
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)1:
實(shí)驗(yàn)代碼:
button.hpp:
#pragma once #include <iostream> #include <string> using std::string; using std::cout; // 按鈕類 class Button { public: Button(const string &text); string get_label() const; void click(); private: string label; }; Button::Button(const string &text): label{text} { } inline string Button::get_label() const { return label; } void Button::click() { cout << "Button '" << label << "' clicked\n"; }
window.hpp:
1 #pragma once 2 #include "button.hpp" 3 #include <vector> 4 #include <iostream> 5 6 using std::vector; 7 using std::cout; 8 using std::endl; 9 10 // 窗口類 11 class Window{ 12 public: 13 Window(const string &win_title); 14 void display() const; 15 void close(); 16 void add_button(const string &label); 17 18 private: 19 string title; 20 vector<Button> buttons; 21 }; 22 23 Window::Window(const string &win_title): title{win_title} { 24 buttons.push_back(Button("close")); 25 } 26 27 inline void Window::display() const { 28 string s(40, '*'); 29 30 cout << s << endl; 31 cout << "window title: " << title << endl; 32 cout << "It has " << buttons.size() << " buttons: " << endl; 33 for(const auto &i: buttons) 34 cout << i.get_label() << " button" << endl; 35 cout << s << endl; 36 } 37 38 void Window::close() { 39 cout << "close window '" << title << "'" << endl; 40 buttons.at(0).click(); 41 } 42 43 void Window::add_button(const string &label) { 44 buttons.push_back(Button(label)); 45 }
task1.cpp:
1 #include "window.hpp" 2 #include <iostream> 3 4 using std::cout; 5 using std::cin; 6 7 void test() { 8 Window w1("new window"); 9 w1.add_button("maximize"); 10 w1.display(); 11 w1.close(); 12 } 13 14 int main() { 15 cout << "用組合類模擬簡(jiǎn)單GUI:\n"; 16 test(); 17 }
實(shí)驗(yàn)截圖:
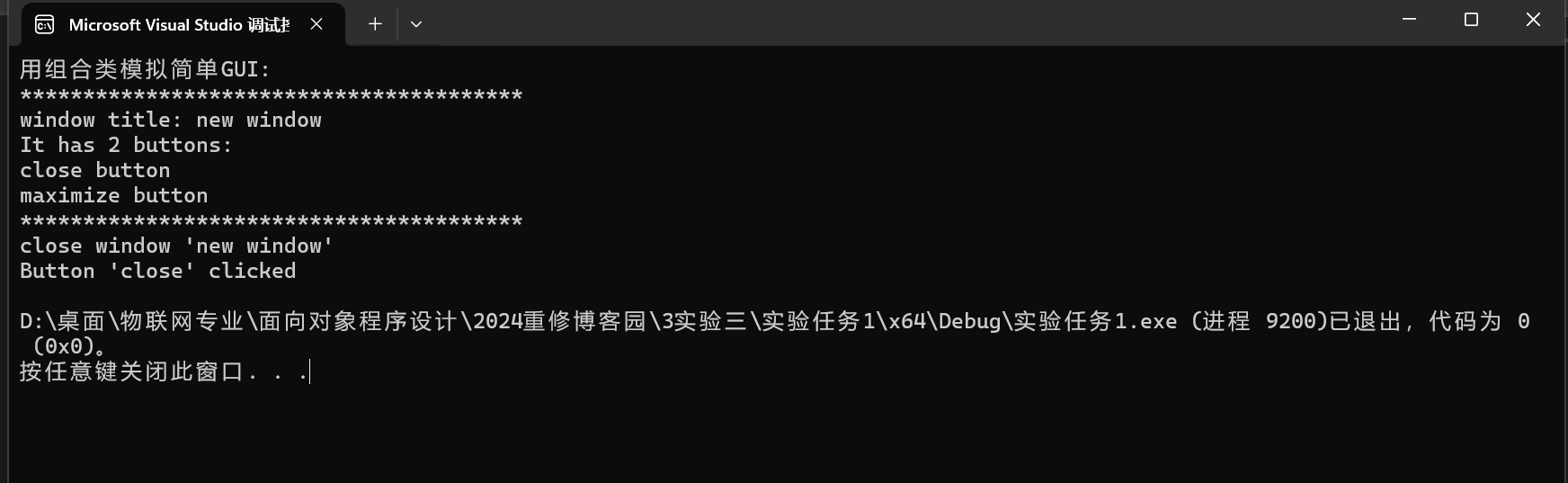
問(wèn)題1:
自定義的類:
Button:用于表示一個(gè)按鈕,包含按鈕的標(biāo)簽和點(diǎn)擊行為。
Window:用于表示一個(gè)窗口,包含窗口的標(biāo)題和一系列按鈕。
使用到的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫(kù)類:
std::string:用于處理和存儲(chǔ)字符串?dāng)?shù)據(jù)。
std::vector:用于動(dòng)態(tài)數(shù)組的管理,這里用來(lái)存儲(chǔ)窗口中的按鈕。
std::cout和 std::endl:用于輸出流,方便調(diào)試和顯示信息。
組合關(guān)系:
Window類中包含了一個(gè) `std::vector<Button>成員變量 buttons,這表明 Window類和 Button 類之間存在組合關(guān)系。具體來(lái)說(shuō),一個(gè) `Window` 對(duì)象可以擁有多個(gè) `Button` 對(duì)象,而這些 `Button` 對(duì)象的生命周期依賴于 `Window` 對(duì)象。
問(wèn)題2:
現(xiàn)有的成員函數(shù)修飾符:
Button::get_label被聲明為 const,表示該方法不會(huì)修改對(duì)象的狀態(tài)。
