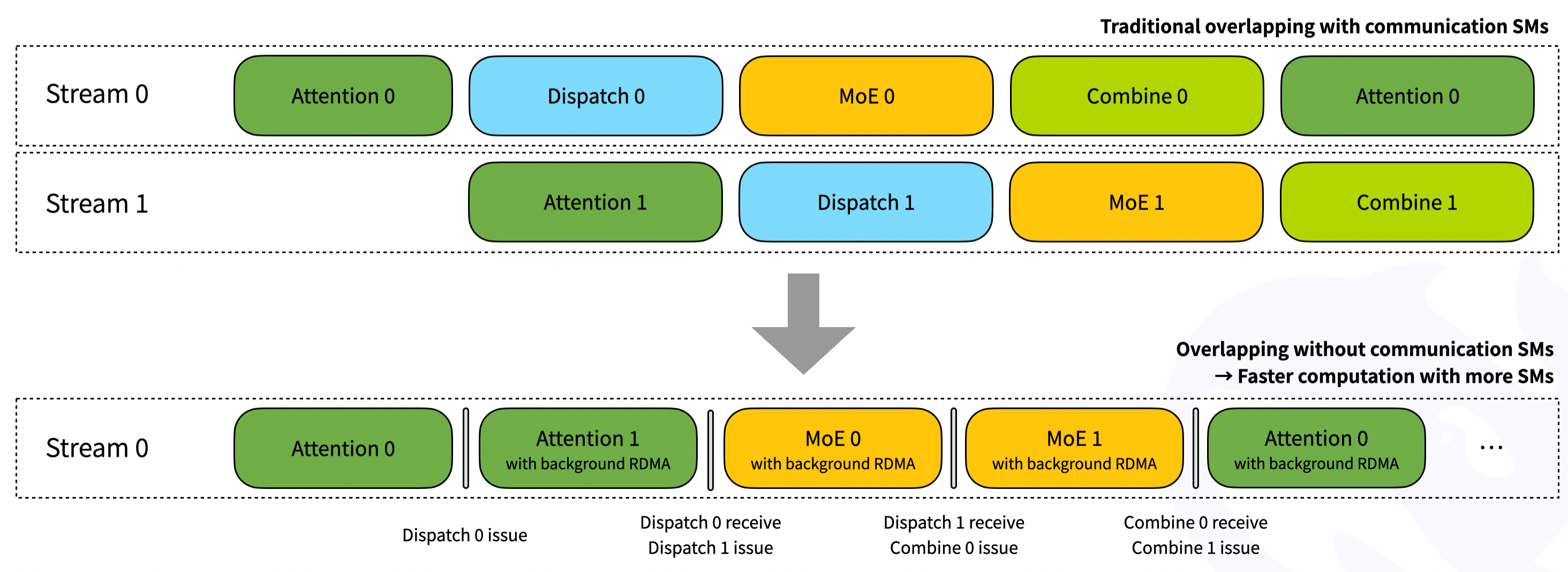
相比于普通模式的dispatch,low_latency_dispatch額外提供了一個return_recv_hook選項。若return_recv_hook=True,則low_latency_dispatch只會發(fā)送RDMA請求,不會接收數(shù)據(jù)。用戶必須調(diào)用recv_hook來確保數(shù)據(jù)到達(dá)。recv_hook的好處是可以避免讓SM一直等待接收數(shù)據(jù)接收完成。比如在下圖,在dispatch 0的發(fā)送請求發(fā)出后,可以直接開始attention 1的計算,計算后再進(jìn)行dispatch 0的接收。
我們接著看low_latency_dispatch內(nèi)部
low_latency模式?jīng)]有notify_dispatch的過程,即不會先進(jìn)行一次通信來確定GPU之間互相發(fā)送token的數(shù)量。取而代之的是,一個rank最多只能發(fā)送num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank個token,而接收端會的每個expert都會準(zhǔn)備能容納num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank * num_ranks個token的buffer,因此內(nèi)存開銷是很高的。
我們看low_latency_dispatch的啟動。代碼在csrc/deep_ep.cpp:
std::tuple<torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor, torch::Tensor, std::optional<EventHandle>, std::optional<std::function<void()>>>
Buffer::low_latency_dispatch(const torch::Tensor& x, const torch::Tensor& topk_idx,
int num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank, int num_experts,
bool async, bool return_recv_hook) {
// Kernel launch
auto next_clean_meta = next_buffer.clean_meta();
auto launcher = [=](int phases) {
internode_ll::dispatch(packed_recv_x.data_ptr(), packed_recv_x_scales.data_ptr<float>(),
packed_recv_src_info.data_ptr<int>(), packed_recv_layout_range.data_ptr<int64_t>(),
buffer.dispatch_rdma_recv_data_buffer, buffer.dispatch_rdma_recv_count_buffer,
buffer.dispatch_rdma_send_buffer,
x.data_ptr(), topk_idx.data_ptr<int64_t>(),