Button::click沒(méi)有被聲明為 const,因?yàn)槔碚撋纤赡軙?huì)改變對(duì)象的狀態(tài)(雖然在這個(gè)例子中它只是輸出信息)。
Window::display 被聲明為 const,表示該方法不會(huì)修改對(duì)象的狀態(tài)。
Window::close沒(méi)有被聲明為 const,因?yàn)樗{(diào)用了 `Button::click`,而 `Button::click` 可能會(huì)修改對(duì)象的狀態(tài)。
Window::add_button 沒(méi)有被聲明為 `const`,因?yàn)樗鼤?huì)修改 `Window` 對(duì)象的狀態(tài)。
建議添加 `const` 和 `inline` 的成員函數(shù):
1. Button::click 添加 const:
理由:當(dāng)前 `Button::click` 只是輸出一條消息,并沒(méi)有修改 `Button` 對(duì)象的狀態(tài)。因此,它可以被聲明為 `const`。
2. Window::close`添加 `const`:
理由:雖然 `Window::close` 調(diào)用了 `Button::click`,但如果 `Button::click` 被聲明為 `const`,那么 `Window::close` 也可以被聲明為 `const`。
3. Window::add_button不適合添加 const:
理由:`Window::add_button` 修改了 `Window` 對(duì)象的狀態(tài)(即向 `buttons` 向量中添加了一個(gè)新的 `Button` 對(duì)象),因此不能被聲明為 `const`。
4. Window::display 保持 `const`:
理由:`Window::display` 不修改 `Window` 對(duì)象的狀態(tài),因此保持 `const` 是合適的。
5. Button::get_label`保持 `const`:
理由:`Button::get_label` 不修改 `Button` 對(duì)象的狀態(tài),因此保持 `const` 是合適的。
6. Button::click` 設(shè)置為 `inline`:
理由:`Button::click` 是一個(gè)非常簡(jiǎn)單的函數(shù),通常適合內(nèi)聯(lián)以提高性能。
7. Window::display` 設(shè)置為 `inline`:
理由:`Window::display` 也是一個(gè)相對(duì)簡(jiǎn)單的函數(shù),適合內(nèi)聯(lián)以提高性能。
問(wèn)題3:
這行代碼的功能是創(chuàng)建一個(gè)包含40個(gè)星號(hào)(`*`)的字符串 `s`。具體來(lái)說(shuō),`string s(40, '*');` 使用了 `std::string` 的構(gòu)造函數(shù),該構(gòu)造函數(shù)接受兩個(gè)參數(shù):第一個(gè)參數(shù)是要?jiǎng)?chuàng)建的字符數(shù),第二個(gè)參數(shù)是要重復(fù)的字符。因此,這行代碼的結(jié)果是一個(gè)長(zhǎng)度為40的字符串,每個(gè)字符都是星號(hào)。
在 `Window::display` 方法中,這個(gè)字符串被用來(lái)在輸出中創(chuàng)建一個(gè)分隔線,以便更清晰地顯示窗口的信息。具體作用如下:
創(chuàng)建分隔線:在窗口信息的頂部和底部各打印一行40個(gè)星號(hào),形成一個(gè)視覺(jué)上的分隔線。
增強(qiáng)可讀性:通過(guò)分隔線,使得窗口標(biāo)題和按鈕列表的顯示更加清晰,便于用戶閱讀和理解。
總結(jié):
問(wèn)題一:
1. 自定義類:`Button` 和 `Window`。
2. 使用到的標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫(kù)類:`std::string`、`std::vector`、`std::cout` 和 `std::endl`。
3. 組合關(guān)系:`Window` 類和 `Button` 類之間存在組合關(guān)系。
問(wèn)題二:
4. 成員函數(shù)的 `const` 和 `inline` 修飾符:
`Button::click` 可以添加 `const` 并設(shè)置為 `inline`。
`Window::close` 可以添加 `const`。
`Window::display` 已經(jīng)是 `const`,可以設(shè)置為 `inline`。
Window::add_button`不能添加 `const`。
問(wèn)題三:
5. `string s(40, '*');` 的功能:創(chuàng)建一個(gè)包含40個(gè)星號(hào)的字符串,用于在輸出中創(chuàng)建分隔線,增強(qiáng)可讀性。
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)2:
實(shí)驗(yàn)代碼:
task2.cpp:
實(shí)驗(yàn)截圖:

問(wèn)題1
這三行代碼的功能分別是:
1. `vector<int> v1(5, 42);`
這行代碼創(chuàng)建了一個(gè)名為 `v1` 的 `vector<int>` 對(duì)象,該對(duì)象包含 5 個(gè)整數(shù),每個(gè)整數(shù)的初始值都是 42。`v1` 的內(nèi)容將是 `[42, 42, 42, 42, 42]`。
2. `const vector<int> v2(v1);`
這行代碼使用 `v1` 的內(nèi)容來(lái)初始化一個(gè)名為 `v2` 的常量 `vector<int>` 對(duì)象。`v2` 將成為 `v1` 的一個(gè)副本,但因?yàn)樗浅A浚云鋬?nèi)容不能被修改。`v2` 的內(nèi)容也將是 `[42, 42, 42, 42, 42]`。
3. `v1.at(0) = -999;`
這行代碼通過(guò) `at(0)` 方法訪問(wèn) `v1` 中索引為 0 的元素,并將其值設(shè)置為 -999。`at()` 方法提供了邊界檢查,如果索引超出范圍,則會(huì)拋出 `std::out_of_range` 異常。修改后,`v1` 的內(nèi)容變?yōu)?`[-999, 42, 42, 42, 42]`。
問(wèn)題2
這三行代碼的功能分別是:
1. `vector<vector<int>> v1{{1, 2, 3}, {4, 5, 6, 7}};`
- 這行代碼創(chuàng)建了一個(gè)名為 `v1` 的二維 `vector<int>` 對(duì)象,其中包含了兩個(gè)子向量,第一個(gè)子向量包含 1, 2, 3,第二個(gè)子向量包含 4, 5, 6, 7。`v1` 的內(nèi)容將是 `[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7]]`。
2. `const vector<vector<int>> v2(v1);`
這行代碼使用 `v1` 的內(nèi)容來(lái)初始化一個(gè)名為 `v2` 的常量二維 `vector<int>` 對(duì)象。`v2` 將成為 `v1` 的一個(gè)副本,但因?yàn)樗浅A浚云鋬?nèi)容不能被修改。`v2` 的內(nèi)容也將是 `[[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6, 7]]`。
3. `v1.at(0).push_back(-999);`
這行代碼首先通過(guò) `at(0)` 訪問(wèn) `v1` 的第一個(gè)子向量,然后調(diào)用 `push_back(-999)` 方法將 -999 添加到該子向量的末尾。`push_back` 方法用于在向量的末尾添加一個(gè)新元素。修改后,`v1` 的內(nèi)容變?yōu)?`[[1, 2, 3, -999], [4, 5, 6, 7]]`。
問(wèn)題3
這四行代碼的功能分別是:
1. `vector<int> t1 = v1.at(0);`
這行代碼通過(guò) `at(0)` 訪問(wèn) `v1` 的第一個(gè)子向量,并將其賦值給一個(gè)新的 `vector<int>` 對(duì)象 `t1`。`t1` 成為了 `v1` 第一個(gè)子向量的一個(gè)副本。`t1` 的內(nèi)容將是 `[1, 2, 3, -999]`。
2. `cout << t1.at(t1.size()-1) << endl;`
這行代碼打印 `t1` 的最后一個(gè)元素。因?yàn)?`t1` 是 `v1` 第一個(gè)子向量的副本,而 `v1` 的第一個(gè)子向量在前面已經(jīng)通過(guò) `push_back` 添加了 -999,所以這行代碼會(huì)輸出 -999。
3. `const vector<int> t2 = v2.at(0);`
這行代碼通過(guò) `at(0)` 訪問(wèn) `v2` 的第一個(gè)子向量,并將其賦值給一個(gè)新的常量 `vector<int>` 對(duì)象 `t2`。`t2` 成為了 `v2` 第一個(gè)子向量的一個(gè)副本,但由于 `v2` 是常量,`t2` 也是常量。`t2` 的內(nèi)容將是 `[1, 2, 3]`。
4. `cout << t2.at(t2.size()-1) << endl;`
這行代碼打印 `t2` 的最后一個(gè)元素。因?yàn)?`t2` 是 `v2` 第一個(gè)子向量的副本,而 `v2` 的內(nèi)容沒(méi)有被修改過(guò),所以這行代碼會(huì)輸出 3(即 `v2` 第一個(gè)子向量的最后一個(gè)元素)。
問(wèn)題4
根據(jù)執(zhí)行結(jié)果,反向分析、推斷:
1. 標(biāo)準(zhǔn)庫(kù)模板類 `vector` 內(nèi)部封裝的復(fù)制構(gòu)造函數(shù),其實(shí)現(xiàn)機(jī)制是深復(fù)制還是淺復(fù)制?
從 `test1` 和 `test2` 的輸出結(jié)果可以看出,當(dāng) `v1` 被修改時(shí),`v2` 的內(nèi)容沒(méi)有受到影響。這表明 `vector` 的復(fù)制構(gòu)造函數(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)了深復(fù)制。如果實(shí)現(xiàn)的是淺復(fù)制,那么修改 `v1` 會(huì)影響到 `v2`,因?yàn)樗鼈儠?huì)共享同一個(gè)內(nèi)存區(qū)域。因此,`vector` 的復(fù)制構(gòu)造函數(shù)實(shí)現(xiàn)的是深復(fù)制。
2. 模板類 `vector` 的接口 `at()`,是否至少需要提供一個(gè) `const` 成員函數(shù)作為接口?