next_clean_meta.first, next_clean_meta.second,
num_tokens, hidden, num_max_dispatch_tokens_per_rank,
num_topk, num_experts, rank, num_ranks,
workspace, launch_stream, phases);
};
launcher(return_recv_hook ? LOW_LATENCY_SEND_PHASE : (LOW_LATENCY_SEND_PHASE | LOW_LATENCY_RECV_PHASE));
}
可以看到,low_latency_dispatch包含兩個階段:LOW_LATENCY_SEND_PHASE和LOW_LATENCY_RECV_PHASE。如果return_recv_hook=true,則dispatch時只會執(zhí)行LOW_LATENCY_SEND_PHASE,在調(diào)用recv_hook的時候才會執(zhí)行LOW_LATENCY_RECV_PHASE;否則,LOW_LATENCY_SEND_PHASE和LOW_LATENCY_RECV_PHASE都需要執(zhí)行。
kernel的代碼在internode_ll.cu,由于代碼比較長,這里還是用文字概括它的主要流程:
kernel啟動
- 啟動\(\lceil\)num_experts / 3\(\rceil\)個SM,每個SM內(nèi)有30個warp,每個warp有32個線程
LOW_LATENCY_SEND_PHASE的流程如下
- 首先,將所有warp分為兩種:
- 所有SM的前29個warp負(fù)責(zé)將token轉(zhuǎn)換為FP8類型,并發(fā)送到目標(biāo)expert的接收buffer上
- 第30個warp負(fù)責(zé)統(tǒng)計發(fā)往每個expert的token數(shù)量
- 然后,每個expert使用一個線程,將每個expert的token數(shù)量發(fā)往遠(yuǎn)端節(jié)點的
rdma_recv_count
LOW_LATENCY_RECV_PHASE的流程如下
- 這里每個expert使用3個warp
- 每個expert使用一個線程負(fù)責(zé)查看接收ibgda消息,讀取
rdma_recv_count - 每個expert的3個warp輪流讀取token,將其拷貝到
recv_x中
到這里low_latency_dispatch就差不多完成了。
low_latency_combine的kernel實現(xiàn)基本就是把low_latency_dispatch反過來。即在SEND_PHASE發(fā)送數(shù)據(jù);在RECV_PHASE接收數(shù)據(jù),進(jìn)行reduce,再把數(shù)據(jù)從FP8轉(zhuǎn)換回BF16。
總結(jié)
DeepEP使用更底層的NVSHMEM接口,達(dá)到了極高的帶寬利用率。此后的工作想要提升all-to-all的性能應(yīng)該就不太容易了,也許可以想象怎么降低all-to-all中對SM的使用,或者將其卸載到CPU上。
本人的閱讀可能不夠細(xì)致,多少會有遺漏或出錯的地方,歡迎補充指正。
| 歡迎來原網(wǎng)站坐坐! >原文鏈接<


 浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號
浙公網(wǎng)安備 33010602011771號