是的,`vector` 的 `at()` 方法確實(shí)提供了 `const` 成員函數(shù)版本。這是為了允許在常量對(duì)象上安全地訪問(wèn)元素。在 `test2` 中,`v2` 是一個(gè)常量 `vector`,但仍然可以使用 `at()` 方法來(lái)訪問(wèn)其元素,這說(shuō)明 `at()` 方法有 `const` 版本。這樣設(shè)計(jì)的好處是可以確保在常量對(duì)象上不會(huì)發(fā)生意外的修改。因此,`vector` 的 `at()` 方法至少需要提供一個(gè) `const` 成員函數(shù)作為接口。
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)3:
實(shí)驗(yàn)代碼:
vectorInt.hpp:
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cassert> 5 6 using std::cout; 7 using std::endl; 8 9 // 動(dòng)態(tài)int數(shù)組對(duì)象類 10 class vectorInt{ 11 public: 12 vectorInt(int n); 13 vectorInt(int n, int value); 14 vectorInt(const vectorInt &vi); 15 ~vectorInt(); 16 17 int& at(int index); 18 const int& at(int index) const; 19 20 vectorInt& assign(const vectorInt &v); 21 int get_size() const; 22 23 private: 24 int size; 25 int *ptr; // ptr指向包含size個(gè)int的數(shù)組 26 }; 27 28 vectorInt::vectorInt(int n): size{n}, ptr{new int[size]} { 29 } 30 31 vectorInt::vectorInt(int n, int value): size{n}, ptr{new int[size]} { 32 for(auto i = 0; i < size; ++i) 33 ptr[i] = value; 34 } 35 36 vectorInt::vectorInt(const vectorInt &vi): size{vi.size}, ptr{new int[size]} { 37 for(auto i = 0; i < size; ++i) 38 ptr[i] = vi.ptr[i]; 39 } 40 41 vectorInt::~vectorInt() { 42 delete [] ptr; 43 } 44 45 const int& vectorInt::at(int index) const { 46 assert(index >= 0 && index < size); 47 48 return ptr[index]; 49 } 50 51 int& vectorInt::at(int index) { 52 assert(index >= 0 && index < size); 53 54 return ptr[index]; 55 } 56 57 vectorInt& vectorInt::assign(const vectorInt &v) { 58 delete[] ptr; // 釋放對(duì)象中ptr原來(lái)指向的資源 59 60 size = v.size; 61 ptr = new int[size]; 62 63 for(int i = 0; i < size; ++i) 64 ptr[i] = v.ptr[i]; 65 66 return *this; 67 } 68 69 int vectorInt::get_size() const { 70 return size; 71 }
task3.cpp:
實(shí)驗(yàn)截圖:
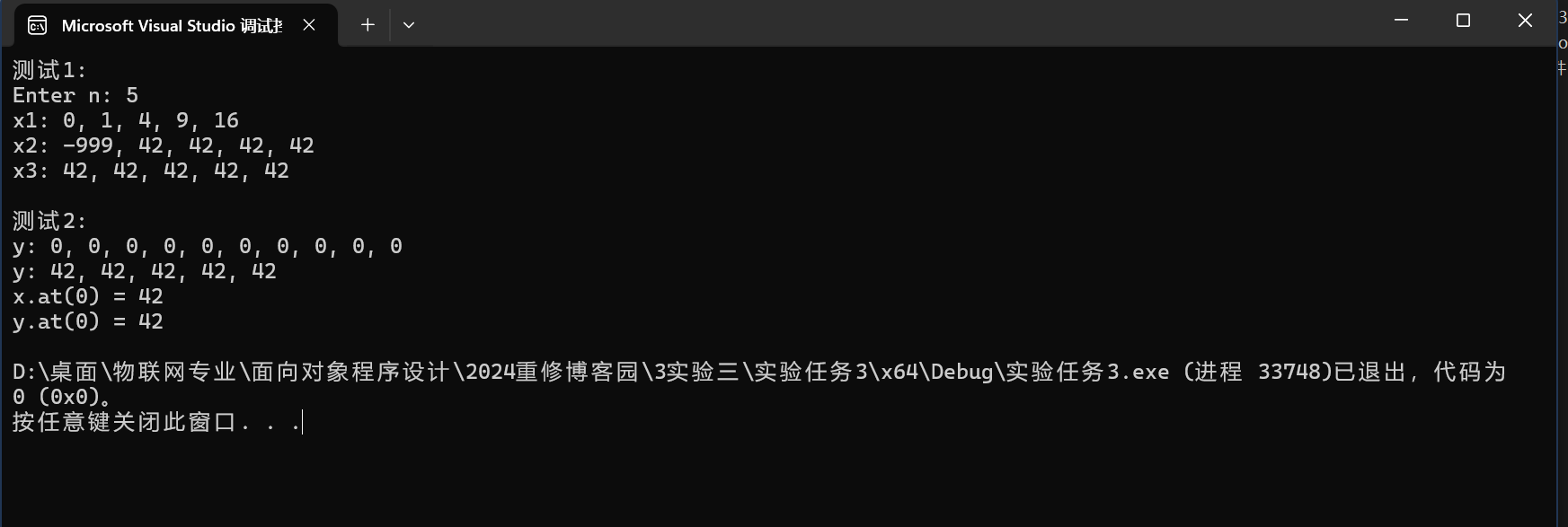
問(wèn)題1:
深復(fù)制。
分析:
在`vectorInt`類的復(fù)制構(gòu)造函數(shù)中,首先創(chuàng)建了一個(gè)新的數(shù)組`ptr{new int[size]}`,然后將源對(duì)象的每個(gè)元素復(fù)制到新分配的數(shù)組中。這種實(shí)現(xiàn)方式確保了兩個(gè)對(duì)象的數(shù)據(jù)是完全獨(dú)立的,即使一個(gè)對(duì)象的數(shù)據(jù)發(fā)生變化,也不會(huì)影響另一個(gè)對(duì)象的數(shù)據(jù)。因此,這是一個(gè)深復(fù)制的例子。
問(wèn)題2:
返回值類型改為int: 測(cè)試代碼可能無(wú)法正確運(yùn)行。
原因:當(dāng)`at()`方法返回一個(gè)`int`類型的值時(shí),它返回的是數(shù)組中元素的一個(gè)副本。這意味著對(duì)返回值的任何修改都不會(huì)影響原始數(shù)組中的數(shù)據(jù)。這將導(dǎo)致無(wú)法通過(guò)`at()`方法修改數(shù)組中的元素,從而可能導(dǎo)致某些功能失效,如`test1`中的`x2.at(0) = -999;`將不起作用。
去掉const:存在潛在的安全隱患。
原因:如果將`const int& at(int index) const`的返回值類型前面的`const`去掉,那么即使是在常量對(duì)象上調(diào)用此方法,也能通過(guò)返回的引用修改數(shù)組中的數(shù)據(jù)。這破壞了常量對(duì)象的不可變性原則,可能導(dǎo)致意外的行為或錯(cuò)誤。
問(wèn)題3:
不可以。
分析:
原因:assign()`方法通常用于將一個(gè)對(duì)象的內(nèi)容替換為另一個(gè)對(duì)象的內(nèi)容,并且通常設(shè)計(jì)為鏈?zhǔn)秸{(diào)用的一部分,即允許連續(xù)調(diào)用多個(gè)方法。例如,`obj1.assign(obj2).someMethod();`。為了支持這樣的鏈?zhǔn)秸{(diào)用,`assign()`方法需要返回當(dāng)前對(duì)象的引用`*this`,而不是一個(gè)新的`vectorInt`對(duì)象。如果返回類型改為`vectorInt`,則每次調(diào)用`assign()`都會(huì)創(chuàng)建并返回一個(gè)新的`vectorInt`對(duì)象,這不僅增加了內(nèi)存開(kāi)銷(xiāo),而且破壞了鏈?zhǔn)秸{(diào)用的可能性。此外,這樣做也不符合C++中常見(jiàn)容器類(如`std::vector`)的設(shè)計(jì)模式。
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)4:
實(shí)驗(yàn)代碼:
matrix.hpp:
1 #pragma once 2 3 #include <iostream> 4 #include <cassert> 5 #include <cstring> // 用于memcpy 6 7 8 using std::cout; 9 using std::endl; 10 11 // 類Matrix的聲明 12 class Matrix { 13 public: 14 Matrix(int n, int m); // 構(gòu)造函數(shù),構(gòu)造一個(gè)n*m的矩陣, 初始值為value 15 Matrix(int n); // 構(gòu)造函數(shù),構(gòu)造一個(gè)n*n的矩陣, 初始值為value 16 Matrix(const Matrix &x); // 復(fù)制構(gòu)造函數(shù), 使用已有的矩陣X構(gòu)造 17 ~Matrix(); 18 19 void set(const double *pvalue); // 用pvalue指向的連續(xù)內(nèi)存塊數(shù)據(jù)按行為矩陣賦值 20 void clear(); // 把矩陣對(duì)象的值置0 21 22 const double& at(int i, int j) const; // 返回矩陣對(duì)象索引(i,j)的元素const引用 23 double& at(int i, int j); // 返回矩陣對(duì)象索引(i,j)的元素引用 24 25 int get_lines() const; // 返回矩陣對(duì)象行數(shù) 26 int get_cols() const; // 返回矩陣對(duì)象列數(shù) 27 28 void display() const; // 按行顯示矩陣對(duì)象元素值 29 30 private: 31 int lines; // 矩陣對(duì)象內(nèi)元素行數(shù) 32 int cols; // 矩陣對(duì)象內(nèi)元素列數(shù) 33 double *ptr; 34 }; 35 36 // 類Matrix的實(shí)現(xiàn):待補(bǔ)足 37 38 39 Matrix::Matrix(int n, int m) : lines(n), cols(m) { 40 ptr = new double[lines * cols]; 41 clear(); 42 } 43 44 Matrix::Matrix(int n) : Matrix(n, n) {} 45 46 Matrix::Matrix(const Matrix& x) : lines(x.lines), cols(x.cols) { 47 ptr = new double[lines * cols]; 48 memcpy(ptr, x.ptr, lines * cols * sizeof(double)); 49 } 50 51 Matrix::~Matrix() { 52 delete[] ptr; 53 } 54 55 void Matrix::set(const double* pvalue) { 56 memcpy(ptr, pvalue, lines * cols * sizeof(double)); 57 } 58 59 void Matrix::clear() { 60 memset(ptr, 0, lines * cols * sizeof(double)); 61 } 62 63 const double& Matrix::at(int i, int j) const { 64 assert(i >= 0 && i < lines && j >= 0 && j < cols); 65 return ptr[i * cols + j]; 66 } 67 68 double& Matrix::at(int i, int j) { 69 assert(i >= 0 && i < lines && j >= 0 && j < cols); 70 return ptr[i * cols + j]; 71 } 72 73 int Matrix::get_lines() const { 74 return lines; 75 } 76 77 int Matrix::get_cols() const { 78 return cols; 79 } 80 81 void Matrix::display() const { 82 for (int i = 0; i < lines; ++i) { 83 for (int j = 0; j < cols; ++j) { 84 cout << at(i, j) << " "; 85 } 86 cout << endl; 87 } 88 }
task4.cpp:
1 #include "matrix.hpp" 2 #include <iostream> 3 #include <cassert> 4 5 using std::cin; 6 using std::cout; 7 using std::endl; 8 9 10 const int N = 1000; 11 12 // 輸出矩陣對(duì)象索引為index所在行的所有元素 13 void output(const Matrix &m, int index) { 14 assert(index >= 0 && index < m.get_lines()); 15 16 for(auto j = 0; j < m.get_cols(); ++j) 17 cout << m.at(index, j) << ", "; 18 cout << "\b\b \n"; 19 } 20 21 22 void test1() { 23 double x[1000] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}; 24 25 int n, m; 26 cout << "Enter n and m: "; 27 cin >> n >> m; 28 29 Matrix m1(n, m); // 創(chuàng)建矩陣對(duì)象m1, 大小n×m 30 m1.set(x); // 用一維數(shù)組x的值按行為矩陣m1賦值 31 32 Matrix m2(m, n); // 創(chuàng)建矩陣對(duì)象m1, 大小m×n 33 m2.set(x); // 用一維數(shù)組x的值按行為矩陣m1賦值 34 35 Matrix m3(2); // 創(chuàng)建一個(gè)2×2矩陣對(duì)象 36 m3.set(x); // 用一維數(shù)組x的值按行為矩陣m4賦值 37 38 cout << "矩陣對(duì)象m1: \n"; m1.display(); cout << endl; 39 cout << "矩陣對(duì)象m2: \n"; m2.display(); cout << endl; 40 cout << "矩陣對(duì)象m3: \n"; m3.display(); cout << endl; 41 } 42 43 void test2() { 44 Matrix m1(2, 3); 45 m1.clear(); 46 47 const Matrix m2(m1); 48 m1.at(0, 0) = -999; 49 50 cout << "m1.at(0, 0) = " << m1.at(0, 0) << endl; 51 cout << "m2.at(0, 0) = " << m2.at(0, 0) << endl; 52 cout << "矩陣對(duì)象m1第0行: "; output(m1, 0); 53 cout << "矩陣對(duì)象m2第0行: "; output(m2, 0); 54 } 55 56 int main() { 57 cout << "測(cè)試1: \n"; 58 test1(); 59 60 cout << "測(cè)試2: \n"; 61 test2(); 62 }
實(shí)驗(yàn)截圖:
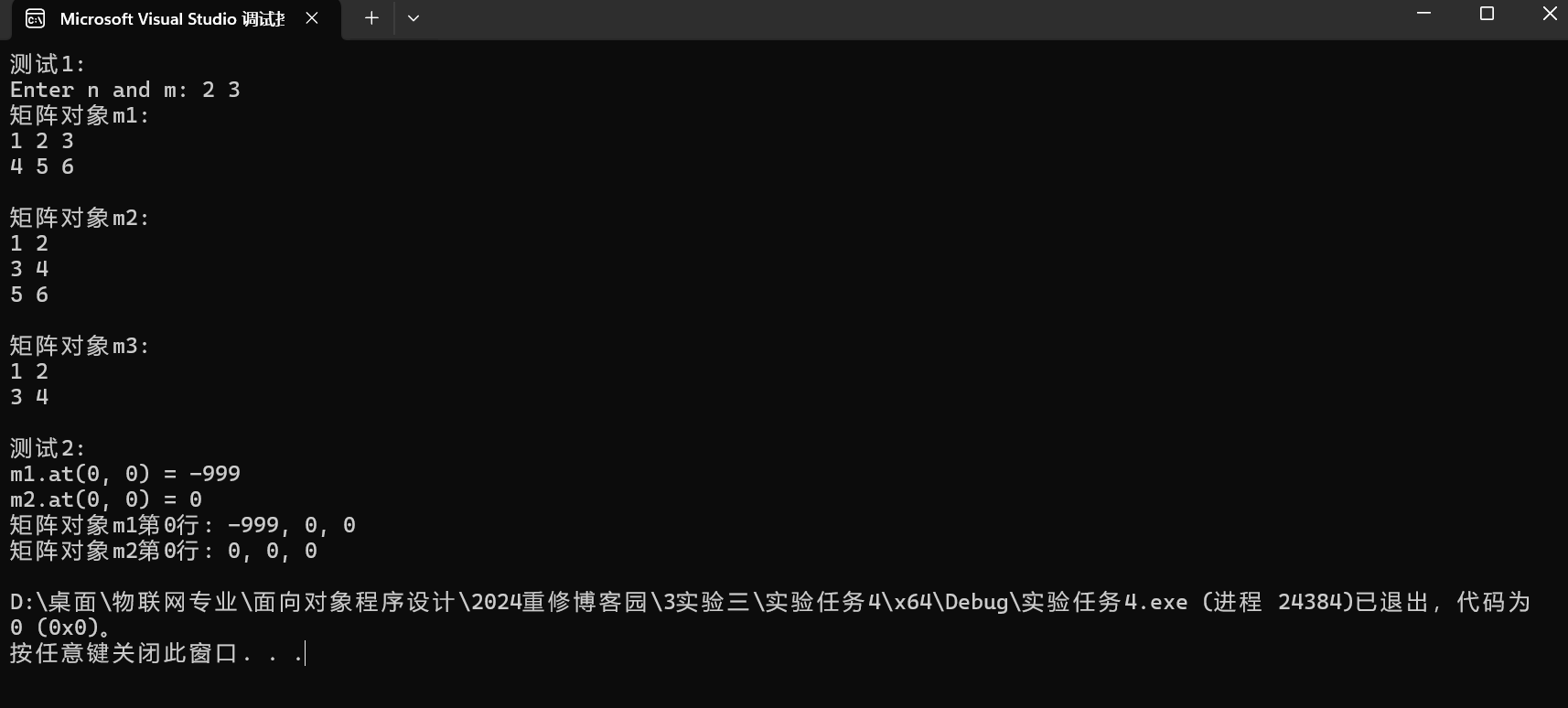

實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)5:
實(shí)驗(yàn)代碼:
user.hpp:
1 #pragma once 2 3 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <string> 6 7 8 class User { 9 private: 10 std::string name; 11 std::string password; 12 std::string email; 13 14 public: 15 // 構(gòu)造函數(shù) 16 User(const std::string& name, const std::string& password = "123456", const std::string& email = ""); 17 18 // 設(shè)置郵箱 19 void set_email(); 20 21 // 修改密碼 22 void change_password(); 23 24 // 顯示用戶信息 25 void display() const; 26 27 private: 28 // 檢查郵箱是否合法 29 bool is_valid_email(const std::string& email) const; 30 31 // 檢查密碼是否正確 32 bool check_password(const std::string& input) const; 33 }; 34 35 // 構(gòu)造函數(shù) 36 User::User(const std::string& name, const std::string& password, const std::string& email) 37 : name(name), password(password), email(email) {} 38 39 // 設(shè)置郵箱 40 void User::set_email() { 41 std::string new_email;std::cout << "Enter email address: "; 42 do { 43 std::cin >> new_email; 44 if (!is_valid_email(new_email)) { 45 std::cout << "illegal email. Please re-enter email:"; 46 } 47 else { 48 email = new_email; 49 std::cout << "email is set successfully…\n"; 50 break; 51 } 52 } while (true); 53 } 54 55 // 修改密碼 56 void User::change_password() { 57 int attempts = 0; 58 std::string old_password; 59 do { 60 std::cout << "Enter old password: "; 61 std::cin >> old_password; 62 if (check_password(old_password)) { 63 std::string new_password; 64 std::cout << "Enter new password: "; 65 std::cin >> new_password; 66 password = new_password; 67 std::cout << "new password is set successfully…\n"; 68 return; 69 } 70 else { 71 std::cout << "passsword inpit error. Please re-enter again."; 72 attempts++; 73 } 74 if (attempts >= 3) { 75 std::cout << "passsword inpit error. Please try again after a while.\n"; 76 return; 77 } 78 } while (true); 79 } 80 81 // 顯示用戶信息 82 void User::display() const { 83 std::cout << "name: " << name << "\n"; 84 std::cout << "pass: "; 85 for (size_t i = 0; i < password.length(); ++i) { 86 std::cout << "*"; 87 } 88 std::cout << "\n"; 89 std::cout << "email: " << email << "\n"; 90 } 91 92 93 // 檢查郵箱是否合法 94 bool User::is_valid_email(const std::string& email) const { 95 return email.find('@') != std::string::npos; 96 } 97 98 // 檢查密碼是否正確 99 bool User::check_password(const std::string& input) const { 100 return input == password; 101 }
task5.cpp:
1 // task5.cpp 2 3 #include "user.hpp" 4 #include <iostream> 5 #include <string> 6 #include <vector> 7 8 using std::cin; 9 using std::cout; 10 using std::endl; 11 using std::string; 12 using std::vector; 13 14 //以下test1、2為測(cè)試 15 using namespace std; 16 // 測(cè)試1 17 void test1() { 18 string s1{ "hello" }; 19 string s2(s1.size(), '*'); // 構(gòu)造字符串對(duì)象s2, 包含和s1長(zhǎng)度相同的* 20 cout << "s1: " << s1 << endl; 21 cout << "s2: " << s2 << endl; 22 } 23 // 測(cè)試2 24 void test2() { 25 vector<string> v{ "xyz@gmail.com", "xyz.gmail.com" }; 26 bool is_valid; 27 for (auto& s : v) { 28 auto pos = s.find("@"); // 在字符串對(duì)象s中查找子串@, 如果找到,返回位置索引npos;否則, 返回常量值npos 29 if (pos == s.npos) 30 is_valid = false; 31 else 32 is_valid = true; 33 cout << s << "\t" << boolalpha << is_valid << endl; 34 } 35 } 36 37 void test() { 38 vector<User> user_lst; 39 40 User u1("Alice", "2024113", "Alice@hotmail.com"); 41 user_lst.push_back(u1); 42 cout << endl; 43 44 User u2("Bob"); 45 u2.set_email(); 46 u2.change_password(); 47 user_lst.push_back(u2); 48 cout << endl; 49 50 User u3("Hellen"); 51 u3.set_email(); 52 u3.change_password(); 53 user_lst.push_back(u3); 54 cout << endl; 55 56 cout << "There are " << user_lst.size() << " users. they are: " << endl; 57 for (auto& i : user_lst) { 58 i.display(); 59 cout << endl; 60 } 61 } 62 63 int main() { 64 cout << "測(cè)試1:" << endl; 65 test1(); 66 cout << "\n測(cè)試2:" << endl; 67 test2(); 68 test(); }
實(shí)驗(yàn)截圖:
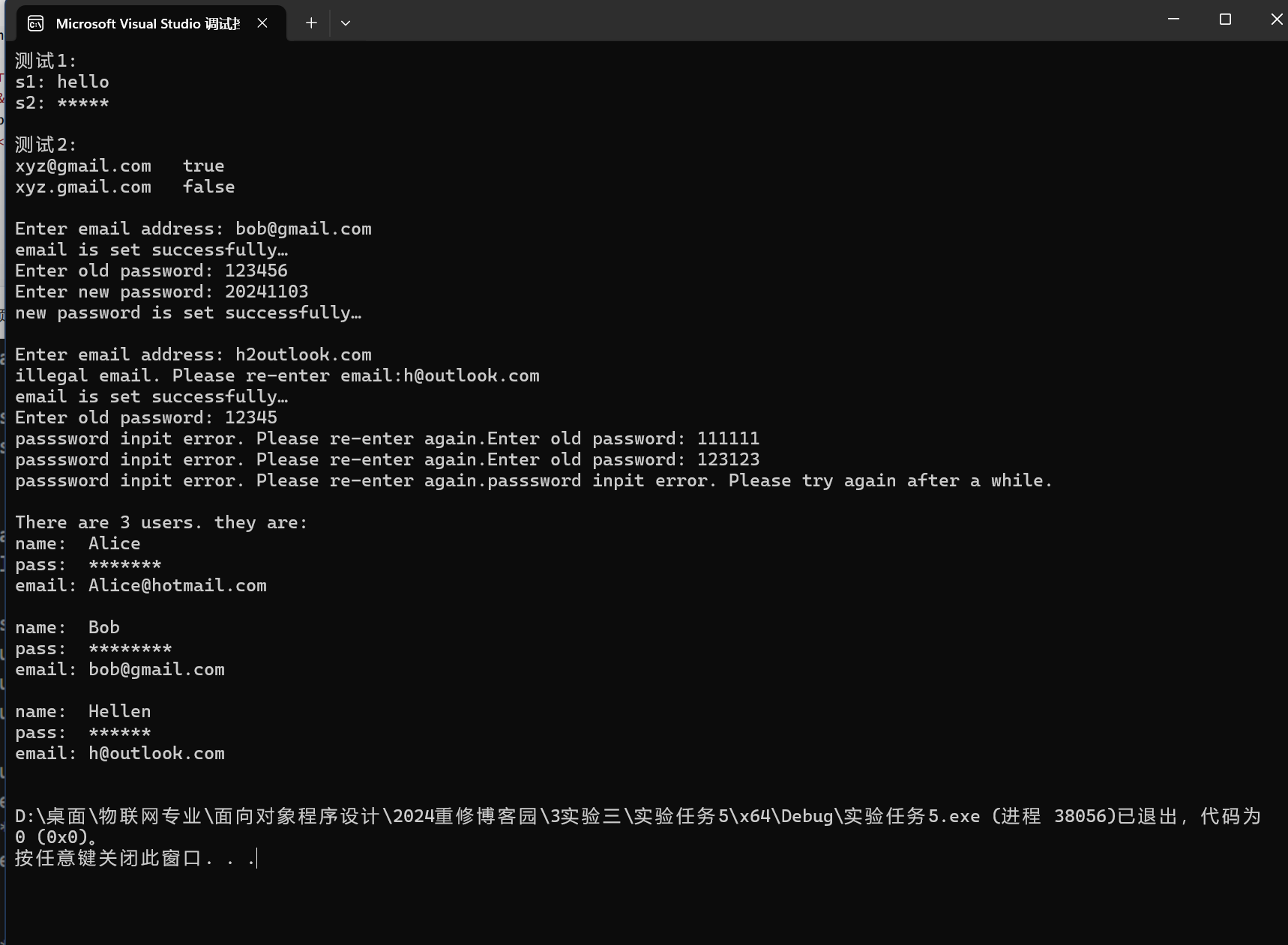
實(shí)驗(yàn)任務(wù)6:
實(shí)驗(yàn)代碼:
date.h:
date.cpp:
account.h:
account.cpp:
6_25.cpp:
實(shí)驗(yàn)截圖:
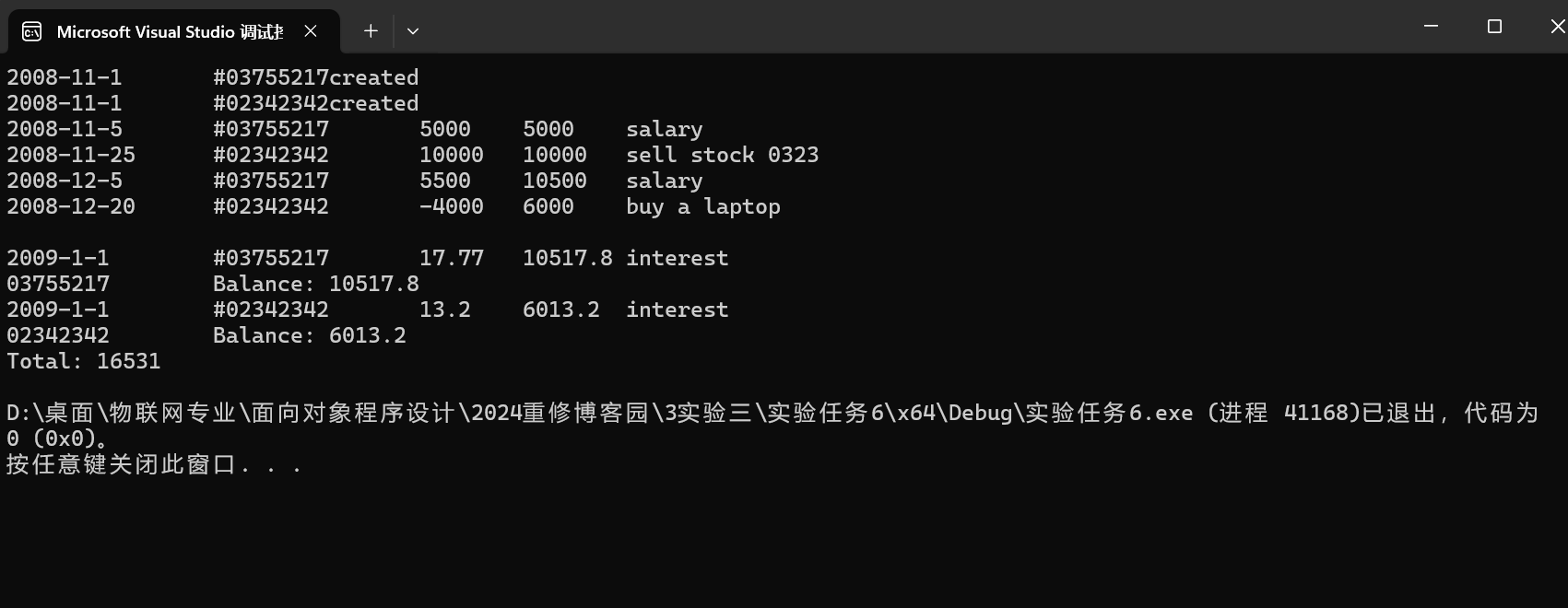

 View Code
View Code